北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 249-254. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.02.008
北京城镇职工2型糖尿病患者缺血性脑卒中发病率及主要危险因素
吴俊慧,武轶群,吴瑶,王紫荆,吴涛,秦雪英,王梦莹,王小文,王伽婷,胡永华( )
)
- 北京大学公共卫生学院流行病与卫生统计学系,北京 100191
Incidence and risk factors of ischemic stroke in patients with type 2 diabetes among urban workers in Beijing, China
WU Jun-hui,WU Yi-qun,WU Yao,WANG Zi-jing,WU Tao,QIN Xue-ying,WANG Meng-ying,WANG Xiao-wen,WANG Jia-ting,HU Yong-hua( )
)
- Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
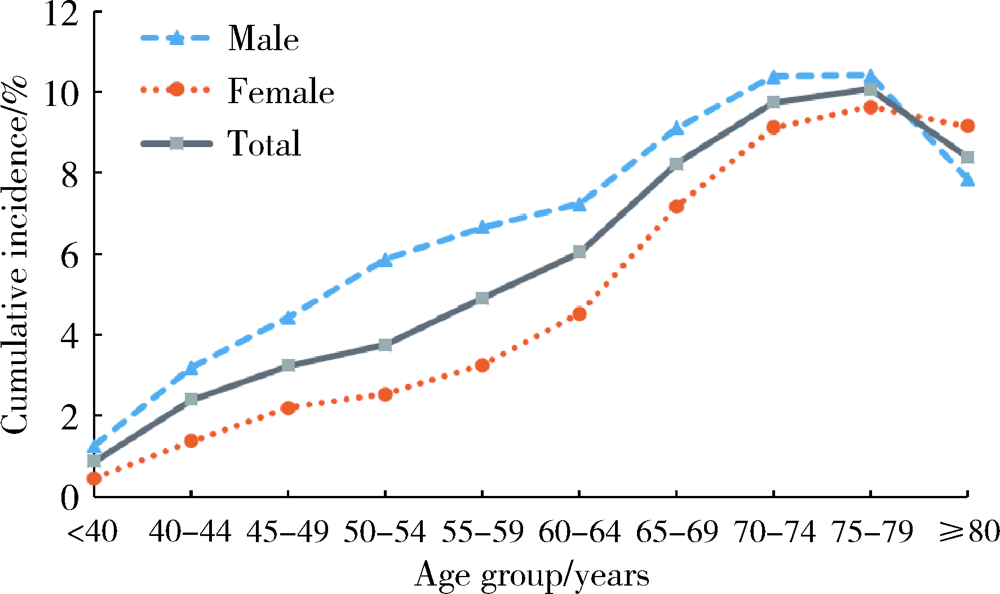
目的: 通过对新发2型糖尿病患者进行前瞻性观察,探究2型糖尿病发病后缺血性脑卒中的发病特点,并进一步分析2型糖尿病患者缺血性脑卒中发病的危险因素。方法: 数据资料来源于北京市城镇职工基本医疗保险信息系统数据库。研究采用前瞻性设计,对2010年新诊断为2型糖尿病的患者在2010—2017年缺血性脑卒中的发病情况进行描述,采用Logistic回归模型分析2型糖尿病患者缺血性脑卒中发病的危险因素。结果: 共纳入185 813例新发2型糖尿病患者,平均年龄(58.5±13.2)岁,男性占49.0%。随访7年内出现新发缺血性脑卒中患者10 393例,累积发病率为5.6%,发病密度为8.1/1 000人年。2型糖尿病患者缺血性脑卒中在各个年龄段均有发生,不同年龄组累积发病率分别为:≤44岁组1.5%(95%CI:1.3%~1.6%),45~54岁组3.6%(95%CI:3.4%~3.7%),55~64岁组5.4%(95%CI:5.2%~5.5%),≥65岁组9.2%(95%CI:9.0%~9.4%),累积发病率随年龄升高而增加(P<0.05)。男性累积发病率(6.8%,95%CI: 6.7%~7.0%)高于女性(4.4%,95%CI: 4.3%~4.6%);<80岁的患者中,男性在各年龄段累积发病率均高于女性;≥80岁的患者中,女性累积发病率(9.2%)高于男性(7.9%)。进一步分析2型糖尿病患者缺血性脑卒中发病的危险因素,发现患有冠心病(OR=3.18,95%CI:2.72~3.72)、心力衰竭(OR=1.53,95%CI:1.32~1.79)、肾衰竭(OR=1.45, 95%CI:1.20~1.75)等合并症与2型糖尿病患者缺血性脑卒中的发病有关。结论: 2型糖尿病患者缺血性脑卒中发病率仍处于较高水平,应针对老年患者加强危险因素管理,尽早筛查2型糖尿病患者的合并症情况并采取针对性的预防控制措施。
中图分类号:
- R181.32
| [1] |
Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: Glo-bal estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2018, 138:271-281.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.02.023 |
| [2] |
Feigin VL, Roth GA, Naghavi M, et al. Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990-2013: A systema-tic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2016, 15(9):913-924.
doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30073-4 |
| [3] |
Yang R, Pedersen NL, Bao C, et al. Type 2 diabetes in midlife and risk of cerebrovascular disease in late life: A prospective nested case-control study in a nationwide Swedish twin cohort[J]. Diabetologia, 2019, 62(8):1403-1411.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4892-3 |
| [4] |
Kissela BM, Khoury J, Kleindorfer D, et al. Epidemiology of ischemic stroke in patients with diabetes: The greater Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky stroke study[J]. Diabetes Care, 2005, 28(2):355-359.
doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.2.355 pmid: 15677792 |
| [5] |
Huang ES, Laiteerapong N, Liu JY, et al. Rates of complications and mortality in older patients with diabetes mellitus: The diabetes and aging study[J]. JAMA Intern Med, 2014, 174(2):251-258.
doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.12956 |
| [6] |
Staszewsky L, Cortesi L, Baviera M, et al. Diabetes mellitus as risk factor for atrial fibrillation hospitalization: Incidence and outcomes over nine years in a region of Northern Italy[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2015, 109(3):476-484.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2015.06.006 |
| [7] |
Li J, Dong Y, Wu T, et al. Differences between Western and Asian type 2 diabetes patients in the incidence of vascular complications and mortality: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials on lowering blood glucose[J]. J Diabetes, 2016, 8(6):824-833.
doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12361 |
| [8] |
Mulnier HE, Seaman HE, Raleigh VS, et al. Risk of stroke in people with type 2 diabetes in the UK: A study using the general practice research database[J]. Diabetologia, 2006, 49(12):2859-2865.
pmid: 17072582 |
| [9] |
Giorda CB, Avogaro A, Maggini M, et al. Incidence and risk factors for stroke in type 2 diabetic patients: The DAI study[J]. Stroke, 2007, 38(4):1154-1160.
pmid: 17332448 |
| [10] |
Gong Q, Zhang P, Wang J, et al. Morbidity and mortality after lifestyle intervention for people with impaired glucose tolerance: 30-year results of the Da Qing diabetes prevention outcome study[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2019, 7(6):452-461.
doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30093-2 |
| [11] |
Banerjee C, Moon YP, Paik MC, et al. Duration of diabetes and risk of ischemic stroke: The Northern Manhattan study[J]. Stroke, 2012, 43(5):1212-1217.
doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.641381 |
| [12] | 任晓宇, 史典, 张德生, 等. 金昌队列人群代谢性疾病与脑卒中发病关系前瞻性研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2019, 40(5):521-525. |
| [13] | 沈卓之, 丁贤彬, 毛德强, 等. 2015年重庆市常住人口脑卒中发病与死亡情况[J]. 公共卫生与预防医学, 2016, 27(5):48-51. |
| [14] | 韩荣荣, 唐爱奇, 方杭燕, 等. 2型糖尿病患者并发脑卒中的前瞻性研究[J]. 预防医学, 2017, 29(2):139-141. |
| [15] |
Luk AOY, Hui EMT, Sin MC, et al. Declining trends of cardiovascular-renal complications and mortality in type 2 diabetes: The Hong Kong diabetes database[J]. Diabetes Care, 2017, 40(7):928-935.
doi: 10.2337/dc16-2354 |
| [16] |
Shen Y, Shi L, Nauman E, et al. Race and sex differences in rates of diabetic complications[J]. J Diabetes, 2019, 11(6):449-456.
doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12869 pmid: 30315628 |
| [17] |
Wang Y, Dai Y, Zheng J, et al. Sex difference in the incidence of stroke and its corresponding influence factors: Results from a follow-up 8.4 years of rural China hypertensive prospective cohort study[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2019, 18(1):72.
doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1010-y |
| [18] |
Barker-Collo S, Bennett DA, Krishnamurthi RV, et al. Sex diffe-rences in stroke incidence, prevalence, mortality and disability-adjusted life years: Results from the global burden of disease study 2013[J]. Neuroepidemiology, 2015, 45(3):203-214.
doi: 10.1159/000441103 pmid: 26505984 |
| [19] |
Madsen TE, Khoury JC, Alwell KA, et al. Sex differences in cardiovascular risk profiles of ischemic stroke patients with diabetes in the Greater Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky stroke study[J]. J Diabetes, 2018, 10(6):496-501.
doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12567 pmid: 28523847 |
| [20] |
Petrea RE, Beiser AS, Seshadri S, et al. Gender differences in stroke incidence and poststroke disability in the Framingham heart study[J]. Stroke, 2009, 40(4):1032-1037.
doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.542894 |
| [21] | 申宏, 方旭东. 重庆市巴南区居民2012—2015年脑卒中发病情况分析[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2016, 13(23):3398-3399. |
| [22] | 叶虹. 2型糖尿病合并缺血性脑血管病的相关危险因素研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2011. |
| [23] |
GBD 2016 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990-2016: A systematic analysis for the glo-bal burden of disease study 2016[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2019, 18(5):439-458.
doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30034-1 |
| [24] | Madan S. Changes in diabetes-related complications in the United States[J]. N Engl J Med, 2014, 371(3):285-286. |
| [25] |
Bui HDT, Jing X, Lu R, et al. Prevalence of and factors related to microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Tianjin, China: A cross-sectional study[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2019, 7(14):325.
doi: 10.21037/atm |
| [1] | 张培恒, 高莹, 吴红花, 张健, 张俊清. 暴发性1型糖尿病合并急性胰腺炎1例及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 923-927. |
| [2] | 马雨佳,卢燃藜,周泽宸,李晓怡,闫泽玉,武轶群,陈大方. 基于两样本孟德尔随机化的失眠与2型糖尿病关联研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 174-178. |
| [3] | 鲍雷,蔡夏夏,张明远,任磊磊. 维生素D3对2型糖尿病小鼠轻度认知障碍的改善作用及机制研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 587-592. |
| [4] | 张晓悦,林雨欣,蒋莹,张蓝超,董芒艳,池海谊,董浩宇,马利军,李智婧,常春. 自我效能在2型糖尿病患者自我管理能力和自我管理行为间的中介效应[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 450-455. |
| [5] | 于欢,杨若彤,王斯悦,吴俊慧,王梦莹,秦雪英,吴涛,陈大方,武轶群,胡永华. 2型糖尿病患者使用二甲双胍与缺血性脑卒中发病风险的队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 456-464. |
| [6] | 杨若彤,王梦莹,李春男,于欢,王小文,吴俊慧,王斯悦,王伽婷,陈大方,吴涛,胡永华. 缺血性脑卒中全基因组关联研究提示阳性基因位点与睡眠行为的交互作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 412-420. |
| [7] | 陈阳阳,周玉博,杨静,花语蒙,原鹏波,刘爱萍,魏瑗. 双胎妊娠孕期体质量对血清高敏C反应蛋白与妊娠期糖尿病关联的影响:一项队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 427-433. |
| [8] | 王佳敏,刘秋萍,张明露,巩超,刘舒丹,陈暐烨,沈鹏,林鸿波,高培,唐迅. 基于马尔可夫模型的社区人群糖尿病筛查预防心血管病的效果评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 450-457. |
| [9] | 邓宇含,姜勇,王子尧,刘爽,汪雨欣,刘宝花. 基于长短期记忆网络和Logistic回归的重症监护病房脑卒中患者院内死亡风险预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 458-467. |
| [10] | 徐欣然,霍芃呈,和璐,孟焕新,朱筠轩,靳东思奇. 伴与不伴糖尿病的牙周炎患者牙周基础治疗的疗效比较及其与白细胞水平的相关分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 48-53. |
| [11] | 任国勇,吴雪梅,李颖,李婕妤,孙伟平,黄一宁. 大血管闭塞性脑卒中亚急性期磁敏感血管征的表现[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1133-1138. |
| [12] | 朱忆颖,闵赛南,俞光岩. 局部注射环孢素A对非肥胖糖尿病小鼠下颌下腺分泌功能及炎症的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 750-757. |
| [13] | 尹雪倩, 张晓玄, 文婧, 刘思奇, 刘欣然, 周若宇, 王军波. 荞麦、燕麦、豌豆复配对糖尿病大鼠血糖的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 447-452. |
| [14] | 郭洪萍,赵艾,薛勇,马良坤,张玉梅,王培玉. 孕期营养素摄入与妊娠期糖尿病孕妇血糖控制效果的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 467-472. |
| [15] | 吴俊慧,陈泓伯,武轶群,吴瑶,王紫荆,吴涛,王梦莹,王斯悦,王小文,王伽婷,于欢,胡永华. 2015—2017年北京市2型糖尿病患者骨关节炎患病的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 518-522. |
|
||