北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 107-112. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.01.017
无牙颌患者鼻唇角变化侧面观的视觉敏感阈值
游浪1,邓珂慧2,李伟伟2,赵一姣2,△( ),孙玉春2,△(
),孙玉春2,△( ),周永胜1
),周永胜1
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院, 修复科, 北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,口腔医学数字化研究中心 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Visual sensitivity threshold of lateral view of nasolabial Angle changes in edentulous jaw patients
Lang YOU1,Ke-hui DENG2,Wei-wei LI2,Yi-jiao ZHAO2,△( ),Yu-chun SUN2,△(
),Yu-chun SUN2,△( ),Yong-sheng ZHOU1
),Yong-sheng ZHOU1
- 1. Center of Digital Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & Department of Prosthodontics, Beijing 100081, China
2. Center of Digital Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
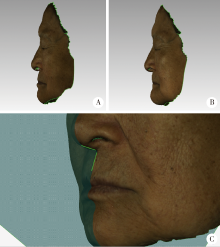
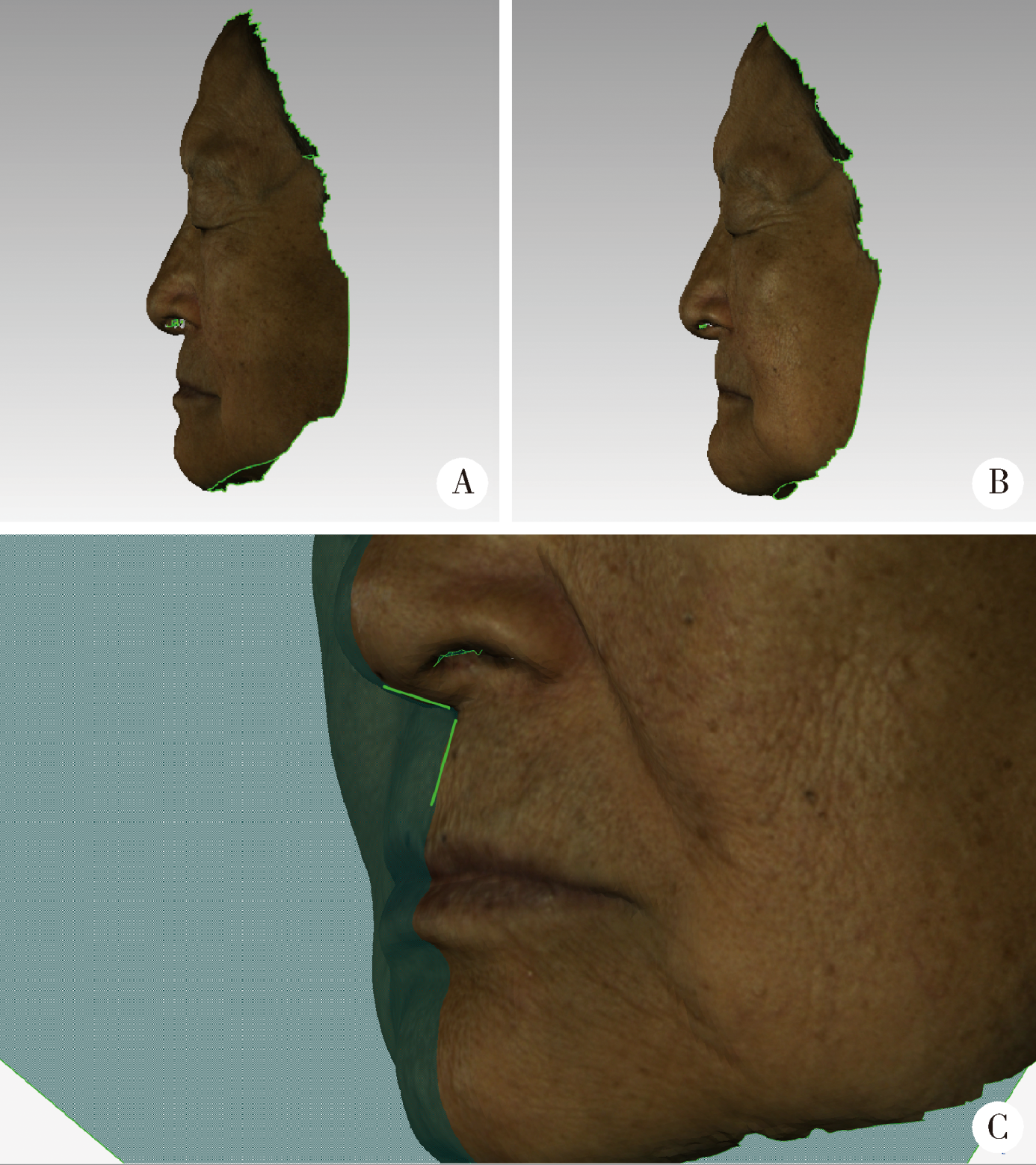
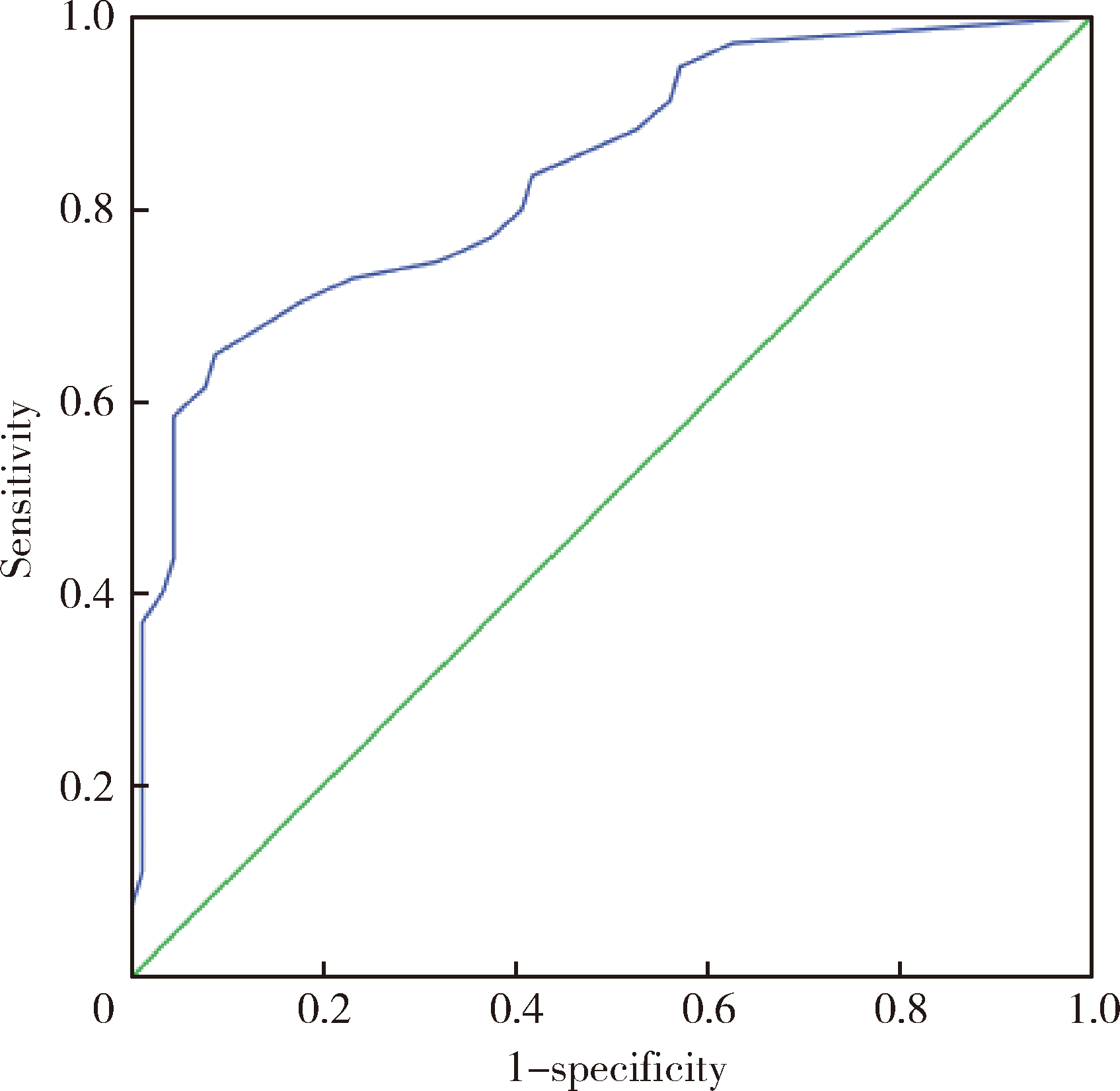
目的:研究医师肉眼对无牙颌患者鼻唇角差异侧面观的视觉敏感阈值,明确人眼可有效识别的鼻唇角差异大小,以期为软组织侧貌审美评价相关研究提供人眼可识别的鼻唇角差异的参考值。方法:获取3名无牙颌患者戴入不同唇部支撑诊断义齿的面部三维数据,对患者的面部三维数据进行同比例侧面截图,以口腔修复科医师(主任医师)和患者肉眼观察双重确认的合适唇丰满度时的侧面截图为参照图片,将其他侧面截图分别与之组合成组,由受试者以随机顺序观察。选择15名口腔医师作为受试者观察每组图片的鼻唇角差异情况,测量计算每组两张图片的鼻唇角差值。实验结果绘制成受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线,使用SPSS 20.0统计软件及约登(Youden)指数计算最佳截断值作为医师肉眼对无牙颌患者鼻唇角差异侧面观的视觉敏感阈值。结果:15名受试者数据分别绘制ROC曲线,其中最佳截断值最大者为5.55°,最小者为3.12°。数据汇总后绘制整体受试者工作特征曲线,其最佳截断值为5.36°(AUC=0.84>0.5, P=0.000<0.05)。当图片的鼻唇角差异在5.36°以上时,受试者能够有效识别。结论:人对鼻唇角变化量的视觉感知存在极限,研究得出了5.36°的鼻唇角差异侧面观的视觉敏感阈值。低于此值的鼻唇角差异可能无临床意义,此结果为软组织侧貌审美评价提供了人眼可识别的鼻唇角变化量阈值的参考值,可应用于软组织侧貌的美学评估,以及作为以鼻唇角为指标进行精度评价的相关研究的误差等级。
中图分类号:
- R783
| [1] | Harris R, Nagarkar P, Amirlak B . Varied definitions of nasolabial angle[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open, 2016,4(6):e752. |
| [2] | 徐安秀, 邓锋, 王芬芬 , 等. 鼻唇角改变对骨性Ⅰ类软组织侧貌影响的审美评价[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2015,33(5):492-496. |
| [3] | 马玥, 任嫒姝, 付钢 , 等. 鼻唇角、颏唇角改变对骨性Ⅱ类和Ⅲ类患者面容影响的三维美学评价[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2017,33(5):647-652. |
| [4] | Desesa CR, Metzler P, Sawh-Martinez R , et al. Three-dimensional nasolabial morphologic alterations following Le Fort I[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open, 2016,4(8):e848. |
| [5] | Aniruddh YV, Ravi K, Edeinton A. Comparative evaluation of soft tissue changes in Class Ⅰ borderline patients treated with extraction and nonextraction modalities[J]. Dental Press J Orthod, 2016,21(4):50-59. |
| [6] | Kamashita Y, Kamada Y, Kawahata N , et al. Influence of lip support on the soft-tissue profile of complete denture wearers[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2006,33(2):102-109. |
| [7] | Kaipatur NR, Flores-Mir C . Accuracy of computer programs in predicting orthognathic surgery soft tissue response[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2009,67(4):751-759. |
| [8] | Raschke GF, Rieger UM, Bader RD , et al. Perioral aging: an anthropometric appraisal[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2014,42(5):e312-e317. |
| [9] | Sierpinska T, Golebiewska M, Kuc J , et al. The influence of the occlusal vertical dimension on masticatory muscle activities and hyoid bone position in complete denture wearers[J]. Adv Med Sci, 2009,54(1):104-108. |
| [10] | Krajicek DD . Guides for natural facial appearance as related to complete denture construction[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 1969,21(6):654-662. |
| [11] | Coleman SR, Grover R . The anatomy of the aging face: volume loss and changes in 3-dimensional topography[J]. Aesthet Surg J, 2006,26(Suppl 1):S4-S9. |
| [12] | Owens EG, Goodacre CJ, Loh PL , et al. A multicenter interracial study of facial appearance. Part 1: A comparison of extraoral parameters[J]. Int J Prosthodont, 2002,15(3):273-282. |
| [13] | Yuan F, Cheng C, Dai N , et al. Prediction of aesthetic reconstruction effects in edentulous patients[J]. Sci Rep, 2017,7(1):18077. |
| [14] | Denes BJ, Bolton C, Illsley CS , et al. Notch coordinates periodontal ligament maturation through regulating lamin A[J]. J Dent Res, 2019,98(12):1357-1366. |
| [15] | Katase H, Kanazawa M, Inokoshi M , et al. Face simulation system for complete dentures by applying rapid prototyping[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2013,109(6):353-360. |
| [16] | Schweiger J, Güth JF, Edelhoff D , et al. Virtual evaluation for cad-cam-fabricated complete dentures[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2017,117(1):28-33. |
| [17] | Franco SGC, Libdy MR, Normando D . Scan time, reliability and accuracy of craniofacial measurements using a 3D light scanner[J]. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res, 2019,9(4):331-335. |
| [18] | Modabber A, Peters F, Kniha K , et al. Evaluation of the accuracy of a mobile and a stationary system for three-dimensional facial scanning[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2016,44(10):1719-1724. |
| [19] | Grant CA, Johnston M, Adam CJ , et al. Accuracy of 3D surface scanners for clinical torso and spinal deformity assessment[J]. Med Eng Phys, 2019,63:63-71. |
| [20] | Li H, Lyu P, Sun Y , et al. A quantitative study of 3D-scanning frequency and Δd of tracking points on the tooth surface[J]. Sci Rep, 2015,5(2):14350. |
| [21] | 萧宁, 王勇, 赵一姣 . 三维颜面部软组织正中矢状面确定方法的研究进展[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2018,53(7):495-499. |
| [22] | Lee JK, Jung PK, Moon CH . Three-dimensional cone beam computed tomographic image reorientation using soft tissues as reference for facial asymmetry diagnosis[J]. Angle Orthod, 2014,84(1):38-47. |
| [23] | Nur RB, Çakan DG, Arun T . Evaluation of facial hard and soft tissue asymmetry using cone-beam computed tomography[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2016,149(2):225-237. |
| [1] | 唐祖南,胡耒豪,陈震,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 增强现实技术在口腔颌面颈部解剖识别中的应用评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 541-545. |
| [2] | 展新新,曹露露,项东,汤皓,夏丹丹,林红. 成型方向对3D打印口腔义齿基托树脂材料物理性能及力学性能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 345-351. |
| [3] | 吕梁,张铭津,温奧楠,赵一姣,王勇,李晶,杨庚辰,柳大为. 应用三维软组织空间线角模板法评价颏部对称性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 106-110. |
| [4] | 毛渤淳,田雅婧,王雪东,李晶,周彦恒. 骨性Ⅱ类高角患者拔牙矫治前后的面部软硬组织变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [5] | 凌晓彤,屈留洋,郑丹妮,杨静,闫雪冰,柳登高,高岩. 牙源性钙化囊肿与牙源性钙化上皮瘤的三维影像特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [6] | 胡攀攀,李彦,刘啸,唐彦超,李梓赫,刘忠军. 自稳式人工椎体在颈椎前路手术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 161-166. |
| [7] | 徐心雨,吴灵,宋凤岐,李自力,张益,刘筱菁. 基于下颌运动轨迹的正颌外科术中下颌骨髁突定位方法及初步精度验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [8] | 李穗,马雯洁,王时敏,丁茜,孙瑶,张磊. 上前牙种植单冠修复体切导的数字化设计正确度[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 81-87. |
| [9] | 黄莹,吴志远,周行红,蔡志刚,张杰. 股前外侧皮瓣修复上颌骨缺损术后面部软组织对称性感观分级[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 708-715. |
| [10] | 张雯,刘筱菁,李自力,张益. 基于解剖标志的鼻翼基底缩窄缝合术对正颌患者术后鼻唇部形态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
| [11] | 欧蒙恩,丁云,唐卫峰,周永胜. 基台边缘-牙冠的平台转移结构中粘接剂流动的三维有限元分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 548-552. |
| [12] | 温奥楠,刘微,柳大为,朱玉佳,萧宁,王勇,赵一姣. 5种椅旁三维颜面扫描技术正确度的初步评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 343-350. |
| [13] | 周华,王仁吉,刘忠军,刘晓光,吴奉梁,党礌,韦峰. 3D打印人工椎体在颈椎脊索瘤全脊椎切除术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 144-148. |
| [14] | 熊士凯,史尉利,王安鸿,谢兴,郭秦炜. 腓骨远端撕脱骨折的影像学诊断:踝关节X线与CT三维重建的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 156-159. |
| [15] | 高梓翔,王勇,温奥楠,朱玉佳,秦庆钊,张昀,王晶,赵一姣. 基于三维下颌骨平均模型的颌骨标志点自动确定方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 174-180. |
|
||