北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 18-23. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.01.003
Zeste同源蛋白2增强子通过调节巨噬细胞趋化影响牙髓炎症反应
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,儿童口腔科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 affects dental pulp inflammation by regulating macrophage chemotaxis
Ying-yi CHEN,Zi-qi HU,Tian-qian HUI( ),He LIU(
),He LIU( )
)
- Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
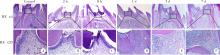
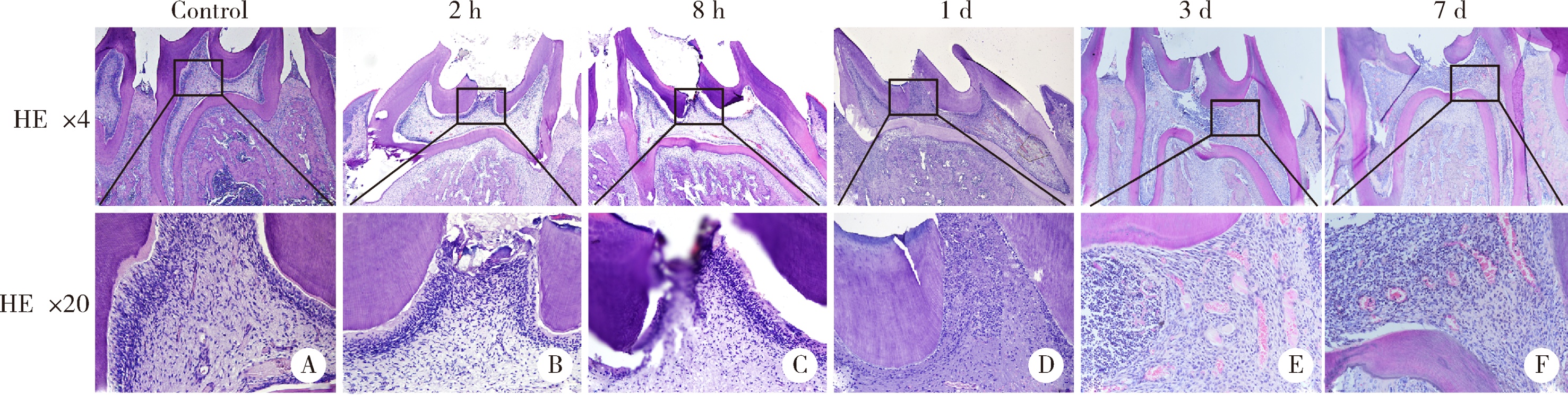
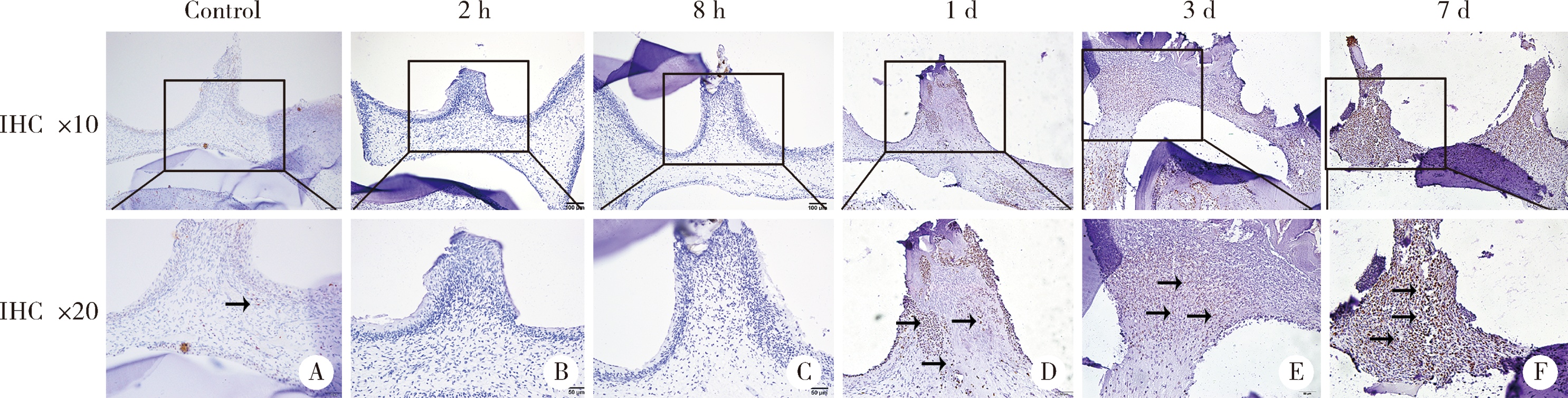
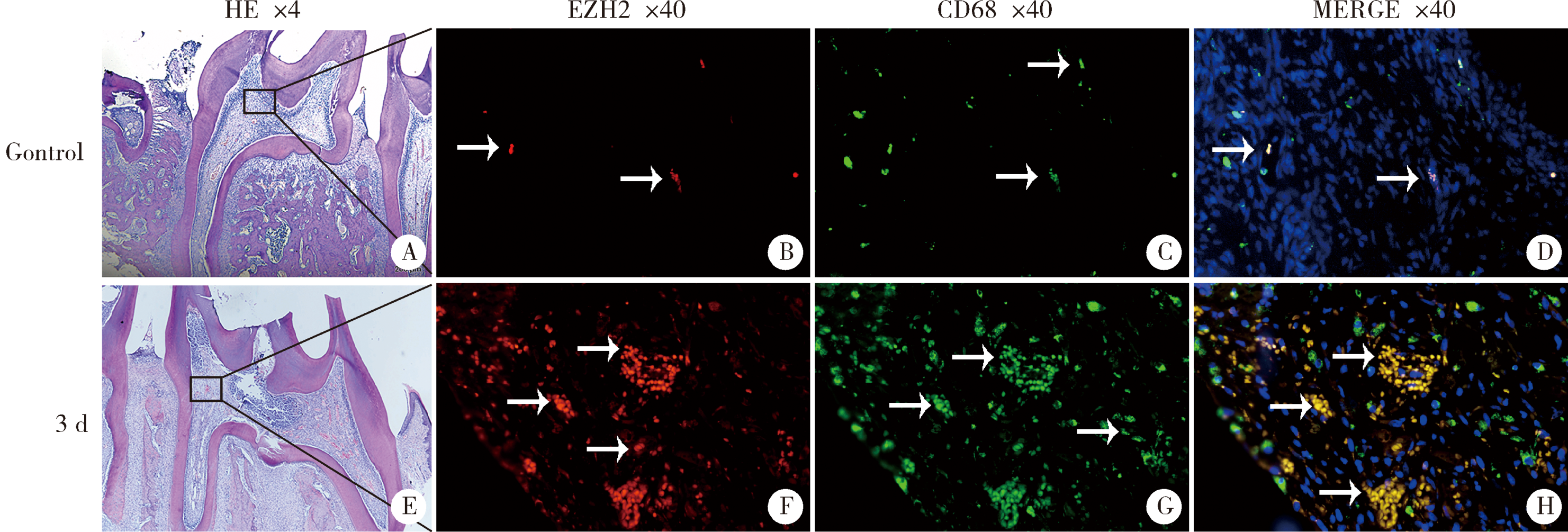
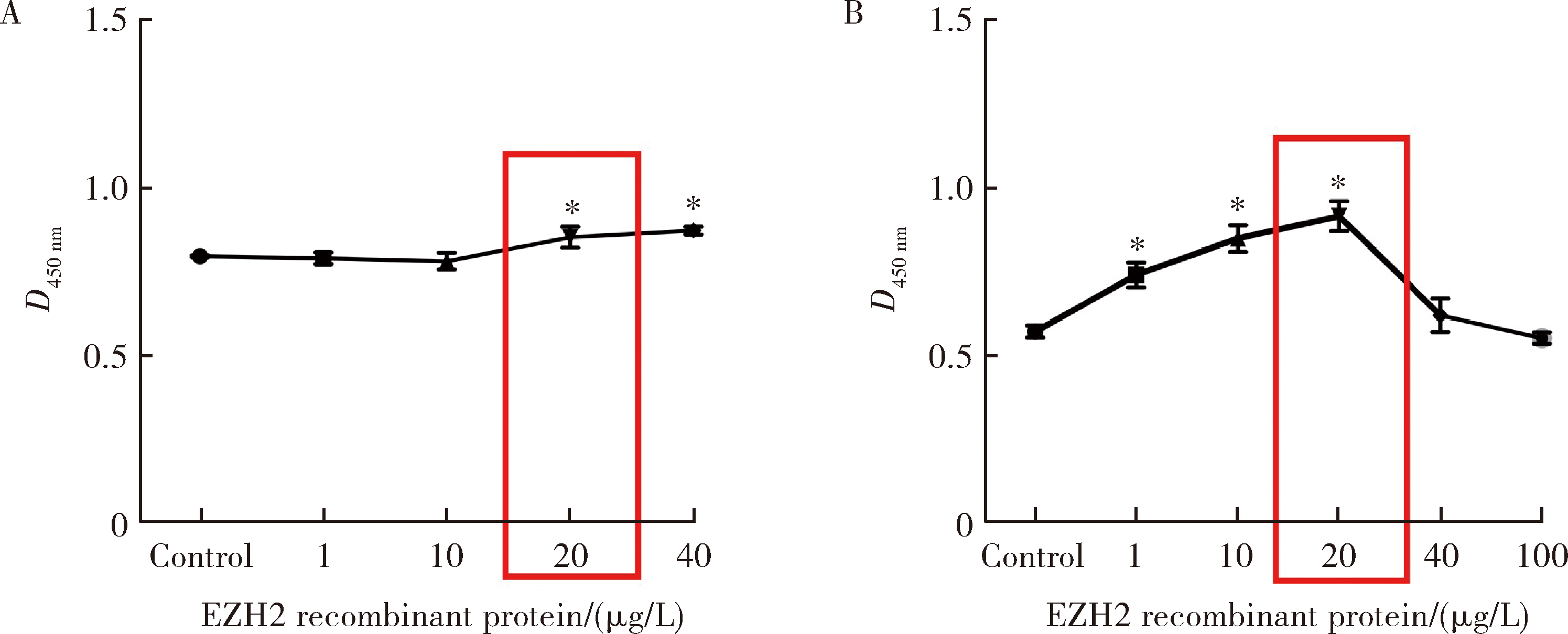
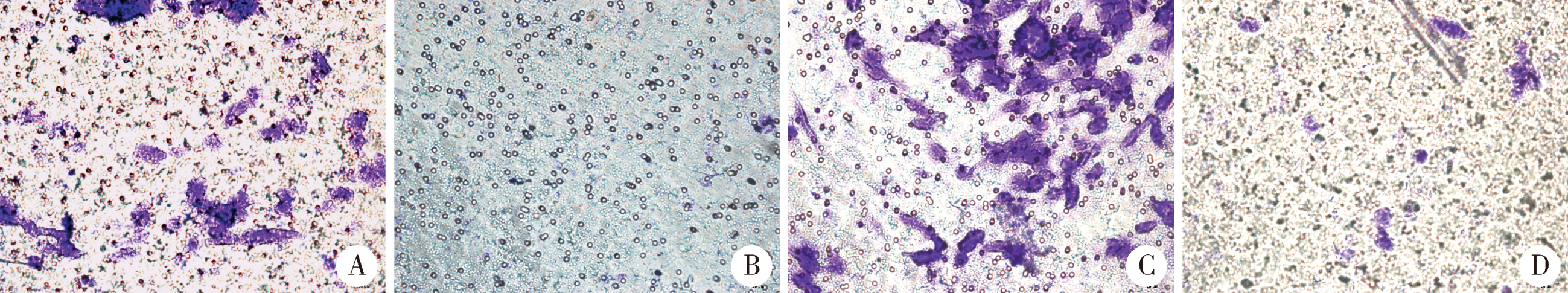
目的:探讨表观遗传调控子zeste同源蛋白2增强子(enhancer of zeste homolog 2,EZH2)在牙髓炎过程中的表达变化及其对巨噬细胞的趋化作用。方法:以10 g/L脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide,LPS)刺激大鼠牙髓,建立大鼠牙髓炎模型。采用免疫组织化学染色检测牙髓炎进展过程中EZH2的表达变化,采用免疫荧光双染法检测EZH2与CD68的表达及两者的共定位,利用CCK-8细胞增殖-毒性试剂盒检测不同浓度(1、10、20、40、100 μg/L)EZH2重组蛋白对人牙髓细胞(human dental pulp cells,hDPCs)及人白血病单核细胞系(human leukaemia-derived monocytic cell line,THP-1)细胞增殖的影响,从而筛选出EZH2重组蛋白刺激hDPCs及THP-1细胞的适宜浓度。采用Transwell迁移实验检测EZH2重组蛋白处理的hDPCs上清液对THP-1细胞迁移作用的影响。结果:HE染色结果表明,在LPS诱导的大鼠牙髓炎模型中,随着LPS刺激时间延长,牙髓炎症反应逐步加重。免疫组织化学结果显示,在LPS诱导牙髓炎8 h内,EZH2表达下降,但在刺激 1、3、7 d后,EZH2表达随刺激时间延长逐步上调。与对照组相比,LPS刺激大鼠牙髓3 d时EZH2与CD68表达显著升高,并且可以检测到两者在巨噬细胞中的共表达。CCK-8结果提示,EZH2重组蛋白刺激hDPCs及THP-1细胞的适宜浓度为20 μg/L。与对照组上清液相比,加入EZH2重组蛋白刺激hDPCs后的上清液可以显著促进巨噬细胞趋化。结论:EZH2参与了牙髓炎发展过程,并促进巨噬细胞的趋化,提示EZH2在牙髓炎发展过程中有重要调控作用。
中图分类号:
- R781.31
| [1] | Aas JA, Griffen AL, Dardis SR , et al. Bacteria of dental caries in primary and permanent teeth in children and young adults[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2008,46(4):1407-1417. |
| [2] | Tokuda M, Sakuta T, Fushuku A , et al. Regulation of interleukin-6 expression in human dental pulp cell cultures stimulated with Prevotella intermedia lipopolysaccharide[J]. J Endod, 2001,27(4):273-277. |
| [3] | Goldberg M, Farges JC, Lacerda-Pinheiro S , et al. Inflammatory and immunological aspects of dental pulp repair[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2008,58(2):137-147. |
| [4] | Zhao Y, Wang CL, Li RM , et al. Wnt5a promotes inflammatory responses via nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways in human dental pulp cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2014,289(30):21028-21039. |
| [5] | Hui T, A P, Zhao Y , et al. EZH2 regulates dental pulp inflammation by direct effect on inflammatory factors[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2018,85(1):16-22. |
| [6] | Li B, Yu F, Wu F , et al. EZH2 Impairs human dental pulp cell mineralization via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. J Dent Res, 2018,97(5):571-579. |
| [7] | Feinberg AP . Phenotypic plasticity and the epigenetics of human disease[J]. Nature, 2007,447(7143):433-440. |
| [8] | Calvanese V, Lara E, Kahn A , et al. The role of epigenetics in aging and age-related diseases[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2009,8(4):268-276. |
| [9] | Bayarsaihan D . Epigenetic mechanisms in inflammation[J]. J Dent Res, 2011,90(1):9-17. |
| [10] | Deng P, Chen QM, Hong C , et al. Histone methyltransferases and demethylases: regulators in balancing osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Int J Oral Sci, 2015,7(4):197-204. |
| [11] | Hui T, A P, Zhao Y , et al. EZH2, a potential regulator of dental pulp inflammation and regeneration[J]. J Endod, 2014,40(8):1132-1138. |
| [12] | Hoang M, Kim JJ, Kim Y , et al. Alcohol-induced suppression of KDM6B dysregulates the mineralization potential in dental pulp stem cells[J]. Stem Cell Res, 2016,17(1):111-121. |
| [13] | Yadav R, Weng HR . EZH2 regulates spinal neuroinflammation in rats with neuropathic pain[J]. Neuroscience, 2017,349(5):106-117. |
| [14] | Arifuzzaman S, Das A, Kim SH , et al. Selective inhibition of EZH2 by a small molecule inhibitor regulates microglial gene expression essential for inflammation[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2017,137(8):61-80. |
| [15] | Liu Y, Peng J, Sun T , et al. Epithelial EZH2 serves as an epigenetic determinant in experimental colitis by inhibiting TNFα-mediated inflammation and apoptosis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2017,114(19):E3796-E3805. |
| [16] | Wu H, He M, Yang R , et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 participates in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in dental pulp cells via NF-kappaB signalling pathway[J]. Int Endod J, 2018,51(10):1130-1138. |
| [17] | Renard E, Gaudin A, Bienvenu G , et al. Immune cells and molecular networks in experimentally induced pulpitis[J]. J Dent Res, 2016,95(2):196-205. |
| [18] | 吴晓恋, 张盛丹, 魏亚娟 , 等. 热休克蛋白27及热休克因子1在牙髓炎中的表达研究[J]. 牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2017,27(1):7-11. |
| [19] | Adrian JC, Bernier JL, Sprague WG . Laser and the dental pulp[J]. J Am Dent Assoc, 1971,83(1):113-117. |
| [20] | 王勤, 张成飞, 林琼光 , 等. 脉冲Nd:YAG激光照射牙本质对牙髓的影响[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 1996,10(1):20-22. |
| [21] | Cleaton-Jones P, Duggal M, Parak R , et al. Pulpitis induction in baboon primary teeth using carious dentine or Streptococcus mutans[J]. SADJ, 2004,59(3):119-122. |
| [22] | Gunawan M, Venkatesan N, Loh JT , et al. The methyltransferase Ezh2 controls cell adhesion and migration through direct methylation of the extranuclear regulatory protein talin[J]. Nat Immunol, 2015,16(5):505-516. |
| [1] | 罗芷筠,吴佳佳,宋优,梅春丽,杜戎. 伴神经精神系统病变的系统性红斑狼疮相关巨噬细胞活化综合征2例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1111-1117. |
| [2] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [3] | 王爽,彭楚芳,刘鹤. 新型生物陶瓷材料用于乳磨牙牙髓切断术的临床疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1196-1201. |
| [4] | 邢晓燕,张筠肖,朱冯赟智,王一帆,周新尧,李玉慧. 皮肌炎合并巨噬细胞活化综合征5例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1214-1218. |
| [5] | 贾园,栗占国. 成人巨噬细胞活化综合征诊断困境和个体化治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 991-994. |
| [6] | 姚海红,王旖旎,张霞,赵金霞,贾园,王昭,栗占国. 67例成人巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特征及治疗转归[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 996-1002. |
| [7] | 王莹,李明慧,张岩,胡晓燕,马瑞霞. 狼疮性肾炎患者足细胞损伤与肾组织巨噬细胞浸润的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 723-727. |
| [8] | 赵彦瑞,刘洋,王东,吕文睿,周君琳. 二氧化硫对大鼠肢体缺血再灌注致急性肺损伤中肺泡巨噬细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 239-244. |
| [9] | 高翔,陈香梅,张婷,张静,陈茉,郭正阳,石岩岩,鲁凤民,丁士刚. 巨噬细胞加帽蛋白与胃癌细胞增殖及迁移能力的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(3): 489-494. |
| [10] | 凌龙,赵玉鸣,葛立宏. 不同炎症状态下犬年轻恒牙牙髓干细胞增殖及成骨分化能力的改变[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(5): 878-883. |
| [11] | 陈红涛, 王文英, 王津, 梁亚平, 王小婷, 侯光敏, 姬爱平. 不同高血压分级患者急性牙髓炎开髓治疗的风险评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(1): 89-93. |
| [12] | 余涛, 姜婷, 魏青梅, 李宜芬, David L. Kaplan. 丝蛋白复合骨形态发生蛋白2在大鼠炎性牙髓愈合中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(5): 814-819. |
| [13] | 赵曼曼, 张巧丽, 闫辉, 杜军保, 耿彬, 唐朝枢, 金红芳. H2S对氧化型低密度脂蛋白诱导人单核巨噬细胞核转录因子-κB的影响及机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(2): 192-. |
| [14] | 张效云, 李蓟龙, 董明纲, 高丽芬, 钟光明. 白介素-17 在沙眼衣原体呼吸道感染中的早期产生可提高局部白介素-6和巨噬细胞炎性蛋白-2的表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010, 42(5): 509-513. |
| [15] | 沈臻霖, 聂海瑜, 王海芳, 杨彬, 钟丽君, 邹霞娟, 娄雅欣, 刘丹, 郭健, 贾光. 表面不同修饰的两种多壁碳纳米管引起RAW264.7细胞蛋白质差异表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010, 42(3): 345-350. |
|
||