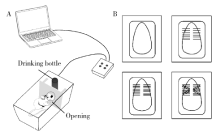
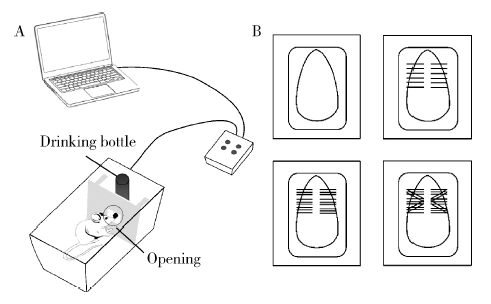
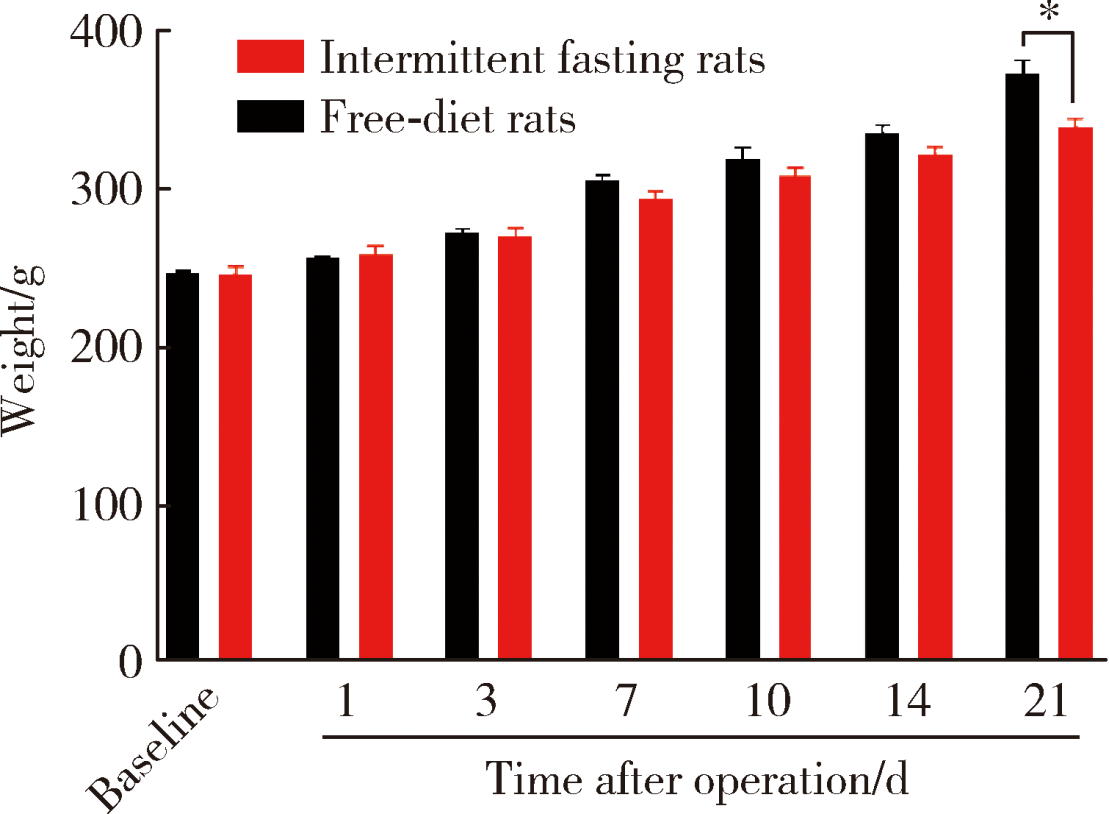
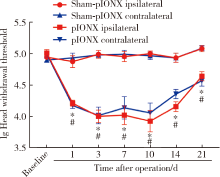
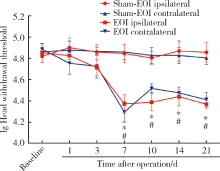
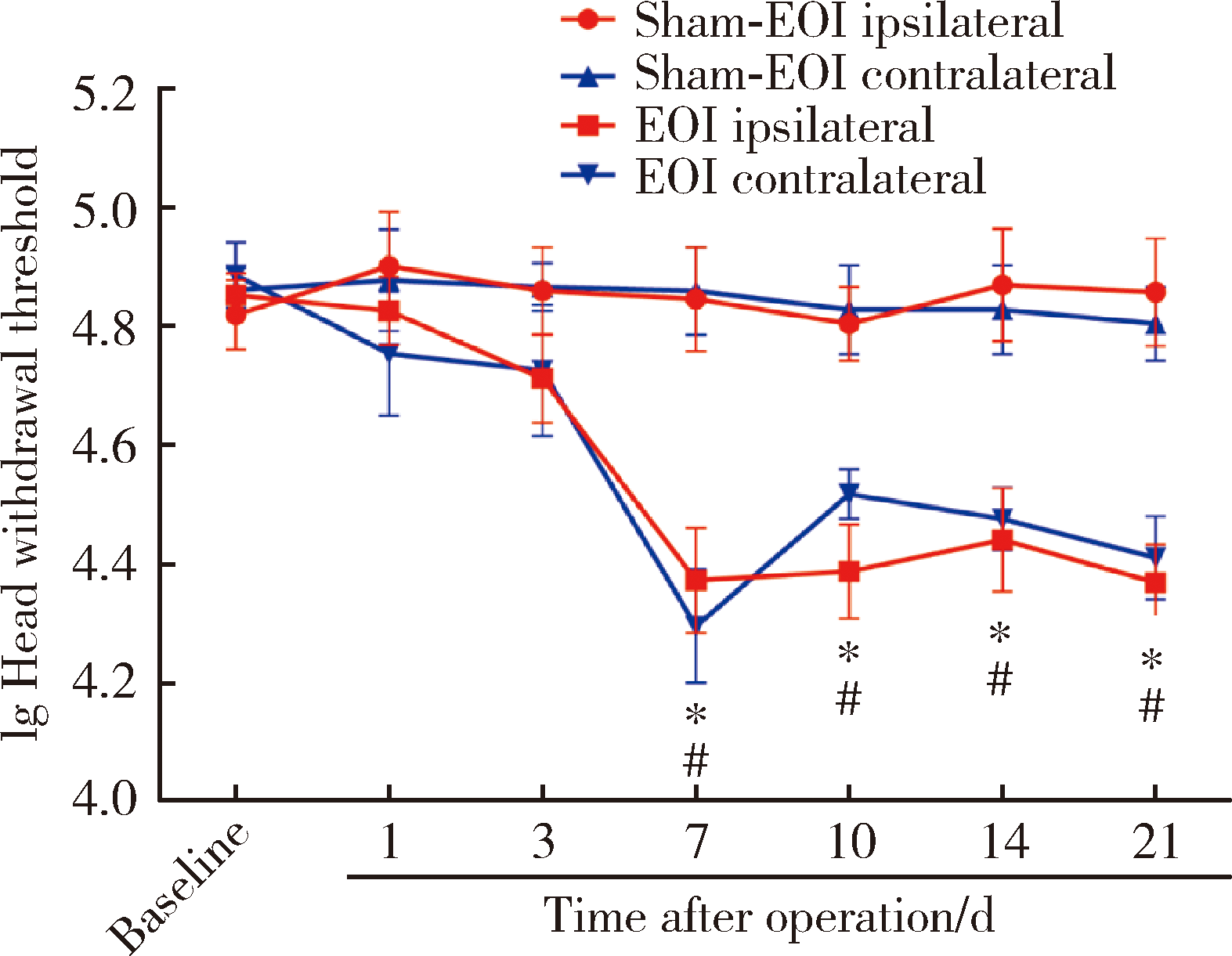
Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 51-57. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.01.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
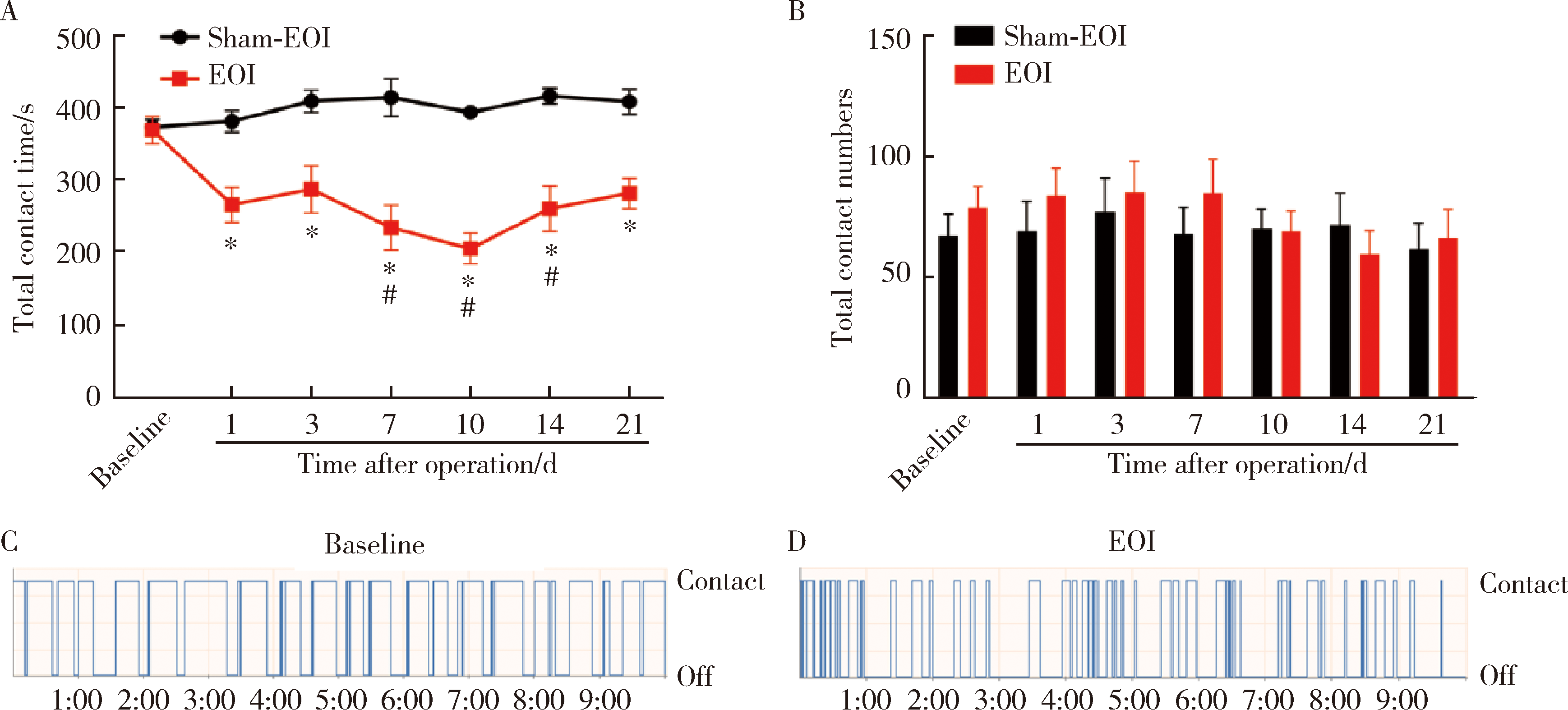
Characteristics of orofacial operant test for orofacial pain sensitivity caused by occlusal interference in rats
Shan-shan BAI1,2,Si-yi MO1,2,Xiao-xiang XU1,2,Yun LIU1,2,Qiu-fei XIE1,2,△( ),Ye CAO1,2,△(
),Ye CAO1,2,△( )
)
- 1. Center for Oral and Jaw Functional Diagnosis, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & Department of Prosthodontics, Beijing 100081, China
2. Center for Oral and Jaw Functional Diagnosis, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R782
| [1] | Alrashdan M, Alkhader M . Psychological factors in oral mucosal and orofacial pain conditions[J]. Eur J Dent, 2017,11(4):548-552. |
| [2] | Haviv Y, Zini A, Etzioni Y , et al. The impact of chronic orofacial pain on daily life: the vulnerable patient and the disruptive pain[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2016,123(1):58-66. |
| [3] | Deuis JR, Dvorakova LS, Irina V . Methods used to evaluate pain behaviors in rodents[J]. Front Mol Neurosci, 2017,10:284. |
| [4] | Tappe-Theodor A, King T, Morgan MM . Pros and cons of clinically relevant methods to assess pain in rodents[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2019,100(5):335-343. |
| [5] | Martinez-Garcia MA, Miguelanez-Medran BC, Goicoechea C . Animal models in the study and treatment of orofacial pain[J]. J Clin Exp Dent, 2019,11(4):e382-e390. |
| [6] | Barrot M . Tests and models of nociception and pain in rodents[J]. Neuroscience, 2012,211(11):39-50. |
| [7] | Woolf CJ . Long term alterations in the excitability of the flexion reflex produced by peripheral tissue injury in the chronic decerebrate rat[J]. Pain, 1984,18(4):325-343. |
| [8] | Cha M, Kohan KJ, Zuo X , et al. Assessment of chronic trigeminal neuropathic pain by the orofacial operant test in rats[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2012,234(1):82-90. |
| [9] | Neubert JK, Widmer CG, Malphurs W , et al. Use of a novel thermal operant behavioral assay for characterization of orofacial pain sensitivity[J]. Pain, 2005,116(3):386-395. |
| [10] | Rohrs EL, Kloefkorn HE, Lakes EH , et al. A novel operant-based behavioral assay of mechanical allodynia in the orofacial region of rats[J]. J Neurosci Methods, 2015,248(13):1-6. |
| [11] | Ramirez HE, Queeney TJ, Dunbar ML , et al. Assessment of an orofacial operant pain assay as a preclinical tool for evaluating analgesic efficacy in rodents[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2015,54(4):426-432. |
| [12] | Araujo-Filho HG, Pereira EWM, Campos AR , et al. Chronic orofacial pain animal models-progress and challenges[J]. Expert Opin Drug Discov, 2018,13(10):949-964. |
| [13] | Kaan TK, Ohara PT, Jasmin L , et al. Orofacial pain models and behavior assessment[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2012,851:159-170. |
| [14] | Deseure K, Hans GH . Differential drug effects on spontaneous and evoked pain behavior in a model of trigeminal neuropathic pain[J]. J Pain Res, 2017,10:279-286. |
| [15] | Romero-Reyes M, Akerman S, Nguyen E , et al. Spontaneous behavioral responses in the orofacial region: a model of trigeminal pain in mouse[J]. Headache, 2013,53(1):137-151. |
| [16] | Zhang Q, Cao DL, Zhang ZJ , et al. Chemokine CXCL13 mediates orofacial neuropathic pain via CXCR5/ERK pathway in the trigeminal ganglion of mice[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2016,13(1):183. |
| [17] | Cao Y, Xie QF, Li K , et al. Experimental occlusal interference induces long-term masticatory muscle hyperalgesia in rats[J]. Pain, 2009,144(3):287-293. |
| [18] | Cao Y, Wang H, Chiang CY , et al. Pregabalin suppresses nociceptive behavior and central sensitization in a rat trigeminal neuropathic pain model[J]. J Pain, 2013,14(2):193-204. |
| [19] | 韩济生 . 疼痛学[M]. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2012: 46. |
| [20] | Chapman CR, Casey KL, Dubner R , et al. Pain measurement: an overview[J]. Pain, 1985,22(1):1-31. |
| [21] | Chesler EJ, Wilson SG, Lariviere WR , et al. Identification and ranking of genetic and laboratory environment factors influencing a behavioral trait, thermal nociception, via computational analysis of a large data archive[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2002,26(8):907-923. |
| [22] | Chung JM . Animal models and experimental tests to study nociception and pain[M] // Gebhart GF, Schmidt RF. Encyclopedia of pain. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2013: 154-157. |
| [23] | Kauppila T, Kontinen VK, Pertovaara A . Influence of spinalization on spinal withdrawal reflex responses varies depending on the submodality of the test stimulus and the experimental pathophysiological condition in the rat[J]. Brain Res, 1998,797(2):234-242. |
| [24] | Ling J, Erol F, Gu JG . Role of KCNQ2 channels in orofacial cold sensitivity: KCNQ2 upregulation in trigeminal ganglion neurons after infraorbital nerve chronic constrictive injury[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2018,664(3):84-90. |
| [25] | Budtz-Jørgensen E . Occlusal dysfunction and stress. An experimental study in Macaque monkeys[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2010,8(1):1-9. |
| [26] | Wang C, Yin X . Occlusal risk factors associated with temporomandibular disorders in young adults with normal occlusions[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2012,114(4):419-423. |
| [27] | Raphael KG, Marbach JJ . Widespread pain and the effectiveness of oral splints in myofascial face pain[J]. J Am Dent Assoc, 2001,132(3):305-316. |
| [28] | Ding TT, Xu XX, Cao Y , et al. Inflammatory pain memory facilitates occlusal interference-induced masticatory muscle hyperalgesia in rats[J]. Eur J Pain, 2016,20(3):353-364. |
| [29] | Xu XX, Cao Y, Mo SY , et al. ACC plasticity maintains masseter hyperalgesia caused by occlusal interference[J]. J Dent Res, 2019,98(5):589-596. |
| [30] | Nag S, Mokha SS . Activation of the trigeminal α2-adrenoceptor produces sex-specific, estrogen dependent thermal antinociception and antihyperalgesia using an operant pain assay in the rat[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2016,314(19):152-158. |
| [31] | Rohrs EL, Neubert JK, Caudle RM , et al. Behavioral characteristics of capsaicin mediated cutaneous, myogenic, and arthrogenic orofacial nociception in rats[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2018,92(8):18-24. |
| [32] | Zimmermann M . Pathobiology of neuropathic pain[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2001,429(1-3):23-37. |
| [33] | Melo LT, Panchalingam V, Cherkas P , et al.( -)-α-Bisabolol reduces nociception and trigeminal central sensitisation in acute orofacial neuropathic pain induced by infraorbital nerve injury[J]. Life Sci, 2019,227(12):122-128. |
| [34] | Meacham K, Shepherd A, Mohapatra DP , et al. Neuropathic pain: central vs. peripheral mechanisms[J]. Curr Pain Headache Rep, 2017,21(6):28. |
| [35] | Cao Y, Li K, Fu KY , et al. Central sensitization and MAPKs are involved in occlusal interference-Induced facial pain in rats[J]. J Pain, 2013,14(8):793-807. |
| [1] | Jiang JIN, Xue CHEN, Yan ZHAO, Jun JIA, Jianzhong ZHANG. The role and its regulatory significance of interleukin-25 in ovalbumin induced atopic dermatitis of mice [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 756-762. |
| [2] | Zhan-yi ZHANG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Cai-guang CAO,Chang-jian LI,Shao-hui DENG,Yue-hao SUN,Tian-liang HUANG,Yun-he GUAN,Nan LI,Min LU,Zhen-hua HU,Shu-dong ZHANG. Near-infrared targeted probe designed for intraoperative imaging of prostatic neurovascular bundles [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 843-850. |
| [3] | Ting-ting YUAN,Shen LI,Yan WU,Hai-tao WU. Establishment and behavioral evaluation of a mouse model of long-term free-choice alcohol drinking [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 315-323. |
| [4] | Ling-wei MENG,Xue LI,Sheng-han GAO,Yue LI,Rui-tao CAO,Yi ZHANG,Shao-xia PAN. Comparison of three methods for establishing rat peri-implantitis model [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 22-29. |
| [5] | HE Wei,YANG Si-wen,CHEN Juan,ZHU Xiao-jun,CHEN Zhi-zhong,MA Wen-jun. Effects of 275 nm and 310 nm ultraviolet irradiation on bone metabolism in ovariectomized osteoporotic rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 236-243. |
| [6] | FAN Ying-ying,LIU Yun,CAO Ye,XIE Qiu-fei. Hippocampus is involved in 17β-estradiol exacerbating experimental occlusal inter-ference-induced chronic masseter hyperalgesia in ovariectomized rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 40-47. |
| [7] | WANG Gui-hong,ZUO Ting,LI Ran,ZUO Zheng-cai. Effect of rebamipide on the acute gouty arthritis in rats induced by monosodium urate crystals [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 716-720. |
| [8] | YIN Xue-qian, ZHANG Xiao-xuan, WEN Jing, LIU Si-qi, LIU Xin-ran, ZHOU Ruo-yu, WANG Jun-bo. Effects of the composite of buckwheat-oat-pea on blood glucose in diabetic rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(3): 447-452. |
| [9] | Di ZHOU,Zhang-jian CHEN,Gui-ping HU,Teng-long YAN,Chang-mao LONG,Hui-min FENG,Guang JIA. Influence of oxidative/antioxidative biomarkers and inflammatory cytokines on rats after sub-acute orally administration of titanium dioxide nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(5): 821-827. |
| [10] | Shuo HAN,Zhang-jian CHEN,Di ZHOU,Pai ZHENG,Jia-he ZHANG,Guang JIA. Effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on fecal metabolome in rats after oral administration for 90 days [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 457-463. |
| [11] | Zhang-jian CHEN,Shuo HAN,Pai ZHENG,Shu-pei ZHOU,Guang JIA. Effect of subchronic combined oral exposure of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and glucose on levels of serum folate and vitamin B12 in young SD rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 451-456. |
| [12] | Jiao HE,Ge-heng YUAN,Jun-qing ZHANG,Xiao-hui GUO. Approach to creating early diabetic peripheral neuropathy rat model [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1150-1154. |
| [13] | Wei WANG,Jin HOU,Wen-qiang HUANG. Temporary acceleration of interstitial fluid drainage in excited brain region induced by movement [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 206-209. |
| [14] | Shu-dong YAN,Guang-ju YANG,Si-yi MO,Yun LIU,Qiu-fei XIE. Effect of long-term resistance exercise on masseter muscle mechanical hyperalgesia in rats [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 21-27. |
| [15] | WANG Yu-jie, GUO Xiang-yang, WANG Jun. Influences of repeated propofol anesthesia on hippocampal apoptosis and long-term learning and memory abilities of neonatal rats [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 310-314. |
|
||