北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 907-914. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.05.016
视觉重建对老年人行走动态足底压力的影响
敖明昕1,李学民1,于媛媛2,时会娟2,黄红拾2,敖英芳2,△( ),王薇1,△(
),王薇1,△( )
)
- 1.北京大学第三医院眼科,眼部神经损伤的重建保护与康复北京市重点实验室
2.北京大学第三医院运动医学科,北京大学运动医学研究所,北京市运动医学关节伤病重点实验室,北京 100191
Effects of visual restoration on dynamic plantar pressure features in elder individuals
AO Ming-xin1,LI Xue-min1,YU Yuan-yuan2,SHI Hui-juan2,HUANG Hong-shi2,AO Ying-fang2,△( ),WANG Wei1,△(
),WANG Wei1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Ophthalmology, Beijing Key Laboratory of Restoration of Damaged Ocular Nerve, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Sports Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital, Institute of Sports Medicine of Peking University, Beijing Key Laboratory of Sports Injuries, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
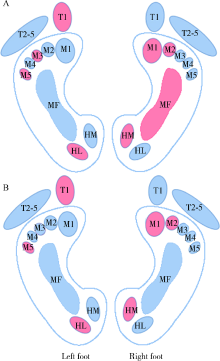
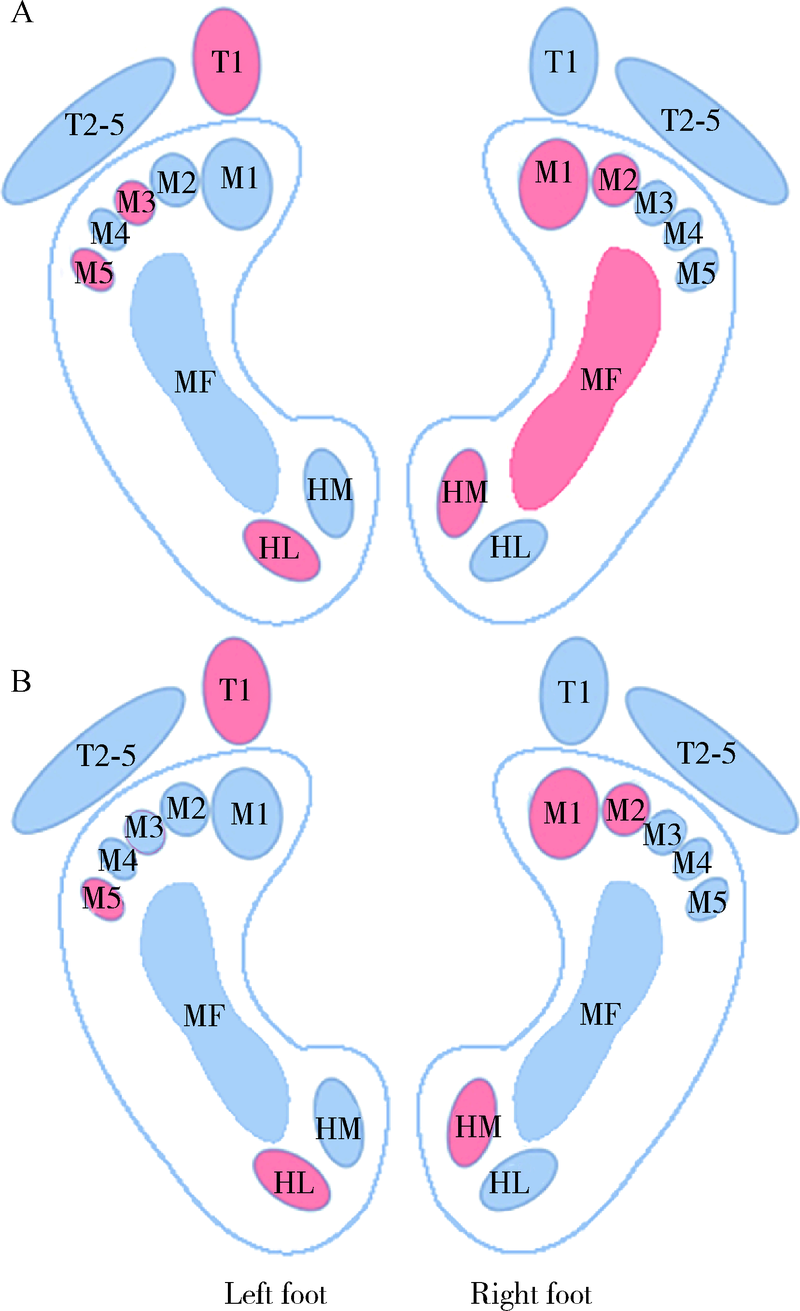
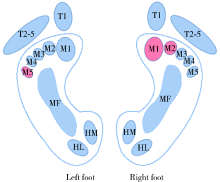
目的: 观察白内障超声乳化联合人工晶体植入术后老年人足底受力情况的变化,探讨视觉重建对老年人足踝部生物力学的影响。方法: 选择2016年10月至2019年12月在北京大学第三医院眼科行双眼白内障手术的32例年龄相关性白内障患者[男5例,女27例,平均年龄(70.1±5.2)岁]进行随访,以Footscan分析系统记录术前及术后1个月平地行走过程中的足底压力参数,对足底第1趾骨(1st toe,T1)、第2~5趾骨(2nd to 5th toe,T2-5)、第1~5跖骨(1st to 5th metatarsal heads,M1~M5)、中足(midfoot,MF)、足跟内侧(heel medial,HM)、足跟外侧(heel lateral,HL)区域触地最大压强(peak pressure,PP),触地冲量(impulse,I),压力时间积分(pressure-time integral,PTI)及触地压强达峰时间(time to peak pressure, TPP)进行对比分析。结果: 术后,患者视功能得到有效重建,双眼视力显著提高(Z=-4.878,-4.801,P<0.001);优势侧(右足)M2区受力较术前增强,PP值(t=2.266,P=0.031)及I值(t=2.152,P=0.039)均增大,其他区域受力强度及时间参数的变化差异均无统计学意义。足底受力分布具有侧向性,术前优势侧M1、M2、MF及HM区PP值大于非优势侧(t=-2.414,-2.478,-2.144,-5.269;P<0.05),非优势侧T1、M3、M5及HL区PP值大于优势侧(t=4.830,3.155,2.686,3.683;P<0.05),优势侧M1、MF及HM区I值大于非优势侧(t=-2.380,-2.185,-5.320;P<0.05),非优势侧T1、M3、M5及HL区I值大于优势侧(t=4.489,2.247,2.838,3.992;P<0.05);术后,M3及MF区双侧受力强度趋于一致;M1(ZPP△=-2.721,P=0.007;ZI△=-2.581,P=0.010)、M2(ZPP△=-2.674,P=0.007;ZI△=-2.375,P=0.018)和M5区(ZPP△=1.991,P=0.046;ZI△=2.150,P=0.032)双侧受力差异幅度有所增大。结论: 白内障手术后足底压力变化以优势侧前足内侧第二跖骨头区受力增大为特征,视觉重建可能加剧优势侧前足内侧着重受力及非优势侧前足外侧着重受力。
中图分类号:
- R779.66
| [1] |
Studenski S, Perera S, Patel K, et al. Gait speed and survival in older adults [J]. JAMA, 2011, 305(1):50-58.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.1923 |
| [2] |
Cuevas-Trisan R. Balance problems and fall risks in the elderly [J]. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am, 2017, 28(4):727-737.
doi: S1047-9651(17)30053-0 pmid: 29031339 |
| [3] |
Rietdyk S, Rhea CK. Control of adaptive locomotion: effect of visual obstruction and visual cues in the environment [J]. Exp Brain Res, 2006, 169(2):272-278.
doi: 10.1007/s00221-005-0345-y |
| [4] |
Saucedo F, Yang F. Effects of visual deprivation on stability among young and older adults during treadmill walking [J]. Gait Posture, 2017, 54:106-111.
doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2017.03.001 |
| [5] |
Dhital A, Pey T, Stanford MR. Visual loss and falls: a review [J]. Eye (Lond), 2010, 24(9):1437-1446.
doi: 10.1038/eye.2010.60 pmid: 20448666 |
| [6] |
Tricco AC, Thomas SM, Veroniki AA, et al. Comparisons of interventions for preventing falls in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. JAMA, 2017, 318(17):1687-1699.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.15006 |
| [7] |
Deshpande N, Metter EJ, Lauretani F, et al. Activity restriction induced by fear of falling and objective and subjective measures of physical function: a prospective cohort study [J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2008, 56(4):615-620.
doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01639.x pmid: 18312314 |
| [8] |
Ayaki M, Nagura T, Toyama Y, et al. Motor function benefits of visual restoration measured in age-related cataract and simulated patients: case-control and clinical experimental studies [J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5:14595.
doi: 10.1038/srep14595 |
| [9] |
Ayaki M, Muramatsu M, Negishi K, et al. Improvements in sleep quality and gait speed after cataract surgery [J]. Rejuvenation Res, 2013, 16(1):35-42.
doi: 10.1089/rej.2012.1369 |
| [10] | Durmus B, Emre S, Cankaya C, et al. Gain in visual acuity after cataract surgery improves postural stability and mobility [J]. Bratisl Lek Listy, 2011, 112(12):701-705. |
| [11] | Duman F, Kilic Z, Ozcan-Eksi EE. Impact of cataract surgery on functional balance skills of adults [J]. Turk J Ophthalmol, 2019, 49(5):243-249. |
| [12] |
Schwartz S, Segal O, Barkana Y, et al. The effect of cataract surgery on postural control [J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2005, 46(3):920-924.
doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0543 |
| [13] |
Chylack LT Jr, Wolfe JK, Singer DM, et al. The lens opacities classification system Ⅲ. The longitudinal study of cataract study group [J]. Arch Ophthalmol, 1993, 111(6):831-836.
doi: 10.1001/archopht.1993.01090060119035 |
| [14] | 朱婷, 马霞, 翟华, 等. 踝关节不同应力位的动态足底压力特征 [J]. 医用生物力学, 2020, 35(40):342-348. |
| [15] |
Koldenhoven RM, Feger MA, Fraser JJ, et al. Surface electromyography and plantar pressure during walking in young adults with chronic ankle instability [J]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 2016, 24(4):1060-1070.
doi: 10.1007/s00167-016-4015-3 |
| [16] |
Snijders AH, van de Warrenburg BP, Giladi N, et al. Neurological gait disorders in elderly people: clinical approach and classification [J]. Lancet Neurol, 2007, 6(1):63-74.
pmid: 17166803 |
| [17] |
Guedes RC, Dias RC, Pereira LS, et al. Influence of dual task and frailty on gait parameters of older community-dwelling individuals [J]. Braz J Phys Ther, 2014, 18(5):445-452.
doi: S1413-35552014000500445 pmid: 25372007 |
| [18] |
Sainburg RL. Handedness: differential specializations for control of trajectory and position [J]. Exerc Sport Sci Rev, 2005, 33(4):206-213.
pmid: 16239839 |
| [19] |
Denyer JR, Hewitt NL, Mitchell AC. Foot structure and muscle reaction time to a simulated ankle sprain [J]. J Athl Train, 2013, 48(3):326-330.
doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-48.2.15 |
| [20] |
Buldt AK, Allan JJ, Landorf KB, et al. The relationship between foot posture and plantar pressure during walking in adults: a systematic review [J]. Gait Posture, 2018, 62:56-67.
doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2018.02.026 |
| [21] | Catan L, Amaricai E, Onofrei RR, et al. The impact of overweight and obesity on plantar pressure in children and adolescents: a systematic review [J/OL]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2020, 17(18):6600(2020-09-10)[2021-05-01]. http://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17186600 . |
| [22] |
Peters M. Footedness: asymmetries in foot preference and skill and neuropsychological assessment of foot movement [J]. Psychol Bull, 1988, 103(2):179-192.
pmid: 3283813 |
| [23] |
Seidler RD, Bernard JA, Burutolu TB, et al. Motor control and aging: links to age-related brain structural, functional, and biochemical effects [J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2010, 34(5):721-733.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.10.005 |
| [1] | 刘园梅, 傅义程, 郝靖欣, 张福春, 刘慧琳. 老年髋部骨折患者住院期间发生术后心力衰竭的列线图预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 874-883. |
| [2] | 张浩宇,石逸雯,潘薇,刘爱萍,孙昕霙,李曼,张旭熙. 基于不同失能水平的老年人照料需求的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 431-440. |
| [3] | 靖婷,江华,李婷,申倩倩,叶兰,曾银丹,梁文欣,冯罡,司徒文佑,张玉梅. 中国西部5城市中老年人血清25羟基维生素D与握力的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 448-455. |
| [4] | 林郁婷,王华丽,田宇,巩俐彤,常春. 北京市老年人认知功能的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 456-461. |
| [5] | 汤华萌,袁典琪,王明星,杨晗冰,郭超. 数字融入和健康生活方式对社会经济状况与老年人抑郁关系的序列中介作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 230-238. |
| [6] | 刘慧丽,吕彦函,王晓晓,李民. 老年患者腹腔镜泌尿系肿瘤根治术后慢性疼痛的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 851-856. |
| [7] | 祝春素,连至炜,崔一民. 中国中老年人抑郁和慢性病的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 606-611. |
| [8] | 刘光奇,庞元捷,吴疆,吕敏,于孟轲,李雨橦,黄旸木. 2013—2019年流感季北京市住院老年人流感疫苗接种趋势分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 505-510. |
| [9] | 刘杰,郭超. 正/负性情绪对中国老年人死亡风险影响的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 255-260. |
| [10] | 李佳,徐钰,王优雅,高占成. 老年流感肺炎的临床特征及D-二聚体与疾病严重程度的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 153-160. |
| [11] | 彭顺壮, 付茜茜, 冯星淋. 中国中老年居民教育程度与失能发生:社会参与的中介作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 549-554. |
| [12] | 侯宗辰,敖英芳,胡跃林,焦晨,郭秦炜,黄红拾,任爽,张思,谢兴,陈临新,赵峰,皮彦斌,李楠,江东. 慢性踝关节不稳患者足底压力特征及相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 279-285. |
| [13] | 陈家丽,金月波,王一帆,张晓盈,李静,姚海红,何菁,李春. 老年发病类风湿关节炎的临床特征及其心血管疾病危险因素分析:一项大样本横断面临床研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1040-1047. |
| [14] | 陈健,左才红,张财义,杨明,张培训. 解剖型髓内钉和股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 283-287. |
| [15] | 徐小凤,陈茜,赵艺璞,胡秀英. 我国西部地区居家老年人生活自理能力调查分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(3): 457-462. |
|
||