北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 298-302. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.02.012
度普利尤单抗治疗老年特应性皮炎的疗效观察
- 1. 首都医科大学附属北京安贞医院皮肤性病科,北京 100029
2. 首都医科大学附属北京安贞医院信息中心,北京 100029
Observation of the efficacy of dupilumab for treatment of atopic dermatitis in the elderly
Ran SUN1, Yuhao WU2, Mei DI1, Xiaoyang WANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Beijing Anzhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100029, China
2. Information Center, Beijing Anzhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100029, China
摘要:
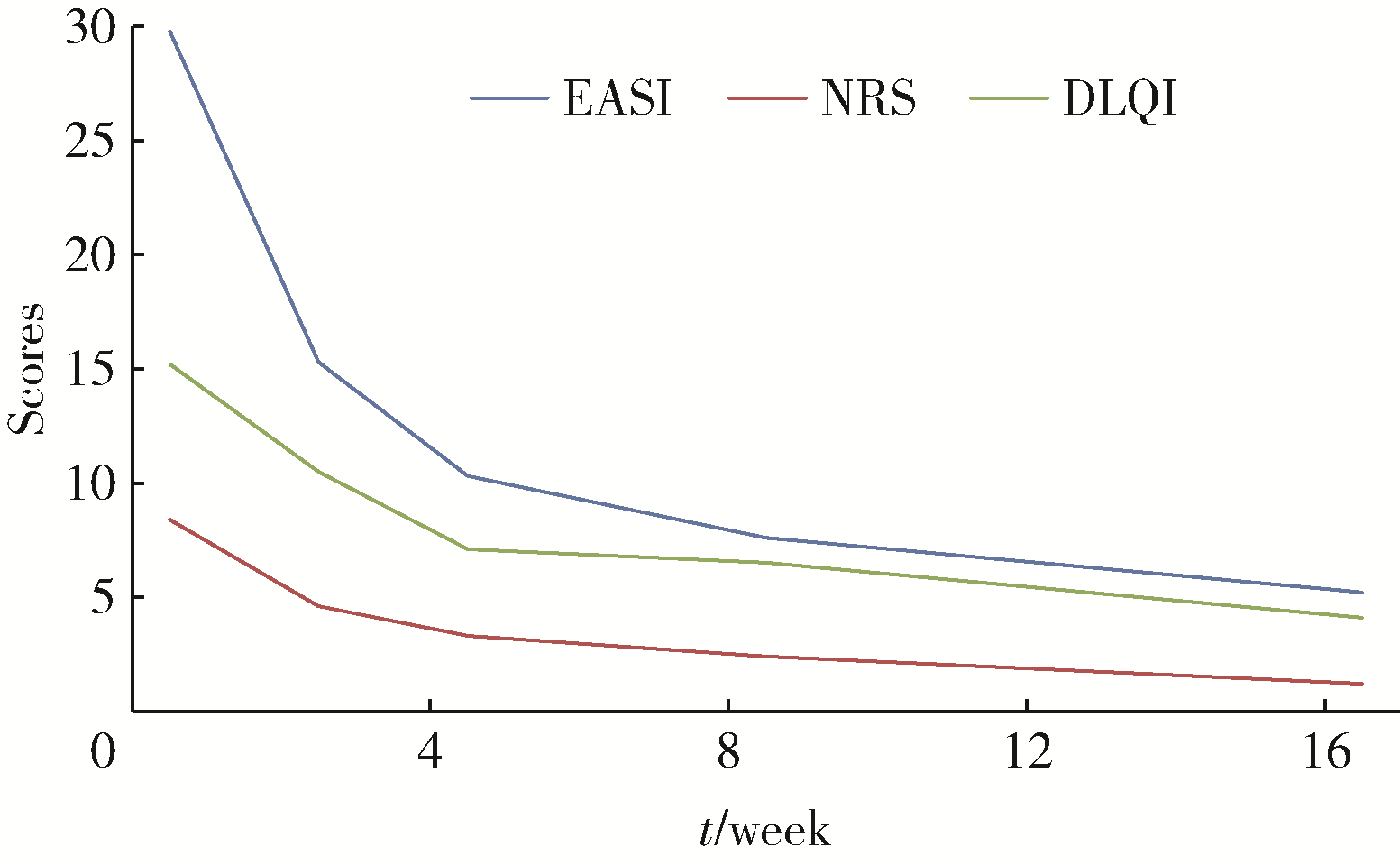
目的: 观察度普利尤单抗治疗老年特应性皮炎(atopic dermatitis, AD)的疗效及安全性。方法: 回顾性收集北京安贞医院皮肤性病科2021年1月至2023年10月收治的接受度普利尤单抗治疗至少16周的老年AD患者, 比较治疗前、治疗期间以及治疗后的临床指标, 包括瘙痒数字评价量表(pruritus numerical rating score, PNRS)、湿疹面积和严重程度指数(eczema area and severity index, EASI)、皮肤病生活质量指数(dermatology life quality index, DLQI), 同时记录发生的不良反应; 比较治疗前及治疗16周后外周血干扰素γ (interferon-γ, IFN-γ)、白细胞介素(interleukin, IL)-4、IL-6表达情况。结果: 共90例老年性特应性皮炎患者纳入本研究, EASI、PNRS、DLQI评分在治疗期间均呈下降趋势, 具体表现为在启动治疗后的前4周内快速下降, 随后下降逐渐趋于平缓。两两时间点比较结果表明, 治疗后第4周EASI、PNRS和DLQI评分均较治疗前明显降低(P<0.001); 治疗后第16周时, 以上疗效指标评分均进一步降低, 与第4周相比差异有统计学意义(P<0.01), 其中EASI评分在各个时间点均比前一时间点明显降低, 表明患者皮损持续明显改善。对度普利尤单抗的总体疗效进行评价, 治疗4周时有62.89%的患者达到EASI-50(即EASI评分下降≥50%), 74.4%的患者DLQI评分下降≥4分; 16周时有57.8%的患者达到EASI-75, 32.2%的患者达到EASI-90, 且所有患者的PNRS、DLQI评分均下降≥4分。外周血炎症指标表达水平检测结果表明, 治疗16周后IL-4、IL-6表达水平分别为(31.62±6.23) ng/L、(14.36±2.25) ng/L, 均较治疗前明显降低(P<0.001), 而IFN-γ的表达水平为(15.37±3.14) ng/L, 较治疗前上升(P<0.001)。不良反应主要为结膜炎(2例)、注射部位反应(3例)及背部多发性细菌性毛囊炎(2例), 对症治疗均可缓解, 未出现严重不良反应。结论: 度普利尤单抗在老年AD治疗中表现出良好的疗效, 可有效改善瘙痒、皮损等临床症状, 并能提高患者生活质量, 治疗期间未出现严重的不良反应, 安全性较好, 值得临床推广。
中图分类号:
- R758.2
| 1 | Teng Y , Zhong H , Yang X , et al. Current and emerging therapies for atopic dermatitis in the elderly[J]. Clin Interv Aging, 2023, 18 (1): 1641- 1652. |
| 2 |
Schuler CF , Billi AC , Maverakis E , et al. Novel insights into atopic dermatitis[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2023, 151 (5): 1145- 1154.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2022.10.023 |
| 3 |
Kim J , Ahn K . Atopic dermatitis endotypes: Knowledge for personalized medicine[J]. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol, 2022, 22 (3): 153- 159.
doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000820 |
| 4 |
Adam DN , Gooderham MJ , Beecker JR , et al. Expert consensus on the systemic treatment of atopic dermatitis in special populations[J]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2023, 37 (6): 1135- 1148.
doi: 10.1111/jdv.18922 |
| 5 |
Reich K , Thyssen JP , Blauvelt A , et al. Efficacy and safety of abrocitinib versus dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: A randomised, double-blind, multicentre phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet, 2022, 400 (10348): 273- 282.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01199-0 |
| 6 |
Narla S , Silverberg JI , Simpson EL . Management of inadequate response and adverse effects to dupilumab in atopic dermatitis[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2022, 86 (3): 628- 636.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.017 |
| 7 | 中华医学会皮肤性病学分会免疫学组, 特应性皮炎协作研究中心. 中国特应性皮炎诊疗指南(2020版)[J]. 中华皮肤科杂志, 2020, 53 (2): 81- 88. |
| 8 |
Hanifin JM , Baghoomian W , Grinich E , et al. The eczema area and severity index: A practical guide[J]. Dermatitis, 2022, 33 (3): 187- 192.
doi: 10.1097/DER.0000000000000895 |
| 9 | Wikström L , Nilsson M , Broström A , et al. Patients' self-reported nausea: Validation of the numerical rating scale and of a daily summary of repeated numerical rating scale scores[J]. J Clin Nurs, 2019, 28 (5/6): 959- 968. |
| 10 |
Finlay AY , Khan GK . Dermatology life quality index (DLQI): A simple practical measure for routine clinical use[J]. Clin Exp Dermatol, 1994, 19 (3): 210- 216.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1994.tb01167.x |
| 11 |
Tavecchio S , Angileri L , Pozzo GF , et al. Efficacy of dupilumab on different phenotypes of atopic dermatitis: One-year experience of 221 patients[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9 (9): 2684.
doi: 10.3390/jcm9092684 |
| 12 | 鞠延娇, 门月华, 谢志强. 度普利尤单抗治疗老年顽固性重度特应性皮炎30例临床观察[J]. 中国皮肤性病学杂志, 2022, 36 (9): 1026- 1031. |
| 13 |
Goh MS , Yun JS , Su JC . Management of atopic dermatitis: A narrative review[J]. Med J Aust, 2022, 216 (11): 587- 593.
doi: 10.5694/mja2.51560 |
| 14 |
Wang S , Zhu R , Gu C , et al. Distinct clinical features and serum cytokine pattern of elderly atopic dermatitis in China[J]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2020, 34 (10): 2346- 2352.
doi: 10.1111/jdv.16346 |
| 15 |
Zhou L , Leonard A , Pavel AB , et al. Age-specific changes in the molecular phenotype of patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis[J]. J Allerge Clin Imm, 2019, 144 (1): 144- 156.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.01.015 |
| 16 |
Paller AS , Simpson EL , Siegfried EC , et al. Dupilumab in children aged 6 months to younger than 6 years with uncontrolled atopic dermatitis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet, 2022, 400 (10356): 908- 919.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01539-2 |
| 17 |
Zhao Y , Wu L , Lu Q , et al. The efficacy and safety of dupilumab in Chinese patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study[J]. Br J Dermatol, 2022, 186 (4): 633- 641.
doi: 10.1111/bjd.20690 |
| 18 |
Faiz S , Giovannelli J , Podevin C , et al. Effectiveness and safety of dupilumab for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in a real-life French multicenter adult cohort[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2019, 81 (1): 143- 151.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.02.053 |
| 19 |
Lasek A , Bellon N , Mallet S , et al. Effectiveness and safety of dupilumab in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in children (6-11 years): Data from a French multicentre retrospective cohort in daily practice[J]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2022, 36 (12): 2423- 2429.
doi: 10.1111/jdv.18450 |
| 20 |
Jang DH , Heo SJ , Jung HJ , et al. Retrospective study of dupilumab treatment for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in Korea: Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in real-world practice[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9 (6): 1982.
doi: 10.3390/jcm9061982 |
| 21 |
Ariёns L , van der Schaft J , Bakker DS , et al. Dupilumab is very effective in a large cohort of difficult-to-treat adult atopic dermatitis patients: First clinical and biomarker results from the BioDay registry[J]. Allergy, 2020, 75 (1): 116- 126.
doi: 10.1111/all.14080 |
| 22 | 刘擘, 宋晓婷, 李若瑜, 等. 度普利尤单抗治疗特应性皮炎的疗效及安全性分析[J]. 中华皮肤科杂志, 2022, 55 (4): 295- 298. |
| 23 |
Blauvelt A , Guttman-Yassky E , Paller AS , et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adolescents with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: Results through week 52 from a phase Ⅲ open-label extension trial (LIBERTY AD PED-OLE)[J]. Am J Clin Dermatol, 2022, 23 (3): 365- 383.
doi: 10.1007/s40257-022-00683-2 |
| 24 | 王上上, 潘晓玉, 李亚楠, 等. 中重度老年特应性皮炎新型系统治疗有效性及安全性的荟萃分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2023, 103 (32): 2509- 2515. |
| 25 |
Vittrup I , Krogh NS , Larsen H , et al. A nationwide 104 weeks real-world study of dupilumab in adults with atopic dermatitis: Ineffectiveness in head-and-neck dermatitis[J]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2023, 37 (5): 1046- 1055.
doi: 10.1111/jdv.18849 |
| 26 |
Patruno C , Fabbrocini G , Longo G , et al. Effectiveness and safety of long-term dupilumab treatment in elderly patients with atopic dermatitis: A multicenter real-life observational study[J]. Am J Clin Dermatol, 2021, 22 (4): 581- 586.
doi: 10.1007/s40257-021-00597-5 |
| 27 |
Napolitano M , Fabbrocini G , Scalvenzi M , et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in atopic dermatitis in elderly patients: A retrospective study[J]. Clin Exp Dermatol, 2020, 45 (7): 888- 890.
doi: 10.1111/ced.14260 |
| 28 |
Gu C , Wu Y , Luo Y , et al. Real-world efficacy and safety of dupilumab in Chinese patients with atopic dermatitis: A single-centre, prospective, open-label study[J]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2022, 36 (7): 1064- 1073.
doi: 10.1111/jdv.18109 |
| 29 |
He H , Olesen CM , Pavel AB , et al. Tape-strip proteomic profiling of atopic dermatitis on dupilumab identifies minimally invasive biomarkers[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11, 1768.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01768 |
| 30 | 孔羽薇. 特应性皮炎相关细胞因子的研究进展[J]. 临床儿科杂志, 2019, 37 (2): 148- 152. |
| 31 | 石娴, 石年, 解崔林, 等. 特应性皮炎患者血清Vit D、tIgE、IL-4和IL-6水平检测及临床意义[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2017, 14 (24): 3605. |
| 32 |
Busse PJ , Birmingham JM , Calatroni A , et al. Effect of aging on sputum inflammation and asthma control[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2017, 139 (6): 1808- 1818.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.09.015 |
| 33 | 李妍, 徐薇, 程海艳, 等. 白介素4、10、12、13、IFN-γ、TGF-β在不同时期特应性皮炎病人血清中的变化[J]. 首都医科大学学报, 2017, 10 (38): 635- 639. |
| [1] | 金江, 陈雪, 赵琰, 贾军, 张建中. 卵清蛋白诱导的特应性皮炎小鼠模型中白细胞介素-25的作用及其调控意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 756-762. |
| [2] | 刘园梅, 傅义程, 郝靖欣, 张福春, 刘慧琳. 老年髋部骨折患者住院期间发生术后心力衰竭的列线图预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 874-883. |
| [3] | 张浩宇,石逸雯,潘薇,刘爱萍,孙昕霙,李曼,张旭熙. 基于不同失能水平的老年人照料需求的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 431-440. |
| [4] | 靖婷,江华,李婷,申倩倩,叶兰,曾银丹,梁文欣,冯罡,司徒文佑,张玉梅. 中国西部5城市中老年人血清25羟基维生素D与握力的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 448-455. |
| [5] | 林郁婷,王华丽,田宇,巩俐彤,常春. 北京市老年人认知功能的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 456-461. |
| [6] | 汤华萌,袁典琪,王明星,杨晗冰,郭超. 数字融入和健康生活方式对社会经济状况与老年人抑郁关系的序列中介作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 230-238. |
| [7] | 刘慧丽,吕彦函,王晓晓,李民. 老年患者腹腔镜泌尿系肿瘤根治术后慢性疼痛的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 851-856. |
| [8] | 祝春素,连至炜,崔一民. 中国中老年人抑郁和慢性病的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 606-611. |
| [9] | 刘光奇,庞元捷,吴疆,吕敏,于孟轲,李雨橦,黄旸木. 2013—2019年流感季北京市住院老年人流感疫苗接种趋势分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 505-510. |
| [10] | 刘杰,郭超. 正/负性情绪对中国老年人死亡风险影响的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 255-260. |
| [11] | 李佳,徐钰,王优雅,高占成. 老年流感肺炎的临床特征及D-二聚体与疾病严重程度的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 153-160. |
| [12] | 敖明昕,李学民,于媛媛,时会娟,黄红拾,敖英芳,王薇. 视觉重建对老年人行走动态足底压力的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 907-914. |
| [13] | 彭顺壮, 付茜茜, 冯星淋. 中国中老年居民教育程度与失能发生:社会参与的中介作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 549-554. |
| [14] | 陈家丽,金月波,王一帆,张晓盈,李静,姚海红,何菁,李春. 老年发病类风湿关节炎的临床特征及其心血管疾病危险因素分析:一项大样本横断面临床研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1040-1047. |
| [15] | 胡宇晴,张建中. 156例特应性皮炎患者血清吸入和食物过敏原特异性免疫球蛋白E及患者自觉过敏情况[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 980-984. |
|
||