北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (1): 126-133. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.01.020
种植体折裂的临床分型与临床治疗方案
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院第四门诊部, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100025
Clinical classification and treatment decision of implant fracture
- Fourth Clinical Division, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100025, China
摘要:
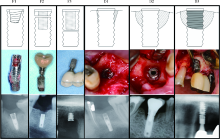
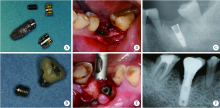
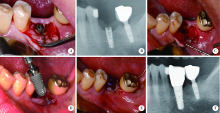
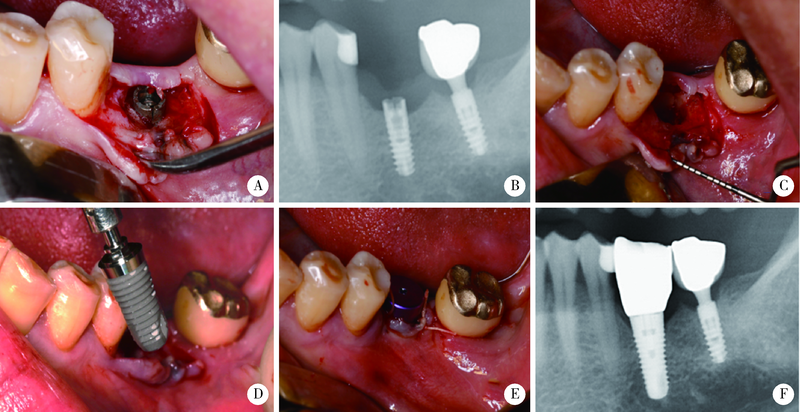
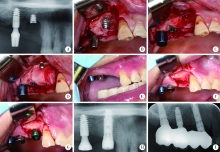
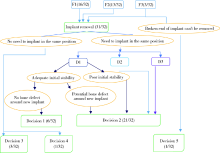
目的: 基于对32枚折裂种植体的再治疗随访观察,拟提出一套基于种植体折裂位置与骨吸收形态的种植体折裂二元临床分型法,并依据此分型归纳总结种植体折裂的治疗决策,为临床工作提供指导。方法: 选择1994年4月至2019年8月在北京大学口腔医院种植科及第四门诊部就诊且由作者团队种植治疗后出现种植体折裂并接受再治疗的病例进行回顾分析和长期随访,提出基于种植体折裂形态与骨吸收的二元临床分型法,并探讨基于种植体折裂新分型的治疗方案。结果: 回顾了5 481例患者(10 642枚种植体), 共发现27例患者(32枚种植体)折裂。在新分型体系下,种植体颈部垂直型折裂(F1,50.0%) 与种植体颈部水平型折裂(F2,40.6%) 多见,深部水平型折裂(F3,9.4%) 少见,植体周围骨缺损的3种类型(D1:无骨吸收或窄骨内袋;D2:四壁杯状骨缺损;D3:杯状骨缺损伴颊侧和/或舌侧骨缺损)则分布均匀。在种植体折裂二元分型体系中,出现频率最高的是F1D1型(31.3%)和F2D2型(25.0%), 其中F1与D1成显著正相关(r=0.592, P<0.001);F2与D2成显著正相关 (r=0.352, P=0.048); F1与D2成显著负相关 (r=-0.465, P=0.007)。种植体折裂最常采用的治疗手段为植体取出+引导骨再生术+延期种植(65.6%);其次为植体取出+同期种植(18.8%)。F1D1分型与植体取出+同期种植的治疗策略显著相关(r=0.367, P=0.039)。结论: 种植体折裂二元新分型法可以较好适应临床应用,并能为种植体折裂的临床治疗提供参考和指导。
中图分类号:
- R783
| [1] | Albrektsson T, Zarb GA, Worthington P, et al. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: A review and proposed criteria of success[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 1986, 1(1):11-25. |
| [2] | 林野, 李健慧, 邱立新. 口腔种植修复临床效果十年回顾研究[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2006, 41(3):131-135. |
| [3] |
Berglundh T, Persson L, Bjorn K. A systematic review of the incidence of biological and technical complications in implant dentistry reported in prospective longitudinal studies of at least 5 years[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2002, 29(Suppl 3):197-212
doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051X.29.s3.12.x |
| [4] |
Adell R, Lekholm U, Rockler B, et al. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw[J]. Int J Oral Surg, 1981, 10(6):387-416.
pmid: 6809663 |
| [5] | Rangert B. Force and moments on branemark implants[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 1989, 4(3):241-247. |
| [6] |
Takeuchi K, Ohara T, Furuta M, et al. Tooth loss and risk of dementia in the community: The hisayama study[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2017, 65(5):95-100.
doi: 10.1111/jgs.14791 pmid: 28272750 |
| [7] | Lee JH, Kin YT, Jeong SN, et al. Incidence and pattern of implant fractures: A long-term follow-up multicenter study[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2018, 20(4):463-469. |
| [8] | Misch CE, Strong JT, Bidez MW. Dental implant prosthetics[M]. St. Louis Missouri: Mosby, 2015: 293-314. |
| [9] |
Chrcanovic BR, Kisch J, Albrektsson T, et al. Factors influencing the fracture of dental implants[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2017, 20(1):58-67.
doi: 10.1111/cid.2018.20.issue-1 |
| [10] | Eckert SE, Salinas TJ, Aka K. Dental implant complications: Etiology, prevention, and treatment, 2[M]. Hoboken New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2015: 132-144. |
| [11] |
Alkharrat AR, Schmitter M, Rues S, et al. Fracture behavior of all-ceramic, implant-supported, and tooth-implant-supported fixed dental prostheses[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2018, 22(4):1663-1673.
doi: 10.1007/s00784-017-2233-9 |
| [12] |
Gealh WC, Valéria M, Barbi F, et al. Osseointegrated implant fracture: Causes and Treatment[J]. J Oral Implantol, 2011, 37(4):499-503.
doi: 10.1563/AAID-JOI-D-09-00135.1 |
| [13] | 张磊, 冯海兰. 种植固定修复后机械并发症的预防和处理[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2016, 51(1):10-14. |
| [14] |
Schwarz MS. Mechanical complications of dental implants[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2000, 11(Suppl 1):156-158.
doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.2000.011S1156.x |
| [15] | 尉华杰, 朱一博, 王兴. 19枚种植体负重不同时间后折裂折断的临床分析[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2018, 53(12):815-820. |
| [16] | Quek HC, Tan KB, Nicholls JI. Load fatigue performance of four implant-abutment interface designs: Effect of torque level and implant system[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 2008, 23(2):253-262. |
| [17] | Wiskott HWA, Jaquet R, Scherrer SS, et al. Resistance of internal-connection implant connectors under rotational fatigue loading[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 2007, 22(2):249-257. |
| [18] |
Shemtov-Yona K, Rittel D, Machtei EE, et al. Effect of dental implant diameter on fatigue performance. Part Ⅱ: Failure analysis[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2014, 16(2):178-184.
doi: 10.1111/cid.2014.16.issue-2 |
| [19] |
Gratton DG, Aquilino SA, Stanford CM. Micromotion and dynamic fatigue properties of the dental implant-abutment interface[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2001, 85(1):47-52.
pmid: 11174678 |
| [20] |
Quirynen M, Naert I, van Steenberghe D. Fixture design and overload influence marginal bone loss and fixture success in the Branemark system[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2010, 3(3):104-111.
doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.1992.030302.x |
| [21] | Morgan MJ, James DF, Pilliar RM. Fractures of the fixture component of an osseointegrated implant[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 1993, 8(4):409-414. |
| [22] |
Silva NR, Nourian P, Coelho PG, et al. Impact fracture resistance of two titanium-abutment systems versus a single-piece ceramic implant[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2011, 13(2):168-173.
doi: 10.1111/cid.2011.13.issue-2 |
| [23] |
Steinebrunner L, Wolfart S, Ludwig K, et al. Implant-abutment interface design affects fatigue and fracture strength of implants[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2009, 19(12):1276-1284.
doi: 10.1111/clr.2008.19.issue-12 |
| [24] | Rangert B. Bending overload and implant fracture: a retrospective clinical analysis[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 1995, 10(3):326-334. |
| [25] |
Muroff F, Fredrick I. Removal and replacement of a fractured dental implant: case report[J]. Implant Dent, 2003, 12(3):206-210.
pmid: 14560479 |
| [26] | Balshi TJ, Hernandez FE, Pryszlak DC, et al. An analysis and management of fractured implants: A clinical report[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 1996, 11(5):660-666. |
| [1] | 展新新,曹露露,项东,汤皓,夏丹丹,林红. 成型方向对3D打印口腔义齿基托树脂材料物理性能及力学性能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 345-351. |
| [2] | 吴美辰,许桐楷,安伟,刘中宁,姜婷. 后牙高嵌体和 |
| [3] | 吕梁,张铭津,温奧楠,赵一姣,王勇,李晶,杨庚辰,柳大为. 应用三维软组织空间线角模板法评价颏部对称性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 106-110. |
| [4] | 毛渤淳,田雅婧,王雪东,李晶,周彦恒. 骨性Ⅱ类高角患者拔牙矫治前后的面部软硬组织变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [5] | 赵思铭,王晓燕. 洞缘设计对CAD/CAM瓷嵌体边缘质量和边缘适应性及微渗漏的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1105-1110. |
| [6] | 丁茜,李文锦,孙丰博,谷景华,林元华,张磊. 表面处理对氧化钇和氧化镁稳定的氧化锆种植体晶相及断裂强度的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 721-728. |
| [7] | 欧蒙恩,丁云,唐卫峰,周永胜. 基台边缘-牙冠的平台转移结构中粘接剂流动的三维有限元分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 548-552. |
| [8] | 吴思妤,李娅宁,张晓,吕珑薇,刘云松,叶红强,周永胜. 上颌中切牙全瓷冠牙体预备学习曲线的预测、分析与应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 108-113. |
| [9] | 潘孟乔,刘建,徐莉,徐筱,侯建霞,李小彤,王晓霞. 牙周-正畸-正颌联合治疗骨性安氏Ⅲ类错 |
| [10] | 付玉,胡鑫浓,崔圣洁,施捷. 骨性Ⅱ类高角错 |
| [11] | 周倩妹,丁瑞宇,李莉,白伟,胡菁颖. 调拌纸板厚度对玻璃离子水门汀抗压强度的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 78-81. |
| [12] | 林久祥,陈莉莉,韩冰,陈斯,孙燕楠,刘晓默,张杰铌. 健康正畸为本 美学正畸为鉴——健康矫治理念的构建与传动矫治技术研发应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 837-841. |
| [13] | 高娟,吕航苗,马慧敏,赵一姣,李小彤. 锥形束CT三维体积测量评估骨性Ⅲ类错 |
| [14] | 罗昊,田福聪,王晓燕. 不同椅旁可切削修复材料序列抛光时间及表面粗糙度与光泽度的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 565-571. |
| [15] | 邓艺,张一,李博文,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华. 不同交联剂处理对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层多孔支架的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 557-564. |
|
||