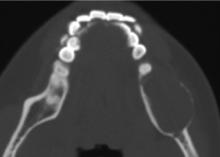
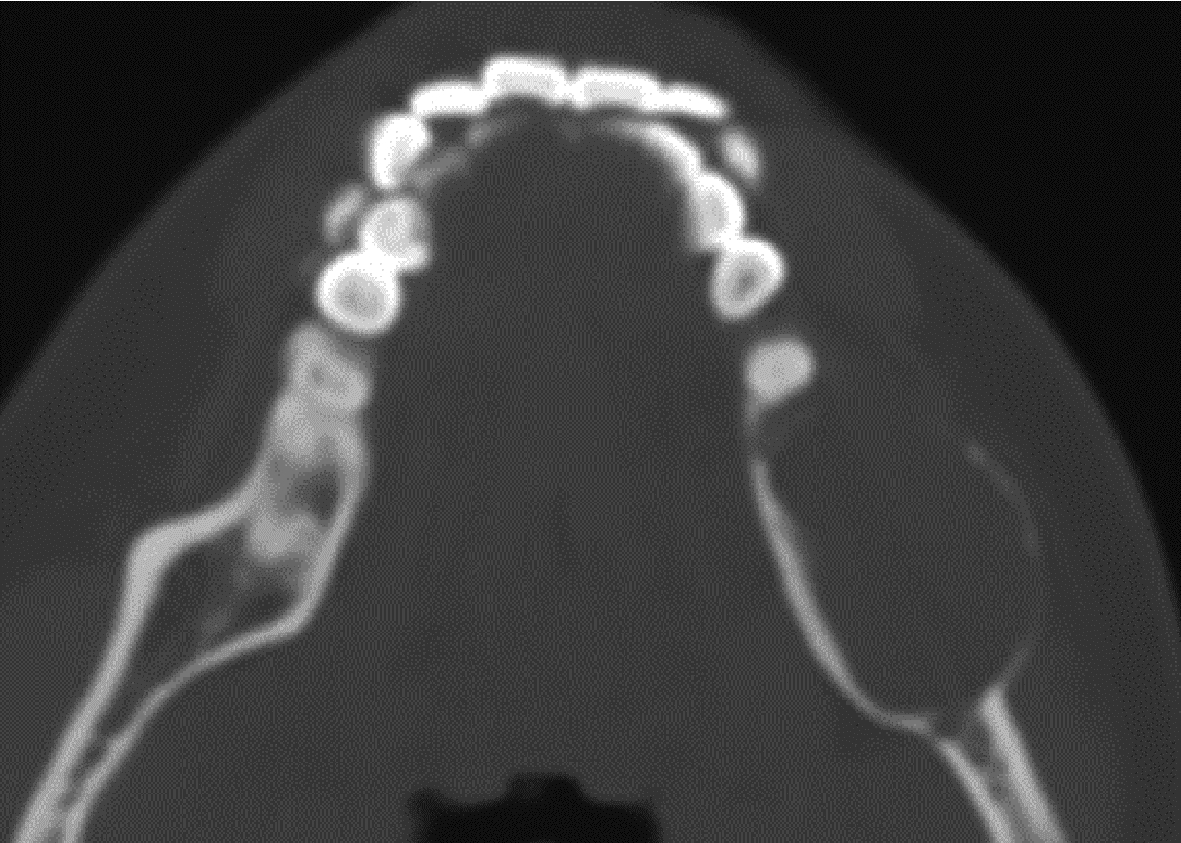
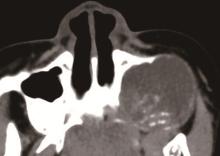
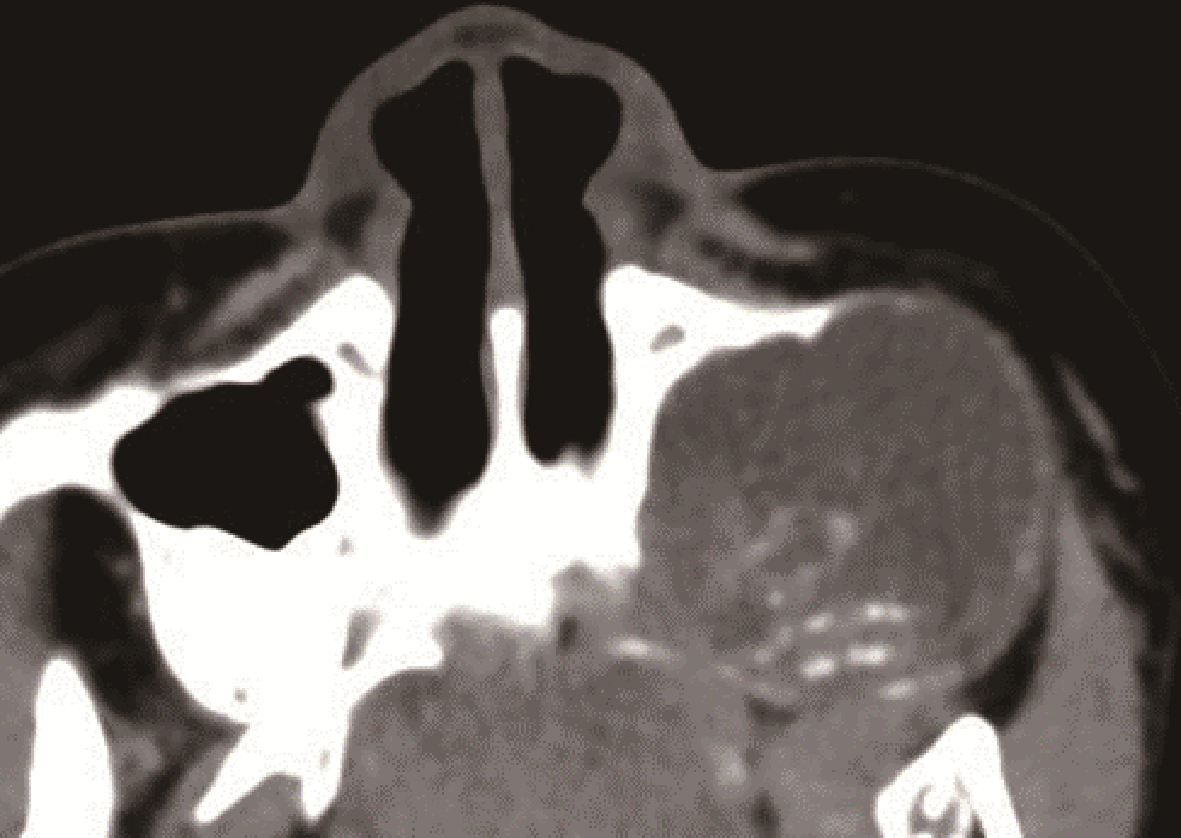
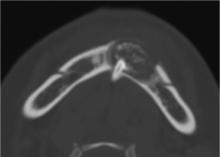
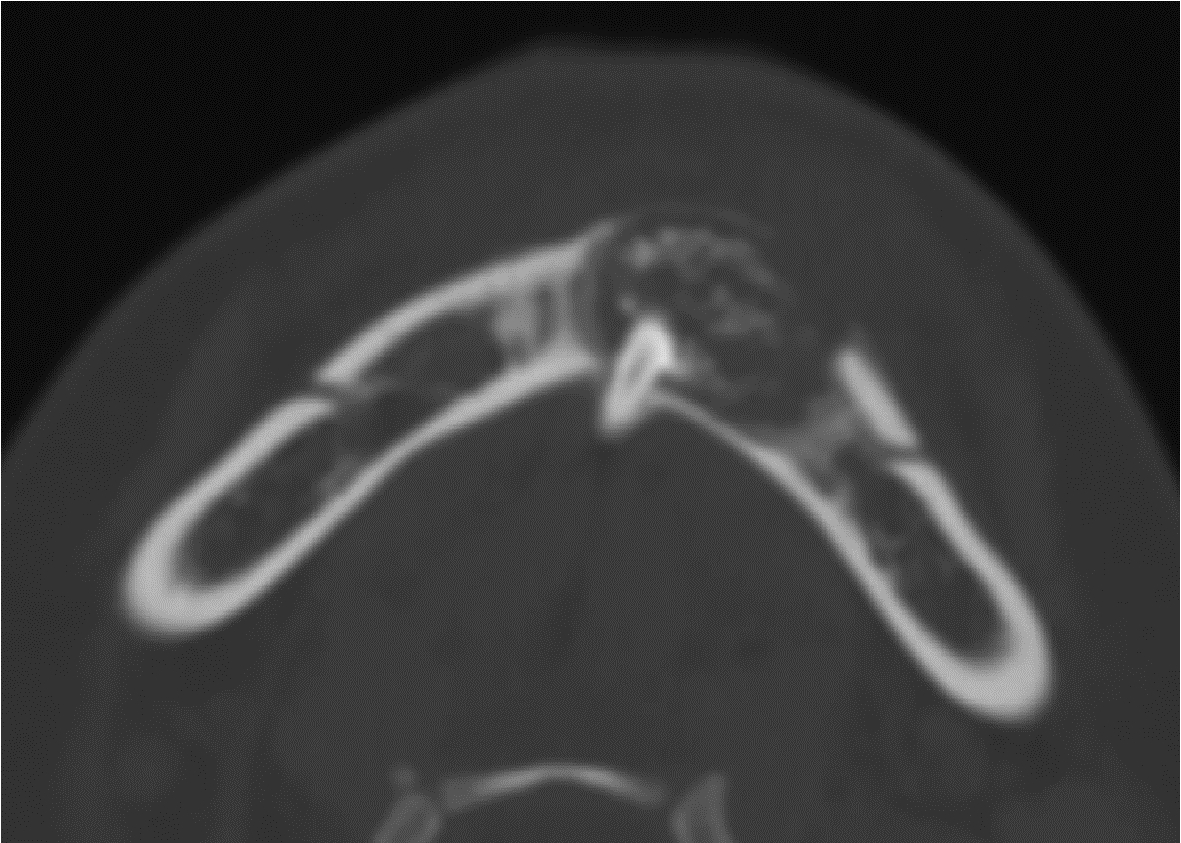
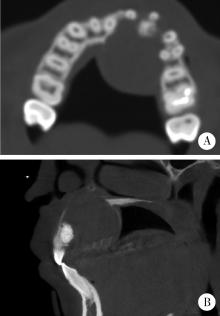
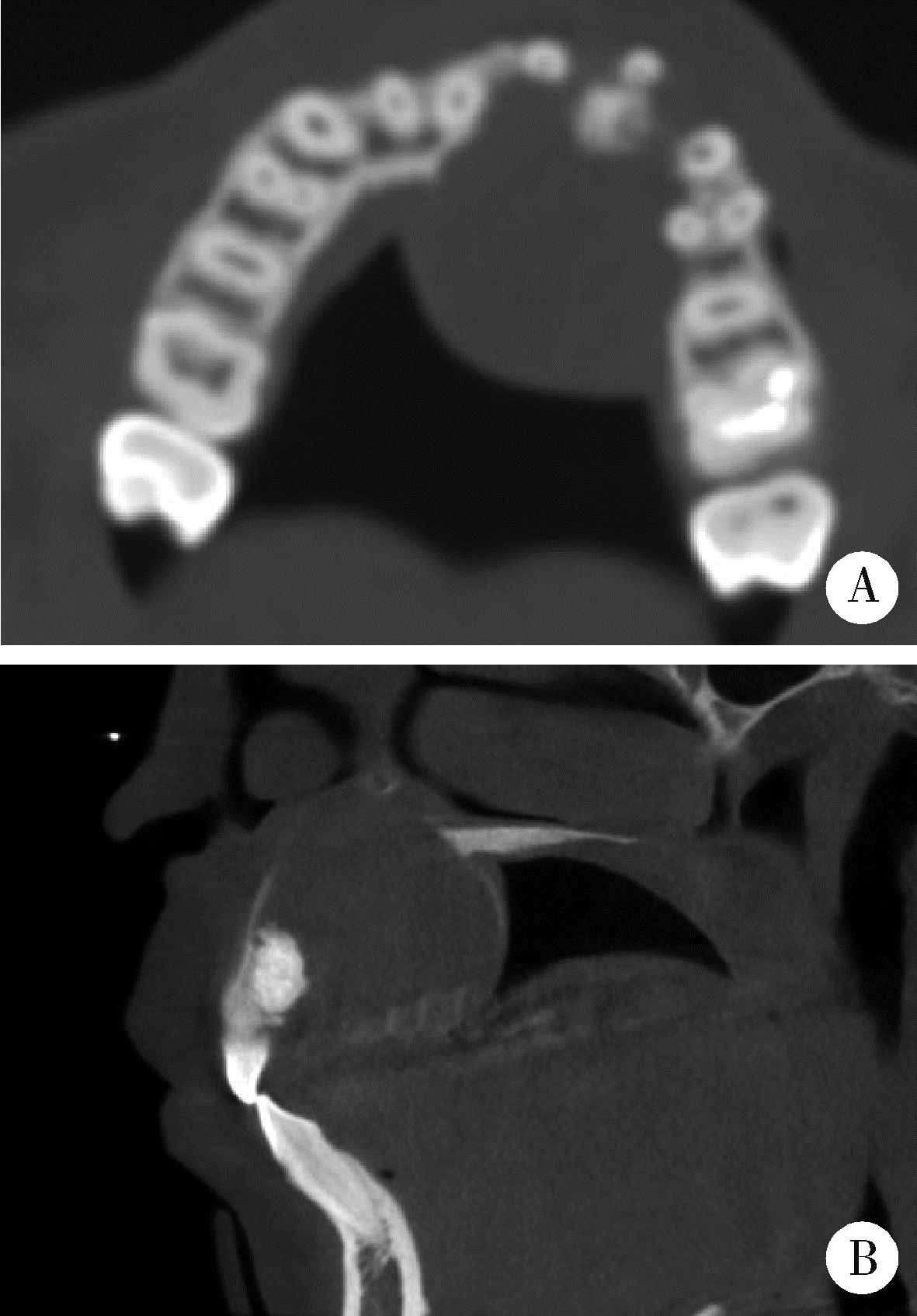
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 131-137. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.01.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
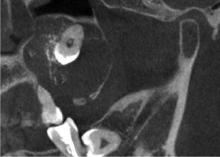
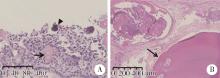
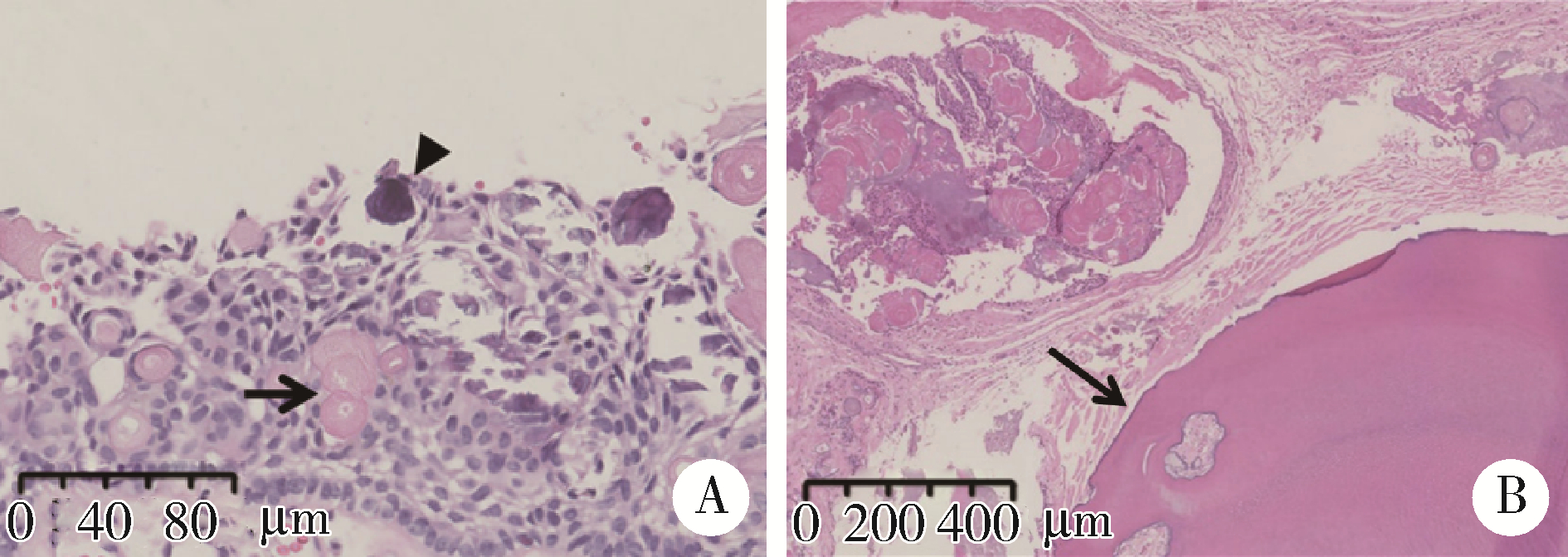
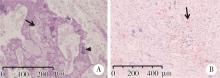
Three-dimensional radiographic features of calcifying odontogenic cyst and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor
Xiaotong LING1,Liuyang QU1,Danni ZHENG1,Jing YANG1,Xuebing YAN2,Denggao LIU1,*( ),Yan GAO3
),Yan GAO3
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
2. Special Dental Department, The First Clinical Division, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
3. Department of Oral Pathology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R739.8
| 1 |
Lee SK , Kim YS . Current concepts and occurrence of epithelial odontogenic tumors: Ⅱ. Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor versus ghost cell odontogenic tumors derived from calcifying odontogenic cyst[J]. Korean J Pathol,, 2014, 48 (3): 175- 187.
doi: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.3.175 |
| 2 | 马绪臣. 口腔颌面医学影像学[M]. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2006. |
| 3 |
Philipsen HP , Reichart PA . Adenomatoid odontogenic tumour: Facts and figures[J]. Oral Oncol, 1999, 35 (2): 125- 131.
doi: 10.1016/S1368-8375(98)00111-0 |
| 4 | Bansal SP , Shaikh S , Arvandekar AS , et al. Analysis of 55 cases of adenomatoid odontogenic tumor in an Indian population and review of literature[J]. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2022, 27 (1): e85- e93. |
| 5 |
陈菲, 张庆庆, 陆东辉, 等. 牙源性钙化囊性瘤临床病理研究[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2012, 28 (8): 891- 894.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7399.2012.08.014 |
| 6 |
付文荣, 程正江. 牙源性钙化上皮瘤3例临床病理观察[J]. 诊断病理学杂志, 2014, 21 (4): 231- 233.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8096.2014.04.012 |
| 7 | Sonone A , Sabane VS , Desai R . Calcifying ghost cell odontogenic cyst: Report of a case and review of literature[J]. Case Rep Dent, 2011, 2011, 328743. |
| 8 |
刘梅, 孙国文, 唐恩溢, 等. 牙源性钙化囊肿的临床病理分析[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2020, 36 (1): 96- 99.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3733.2020.01.021 |
| 9 |
陶谦, 梁培盛. 2017版WHO牙源性肿瘤新分类之述评[J]. 口腔疾病防治, 2017, 25 (12): 749- 754.
doi: 10.12016/j.issn.2096-1456.2017.12.001 |
| 10 | Soluk-Tekkesin M , Wright JM . The World Health Organization classification of odontogenic lesions: A summary of the changes of the 2022 (5th) edition[J]. Turk Patoloji Derg, 2022, 38 (2): 168- 184. |
| 11 |
Buchner A . The central (intraosseous) calcifying odontogenic cyst: An analysis of 215 cases[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1991, 49 (4): 330- 339.
doi: 10.1016/0278-2391(91)90365-S |
| 12 | Ahmad SA , Popli DB , Sircar K , et al. Calcifying odontogenic cyst: Report of an uncommon entity with a brief literature review[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol, 2022, 26 (1): 131. |
| 13 | Chandran A , Nachiappan S , Selvakumar R , et al. Calcifying epithelial odontogenic cyst of maxilla: Report of a case and review and discussion on the terminology and classification[J]. J Microsc Ultrastruct, 2020, 9 (2): 98- 102. |
| 14 |
de Arruda JAA , Schuch LF , Abreu LG , et al. A multicenter study of 268 cases of calcifying odontogenic cysts and a literature review[J]. Oral Dis, 2018, 24 (7): 1282- 1293.
doi: 10.1111/odi.12906 |
| 15 |
Rojo R , Prados-Frutos JC , Gutierrez Lázaro I , et al. Calcifying odontogenic cysts[J]. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2017, 118 (2): 122- 124.
doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2016.10.007 |
| 16 |
Chindasombatjaroen J , Poomsawat S , Boonsiriseth K . Two unique cases of calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor in the maxillary posterior region[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2014, 118 (4): 497- 504.
doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2014.06.006 |
| 17 | Santos HBP , de Morais EF , Moreira DGL , et al. Calcifying odontogenic cyst with extensive areas of dentinoid: uncommon case report and update of main findings[J]. Case Rep Pathol, 2018, 2018, 8323215. |
| 18 | Gamoh S , Akiyama H , Furukawa C , et al. Calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor accompanied by a dentigerous cyst: A case report[J]. Oncol Lett, 2017, 14 (5): 5785- 5790. |
| 19 |
Hirshberg A , Kaplan I , Buchner A . Calcifying odontogenic cyst associated with odontoma: A possible separate entity (odontocalcifying odontogenic cyst)[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1994, 52 (6): 555- 558.
doi: 10.1016/0278-2391(94)90087-6 |
| 20 |
Vizuete-Bolaños MX , Salgado-Chavarria F , Ramírez-Martínez CM , et al. Compound odontoma associated with a calcifying odontogenic cyst. Case report and systematic review[J]. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2022, 123 (3): e97- e105.
doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2021.10.008 |
| 21 |
张艳宁, 侯亚丽, 于美清, 等. 牙源性钙化上皮瘤1例临床病理分析及文献复习[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2021, 37 (3): 431- 433.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3733.2021.03.032 |
| 22 | Mujib BR , Kulkarni PG , Lingappa A , et al. An atypical presentation of Pindborg tumor in anterior maxilla[J]. Dent Res J (Isfahan), 2012, 9 (4): 495- 498. |
| 23 |
Ibituruna ACH , Costa ARGF , Paulo LFB , et al. Multiple calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor: Case report and review of the literature[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2019, 128 (3): 268- 272.
doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2019.03.018 |
| 24 |
Zhang A , Chaw SY , Talacko AA , et al. Central calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumour in the posterior maxilla: A case report[J]. Aust Dent J, 2016, 61 (3): 381- 385.
doi: 10.1111/adj.12384 |
| 25 | 王凯利, 郑广宁, 刘莉, 等. 牙源性钙化上皮瘤2例[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2016, 34 (1): 104- 107. |
| 26 |
Vered M , Wright JM . Update from the 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of head and neck tumors: Odontogenic and maxillofacial bone tumours[J]. Head Neck Pathol, 2022, 16 (1): 63- 75.
doi: 10.1007/s12105-021-01404-7 |
| 27 |
王丽, 汪说之, 陈新明, 等. 牙源性钙化上皮瘤中朗格汉斯细胞的研究[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2005, 21 (6): 645- 648.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7651.2005.06.016 |
| 28 |
Hong SP , Ellis GL , Hartman KS . Calcifying odontogenic cyst. A review of ninety-two cases with reevaluation of their nature as cysts or neoplasms, the nature of ghost cells, and subclassification[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol, 1991, 72 (1): 56- 64.
doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(91)90190-N |
| 29 | 刘轶芳. 245例颌骨良恶性肿瘤的CT影像学特征的对比研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2020. |
| 30 | 叶婷婷, 陈蔚华, 裴婧, 等. 青少年牙本质生成性影细胞瘤1例[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2022, 38 (10): 995- 996. |
| 31 | 王予江, 李琳琳. 外周型牙源性钙化囊性瘤病例报道[C]//中华口腔医学会口腔颌面外科专业委员会. 第十四次中国口腔颌面外科学术会议论文汇编. 重庆: [出版者不详], 2018: 1. |
|
||