北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1079-1085. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.004
类风湿关节炎合并下肢静脉血栓患者的临床特点
- 1. 北京大学第三医院风湿免疫科,北京 100191
2. 北京大学第三医院延安分院(延安市中医医院)急诊科,陕西延安 716000
Clinical characteristics of patients with rheumatoid arthritis complicated with venous thrombosis of lower extremities
Rui LIU1,Jin-xia ZHAO1,*( ),Liang YAN1,2
),Liang YAN1,2
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Emergency, Yan'an Branch of Peking University Third Hospital (Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Yan'an), Yan'an 716000, Shaanxi, China
摘要:
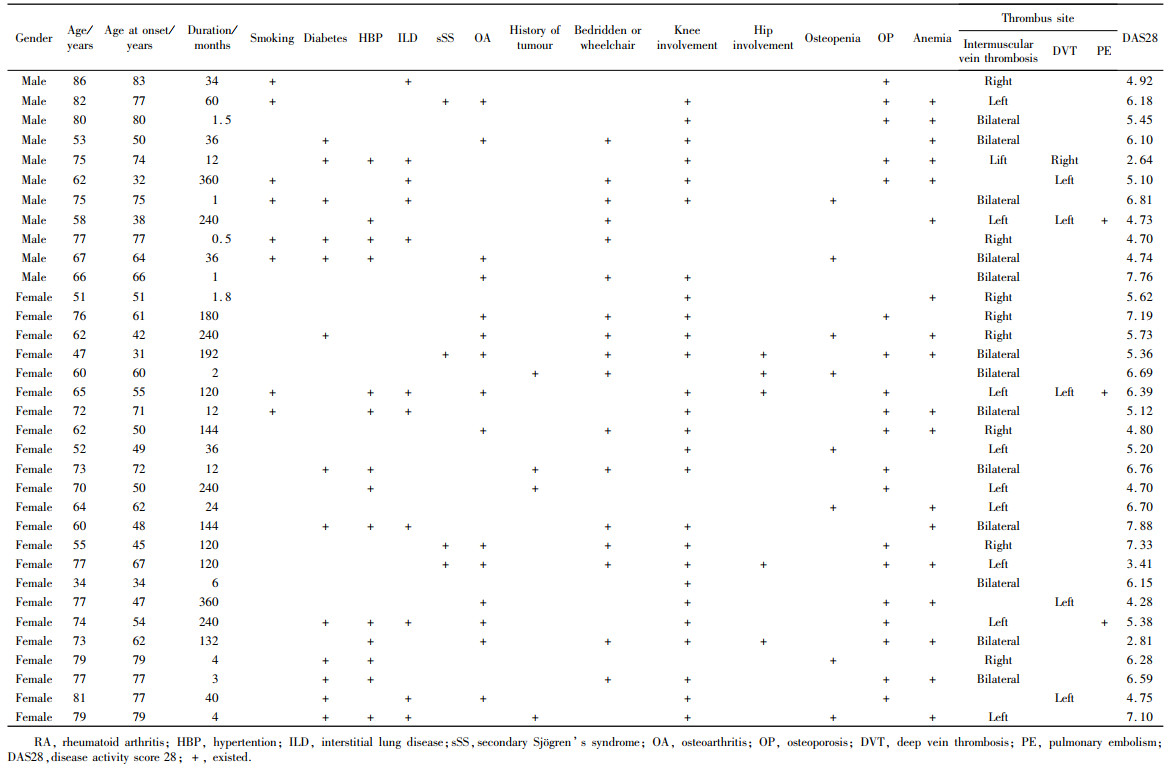
目的: 分析类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis,RA)合并下肢静脉血栓患者的临床特点,提高对该病的认识。方法: 选择自2013年11月1日至2020年12月31日期间在北京大学第三医院风湿免疫科住院的RA患者502例,回顾性分析入院诊断无下肢静脉血栓,出院诊断包含下肢静脉血栓的RA患者的临床和实验室检查指标特点,并将该组患者定义为血栓组,其他不合并下肢静脉血栓的患者作为对照组,进行两组间单因素分析,并对差异有统计学意义的因素进行多因素Logistic回归分析。结果: 血栓组患者34例(6.77%),对照组468例(93.23%)。血栓组年龄34~86岁(中位年龄71岁),女性23例,男性11例;单侧下肢静脉血栓20例(58.8%),双侧下肢静脉血栓14例(41.2%),其中3例(8.8%)合并肺栓塞(低危)。血栓组中17例(50.0%)患者入院前卧床大于1周或需要借助拐杖/轮椅活动,29例(85.3%)患者存在下肢大关节受累,髋关节、膝关节、踝关节以及膝、髋关节同时受累的患者分别为1、22、2和4例。血栓组28个关节疾病活动度评分(disease activity scores 28,DAS28)处于高、中、低疾病活动的患者分别为23例(67.6%)、9例(26.5%)和2例(5.9%)。有21例血栓组患者完善了易栓症相关检查,1例抗心磷脂抗体阳性,2例狼疮抗凝物阳性,1例抗β2-糖蛋白1抗体阳性,其余均为阴性。血栓组患者年龄[71(60, 77)岁vs. 60 (51, 68)岁,Z =-3.873, P<0. 01)]和血小板(platelet, PLT)水平[(328.53×109±119.06×109) /L vs.(278.68×109±104.50×109)/L, t =2.660, P<0.01] 均显著高于对照组,血栓组D-二聚体升高(94.1% vs.66.4%, χ2=11.192,P<0.01)以及类风湿因子(rheumatoid factor, RF)阳性(85.3% vs.67.1%,χ2 =4.852,P<0.05)的比例均显著高于对照组。Logistic回归分析发现RA发生下肢静脉血栓的危险因素包括年龄(OR =1.063, 95%CI: 1.026 ~ 1.101, P =0.001)、D-二聚体升高(OR =4.968, 95%CI: 1.136 ~ 21.730,P =0.033)和PLT水平(OR =1.004, 95%CI: 1.001 ~ 1.007, P =0.022)。结论: RA患者具有潜在下肢静脉血栓的风险,对于年龄大、D-二聚体和PLT升高,尤其是长时间卧床制动、高疾病活动度的RF阳性患者,需高度警惕下肢静脉血栓的风险。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| 1 |
Li LY , Lu N , Avina-Galindo AM , et al. The risk and trend of pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis in rheumatoid arthritis: A general population-based study[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2021, 60 (1): 188- 195.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa262 |
| 2 |
Matta F , Singala R , Yaekoub AY , et al. Risk of venous thromboembolism with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2009, 101 (1): 134- 138.
doi: 10.1160/TH08-08-0551 |
| 3 |
Arnett FC , Edworthy SM , Bloch DA , et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1988, 31 (3): 315- 324.
doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302 |
| 4 |
Britsemmer K , Ursum J , Gerritsen M , et al. Validation of the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: Slight improvement over the 1987 ACR criteria[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2011, 70 (8): 1468- 1470.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.148619 |
| 5 |
Chopard R , Albertsen IE , Piazza G . Diagnosis and treatment of lower extremity venous thromboembolism: A review[J]. JAMA, 2020, 324 (17): 1765- 1776.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.17272 |
| 6 |
Arshad N , Isaksen T , Hansen JB , et al. Time trends in incidence rates of venous thromboembolism in a large cohort recruited from the general population[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2017, 32 (4): 299- 305.
doi: 10.1007/s10654-017-0238-y |
| 7 |
Meng K , Hu X , Peng X , et al. Incidence of venous thromboembolism during pregnancy and the puerperium: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med, 2015, 28 (3): 245- 253.
doi: 10.3109/14767058.2014.913130 |
| 8 | Croles FN , Nasserinejad K , Duvekot JJ , et al. Pregnancy, thrombophilia, and the risk of a first venous thrombosis: systematic review and Bayesian meta-analysis[J]. BMJ, 2017, 359, j4452. |
| 9 | Crous-Bou M , de Vivo I , Camargo CA Jr. , et al. Interactions of established risk factors and a GWAS-based genetic risk score on the risk of venous thromboembolism[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2016, 116 (4): 705- 713. |
| 10 | Heit JA , Ashrani A , Crusan DJ , et al. Reasons for the persistent incidence of venous thromboembolism[J]. ThrombHaemost, 2017, 117 (2): 390- 400. |
| 11 |
Mean M , Limacher A , Stalder O , et al. Do factor V Leiden and prothrombin G20210A mutations predict recurrent venous thromboembolism in older patients?[J]. Am J Med, 2017, 130 (10): 1220.e17- 1220.e22.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.05.026 |
| 12 |
Gregson J , Kaptoge S , Bolton T , et al. Cardiovascular risk factors associated with venous thromboembolism[J]. JAMA Cardiol, 2019, 4 (2): 163- 173.
doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.4537 |
| 13 |
Peng YH , Lin YS , Chen CH , et al. Type 1 diabetes is associated with an increased risk of venous thromboembolism: A retrospective population-based cohort study[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15 (1): e0226997.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226997 |
| 14 |
Riva N , Donadini MP , AgenoW . Epidemiology and pathophysiology of venous thromboembolism: Similarities with atherothrombosis and the role of inflammation[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2015, 113 (6): 1176- 1183.
doi: 10.1160/TH14-06-0563 |
| 15 |
Chen CY , Liao KM . The incidence of deep vein thrombosis in Asian patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2015, 94 (44): e1741.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001741 |
| 16 |
Ogdie A , McGill NK , Shin DB , et al. Risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis: A general population-based cohort study[J]. Eur Heart J, 2018, 39 (39): 3608- 3614.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx145 |
| 17 |
Lurie JM , Png CYM , Subramaniam S , et al. Virchow's triad in "silent" deep vein thrombosis[J]. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord, 2019, 7 (5): 640- 645.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2019.02.011 |
| 18 | Broussard J , Berlinger M , Lauret D . A clot (possibly): Due to loss of TNF-α supression[J]. J La State Med Soc, 2017, 169 (2): 52. |
| 19 |
Mease P , Charles-Schoeman C , Cohen S , et al. Incidence of venous and arterial thromboembolic events reported in the tofacitinib rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis development programmes and from real-world data[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020, 79 (11): 1400- 1413.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216761 |
| 20 |
Arshad N , Isaksen T , Hansen JB , et al. Time trends in incidence rates of venous thromboembolism in a large cohort recruited from the general population[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2017, 32 (4): 299- 305.
doi: 10.1007/s10654-017-0238-y |
| [1] | 刘东武, 陈杰, 高明利, 于静. 类风湿关节炎伴发淋巴结Castleman样病理改变1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [2] | 黄会娜,赵静,赵祥格,白自然,李霞,王冠. 乳酸对类风湿关节炎患者外周血CD4+T细胞亚群的调控作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [3] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [4] | 邹雪,白小娟,张丽卿. 艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [5] | 冯璐,翟佳羽,赵金霞. IgG4相关性疾病患者就诊情况及其临床特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1028-1032. |
| [6] | 吴琦,蔡月明,何娟,黄文蒂,王庆文. 血脂异常与类风湿关节炎肺间质病变的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 982-992. |
| [7] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 体重指数与类风湿关节炎临床特征的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [8] | 彭清,刘佳君,刘焱,尚华,唐果,韩雅欣,龙丽. Padua预测评分和血清白蛋白水平在评估风湿病住院患者静脉血栓栓塞中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 625-630. |
| [9] | 金银姬,孙琳,赵金霞,刘湘源. 血清IgA型抗鼠科肉瘤病毒癌基因同源物B1抗体在类风湿关节炎中的意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 631-635. |
| [10] | 蔡文心,李仕成,刘一鸣,梁如玉,李静,郭建萍,胡凡磊,孙晓麟,李春,刘栩,叶华,邓立宗,李茹,栗占国. 类风湿关节炎临床分层及其特征的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1068-1073. |
| [11] | 程昉,杨邵英,房星星,王璇,赵福涛. CCL28-CCR10通路在类风湿关节炎单核细胞迁移中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1074-1078. |
| [12] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 类风湿关节炎患者生活质量与疾病活动度的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1086-1093. |
| [13] | 李敏,侯林卿,金月波,何菁. 系统性红斑狼疮合并视网膜病变的临床及免疫学特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1106-1111. |
| [14] | 高超,陈立红,王莉,姚鸿,黄晓玮,贾语博,刘田. 类风湿关节炎合并纤维肌痛简易分类标准的临床验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 278-282. |
| [15] | 娄雪,廖莉,李兴珺,王楠,刘爽,崔若玫,徐健. 类风湿关节炎患者外周血TWEAK基因启动子区甲基化状态及其表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1020-1025. |
|
||