北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 727-734. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.016
敲减Blimp1基因表达对CCl4诱导的小鼠肝纤维化模型早期肝损伤的保护作用
秦秋实1, 李蕊2,3, 周妍希2,3, 张玥2,3, 韩铭2,3, 朱鏐娈1,2,3,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学地坛医院教学医院, 北京 100015
2. 首都医科大学附属北京地坛医院传染病研究所, 新发突发传染病研究北京市重点实验室, 北京 100015
3. 北京市感染性疾病研究中心, 北京 100015
Protective effect of knock-down the expression of Blimp1 gene on early liver injury in CCl4-induced mouse model of liver fibrosis
Qiushi QIN1, Rui LI2,3, Yanxi ZHOU2,3, Yue ZHANG2,3, Ming HAN2,3, Liuluan ZHU1,2,3,*( )
)
- 1. Peking University Ditan Teaching Hospital, Beijing 100015, China
2. Beijing Key Laboratory of Emerging Infectious Diseases, Institute of Infectious Diseases, Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100015, China
3. Beijing Institute of Infectious Diseases, Beijing 100015, China
摘要:
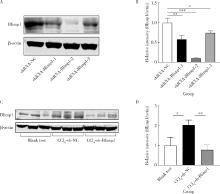
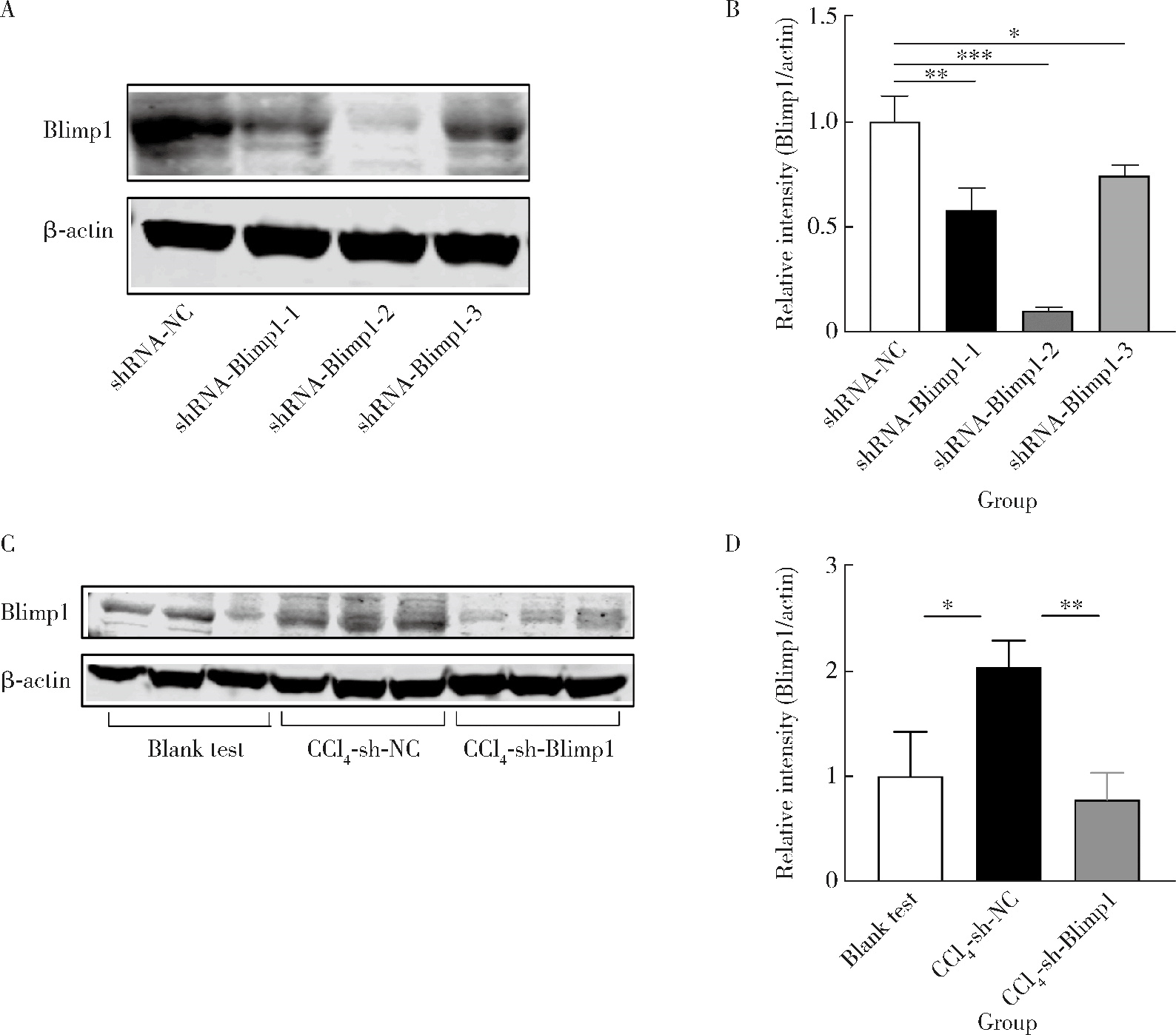
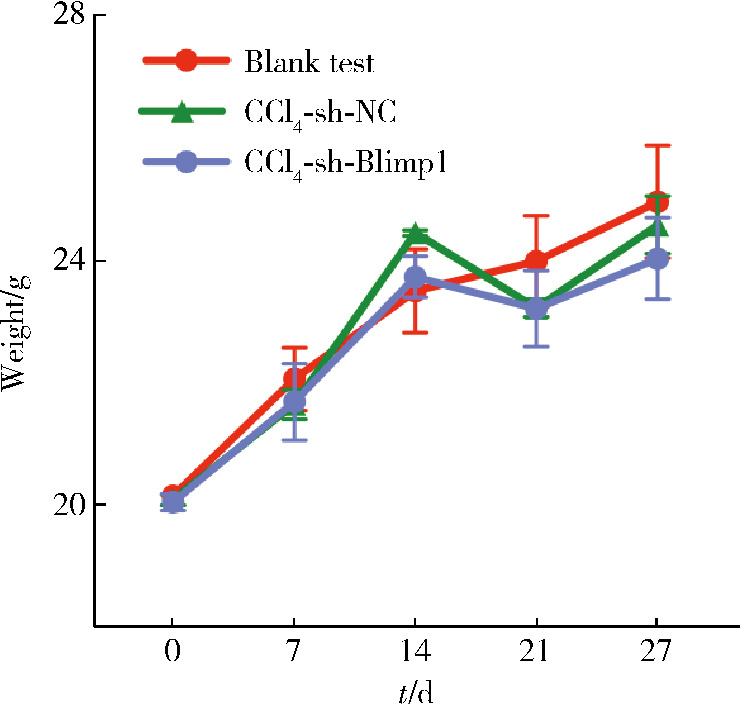
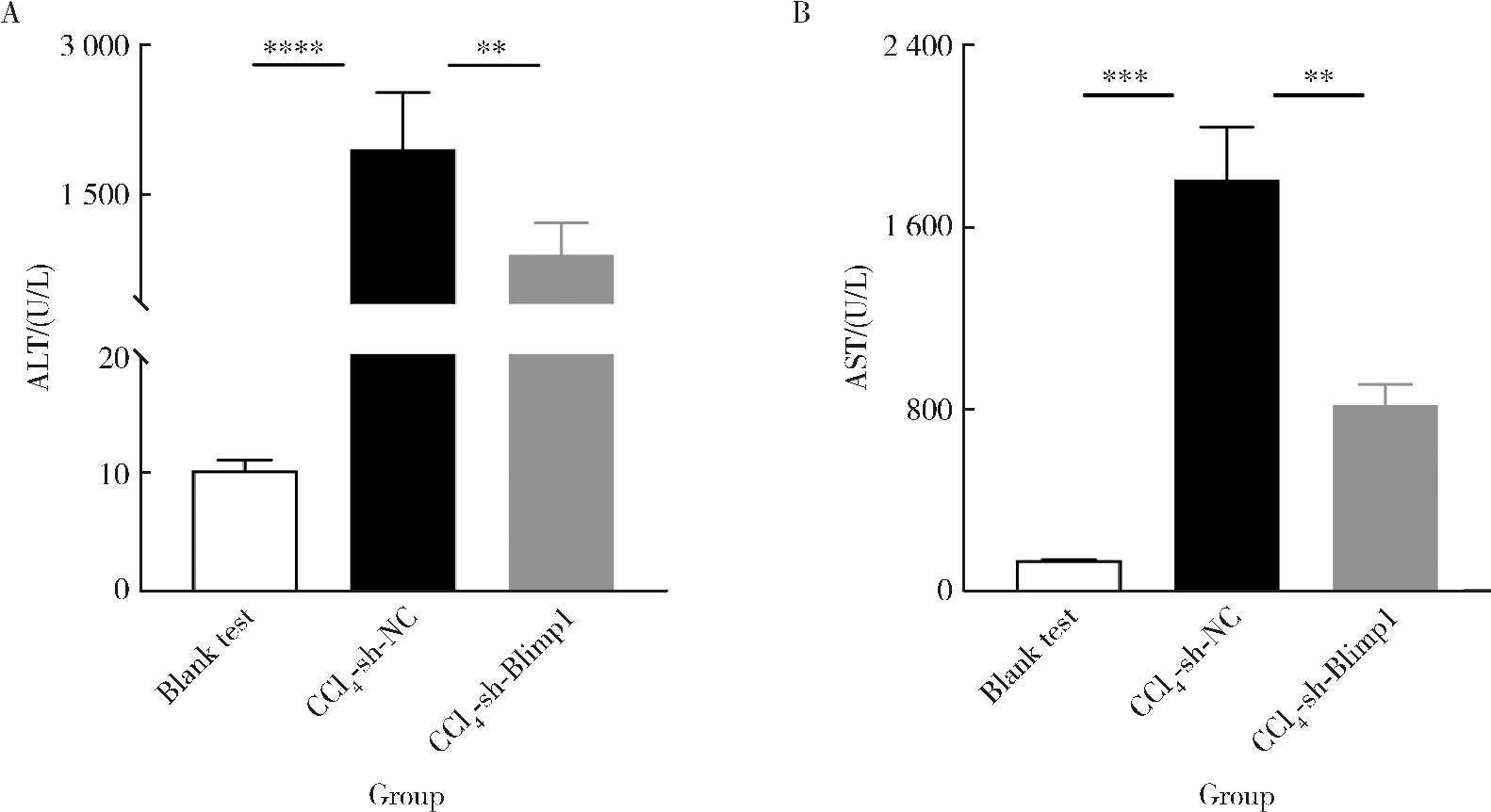
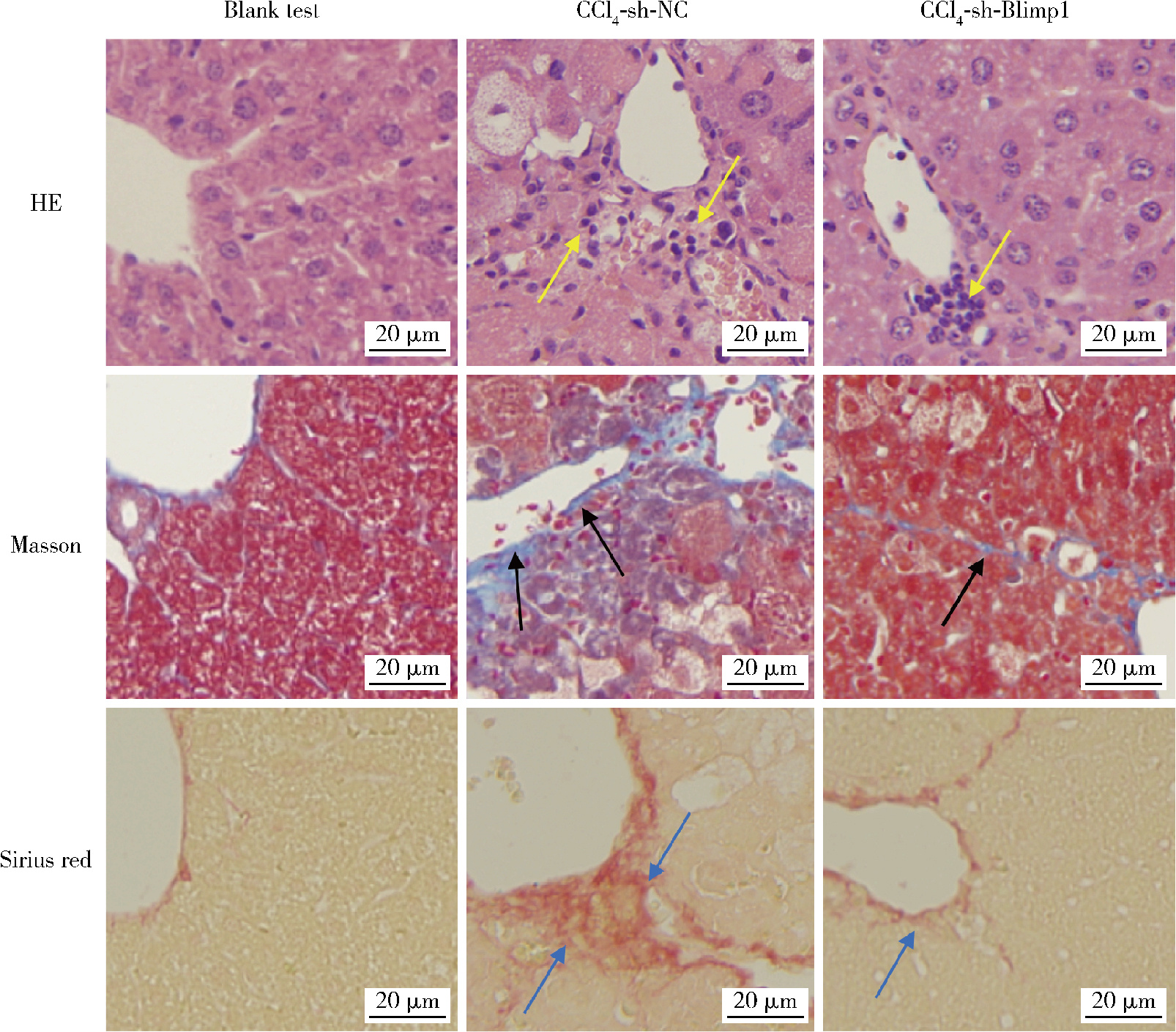
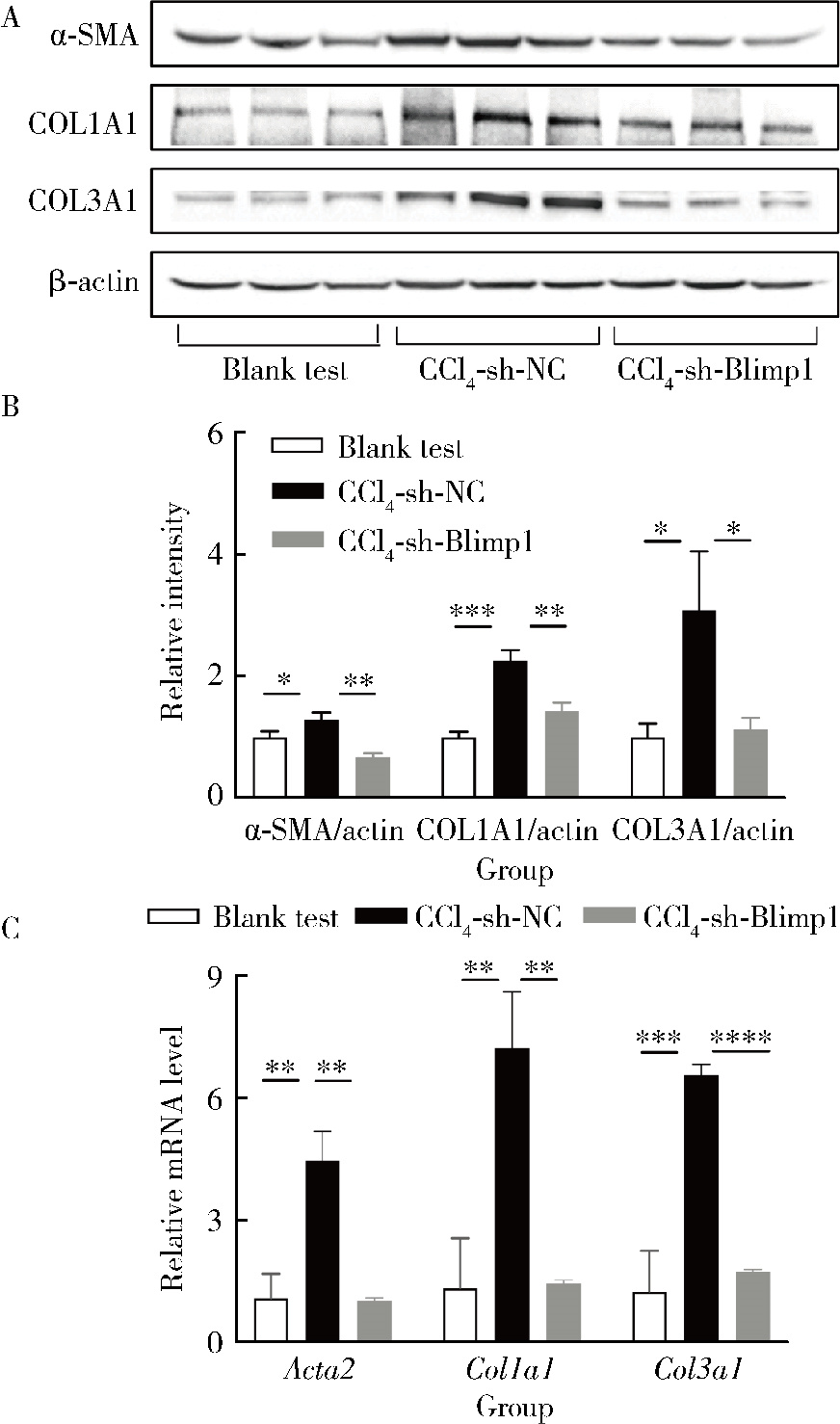
目的: 探讨敲减转录因子B淋巴细胞诱导成熟蛋白1(B lymphocyte induced maturation protein 1, Blimp1)基因对四氯化碳(carbon tetrachloride, CCl4)诱导的小鼠肝纤维化模型早期肝损伤的保护作用。方法: 采用C57BL/6小鼠腹腔注射5%(体积分数)CCl4橄榄油溶液制备肝纤维化小鼠模型,采用小鼠腹腔注射短发夹RNA (short hairpin RNA, shRNA)腺相关病毒(adeno-associated virus, AAV)敲减Blimp1基因表达。将小鼠随机分为3组,空白实验组(n=10),无意义RNA对照组(n=10)和Blimp1敲减组(n=10)。CCl4诱导的小鼠肝纤维化模型制备27 d后取材,通过Western blot和real-time PCR检测小鼠肝组织Blimp1蛋白、α平滑肌肌动蛋白(α-smooth muscle actin, α-SMA)、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白(collagen type Ⅰ alpha 1, COL1A1)、Ⅲ型胶原蛋白(collagen type Ⅲ alpha 1, COL3A1)及其mRNA表达水平;测定各组小鼠血清中天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶(aspartate transaminase, AST)、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(alanine transaminase, ALT)水平;采用苏木素-伊红染色、Masson染色和天狼星红染色法鉴定小鼠肝组织的病理变化及肝纤维化程度。结果: 与空白实验组相比,无意义RNA对照组小鼠肝脏Blimp1蛋白表达水平显著升高(2.036±0.244, t=3.690, P=0.002),Blimp1敲减组小鼠Blimp1蛋白表达降低至基础水平(0.783±0.249, t=6.223, P=0.003)。与无意义RNA对照组小鼠血清ALT [(1 957.8±633.6) U/L]和AST [(1 808.8±260.1) U/L]相比,Blimp1敲减组小鼠血清ALT [(894.0±360.1) U/L, t=3.998, P=0.003]和AST [(820.0±100.6) U/L, t=6.141, P=0.004]水平均显著降低,肝组织炎性细胞浸润减少、纤维化程度减轻,肝脏α-SMA(0.676±0.064, t=7.930, P=0.001)、COL1A1(1.426±0.143, t=6.364, P=0.003)、COL3A1(1.124±0.198, t=3.440, P=0.026)蛋白表达水平降低,且mRNA表达与蛋白水平变化一致。结论: Blimp1在CCl4诱导的小鼠肝纤维化中发挥重要作用,敲减Blimp1表达有利于保护小鼠的早期肝损伤。
中图分类号:
- R575.2
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| [1] | 柯涵炜, 王起, 许克新. 优化环磷酰胺剂量在间质性膀胱炎/膀胱疼痛综合征啮齿动物模型中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 908-912. |
| [2] | 王磊,金香淑,董慧君,欧国敏,赖鑫源,庄辉,李彤,向宽辉. 基于COL1A1启动子和增强型绿色荧光蛋白基因建立人肝星状细胞活化的细胞模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 876-885. |
| [3] | 孟令玮,李雪,高胜寒,李悦,曹瑞涛,张毅,潘韶霞. 三种方法建立大鼠种植体周炎模型的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 22-29. |
| [4] | 梁秀睿,闪雪纯,关晶,张锐,杨静,张怡,金佳琦,张誉馨,徐凡,傅继华. 高血糖诱导肝星状细胞5-羟色胺降解在2型糖尿病致肝脏炎症和纤维化时的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1141-1150. |
| [5] | 朱琳,张维宇,许克新. 环磷酰胺诱导SD大鼠膀胱疼痛综合征模型的有效性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 735-740. |
| [6] | 王贵红,左婷,李然,左正才. 瑞巴派特在大鼠痛风性关节炎急性发作中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 716-720. |
| [7] | 胡卫国, 王晓峰, 徐涛, 李建兴, 陈亮, 于澄钒, 黄晓波. 纳米细菌大鼠肾结石模型初步建立及成石因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010, 42(4): 433-435. |
| [8] | 邱永祥, 阮明, 贾凤兰, 邱飞婵, 李雪婷, 尚兰琴, 张宝旭. 金属硫蛋白对秋水仙碱致肝毒性的保护作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2005, 37(5): 558-559. |
| [9] | 于洁, 张芳婷, 万汇涓, 叶静, 龙霞, 房家智. 体外模拟肝损伤环境下人脐血细胞向类肝细胞的转化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2005, 37(4): 402-405. |
|
||