Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 821-827. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
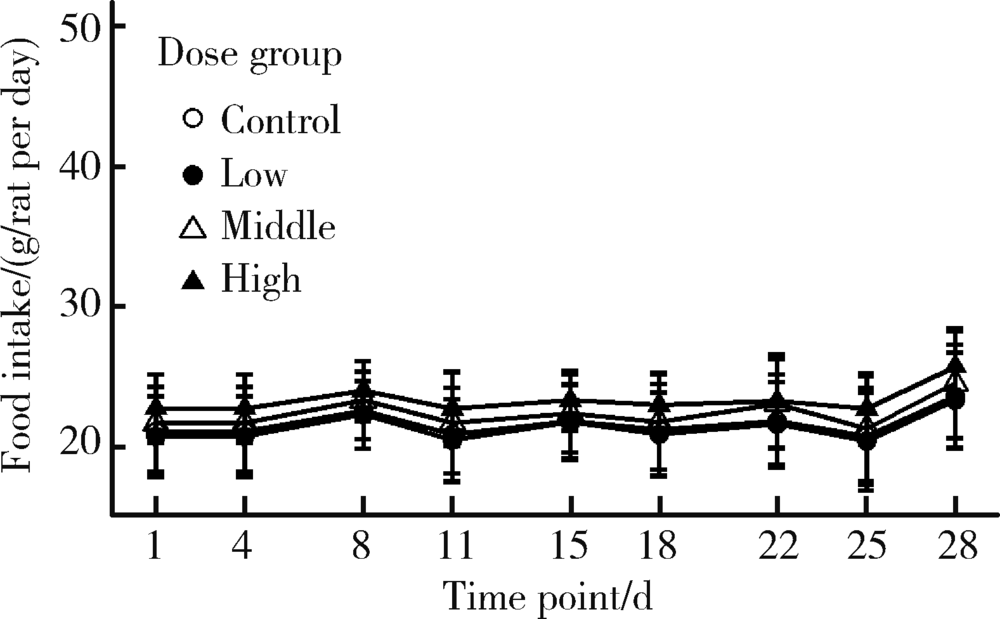
Influence of oxidative/antioxidative biomarkers and inflammatory cytokines on rats after sub-acute orally administration of titanium dioxide nanoparticles
Di ZHOU,Zhang-jian CHEN,Gui-ping HU,Teng-long YAN,Chang-mao LONG,Hui-min FENG,Guang JIA( )
)
- Department of Occupational and Environmental Health Sciences, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R155.3
| [1] |
Warheit DB, Donner EM. Risk assessment strategies for nanoscale and fine-sized titanium dioxide particles:Recognizing hazard and exposure issues[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2015,85:138-147.
doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2015.07.001 pmid: 26362081 |
| [2] |
Weir A, Westerhoff P, Fabricius L, et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food and personal care products[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2012,46(4):2242-2250.
doi: 10.1021/es204168d pmid: 22260395 |
| [3] |
Yang Y, Doudrick K, Bi X, et al. Characterization of food-grade titanium dioxide: the presence of nanosized particles[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2014,48(11):6391-6400.
doi: 10.1021/es500436x pmid: 24754874 |
| [4] |
Robichaud CO, Uyar AE, Darby MR, et al. Estimates of upper bounds and trends in nano-TiO2 production as a basis for exposure assessment[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2009,43(12):4227-4233.
doi: 10.1021/es8032549 pmid: 19603627 |
| [5] |
Rompelberg C, Heringa MB, van Donkersgoed GC, et al. Oral intake of added titanium dioxide and its nanofraction from food products, food supplements and toothpaste by the Dutch population[J]. Nanotoxicology, 2016,10(10):1404-1414.
doi: 10.1080/17435390.2016.1222457 pmid: 27619007 |
| [6] |
Scherbart AM, Langer J, Bushmelev A, et al. Contrasting macrophage activation by fine and ultrafine titanium dioxide particles is associated with different uptake mechanisms[J]. Part Fibre Toxicol, 2011,8(31):1-19.
doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-8-1 |
| [7] |
Katsumiti A, Berhanu D, Howard KT, et al. Cytotoxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles to mussel hemocytes and gill cells in vitro: influence of synjournal method, crystalline structure, size and additive[J]. Nanotoxicology, 2015,9(5):543-553.
doi: 10.3109/17435390.2014.952362 pmid: 25188678 |
| [8] |
Takaki K, Higuchi Y, Hashii M, et al. Induction of apoptosis associated with chromosomal DNA fragmentation and caspase-3 activation in leukemia L1210 cells by TiO2 nanoparticles[J]. J Biosci Bioeng, 2014,117(1):129-133.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.06.003 |
| [9] |
Zhang Z, Liang ZC, Zhang JH, et al. Nano-sized TiO2 (nTiO2) induces metabolic perturbations in Physarum polycephalum macroplasmodium to counter oxidative stress under dark conditions[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2018,154:108-117.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.02.012 pmid: 29454986 |
| [10] |
Ammendolia MG, Iosi F, Maranghi F, et al. Short-term oral exposure to low doses of nano-sized TiO2 and potential modulatory effects on intestinal cells[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2017,102:63-75.
doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2017.01.031 pmid: 28159593 |
| [11] |
Bachler G, von Goetz N, Hungerbuhler K. Using physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling for dietary risk assessment of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles[J]. Nanotoxicology, 2015,9(3):373-380.
doi: 10.3109/17435390.2014.940404 pmid: 25058655 |
| [12] | Huybrechts I, Sioena I, Boon PE, et al. Long-term dietary exposure to different food colours in young children living in different European countries[J]. EFSA Support Publ, 2010,7(5):53E. |
| [13] |
Cui YL, Gong XL, Duan YM, et al. Hepatocyte apoptosis and its molecular mechanisms in mice caused by titanium dioxide nanoparticles[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2010,183(1-3):874-880.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.07.109 pmid: 20724067 |
| [14] |
He J, Wang T, Wang P, et al. A novel mechanism underlying the susceptibility of neuronal cells to nitric oxide: the occurrence and regulation of protein S-nitrosylation is the checkpoint[J]. J Neurochem, 2007,102(6):1863-1874.
doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04651.x pmid: 17767703 |
| [15] |
Lugrin J, Rosenblatt VN, Parapanov R, et al. The role of oxidative stress during inflammatory processes[J]. Biol Chem, 2014,395(2):203-230.
doi: 10.1515/hsz-2013-0241 pmid: 24127541 |
| [16] |
Lei XG, Zhu JH, Cheng WH, et al. Paradoxical roles of antioxidant enzymes: basic mechanisms and health implications[J]. Physiol Rev, 2016,96(1):307-364.
doi: 10.1152/physrev.00010.2014 pmid: 26681794 |
| [17] |
Huang XZ, Lan YW, Liu ZK, et al. Salinity mediates the toxic effect of nano-TiO2 on the juvenile olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus [J]. Sci Total Environ, 2018, 640-641:726-735.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.350 pmid: 29879661 |
| [18] |
Sentellas S, Morales IO, Zanuy M, et al. GSSG/GSH ratios in cryopreserved rat and human hepatocytes as a biomarker for drug induced oxidative stress[J]. Toxicol Vitr, 2014,28(5):1006-1015.
doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2014.04.017 |
| [19] |
Hu HL, Guo Q, Wang CL, et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles increase plasma glucose via reactive oxygen species-induced insulin resistance in mice[J]. J Appl Toxicol, 2015,35(10):1122-1132.
doi: 10.1002/jat.3150 pmid: 25826740 |
| [20] |
Shukla RK, Kumar A, Vallabani NVS, et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress triggers DNA damage and hepatic injury in mice[J]. Nanomedicine, 2014,9(9):1423-1434.
doi: 10.2217/NNM.13.100 |
| [21] |
Gornati R, Longo A, Rossi F, et al. Effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticle exposure in Mytilus galloprovincialis gills and digestive gland[J]. Nanotoxicology, 2016,10(6):807-817.
doi: 10.3109/17435390.2015.1132348 pmid: 26846715 |
| [22] |
Chen ZJ, Wang Y, Zhuo L, et al. Effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the cardiovascular system after oral administration[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2015,239(2):123-130.
doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.09.013 pmid: 26387441 |
| [23] |
Sycheva LP, Zhurkov VS, Iurchenko VV, et al. Investigation of genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of micro- and nanosized titanium dioxide in six organs of mice in vivo[J]. Mutat Res, 2011,726(1):8-14.
doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2011.07.010 pmid: 21871579 |
| [1] | Zhan-yi ZHANG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Cai-guang CAO,Chang-jian LI,Shao-hui DENG,Yue-hao SUN,Tian-liang HUANG,Yun-he GUAN,Nan LI,Min LU,Zhen-hua HU,Shu-dong ZHANG. Near-infrared targeted probe designed for intraoperative imaging of prostatic neurovascular bundles [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 843-850. |
| [2] | Jia-qi SHI,Ying MA,Yi ZHANG,Zhang-jian CHEN,Guang JIA. Effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on circRNA expression profiles in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells HepG2 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 392-399. |
| [3] | Ling-wei MENG,Xue LI,Sheng-han GAO,Yue LI,Rui-tao CAO,Yi ZHANG,Shao-xia PAN. Comparison of three methods for establishing rat peri-implantitis model [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 22-29. |
| [4] | Jia-he ZHANG,Jia-qi SHI,Zhang-jian CHEN,Guang JIA. Effects of nano titanium dioxide on gut microbiota based on human digestive tract microecology simulation system in vitro [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 468-476. |
| [5] | HE Wei,YANG Si-wen,CHEN Juan,ZHU Xiao-jun,CHEN Zhi-zhong,MA Wen-jun. Effects of 275 nm and 310 nm ultraviolet irradiation on bone metabolism in ovariectomized osteoporotic rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 236-243. |
| [6] | WANG Gui-hong,ZUO Ting,LI Ran,ZUO Zheng-cai. Effect of rebamipide on the acute gouty arthritis in rats induced by monosodium urate crystals [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 716-720. |
| [7] | YIN Xue-qian, ZHANG Xiao-xuan, WEN Jing, LIU Si-qi, LIU Xin-ran, ZHOU Ruo-yu, WANG Jun-bo. Effects of the composite of buckwheat-oat-pea on blood glucose in diabetic rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(3): 447-452. |
| [8] | Zhang-jian CHEN,Shuo HAN,Pai ZHENG,Shu-pei ZHOU,Guang JIA. Effect of subchronic combined oral exposure of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and glucose on levels of serum folate and vitamin B12 in young SD rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 451-456. |
| [9] | Shuo HAN,Zhang-jian CHEN,Di ZHOU,Pai ZHENG,Jia-he ZHANG,Guang JIA. Effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on fecal metabolome in rats after oral administration for 90 days [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 457-463. |
| [10] | Shan-shan BAI,Si-yi MO,Xiao-xiang XU,Yun LIU,Qiu-fei XIE,Ye CAO. Characteristics of orofacial operant test for orofacial pain sensitivity caused by occlusal interference in rats [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2020, 52(1): 51-57. |
| [11] | Jiao HE,Ge-heng YUAN,Jun-qing ZHANG,Xiao-hui GUO. Approach to creating early diabetic peripheral neuropathy rat model [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1150-1154. |
| [12] | Wei WANG,Jin HOU,Wen-qiang HUANG. Temporary acceleration of interstitial fluid drainage in excited brain region induced by movement [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 206-209. |
| [13] | DUAN Shu-min, ZHANG Yong-liang, WANG Yun. Effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and lipopolysaccharide on antioxidant function of liver tissues in mice [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(3): 395-400. |
| [14] | WANG Huan, QIN Xiao-ya, LI Zi-yuan, ZHENG Zhuo-zhao, FAN Tian-yuan. Preparation and characterization of citric acid-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(2): 340-346. |
| [15] | ZHANG Yong-liang, CHEN Zhang-jian, CHEN Shi, ZHUO lin, JIA Guang, WANG Yun. Effect of nano-TiO2 on intestinal glucose absorption in young rat on the everted gut sac model [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(3): 376-382. |
|
||