北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 209-216. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.02.002
CACNA1H基因敲除对小鼠孤独症样行为及海马神经元形态学的影响
焦翠1,王俭妹1,况海霞1,武志红1,△( ),柳涛1,2,△(
),柳涛1,2,△( )
)
- 1.南昌大学第一附属医院 儿科,南昌 330006
2.南昌大学第一附属医院 医学科研中心,南昌 330006
Effects of CACNA1H gene knockout on autistic-like behaviors and the morphology of hippocampal neurons in mice
JIAO Cui1,WANG Jian-mei1,KUANG Hai-xia1,WU Zhi-hong1,△( ),LIU Tao1,2,△(
),LIU Tao1,2,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Pediatrics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, China
2. Center for Experimental Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, China
摘要:
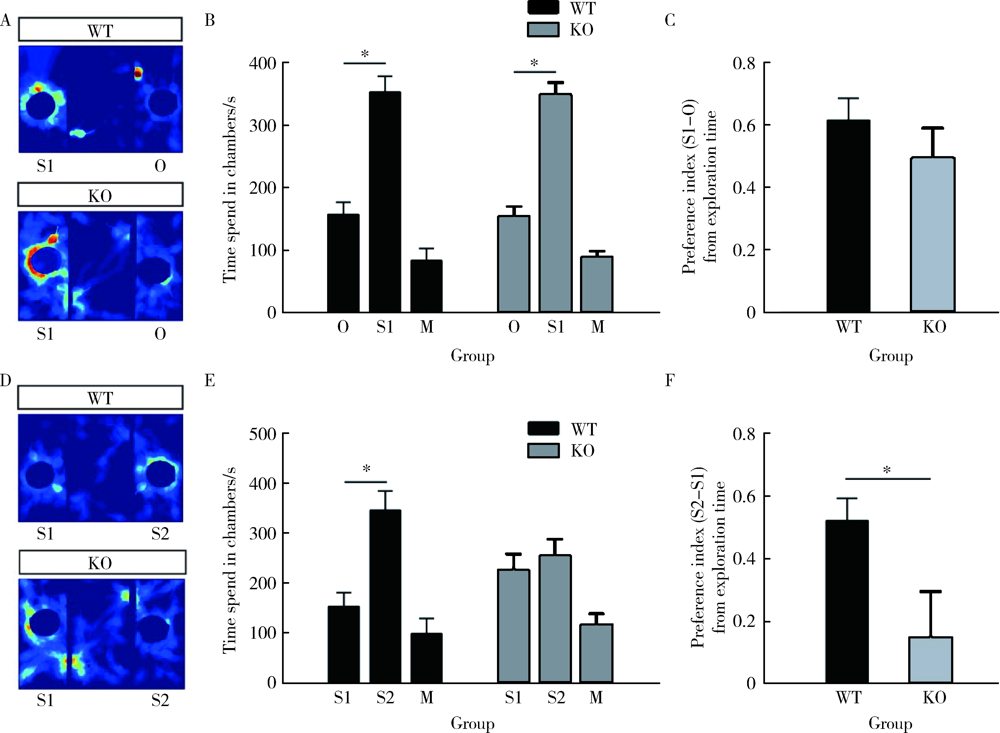
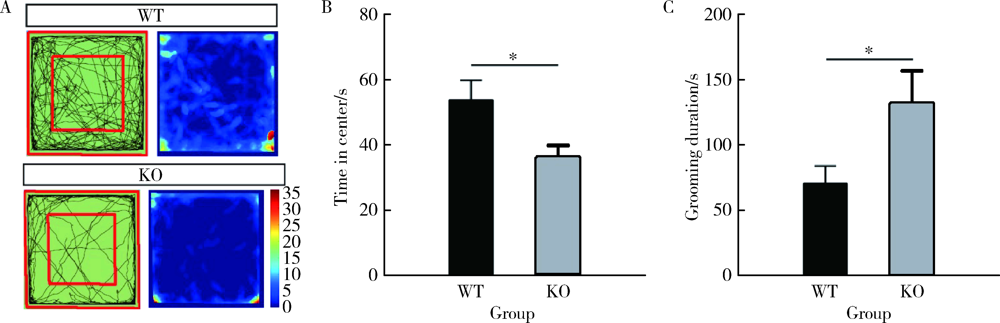
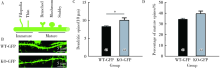
目的: 研究CACNA1H基因敲除(knockout, KO)对小鼠孤独症样行为及海马神经元形态学的影响。方法: 25只3~4周龄C57BL/6背景的CACNA1H KO小鼠作为实验组,26只同年龄同背景的野生型(wild type,WT)小鼠作为对照组。通过三箱实验和旷场实验观察小鼠社交、焦虑和重复刻板行为后测量其脑质量与脑体积,用尼氏染色法(Nissl staining)观察海马神经元数目。将CACNA1H杂合子小鼠与Thy1-GFP-O小鼠杂交,构建CACNA1H-/--Thy1+(KO-GFP)及CACNA1H+/+-Thy1+(WT-GFP)小鼠,观察海马神经元树突棘密度及成熟度。结果: 三箱实验中,社交测试阶段,KO小鼠在陌生鼠箱中的时间比空箱更长(F1,14=95.086,P<0.05;Post-Hoc:P<0.05),探索的偏好指数与对照组相比差异无统计学意义(t=1.044,P>0.05);新社交对象识别测试阶段,KO小鼠在新陌生鼠箱与陌生鼠箱中的时间差异无统计学意义(F1,14=18.062,P<0.05;Post-Hoc:P>0.05),探索的偏好指数低于对照组(t=2.390,P<0.05)。旷场实验中,KO小鼠在旷场中心活动时间明显少于对照组(t=2.503,P<0.05),自梳理时间明显多于对照组(t=-2.299,P<0.05)。形态学结果显示,KO小鼠脑质量/体质量和脑体积与对照组相比差异均无统计学意义(t=0.356,P>0.05;t=-0.660,P>0.05),但其海马齿状回区神经元数目较对照组减少(t=2.323,P<0.05),且KO-GFP小鼠海马齿状回区树突棘密度较对照组增加(t=-2.374,P<0.05),而成熟度差异无统计学意义(t=-1.935,P>0.05)。结论: CACNA1H KO小鼠具有孤独症样行为,可能与海马齿状回区神经元数目减少及树突棘密度增高有关。
中图分类号:
- R749.94
| [1] |
Baio J, Wiggins L, Christensen DL, et al. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years: Autism and Deve-lopmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2014[J]. MMWR Surveill Summ, 2018, 67(6):1-23.
doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6706a1 pmid: 29701730 |
| [2] |
Bai D, Yip BHK, Windham GC, et al. Association of genetic and environmental factors with autism in a 5-country cohort[J]. JAMA Psychiatry, 2019, 76(10):1035-1043.
doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.1411 |
| [3] |
Iakoucheva LM, Muotri AR, Sebat J. Getting to the cores of autism[J]. Cell, 2019, 178(6):1287-1298.
doi: S0092-8674(19)30836-0 pmid: 31491383 |
| [4] |
Andrade A, Brennecke A, Mallat S, et al. Genetic associations between voltage-gated calcium channels and psychiatric disorders[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(14):3537.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20143537 |
| [5] |
Rebellato P, Kaczynska D, Kanatani S, et al. The T-type Ca2+ channel Cav3.2 regulates differentiation of neural progenitor cells during cortical development via caspase-3[J]. Neuroscience, 2019, 402:78-89.
doi: S0306-4522(19)30035-1 pmid: 30677486 |
| [6] |
Souza IA, Gandini MA, Zhang FX, et al. Pathogenic Cav3.2 channel mutation in a child with primary generalized epilepsy[J]. Mol Brain, 2019, 12(1):86.
doi: 10.1186/s13041-019-0509-5 |
| [7] |
Splawski I, Yoo DS, Stotz SC, et al. CACNA1H mutations in autism spectrum disorders[J]. J Biol Chem, 2006, 281(31):22085-22091.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603316200 pmid: 16754686 |
| [8] |
Chourasia N, Osso-Rivera H, Ghosh A, et al. Expanding the phenotypic spectrum of CACNA1H mutations[J]. Pediatr Neurol, 2019, 93:50-55.
doi: S0887-8994(18)30384-9 pmid: 30686625 |
| [9] | Feng XJ, Ma LX, Jiao C, et al. Nerve injury elevates functional Cav3.2 channels in superficial spinal dorsal horn[J]. Mol Pain, 2019, 15:1744806919836569. |
| [10] |
Takumi T, Tamada K, Hatanaka F, et al. Behavioral neuroscience of autism[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2020, 110:60-76.
doi: S0149-7634(18)30372-5 pmid: 31059731 |
| [11] | Kaidanovich-Beilin O, Lipina T, Vukobradovic I, et al. Assessment of social interaction behaviors[J]. J Vis Exp, 2011(48):e2473. |
| [12] | Seibenhener ML, Wooten MC. Use of the Open Field Maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in mice[J]. J Vis Exp, 2015(96):e52434. |
| [13] |
Harris KM, Jensen FE, Tsao B. Three-dimensional structure of dendritic spines and synapses in rat hippocampus (CA1) at postnatal day 15 and adult ages: Implications for the maturation of synaptic physiology and long-term potentiation[J]. J Neurosci, 1992, 12(7):2685-2705.
pmid: 1613552 |
| [14] |
Bader PL, Faizi M, Kim LH, et al. Mouse model of Timothy syndrome recapitulates triad of autistic traits[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108(37):15432-15437.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112667108 |
| [15] |
Iossifov I, O’roak BJ, Sanders SJ, et al. The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder[J]. Nature, 2014, 515(7526):216-221.
doi: 10.1038/nature13908 |
| [16] |
D’gama AM, Pochareddy S, Li M, et al. Targeted DNA sequencing from autism spectrum disorder brains implicates multiple genetic mechanisms[J]. Neuron, 2015, 88(5):910-917.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.11.009 |
| [17] | Lee YH, Yamrom B, Wigler M, et al. Low load for disruptive mutations in autism genes and their biased transmission[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2015, 112(41):E5600-E5607. |
| [18] |
Takata A, Miyake N, Tsurusaki Y, et al. Integrative analyses of de novo mutations provide deeper biological insights into autism spectrum disorder[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 22(3):734-747.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.12.074 |
| [19] |
Gangarossa G, Laffray S, Bourinet E, et al. T-type calcium channel Cav3.2 deficient mice show elevated anxiety, impaired memory and reduced sensitivity to psychostimulants[J]. Front Behav Neurosci, 2014, 8:92.
doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00092 pmid: 24672455 |
| [20] |
Tao J, Hildebrand ME, Liao P, et al. Activation of corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1 selectively inhibits Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels[J]. Mol Pharmacol, 2008, 73(6):1596-1609.
doi: 10.1124/mol.107.043612 |
| [21] |
Henbid MT, Marks WN, Collins MJ, et al. Sociability impairments in genetic absence epilepsy rats from Strasbourg: Reversal by the T-type calcium channel antagonist Z944[J]. Exp Neurol, 2017, 296:16-22.
doi: S0014-4886(17)30161-9 pmid: 28658605 |
| [22] |
Chen CC, Shen JW, Chung NC, et al. Retrieval of context-asso-ciated memory is dependent on the Ca(v)3.2 T-type calcium channel[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(1):e29384.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029384 |
| [23] |
Bauman M, Kemper TL. Histoanatomic observations of the brain in early infantile autism[J]. Neurology, 1985, 35(6):866-874.
pmid: 4000488 |
| [24] |
Courchesne E, Mouton PR, Calhoun ME, et al. Neuron number and size in prefrontal cortex of children with autism[J]. Jama, 2011, 306(18):2001-2010.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.1638 pmid: 22068992 |
| [25] |
Chemin J, Nargeot J, Lory P. Neuronal T-type alpha 1H calcium channels induce neuritogenesis and expression of high-voltage-activated calcium channels in the NG108-15 cell line[J]. J Neurosci, 2002, 22(16):6856-6862.
pmid: 12177183 |
| [26] | Cai Y, Tang X, Chen X, et al. Liver X receptor beta regulates the development of the dentate gyrus and autistic-like behavior in the mouse[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018, 115(12):E2725-E2733. |
| [27] |
Ito H, Morishita R, Nagata KI. Autism spectrum disorder-asso-ciated genes and the development of dentate granule cells[J]. Med Mol Morphol, 2017, 50(3):123-129.
doi: 10.1007/s00795-017-0161-z |
| [28] |
Bernal Sierra YA, Haseleu J, Kozlenkov A, et al. Genetic tracing of Cav3.2 T-type calcium channel expression in the peripheral nervous system[J]. Front Mol Neurosci, 2017, 10:70.
doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00070 pmid: 28360836 |
| [29] |
Martínez-Cerdeño V. Dendrite and spine modifications in autism and related neurodevelopmental disorders in patients and animal models[J]. Dev Neurobiol, 2017, 77(4):393-404.
doi: 10.1002/dneu.22417 pmid: 27390186 |
| [30] |
Katsarou AM, Galanopoulou AS, Moshe SL. Epileptogenesis in neonatal brain[J]. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med, 2018, 23(3):159-167.
doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2017.12.004 |
| [31] | Aguado C, Garcia-Madrona S, Gil-Minguez M, et al. Ontogenic changes and differential localization of T-type Ca(2+) channel subunits Cav3.1 and Cav3.2 in mouse hippocampus and cerebellum[J]. Front Neuroanat, 2016, 10:83. |
| [32] |
Huang IY, Hsu YL, Chen CC, et al. Excavatolide-B enhances contextual memory retrieval via repressing the delayed rectifier potassium current in the hippocampus[J]. Mar Drugs, 2018, 16(11):405.
doi: 10.3390/md16110405 |
| [1] | 袁婷婷,李燊,吴燕,吴海涛. 长期自由选择饮酒小鼠模型的建立及其行为学评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 315-323. |
| [2] | 赵亚楠,范慧芸,王翔宇,罗雅楠,张嵘,郑晓瑛. 孤独症患者过早死亡风险及死亡原因[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 375-383. |
| [3] | 张京,宋佳桂,王振斌,龚玉清,王天卓,周津羽,战军,张宏权. Kindlin-2通过mTOR和Hippo信号通路调节小鼠子宫内膜发育[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 846-852. |
| [4] | 贾睿璇,姜尚伟,赵琳,杨丽萍. Cyp4v3基因敲除小鼠模型的表型分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1099-1106. |
| [5] | 朱忆颖,闵赛南,俞光岩. 局部注射环孢素A对非肥胖糖尿病小鼠下颌下腺分泌功能及炎症的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 750-757. |
| [6] | 朱梅青,崔蓉. 高效液相色谱法测定小鼠血浆中苯并三唑类紫外线吸收剂UV-327和UV-328[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 591-596. |
| [7] | 张晓威,殷华奇,李清,赵永平,KiteBrandes,白文俊,徐涛. 人类趋化素样因子超家族2参与小鼠精子形成[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 228-233. |
| [8] | 吴天伟,崔蓉,张宝旭. 高效液相色谱法测定小鼠血浆中8-甲氧基补骨脂素及其药代动力学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 792-796. |
| [9] | 康磊,霍焱,王荣福,张春丽,闫平,徐小洁. MicroRNA-155靶向的放射性标记探针对乳腺癌小鼠模型的活体显像[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 326-330. |
| [10] | 张伟,庞春艳,王永福. 脂肪间充质干细胞对MRL/lpr小鼠的治疗效果及对脾脏Th17/Treg细胞平衡的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(6): 974-978. |
| [11] | 石慧峰, 张敬旭, 张嵘, 王晓莉. 中国0~6岁儿童孤独症谱系障碍患病率的meta分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 798-806. |
| [12] | 孙睿, 高波, 郭传瑸. 裸小鼠淋巴结的解剖和组织学特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 893-898. |
| [13] | 高丽,于晓潜,蔡宇. 丝线结扎及局部涂抹牙龈卟啉单胞菌对小鼠牙槽骨骨吸收的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 31-035. |
| [14] | 王志华,张伟,张艳清,庞春艳,王永福. CD40 siRNA对 MRL/Lpr狼疮小鼠炎症反应的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(5): 771-776. |
| [15] | 陈小梅,李富强,严速,吴小翠,唐翠兰. 尼古丁减轻高脂高果糖诱导的非酒精性脂肪性肝炎小鼠的肝脏炎症[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(5): 777-782. |
|
||