北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 468-476. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.03.011
基于人消化道微生态体外模拟系统观察纳米二氧化钛对肠道菌群的影响
- 北京大学公共卫生学院劳动卫生与环境卫生学系, 食品安全毒理学研究与评价北京市重点实验室, 北京 100191
Effects of nano titanium dioxide on gut microbiota based on human digestive tract microecology simulation system in vitro
Jia-he ZHANG,Jia-qi SHI,Zhang-jian CHEN,Guang JIA*( )
)
- Department of Occupational and Environmental Health Sciences, Peking University School of Public Health; Beijing Key Laboratory of Toxicological Research and Risk Assessment for Food Safety, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
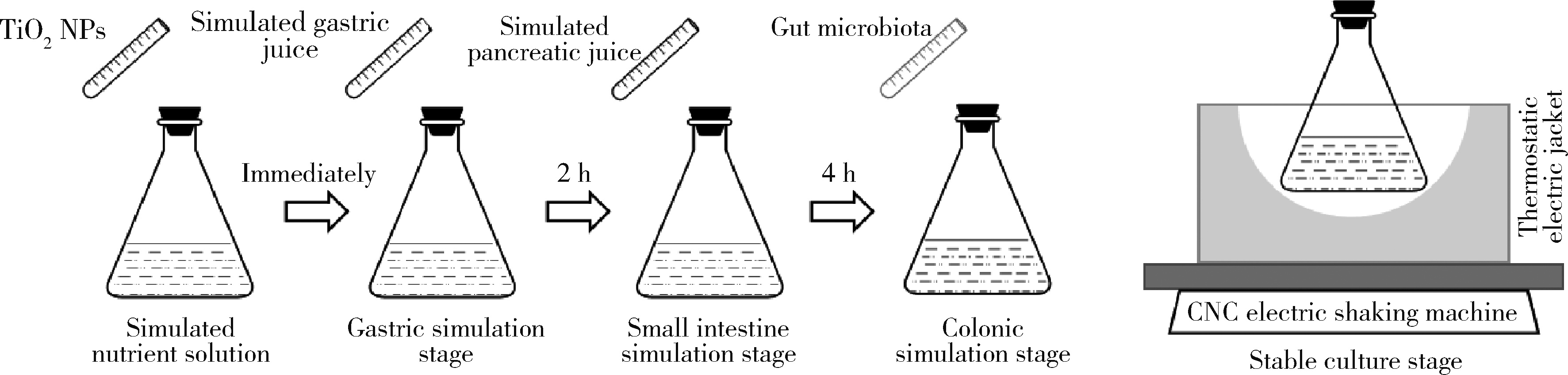
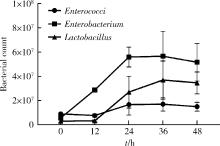
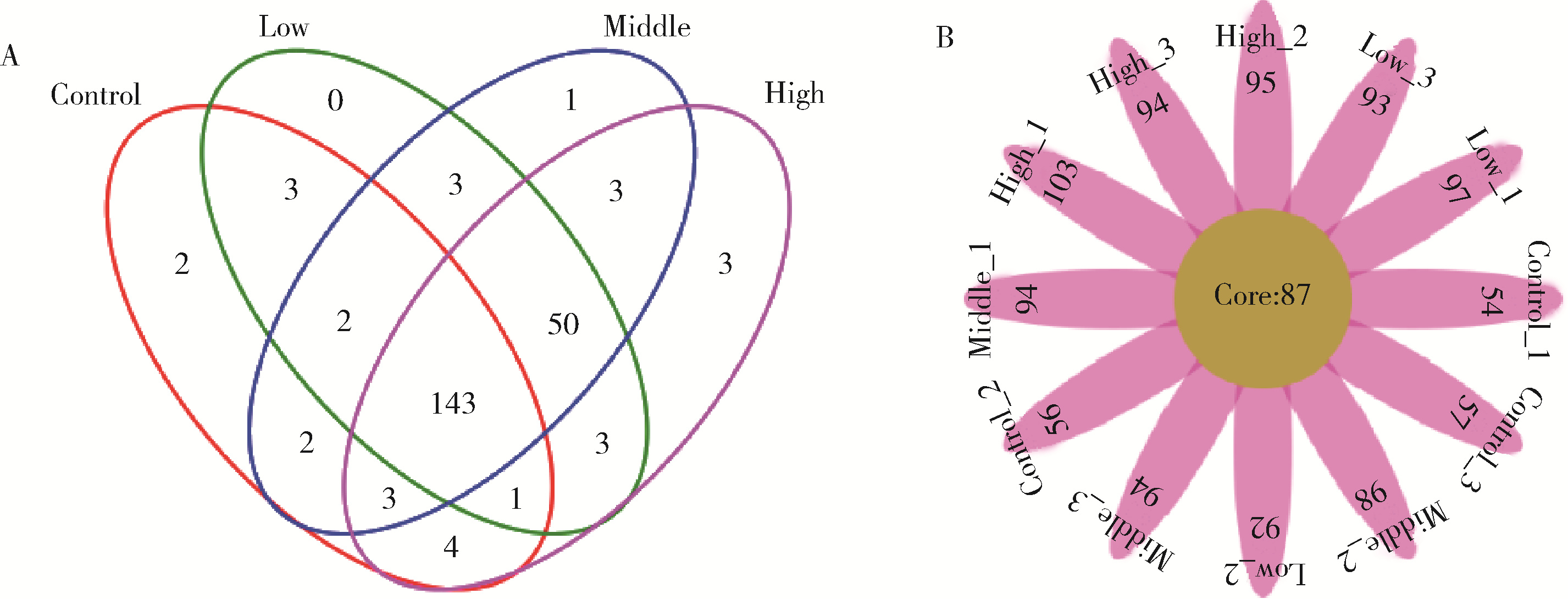
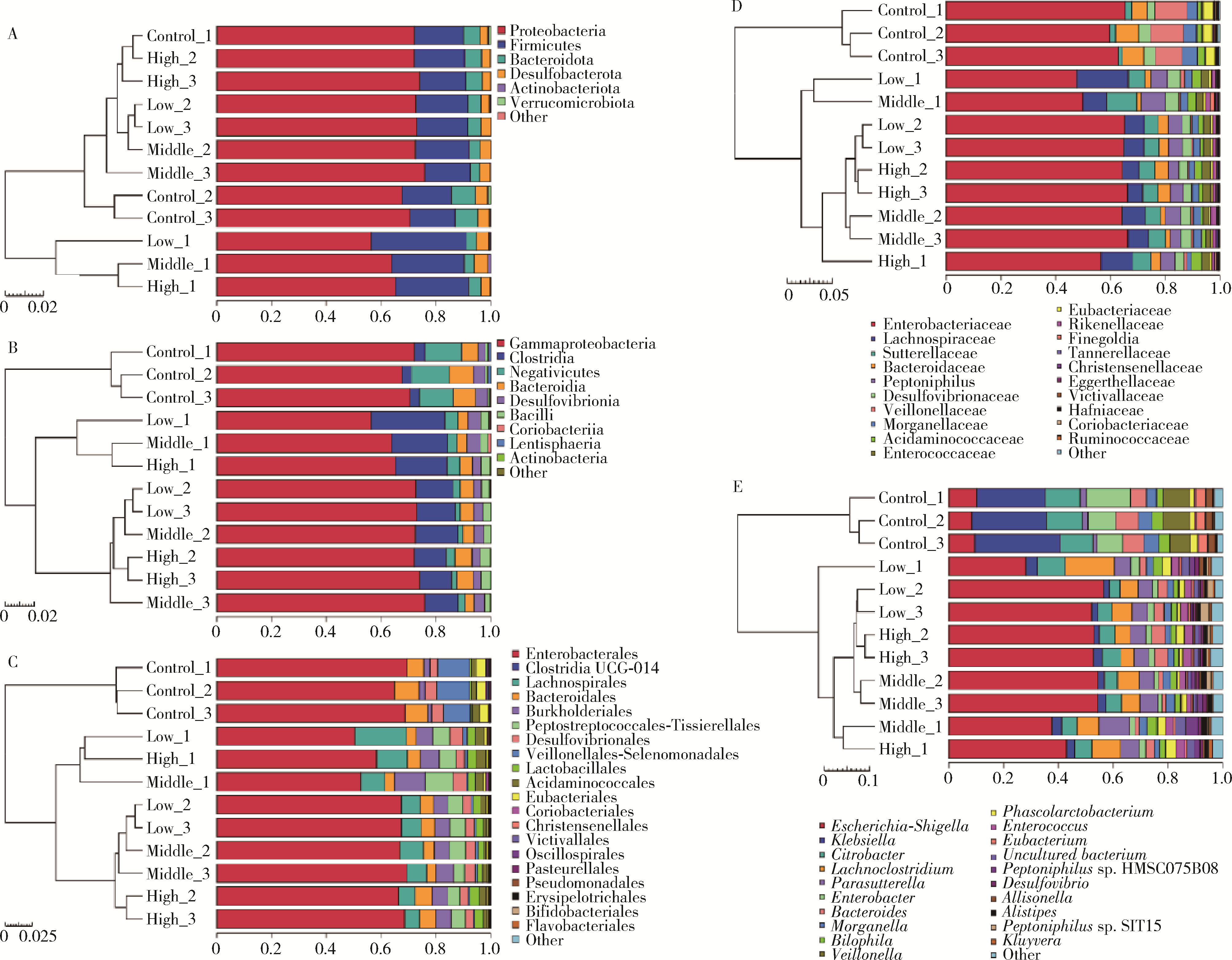
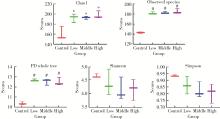
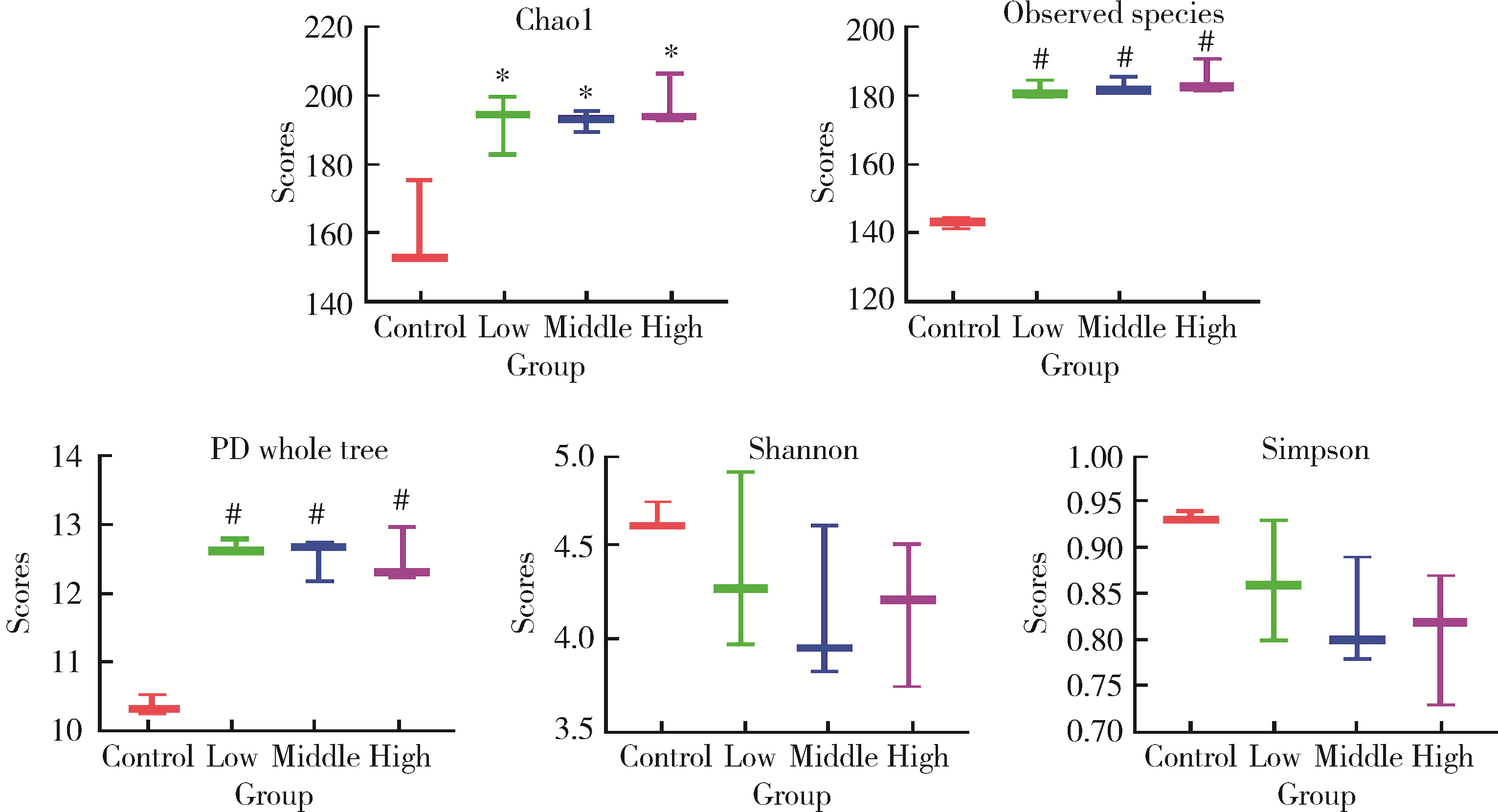
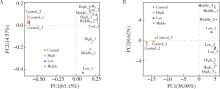
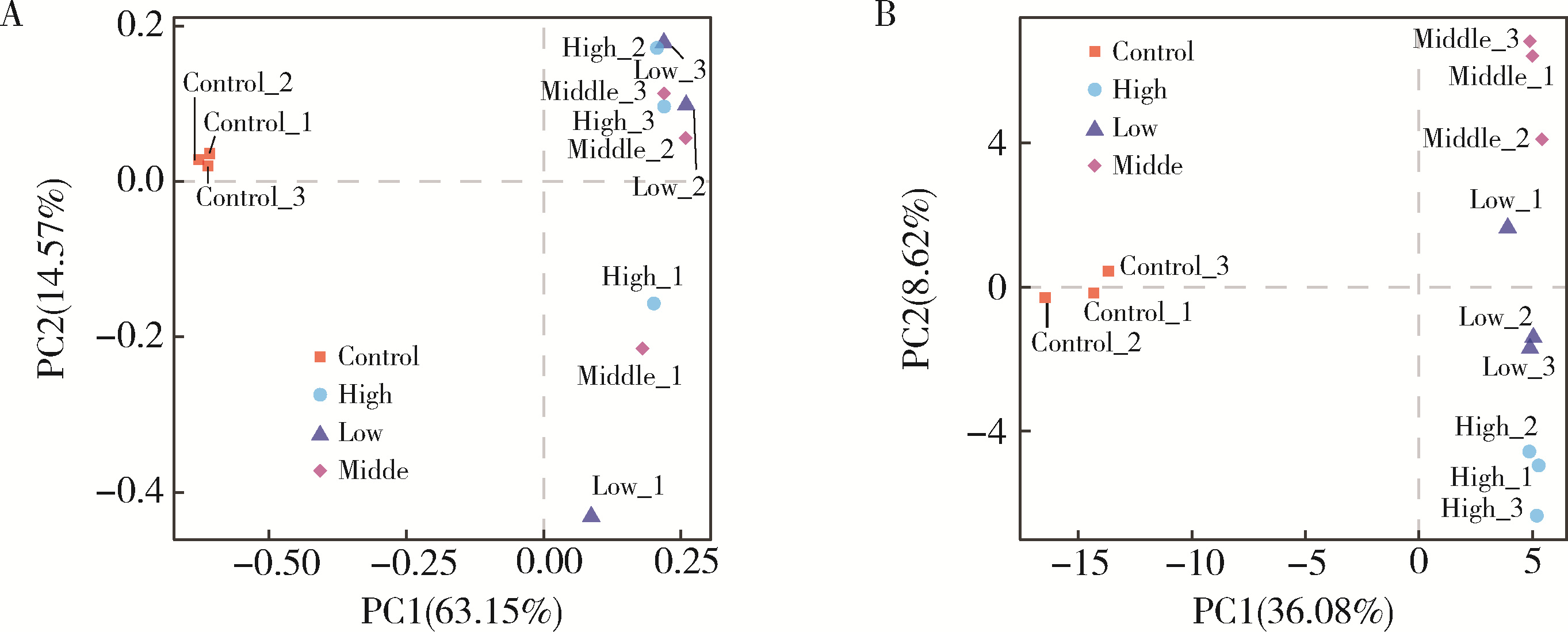
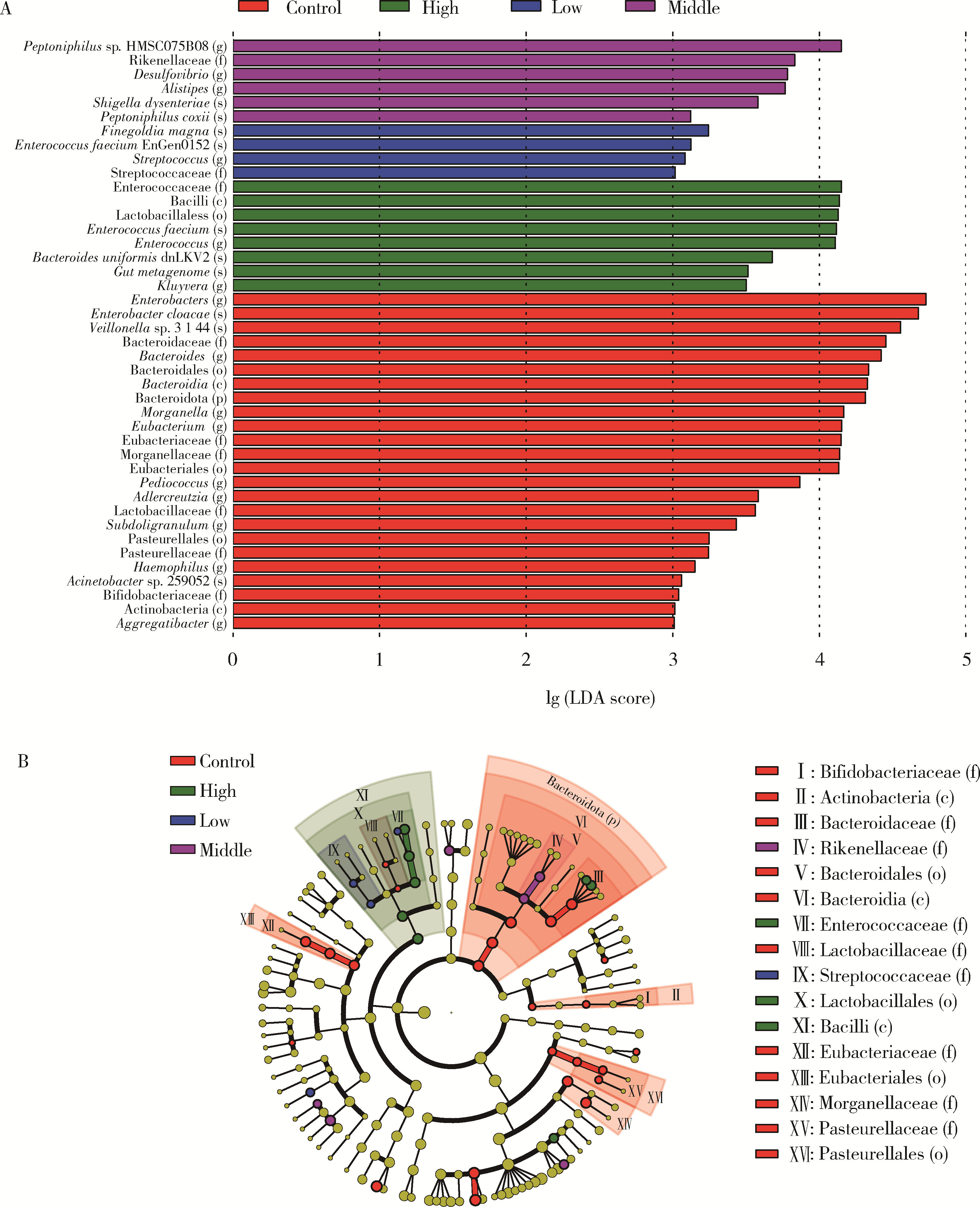
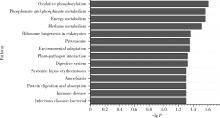
目的: 通过消化道微生态体外模拟系统探索纳米二氧化钛(titanium dioxide nanoparticles,TiO2 NPs)对人源肠道菌群组成和结构的影响。方法: 对TiO2 NPs进行粒径、形状、晶型和团聚程度的表征。通过模拟胃、小肠、结肠的液体环境和物理条件建立体外人消化道微生态模拟系统,并对模拟系统的稳定性进行评价。从人粪便中提取菌群,采用该模拟系统稳定培养,分别暴露于0、20、100、500 mg/L TiO2 NPs中,收集染毒24 h后的菌液,通过16S rRNA测序技术分析TiO2 NPs对人源肠道菌群组成和结构的影响,利用线性判别效应量分析(linear discriminant analysis effect size,LEfSe)筛选差异细菌,根据京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes,KEGG)数据库进行功能预测。结果: TiO2 NPs为球形粒径,直径(25.12±5.64) nm,晶体结构为锐钛矿,在超纯水中水合粒径为(609.43±60.35) nm,Zeta电位为(-8.33±0.22) mV。体外消化道模拟系统培养人源肠道菌群24 h后达到相对稳定状态,肠球菌(Enterococci)、大肠杆菌(Enterobacterium)和乳酸杆菌(Lactobacillus)计数可分别达到(1.60±0.85)×107个、(5.60±0.82)×107个和(2.70±1.32)×107个。16S rRNA测序结果显示,与对照组相比,TiO2 NPs染毒组(20、100和500 mg/L)在门、纲、目、科、属水平上,肠道菌群的物种数量和均匀度未受到明显影响,但部分菌种的相对丰度发生显著变化。TiO2 NPs染毒组(20、100和500 mg/L)与对照组之间共筛选出42种不同的差异细菌(线性判别分析分数,linear discriminant analysis score,LDA score>3),以肠杆菌属(Enterobacter)、拟杆菌科(Bacteroidaceae)、乳酸杆菌科(Lactobacillaceae)、双歧杆菌科(Bifidobacteriaceae)和梭菌属(Clostridium)等为代表。进一步的肠道菌群功能预测分析显示,TiO2 NPs可能影响肠道菌群的氧化磷酸化、能量代谢、磷酸盐和磷酸盐代谢、甲烷代谢等代谢和功能(P < 0.05)。结论: 体外人消化道微生态模拟系统下,TiO2 NPs可以显著改变人源肠道菌群的组成和结构,以肠杆菌属和益生菌为代表,并可能进而影响机体多种物质的代谢和功能。
中图分类号:
- R155.5
| 1 | Aguilar F, Crebelli R, Di Domenico A, et al. Re-evaluation of titanium dioxide (E 171) as a food additive[J/OL]. EFSA Journal, 2016, 14(9): 4545. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2016.4545. |
| 2 |
Yang Y , Doudrick K , Bi X , et al. Characterization of food-grade titanium dioxide: The presence of nanosized particles[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2014, 48 (11): 6391- 6400.
doi: 10.1021/es500436x |
| 3 |
Chen ZJ , Han S , Zhou SP , et al. Review of health safety aspects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food application[J]. Nanoimpact, 2020, 18, 100224.
doi: 10.1016/j.impact.2020.100224 |
| 4 |
Shakeel M , Jabeen F , Shabbir S , et al. Toxicity of nano-titanium dioxide (TiO2-NP) through various routes of exposure: A review[J]. Biol Trace Elem Res, 2016, 172 (1): 1- 36.
doi: 10.1007/s12011-015-0550-x |
| 5 | Alavi M , Karimi N . Characterization, antibacterial, total antioxidant, scavenging, reducing power and ion chelating activities of green synthesized silver, copper and titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Artemisia haussknechtii leaf extract[J]. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol, 2018, 46 (8): 2066- 2081. |
| 6 |
Hajipour MJ , Fromm KM , Ashkarran AA , et al. Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles[J]. Trends Biotechnol, 2012, 30 (10): 499- 511.
doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2012.06.004 |
| 7 | Daou I , Moukrad N , Zegaoui O , et al. Antimicrobial activity of ZnO-TiO2 nanomaterials synthesized from three different precursors of ZnO: Influence of ZnO/TiO2 weight ratio[J]. Water Sci Technol, 2018, 77 (5/6): 1238- 1249. |
| 8 |
Chen L , Guo Y , Hu C , et al. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota by chronic coexposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles and bisphenol A: Implications for host health in zebrafish[J]. Environ Pollut, 2018, 234, 307- 317.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.074 |
| 9 |
Chen Z , Han S , Zhou D , et al. Effects of oral exposure to tita-nium dioxide nanoparticles on gut microbiota and gut-associated metabolism in vivo[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11 (46): 22398- 22412.
doi: 10.1039/C9NR07580A |
| 10 |
Chen Z , Zhou D , Han S , et al. Hepatotoxicity and the role of the gut-liver axis in rats after oral administration of titanium dioxide nanoparticles[J]. Part Fibre Toxicol, 2019, 16 (1): 48.
doi: 10.1186/s12989-019-0332-2 |
| 11 |
Mu W , Wang Y , Huang C , et al. Effect of long-term intake of dietary titanium dioxide nanoparticles on intestine inflammation in mice[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2019, 67 (33): 9382- 9389.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b02391 |
| 12 |
Li J , Yang S , Lei R , et al. Oral administration of rutile and anatase TiO2 nanoparticles shifts mouse gut microbiota structure[J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10 (16): 7736- 7745.
doi: 10.1039/C8NR00386F |
| 13 | 刘倩, 姜建辉, 吴瑛. 纳米二氧化钛对果蝇肠道共生菌的影响[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2017, (9): 94- 97. |
| 14 |
Brodkorb A , Egger L , Alminger M , et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion[J]. Nat Protoc, 2019, 14 (4): 991- 1014.
doi: 10.1038/s41596-018-0119-1 |
| 15 |
Molly K , Woestyne MV , Verstraete W . Development of a 5-step multichamber reactor as a simulation of the human intestinal microbial ecosystem[J]. Appl Microbiol Biot, 1993, 39 (2): 254- 258.
doi: 10.1007/BF00228615 |
| 16 |
杨立娜, 黄靖航, 赵亚凡, 等. 胃肠道体外模拟系统在调控肠道菌群研究中的应用进展[J]. 渤海大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 39 (4): 320- 329.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0569.2018.04.007 |
| 17 |
Laird BD , van de Wiele TR , Corriveau MC , et al. Gastrointestinal microbes increase arsenic bioaccessibility of ingested mine tai-lings using the simulator of the human intestinal microbial ecosystem[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2007, 41 (15): 5542- 5547.
doi: 10.1021/es062410e |
| 18 | 叶峰, 王晓艳. 粪菌保存液及其保存粪菌的方法, CN105385599A[P/OL]. (2016-03-09)[2022-02-16]. https://pss-system.cponline.cnipa.gov.cn/documents/detail?prevPageTit=chagngui. |
| 19 |
Schiller C , Frohlich CP , Giessmann T , et al. Intestinal fluid vo-lumes and transit of dosage forms as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Aliment Pharm Ther, 2005, 22 (10): 971- 979.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02683.x |
| 20 |
Khan ST , Saleem S , Ahamed M , et al. Survival of probiotic bacteria in the presence of food grade nanoparticles from chocolates: An in vitro and in vivo study[J]. Appl Microbiol Biot, 2019, 103 (16): 6689- 6700.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09918-5 |
| 21 | Baranowska-Wójcik E, Szwajgier D, Gustaw K. Effect of TiO2 on selected pathogenic and opportunistic intestinal bacteria[J/OL]. Biol Trace Elem Res, (2021-07-23)[2021-12-08]. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02843-7. |
| 22 |
Lucas-González R , Viuda-Martos M , Pérez-Alvarez JA , et al. In vitro digestion models suitable for foods: Opportunities for new fields of application and challenges[J]. Food Research International, 2018, 107, 423- 436.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.02.055 |
| 23 | Dudefoi W , Moniz K , Allen-Vercoe E , et al. Impact of food grade and nano-TiO2 particles on a human intestinal community[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2017, 106 (Pt A): 242- 249. |
| 24 |
Gomaa EZ . Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and di-seases: A review[J]. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2020, 113 (12): 2019- 2040.
doi: 10.1007/s10482-020-01474-7 |
| 25 |
Nogueira CM , de Azevedo WM , Dagli ML , et al. Titanium dio-xide induced inflammation in the small intestine[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2012, 18 (34): 4729- 4735.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i34.4729 |
| 26 | 刘静. 纳米TiO2对肠上皮紧密连接蛋白Occludin和ZO-1的表达及相关细胞信号通道的影响[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2019. |
| 27 | 陈章健, 王云, 贾光. 纳米二氧化钛食品安全性研究进展[J]. 卫生研究, 2015, 44 (6): 1036- 1041. |
| [1] | 史佳琪,马莺,张奕,陈章健,贾光. 纳米二氧化钛颗粒对人肝癌细胞HepG2中circRNA表达谱的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 392-399. |
| [2] | 包文晗,唐雯. 初诊IgA肾病患者的肠道菌群及其与疾病进展因素的相关分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 124-132. |
| [3] | 陈章健,韩硕,郑湃,贾光. 锐钛矿型纳米二氧化钛经口暴露90天对Sprague-Dawley大鼠血常规指标的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1205-1208. |
| [4] | 王子靖,李在玲. 有幽门螺杆菌感染家族史儿童胃部菌群的特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1115-1121. |
| [5] | 周迪,陈章健,胡贵平,阎腾龙,龙昌茂,冯慧敏,贾光. 纳米二氧化钛亚急性经口暴露对大鼠氧化/抗氧化生物标志和炎性因子的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 821-827. |
| [6] | 韩硕,陈章健,周迪,郑湃,张家赫,贾光. 纳米二氧化钛经口暴露90天对大鼠粪便代谢组的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 457-463. |
| [7] | 陈章健,韩硕,郑湃,周淑佩,贾光. 纳米二氧化钛与葡萄糖亚慢性联合经口暴露对幼年大鼠血清叶酸和维生素B12水平的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 451-456. |
| [8] | 段淑敏,张永亮,王云. 纳米二氧化钛与脂多糖对小鼠肝脏抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(3): 395-400. |
| [9] | 张永亮,陈章健,陈实,卓琳,贾光,王云. 体外翻转肠囊法研究纳米二氧化钛对幼年大鼠小肠葡萄糖吸收的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(3): 376-382. |
| [10] | 耿良,范敬,高启龙,俞静,花宝金. 人参皂苷Rg3和PEG-PLGA-Rg3纳米微粒对Lewis肺癌小鼠的作用及其机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(3): 496-501. |
| [11] | 王云, 陈章健, 巴特, 濮吉, 崔枭醒, 贾光. 纳米二氧化钛对幼年和成年大鼠肝、肾组织抗氧化功能及元素含量的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(3): 395-399. |
| [12] | 秦宇, 邓芙蓉, 魏红英, 韩丽敏, 许珺辉, 郭新彪. 纳米银材料中可溶性银离子对皮肤细胞间隙连接通讯的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(03): 412-416. |
| [13] | 祁琨, 邓芙蓉, 郭新彪. 纳米二氧化钛颗粒对人肺成纤维细胞缝隙连接通讯的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009, 41(3): 297-301. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 195
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 904
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||