Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 184-189. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2026.01.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
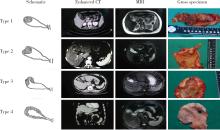
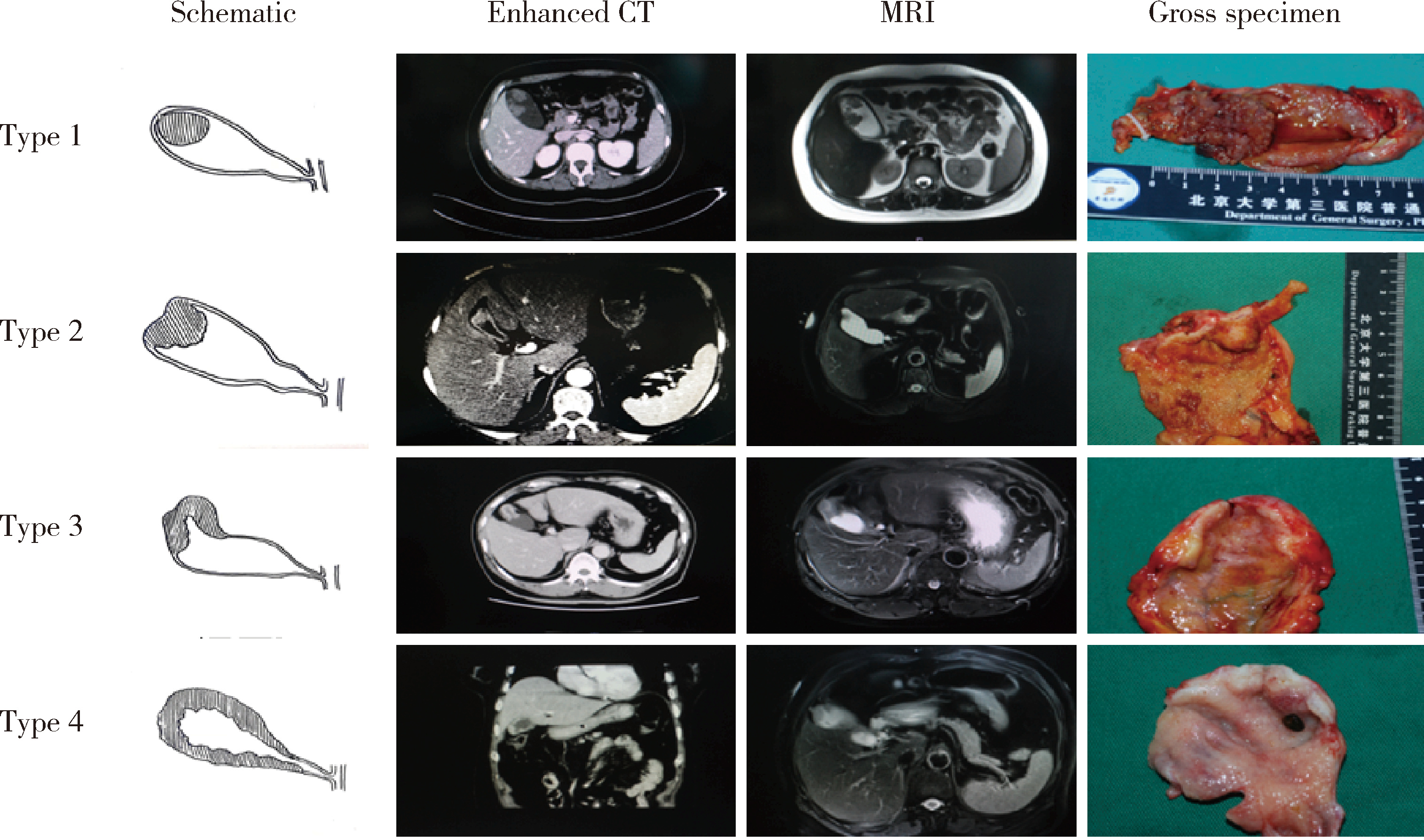
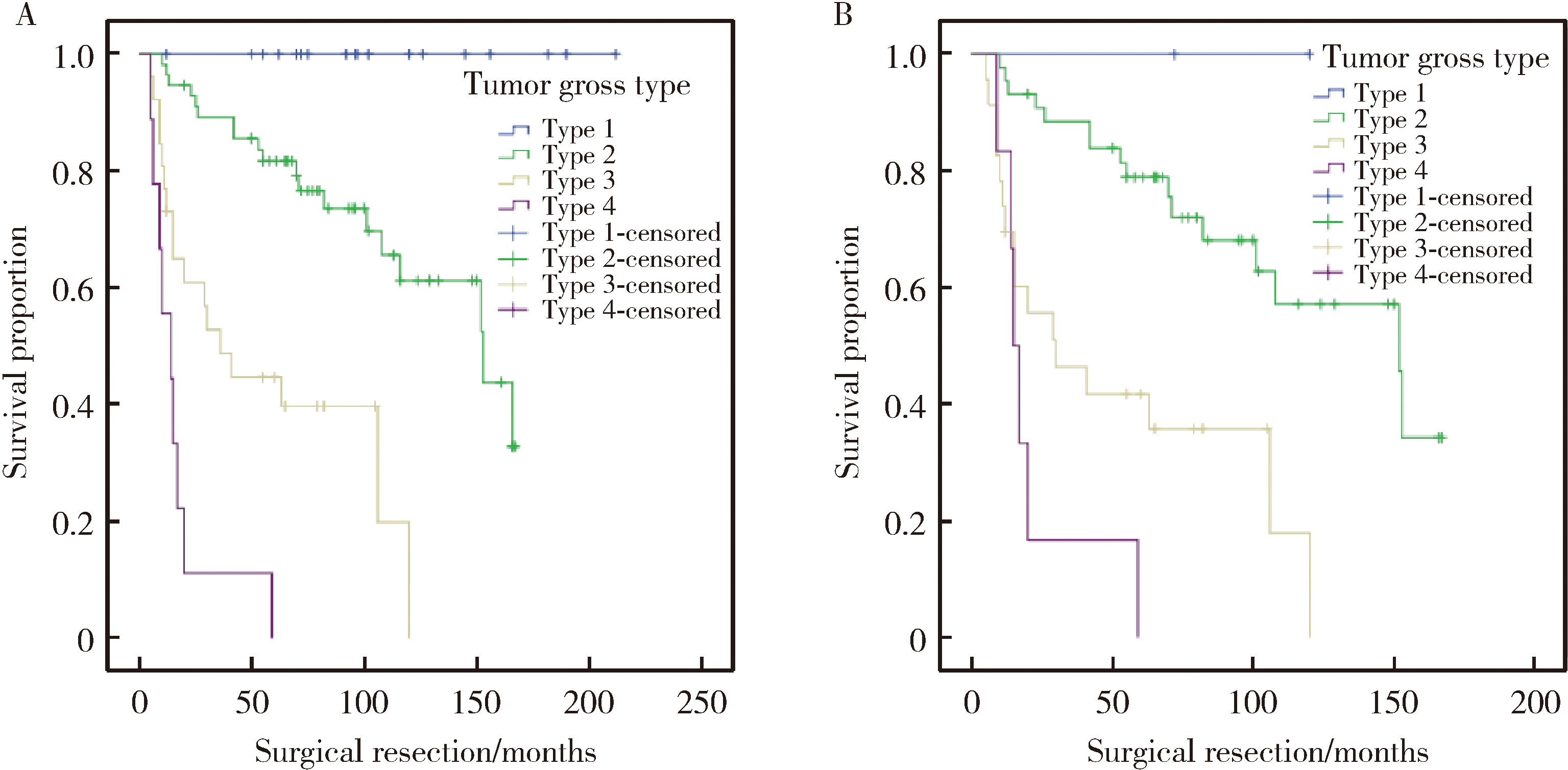
Gross classification of gallbladder cancer with primary lesion limited to the gallbladder wall and its correlation with prognosis and precancerous lesions
Lingfu ZHANG1, Ming CHEN2, Xiaoyu ZHAO1, Gang WANG1, Long CUI1, Xiaofeng LING1, Lixin WANG1, Zhi XU1, Limei GUO3,*( ), Chunsheng HOU1,*(
), Chunsheng HOU1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of General Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
3. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R735.8
| 1 |
doi: 10.1038/s41572-022-00398-y |
| 2 |
张铃福, 侯纯升, 徐智, 等. 腹腔镜胆囊切除术中或术后意外胆囊癌腹腔镜手术治疗: 单中心10年回顾性分析[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2019, 57 (4): 277- 281.
|
| 3 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2020.07.006 |
| 4 |
doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2021.05.001 |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2022.151911 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.2001.01749.x |
| 7 |
张铃福, 侯纯升, 郭丽梅, 等. 术中冰冻或术后石蜡病理报告T1b期胆囊癌的外科治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49 (6): 1034- 1037.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2017.06.017 |
| 8 |
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3567 |
| 9 |
doi: 10.3892/or.2012.1971 |
| 10 |
doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2021.101693 |
| [1] | Boda GUO, Min LU, Guoliang WANG, Hongxian ZHANG, Lei LIU, Xiaofei HOU, Lei ZHAO, Xiaojun TIAN, Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological and prognostic differences between clear cell and non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(4): 644-649. |
| [2] | Weihao LI, Jing LI, Xuemin ZHANG, Wei LI, Qingle LI, Xiaoming ZHANG. Effect of intraoperative blood salvage autotransfusion on the prognosis of patients after carotid body tumor resection [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(2): 272-276. |
| [3] | Yaqing MAO, Zhen CHEN, Yao YU, Wenbo ZHANG, Yang LIU, Xin PENG. Impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on the prognosis of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1089-1096. |
| [4] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [5] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [6] | Le YU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [7] | Zezhen ZHOU,Shaohui DENG,Ye YAN,Fan ZHANG,Yichang HAO,Liyuan GE,Hongxian ZHANG,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Predicting the 3-year tumor-specific survival in patients with T3a non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [8] | Yangyi FANG,Qiang LI,Zhigao HUANG,Min LU,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour of the tunica vaginalis: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [9] | Yuanyuan ZENG,Yun XIE,Daonan CHEN,Ruilan WANG. Related factors of euthyroid sick syndrome in patients with sepsis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [10] | Jian-bin LI,Meng-na LYU,Qiang CHI,Yi-lin PENG,Peng-cheng LIU,Rui WU. Early prediction of severe COVID-19 in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [11] | Huan-rui LIU,Xiang PENG,Sen-lin LI,Xin GOU. Risk modeling based on HER-2 related genes for bladder cancer survival prognosis assessment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [12] | Zi-xuan XUE,Shi-ying TANG,Min QIU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Min LU,Jing-han DONG,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG. Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of young renal tumors with tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [13] | Han LU,Jian-yun ZHANG,Rong YANG,Le XU,Qing-xiang LI,Yu-xing GUO,Chuan-bin GUO. Clinical factors affecting the prognosis of lower gingival squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [14] | Yun-fei SHI,Hao-jie WANG,Wei-ping LIU,Lan MI,Meng-ping LONG,Yan-fei LIU,Yu-mei LAI,Li-xin ZHOU,Xin-ting DIAO,Xiang-hong LI. Analysis of clinicopathological and molecular abnormalities of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
| [15] | Xiao-juan ZHU,Hong ZHANG,Shuang ZHANG,Dong LI,Xin LI,Ling XU,Ting LI. Clinicopathological features and prognosis of breast cancer with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 low expression [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 243-253. |
|
||