北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 458-467. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.03.010
基于长短期记忆网络和Logistic回归的重症监护病房脑卒中患者院内死亡风险预测
邓宇含1,姜勇2,3,王子尧1,刘爽1,汪雨欣1,刘宝花1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学公共卫生学院社会医学与健康教育学系,北京 100191
2. 国家神经系统疾病临床医学研究中心,首都医科大学附属北京天坛医院神经病学中心,北京 100050
3. 北京大数据精准医疗高精尖创新中心(北京航空航天大学&首都医科大学),北京 100070
Long short-term memory and Logistic regression for mortality risk prediction of intensive care unit patients with stroke
Yu-han DENG1,Yong JIANG2,3,Zi-yao WANG1,Shuang LIU1,Yu-xin WANG1,Bao-hua LIU1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Social Medicine and Health Education, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. China National Clinical Research Center for Neurological Diseases, Department of Neurology, Beijing Tian Tan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China
3. Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Big Data-Based Precision Medicine (Beihang University & Capital Medical University), Beijing 100070, China
摘要:
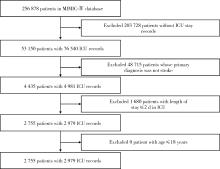
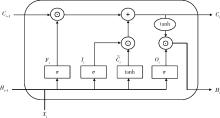
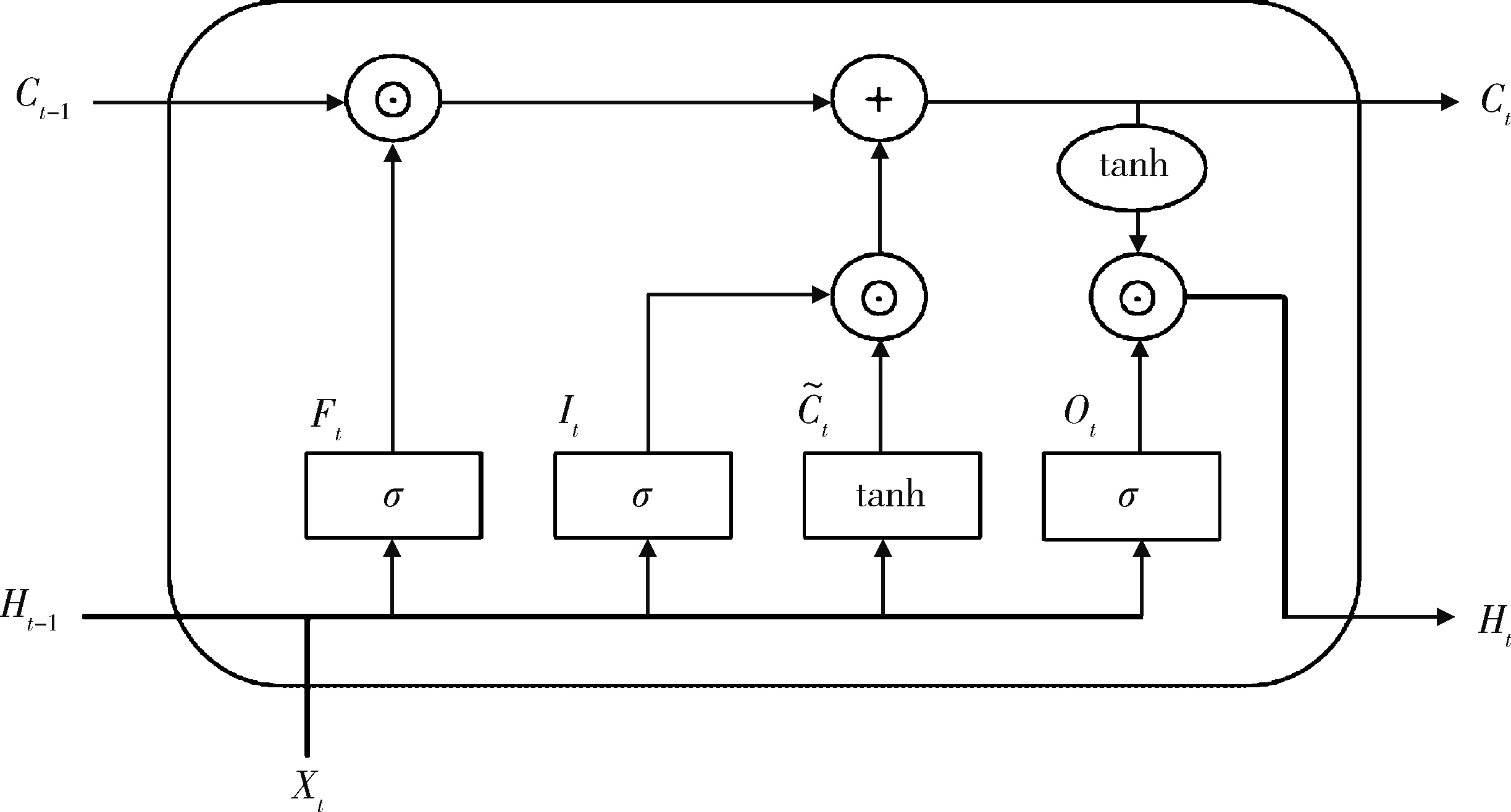
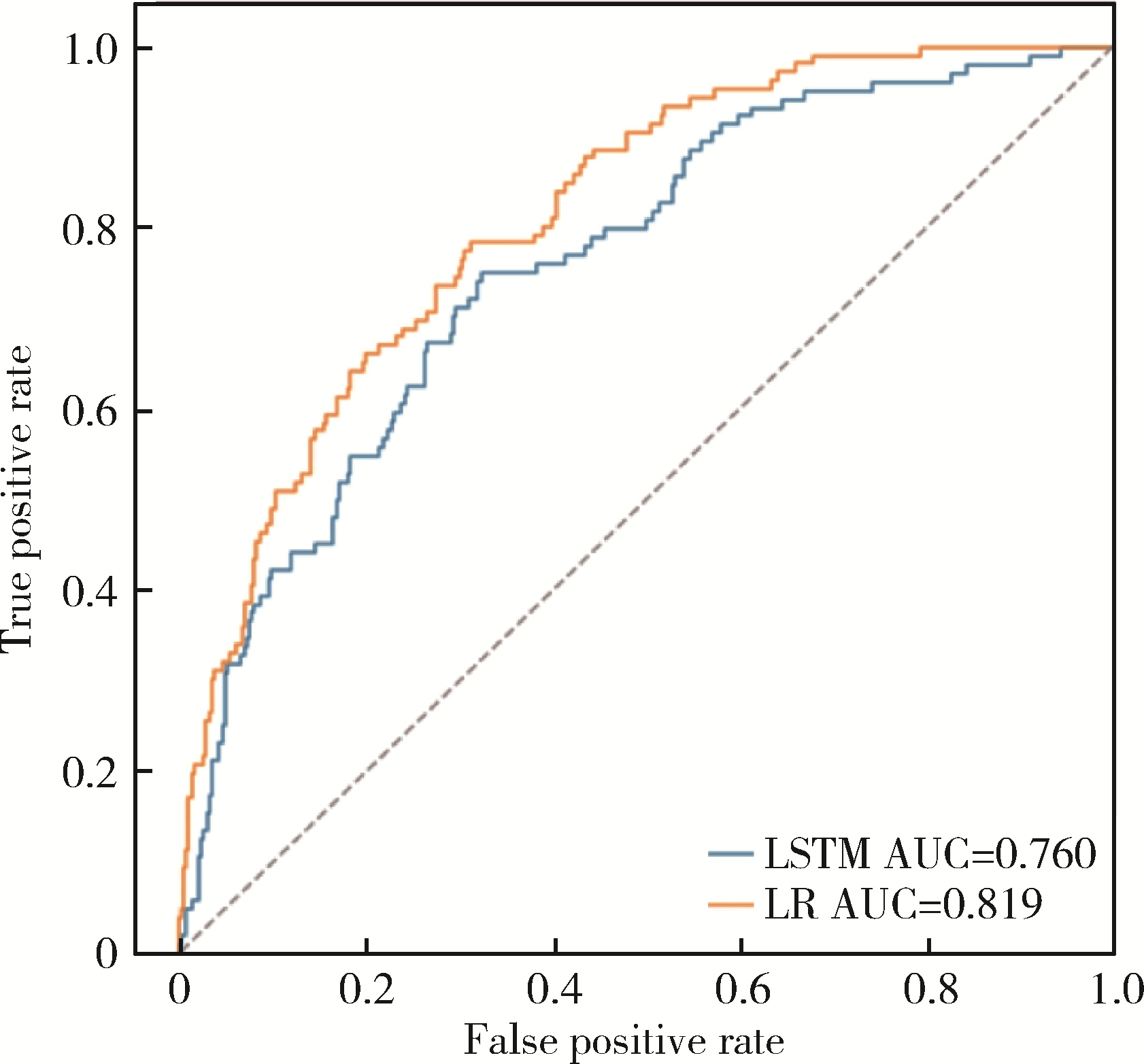
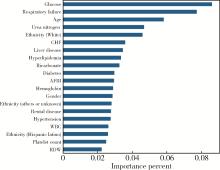
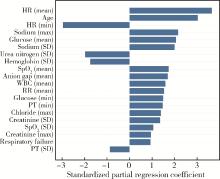
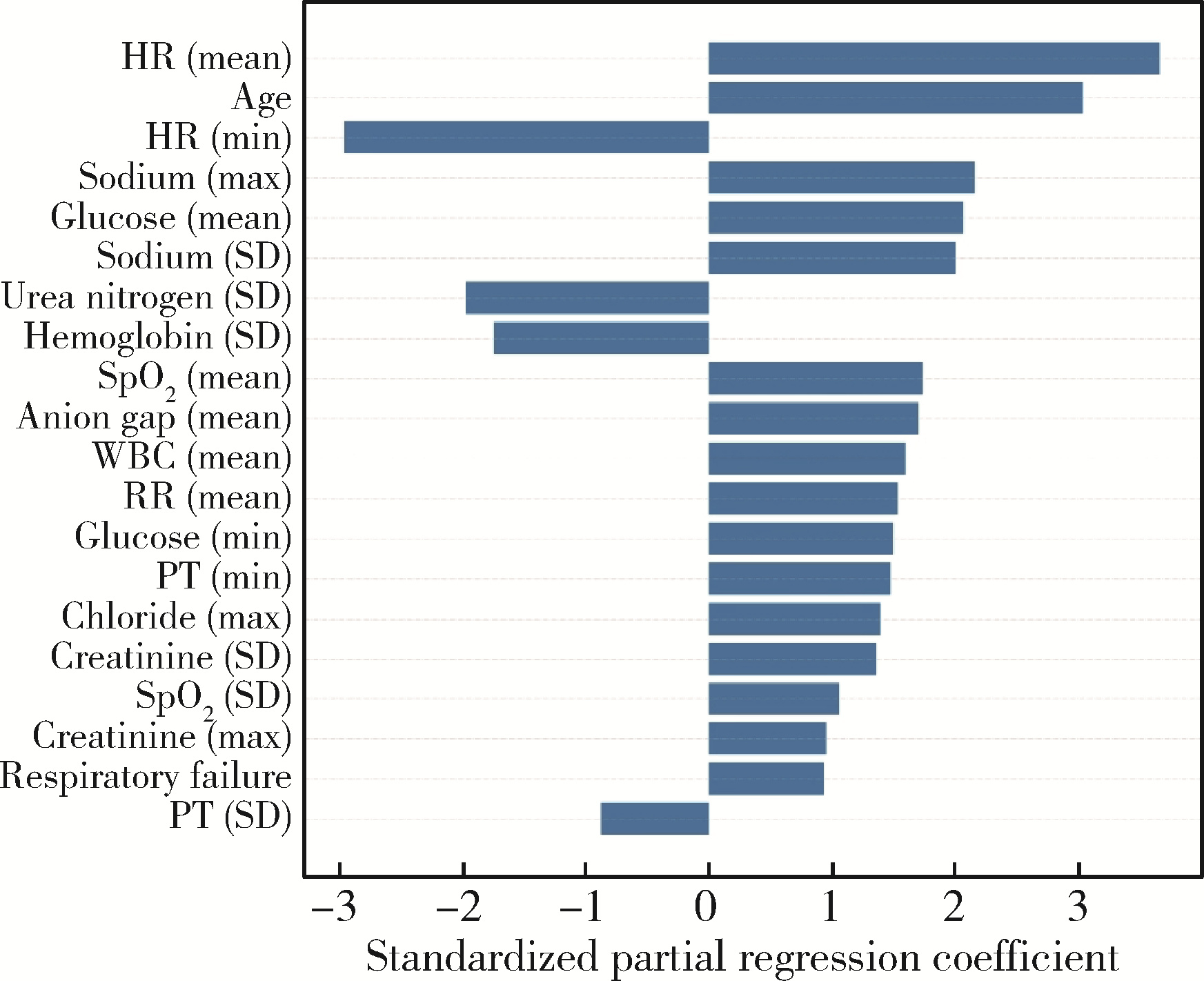
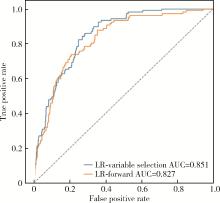
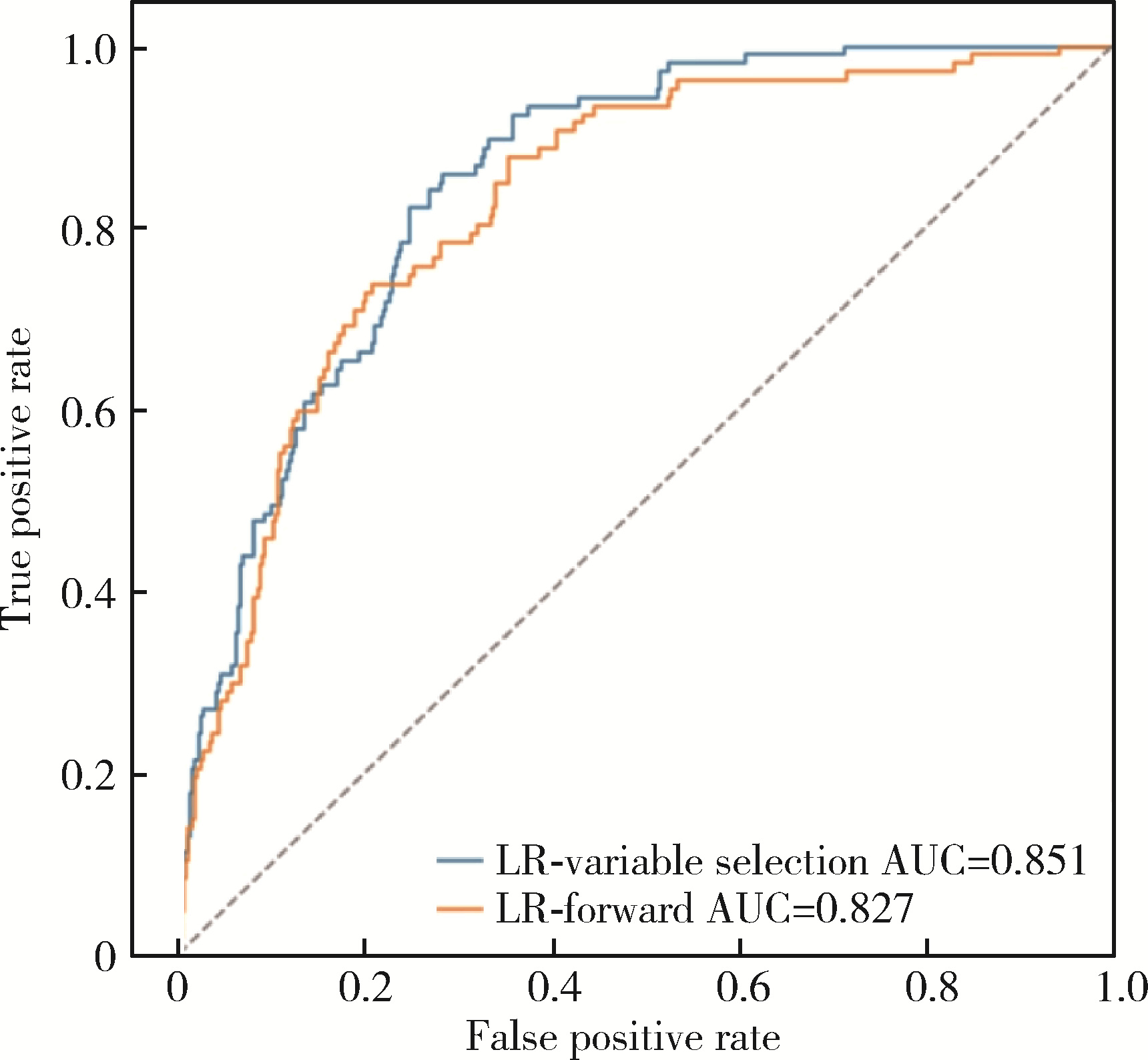
目的: 基于引入注意力机制的长短期记忆网络(long short-term memory,LSTM)和L1正则化的Logistic回归筛选变量,再通过传统的Logistic回归建立重症监护病房(intensive care unit,ICU)脑卒中患者院内死亡风险预测模型并评价模型效果。方法: 选取重症医学信息数据库(Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care-Ⅳ,MIMIC-Ⅳ)中的脑卒中患者作为研究对象,以是否发生院内死亡作为结局变量,备选预测因子包括人口学特征、合并症、入院48 h内实验室检查和生命体征检查等。将数据根据结局指标以8 ∶2的比例随机进行10次训练集和测试集的划分,在训练集上构建LSTM和L1正则化的Logistic回归模型,在测试集上选取重要程度排名前10的变量的并集纳入Logistic回归建立预测模型,以受试者工作特征曲线下面积(area under curve, AUC)、灵敏度、特异度、预测准确度为指标对模型进行评价,并与未预先进行变量筛选的前进法Logistic回归模型的预测效果进行比较。结果: 共纳入2 755例脑卒中患者的2 979条ICU入院记录,其中院内死亡记录占17.66%。两个变量筛选模型中,L1正则化的Logistic回归模型的AUC显著优于LSTM模型(0.819±0.031 vs. 0.760±0.018, P < 0.001),两个模型中重要程度均位于前10的变量包括年龄、血糖和尿素氮。最终预测模型的AUC为0.85,灵敏度为85.98%,特异度为71.74%,预测准确率为74.26%,优于未预先进行变量筛选的前进法Logistic回归模型。结论: 用引入注意力机制的LSTM和L1正则的Logistic回归筛选出的变量的预测效果较好,具有一定的临床价值。
中图分类号:
- R743.3
| 1 |
Katan M , Luft A . Global burden of stroke[J]. Semin Neurol, 2018, 38 (2): 208- 211.
doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1649503 |
| 2 |
Rochmah TN , Rahmawati IT , Dahlui M , et al. Economic burden of stroke disease: A systematic review[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021, 18 (14): 7552.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph18147552 |
| 3 |
Sarti C , Rastenyte D , Cepaitis Z , et al. International trends in mortality from stroke, 1968 to 1994[J]. Stroke, 2000, 31 (7): 1588- 1601.
doi: 10.1161/01.STR.31.7.1588 |
| 4 |
Handschu R , Haslbeck M , Hartmann A , et al. Mortality prediction in critical care for acute stroke: Severity of illness-score or coma-scale?[J]. J Neurol, 2005, 252 (10): 1249- 1254.
doi: 10.1007/s00415-005-0853-5 |
| 5 |
Ryan L , Lam C , Mataraso S , et al. Mortality prediction model for the triage of COVID-19, pneumonia, and mechanically ventilated ICU patients: A retrospective study[J]. Ann Med Surg (Lond), 2020, 59, 207- 216.
doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2020.09.044 |
| 6 |
Nemati S , Holder A , Razmi F , et al. An interpretable machine learning model for accurate prediction of sepsis in the ICU[J]. Crit Care Med, 2018, 46 (4): 547- 553.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002936 |
| 7 |
LeCun Y , Bengio Y , Hinton G . Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521 (7553): 436- 444.
doi: 10.1038/nature14539 |
| 8 |
Cheng JZ , Ni D , Chou YH , et al. Computer-aided diagnosis with deep learning architecture: Applications to breast lesions in US images and pulmonary nodules in CT scans[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6, 24454.
doi: 10.1038/srep24454 |
| 9 |
Kooi T , Litjens G , van Ginneken B , et al. Large scale deep learning for computer aided detection of mammographic lesions[J]. Med Image Anal, 2017, 35, 303- 312.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2016.07.007 |
| 10 | Choi E , Bahadori MT , Schuetz A , et al. Doctor AI: Predicting clinical events via recurrent neural networks[J]. JMLR Workshop Conf Proc, 2016, 56, 301- 318. |
| 11 |
Hochreiter S , Schmidhuber J . Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Comput, 1997, 9 (8): 1735- 1780.
doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 |
| 12 |
Thorsen-Meyer HC , Nielsen AB , Nielsen AP , et al. Dynamic and explainable machine learning prediction of mortality in patients in the intensive care unit: A retrospective study of high-frequency data in electronic patient records[J]. Lancet Digit Health, 2020, 2 (4): e179- e191.
doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30018-2 |
| 13 | Xia J , Pan S , Zhu M , et al. A long short-term memory ensemble approach for improving the outcome prediction in intensive care unit[J]. Comput Math Methods Med, 2019, 2019, 8152713. |
| 14 |
Maheshwari S , Agarwal A , Shukla A , et al. A comprehensive evaluation for the prediction of mortality in intensive care units with LSTM networks: Patients with cardiovascular disease[J]. Biomed Tech (Berl), 2020, 65 (4): 435- 446.
doi: 10.1515/bmt-2018-0206 |
| 15 |
Ho LV , Aczon M , Ledbetter D , et al. Interpreting a recurrent neural network's predictions of ICU mortality risk[J]. J Biomed Inform, 2021, 114, 103672.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2021.103672 |
| 16 | 王琦琦, 于石成, 亓晓, 等. Logistic族回归及其应用[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2019, 53 (9): 955- 960. |
| 17 |
Jhou HJ , Chen PH , Yang LY , et al. Plasma anion gap and risk of in-hospital mortality in patients with acute ischemic stroke: Analysis from the MIMIC-Ⅳ database[J]. J Pers Med, 2021, 11 (10): 1004.
doi: 10.3390/jpm11101004 |
| 18 |
Zhao N , Hu W , Wu Z , et al. The red blood cell distribution width-albumin ratio: A promising predictor of mortality in stroke patients[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2021, 14, 3737- 3747.
doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S322441 |
| 19 | 邱锡鹏. 神经网络与深度学习[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2020: 141- 145. |
| 20 |
Kaji DA , Zech JR , Kim JS , et al. An attention based deep lear-ning model of clinical events in the intensive care unit[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14 (2): e0211057.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211057 |
| 21 |
Lopez Bernal J , Soumerai S , Gasparrini A . A methodological framework for model selection in interrupted time series studies[J]. J Clin Epidemiol, 2018, 103, 82- 91.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.05.026 |
| 22 |
Yu Y , Si X , Hu C , et al. A review of recurrent neural networks: LSTM cells and network architectures[J]. Neural Comput, 2019, 31 (7): 1235- 1270.
doi: 10.1162/neco_a_01199 |
| 23 |
Gandin I , Scagnetto A , Romani S , et al. Interpretability of time-series deep learning models: A study in cardiovascular patients admitted to intensive care unit[J]. J Biomed Inform, 2021, 121, 103876.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2021.103876 |
| 24 |
Weimar C , Ziegler A , Konig IR , et al. Predicting functional outcome and survival after acute ischemic stroke[J]. J Neurol, 2002, 249 (7): 888- 895.
doi: 10.1007/s00415-002-0755-8 |
| 25 | Koyama T , Uchiyama Y , Domen K . Outcome in stroke patients is associated with age and fractional anisotropy in the cerebral peduncles: A multivariate regression study[J]. Prog Rehabil Med, 2020, 5, 20200006. |
| 26 |
Duarte E , Marco E , Muniesa JM , et al. Early detection of non-ambulatory survivors six months after stroke[J]. NeuroRehabilitation, 2010, 26 (4): 317- 323.
doi: 10.3233/NRE-2010-0568 |
| 27 |
Fuentes B , Castillo J , San Jose B , et al. The prognostic value of capillary glucose levels in acute stroke[J]. Stroke, 2009, 40 (2): 562- 568.
doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.519926 |
| 28 |
Baird TA , Parsons MW , Phanh T , et al. Persistent poststroke hyperglycemia is independently associated with infarct expansion and worse clinical outcome[J]. Stroke, 2003, 34 (9): 2208- 2214.
doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000085087.41330.FF |
| 29 |
Förstermann U , Münzel T . Endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular disease: From marvel to menace[J]. Circulation, 2006, 113 (13): 1708- 1714.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.602532 |
| 30 |
Virley D , Hadingham SJ , Roberts JC , et al. A new primate model of focal stroke: Endothelin-1-induced middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion in the common marmoset[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2004, 24 (1): 24- 41.
doi: 10.1097/01.WCB.0000095801.98378.4A |
| 31 |
Martini SR , Kent TA . Hyperglycemia in acute ischemic stroke: A vascular perspective[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2007, 27 (3): 435- 451.
doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600355 |
| 32 |
You S , Zheng D , Zhong C , et al. Prognostic significance of blood urea nitrogen in acute ischemic stroke[J]. Circ J, 2018, 82 (2): 572- 578.
doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-17-0485 |
| 33 |
Cheng J , Sun J , Yao K , et al. A variable selection method based on mutual information and variance inflation factor[J]. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc, 2022, 268, 120652.
doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.120652 |
| 34 | Ge W , Huh JW , Park YR , et al. An interpretable ICU mortality prediction model based on Logistic regression and recurrent neural networks with LSTM units[J]. AMIA Annu Symp Proc, 2018, 2018, 460- 469. |
| 35 |
Koppe G , Meyer-Lindenberg A , Durstewitz D . Deep learning for small and big data in psychiatry[J]. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2021, 46 (1): 176- 190.
doi: 10.1038/s41386-020-0767-z |
| [1] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [2] | 颜野,李小龙,夏海缀,朱学华,张羽婷,张帆,刘可,刘承,马潞林. 前列腺癌根治术后远期膀胱过度活动症的危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 589-593. |
| [3] | 刘帅,刘磊,刘茁,张帆,马潞林,田晓军,侯小飞,王国良,赵磊,张树栋. 伴静脉癌栓的肾上腺皮质癌的临床治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [4] | 何海龙,李清,徐涛,张晓威. 构建显微精索手术治疗精索疼痛的术后疼痛缓解预测模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 646-655. |
| [5] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [6] | 周泽臻,邓绍晖,颜野,张帆,郝一昌,葛力源,张洪宪,王国良,张树栋. 非转移性T3a肾细胞癌患者3年肿瘤特异性生存期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [7] | 方杨毅,李强,黄志高,陆敏,洪锴,张树栋. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮肿瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [8] | 曾媛媛,谢云,陈道南,王瑞兰. 脓毒症患者发生正常甲状腺性病态综合征的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [9] | 苏俊琪,王晓颖,孙志强. 舌鳞状细胞癌根治性切除术后患者预后预测列线图的构建与验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 120-130. |
| [10] | 李建斌,吕梦娜,池强,彭一琳,刘鹏程,吴锐. 干燥综合征患者发生重症新型冠状病毒肺炎的早期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [11] | 刘欢锐,彭祥,李森林,苟欣. 基于HER-2相关基因构建风险模型用于膀胱癌生存预后评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [12] | 薛子璇,唐世英,邱敏,刘承,田晓军,陆敏,董靖晗,马潞林,张树栋. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [13] | 彭清,刘佳君,刘焱,尚华,唐果,韩雅欣,龙丽. Padua预测评分和血清白蛋白水平在评估风湿病住院患者静脉血栓栓塞中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 625-630. |
| [14] | 卢汉,张建运,杨榕,徐乐,李庆祥,郭玉兴,郭传瑸. 下颌牙龈鳞状细胞癌患者预后的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [15] | 于欢,杨若彤,王斯悦,吴俊慧,王梦莹,秦雪英,吴涛,陈大方,武轶群,胡永华. 2型糖尿病患者使用二甲双胍与缺血性脑卒中发病风险的队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 456-464. |
|
||