北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (1): 134-139. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.01.021
深度学习算法辅助构建三维颜面正中矢状平面
朱玉佳1,2,许晴3,赵一姣1,2,张磊1,2,付子旺3,温奥楠1,2,高梓翔1,2,张昀4,傅湘玲3,△( ),王勇1,2,△(
),王勇1,2,△( )
)
- 1.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔医学数字化研究中心,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心,国家药品监督管理局口腔生物材料重点实验室,北京 100081
2.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔修复科,北京 100081
3.北京邮电大学计算机学院(国家示范性软件学院),北京 100876
4.兰州市口腔医院特诊科,兰州 730000
Deep learning-assisted construction of three-demensional facial midsagittal plane
ZHU Yu-jia1,2,XU Qing3,ZHAO Yi-jiao1,2,ZHANG Lei1,2,FU Zi-wang3,WEN Ao-nan1,2,GAO Zi-xiang1,2,ZHANG Jun4,FU Xiang-ling3,△( ),WANG Yong1,2,△(
),WANG Yong1,2,△( )
)
- 1. Center of Digital Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
3. School of Computer Science, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications(National Pilot Software Engineering School), Beijing 100876, China
4. Department of Geriatric Dentistry, Lanzhou Stomatological Hospital, Lanzhou 730000, China
摘要:
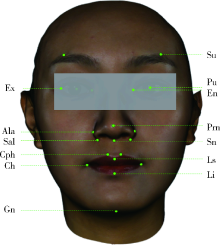
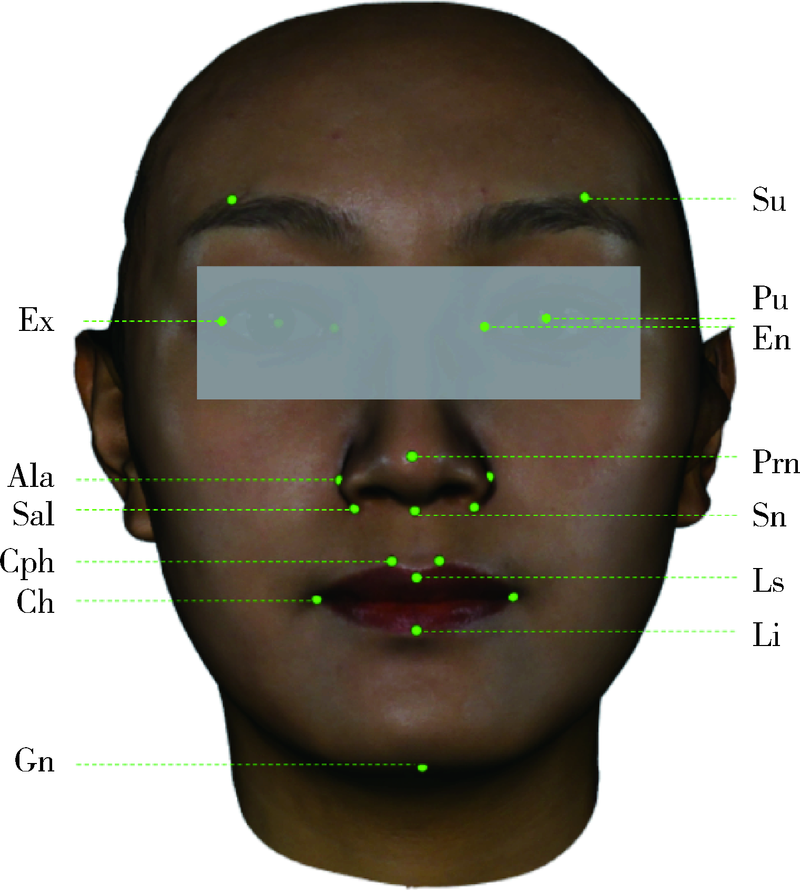
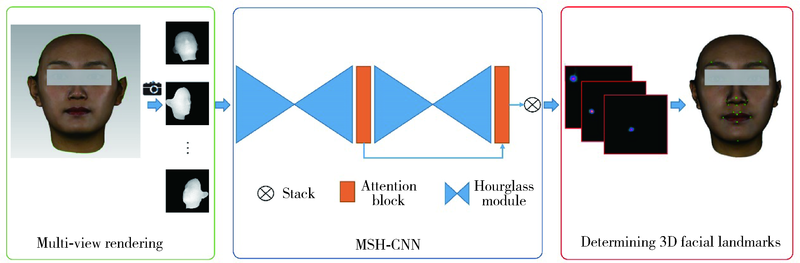
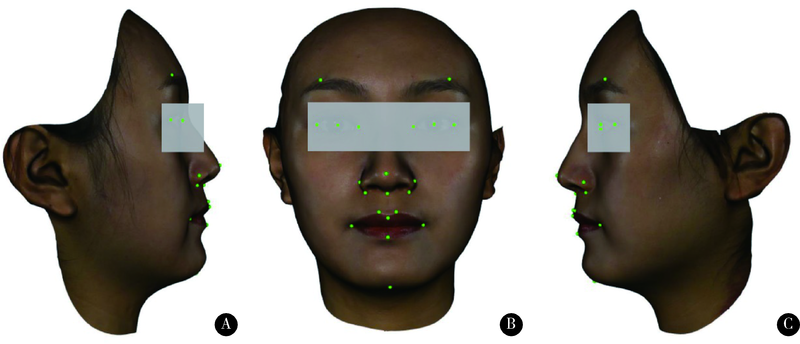
目的: 旨在建立一种可准确确定三维颜面解剖标志点的深度学习算法——多视图堆叠沙漏神经网络(multi-view stacked hourglass convolutional neural networks,MSH-CNN), 并结合赋权普氏分析算法实现三维颜面正中矢状平面的自动构建。方法: 收集面部无明显畸形的受试者100例,获取三维颜面数据,由专家进行颜面标志点(21个)和正中矢状平面的标注。以上述其中80例受试者三维颜面数据作为训练集数据,训练并建立本研究的MSH-CNN算法模型。以其余20例作为测试集数据,由训练后的深度学习算法自动确定每例数据的三维颜面解剖标志点(21个), 并评价算法标点与专家标点间“定点误差”。将MSH-CNN自动确定的三维颜面解剖标志点应用于本课题组前期研究建立的赋权普氏分析算法,可自动构建出20例受试者的三维颜面正中矢状平面。计算MSH-CNN结合赋权普氏分析算法构建的正中矢状平面与专家正中矢状平面间“角度误差”,评价三维颜面正中矢状平面自动构建方法的效果。结果: 针对20例面部无明显畸形的受试者,基于MSH-CNN和赋权普氏分析算法构建正中矢状平面与专家平面间的角度误差平均为0.73°±0.50°,其中MSH-CNN自动确定颜面21个解剖标志点的定点误差平均为(1.13±0.24) mm,眶区定点误差最大平均为(1.31±0.54) mm,鼻区定点误差最小平均为(0.79±0.36) mm。结论: 将深度学习算法与赋权普氏分析算法结合应用,实现了三维颜面正中矢状平面的全自动构建,初步达到了临床专家的构建效果,为自主知识产权的软件开发奠定了基础。
中图分类号:
- R783.2
| [1] |
O’Grady K, Antonyshyn O. Facial asymmetry: three-dimensional analysis using laser surface scanning[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1999, 104(4):928-937.
doi: 10.1097/00006534-199909020-00006 |
| [2] |
Silva BP, Mahn E, Stanley K, et al. The facial flow concept: an organic orofacial analysis-the vertical component[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2019, 121(2):189-194.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2018.03.023 |
| [3] |
Staderini E, Patini R, Camodeca A, et al. Three-dimensional assessment of morphological changes following nasoalveolar molding therapy in cleft lip and palate patients: a case report[J]. Dent J, 2019, 7(1):27-33.
doi: 10.3390/dj7010027 |
| [4] | 郭宏铭, 白玉兴, 周立新, 等. 北京地区正常牙合面部软组织不对称性的三维测量研究[J]. 北京口腔医学, 2006, 14(1):50-52. |
| [5] |
Hartmann J, Meyer-Marcotty P, Benz M, et al. Reliability of a method for computing facial symmetry plane and degree of asymmetry based on 3D-data[J]. J Orofac Orthop, 2007, 68(6):477-490.
pmid: 18034288 |
| [6] |
Klingenberg CP, Barluenga M, Meyer A. Shape analysis of symmetric structures: quantifying variation among individuals and asymmetry[J]. Evolution, 2002, 56(10):1909-1920.
pmid: 12449478 |
| [7] | 熊玉雪, 杨慧芳, 赵一姣, 等. 两种评价面部三维表面数据不对称度方法的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(2):340-343. |
| [8] |
Zhu YJ, Zheng SW, Yang GS, et al. A novel method for 3D face symmetry reference plane based on weighted Procrustes analysis algorithm[J]. Bmc Oral Health, 2020, 20(1):1-11.
doi: 10.1186/s12903-019-0991-2 |
| [9] | 朱玉佳, 赵一姣, 郑盛文, 等. 基于赋权形态学分析的三维面部对称参考平面构建方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 53(1):220-226. |
| [10] |
de Mom E, Chapuis J, Pappas I, et al. Automatic extraction of the mid-facial plane for cranio-maxillofacial surgery planning[J]. Int J Oral Max Surg, 2006, 35(7):636-642.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2006.01.028 |
| [11] | Benz M, Laboureux X, Maier T, et al. The symmetry of faces[C]. Germany: Aka GmbH, 2002. |
| [12] | 田凯月. 下颌前突偏斜畸形数字化矫治方案设计[D]. 北京:北京大学医学部, 2015. |
| [13] |
Xiong YX, Zhao YJ, Yang HF, et al. Comparison between interactive closest point and procrustes analysis for determining the median sagittal plane of three-dimensional facial data[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2016, 27(2):441-444.
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000002376 |
| [14] | Zelditch, Leah M. Geometric morphometrics for biologists: a primer [M]. New York and London: Elsevier Academic Press, 2004: 293-319. |
| [15] |
Katina S, Mcneil K, Ayoub A, et al. The definitions of three-dimensional landmarks on the human face: an interdisciplinary view[J]. J Anat, 2016, 228(3):355-365.
doi: 10.1111/joa.2016.228.issue-3 |
| [16] | Agbolade O, Nazri A, Yaakob R, et al. Homologous multi-points warping: an algorithm for automatic 3D facial landmark[C]. China: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 2019. |
| [17] |
Creusot C, Pears N, Austin J. A machine-learning approach to keypoint detection and landmarking on 3D meshes[J]. Int J Comput Vision, 2013, 102(1/2/3):146-179.
doi: 10.1007/s11263-012-0605-9 |
| [18] | Su H, Maji S, Kalogerakis E, et al. Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3D shape recognition[C]. Chile: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 2015. |
| [19] | Paulsen RR, Juhl KA, Haspang TM, et al. Multi-view consensus CNN for 3D facial landmark placement[C]. Australia: Springer, 2018. |
| [20] | Ding ML, Fan Y, Qin M, et al. Facial morphological changes following denture treatment in children with hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia[J]. Pediatr Dent, 2020, 42(4):315-320. |
| [21] | 萧宁, 王勇, 赵一姣. 三维颜面部软组织正中矢状面确定方法的研究进展[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2018, 53(7):495-499. |
| [22] |
Erten O, Yilmaz BN. Three-dimensional imaging in orthodontics[J]. Turk J Orthod, 2018, 31(3):86-94.
doi: 10.5152/TurkJOrthod. |
| [23] | 王斯维, 杨慧芳, 赵一姣, 等. 3种生成大视野锥形束CT数据正中矢状面方法的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(2):330-335. |
| [1] | 许克新,丁泽华. 人工智能在功能泌尿外科的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 771-774. |
| [2] | 朱玉佳,赵一姣,郑盛文,温奥楠,傅湘玲,王勇. 基于赋权形态学分析的三维面部对称参考平面构建方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 220-226. |
| [3] | 熊玉雪, 杨慧芳, 赵一姣, 王勇. 两种评价面部三维表面数据不对称度方法的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(2): 340-343. |
|
||