北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 58-63. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.01.009
植体周炎再生治疗短期疗效观察
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,牙周科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Short-term outcome of regenerative surgery treating peri-implantitis
Dong SHI,Jie CAO,Shi-ai DAI,Huan-xin MENG( )
)
- Department of Periodontology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
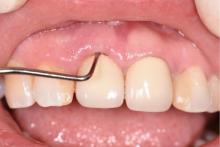
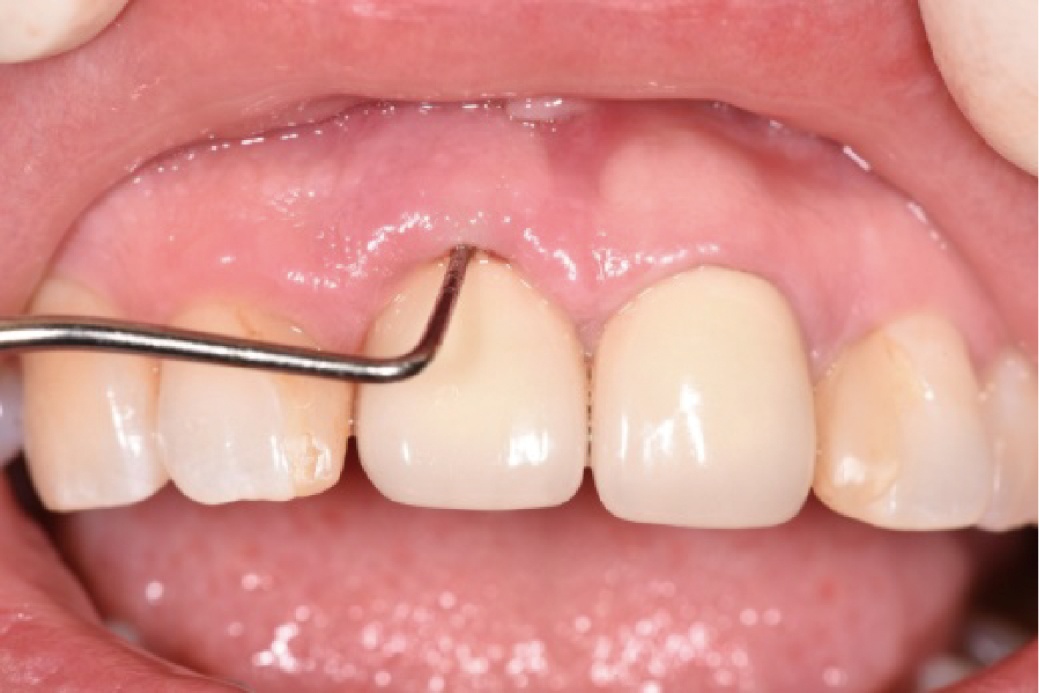
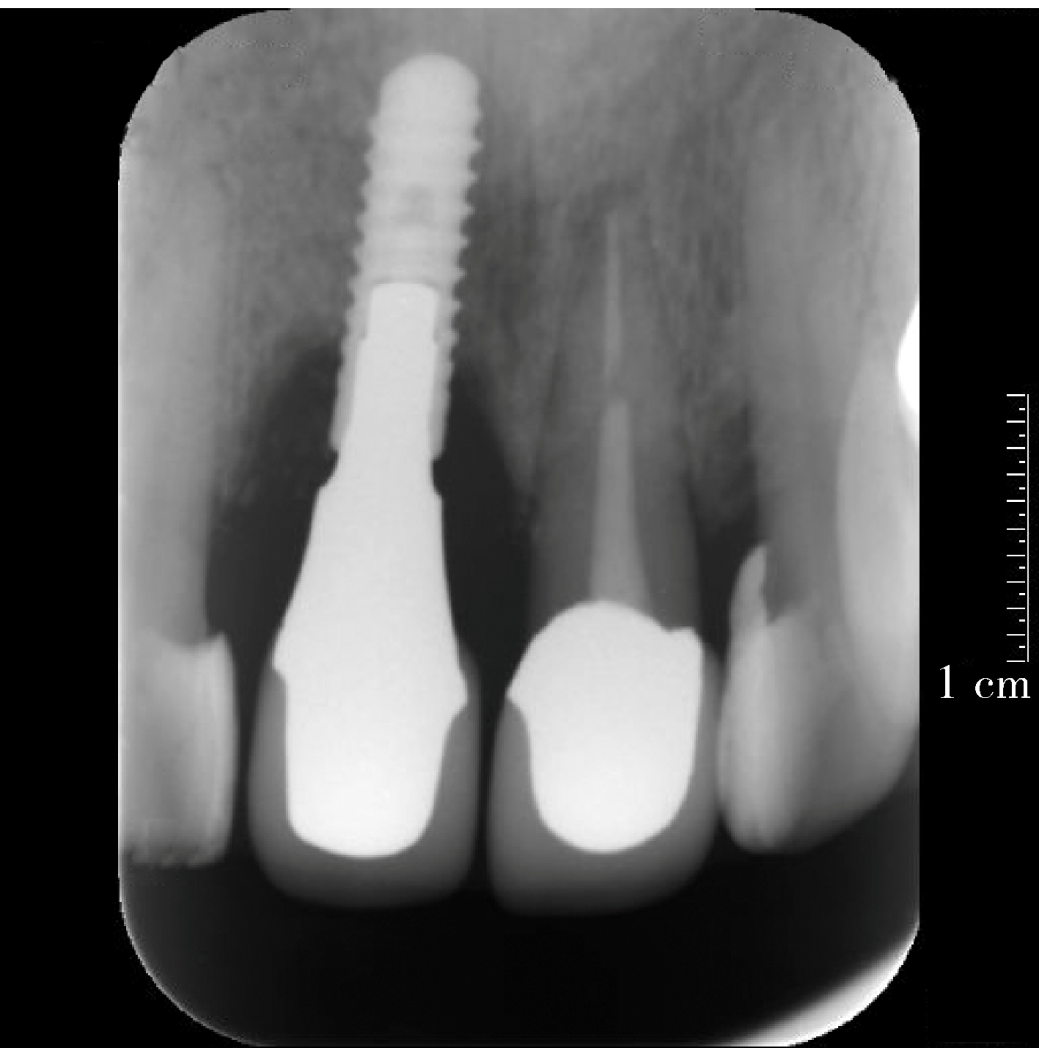
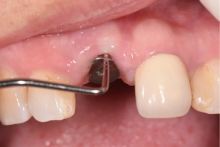
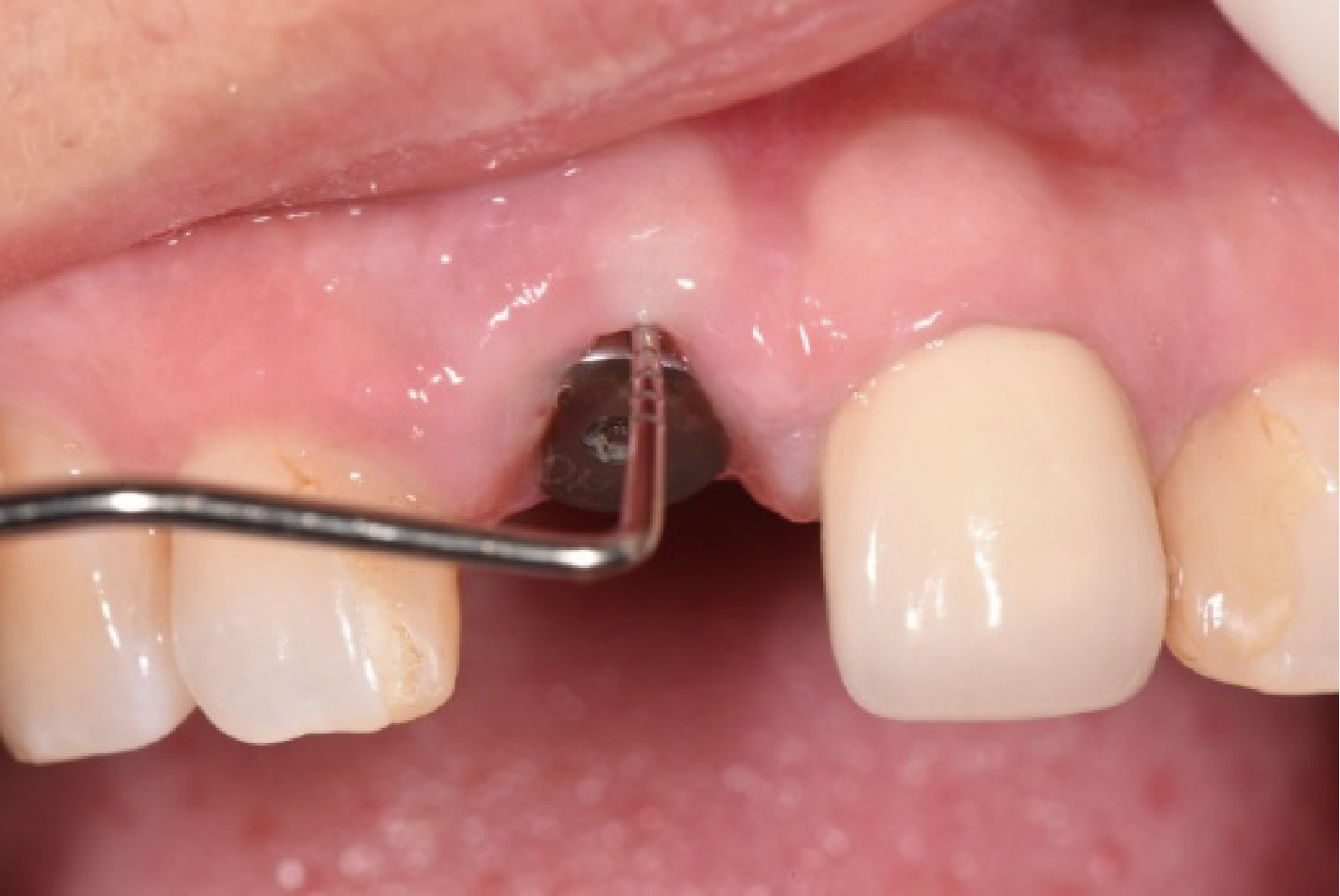
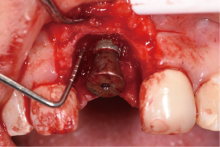
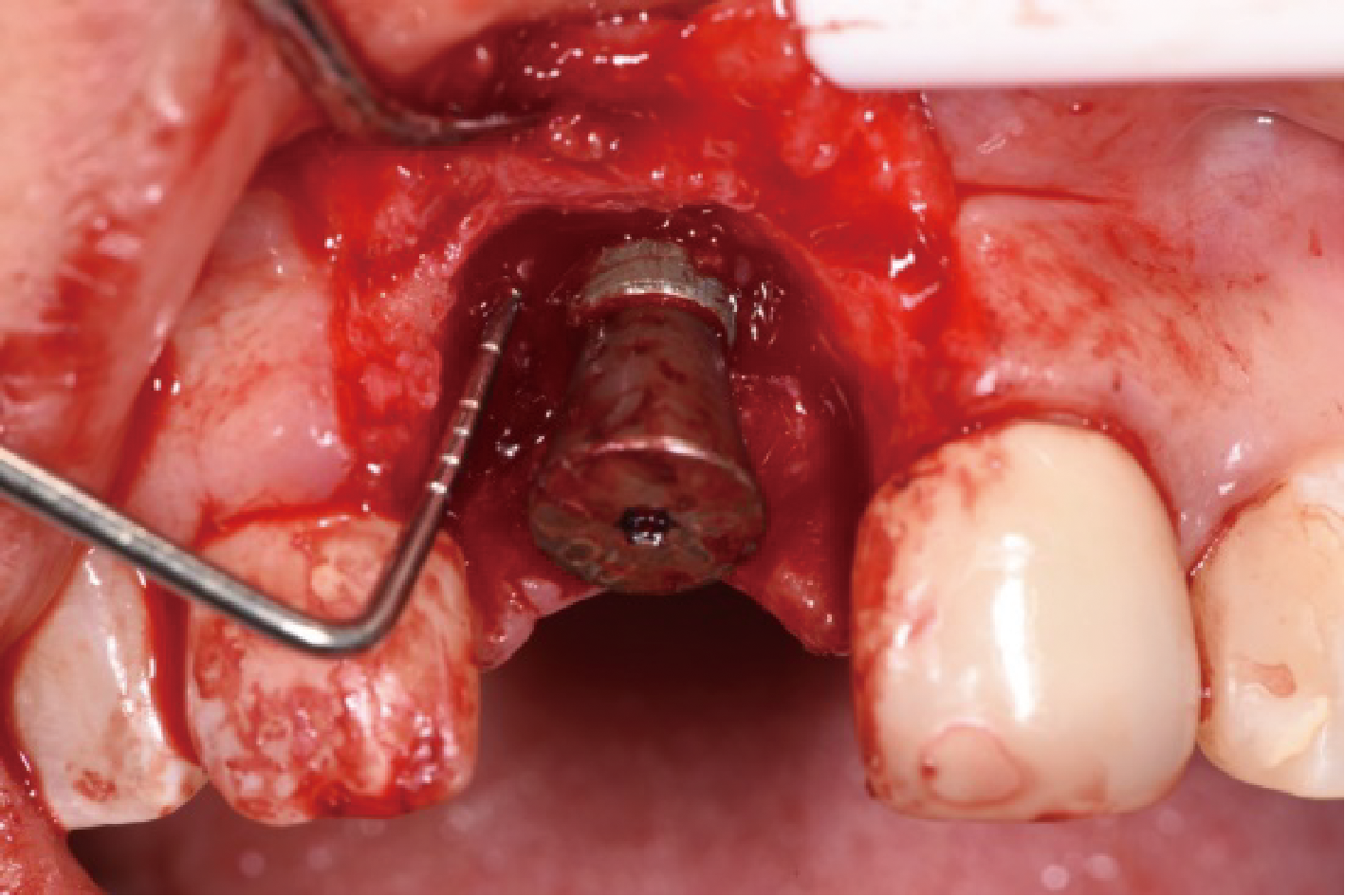
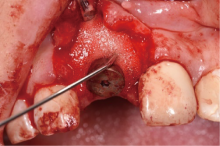
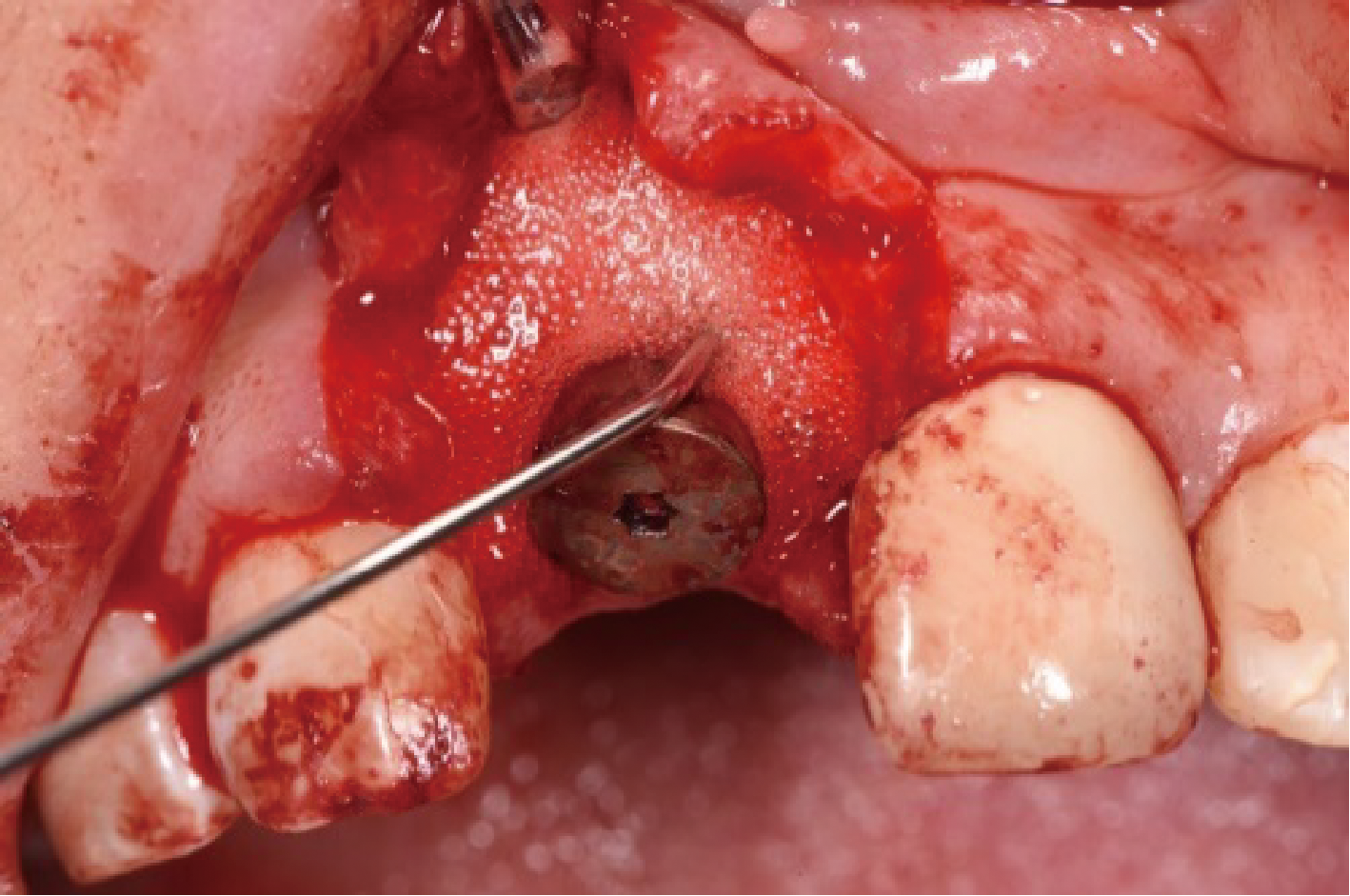
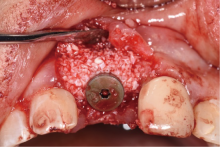
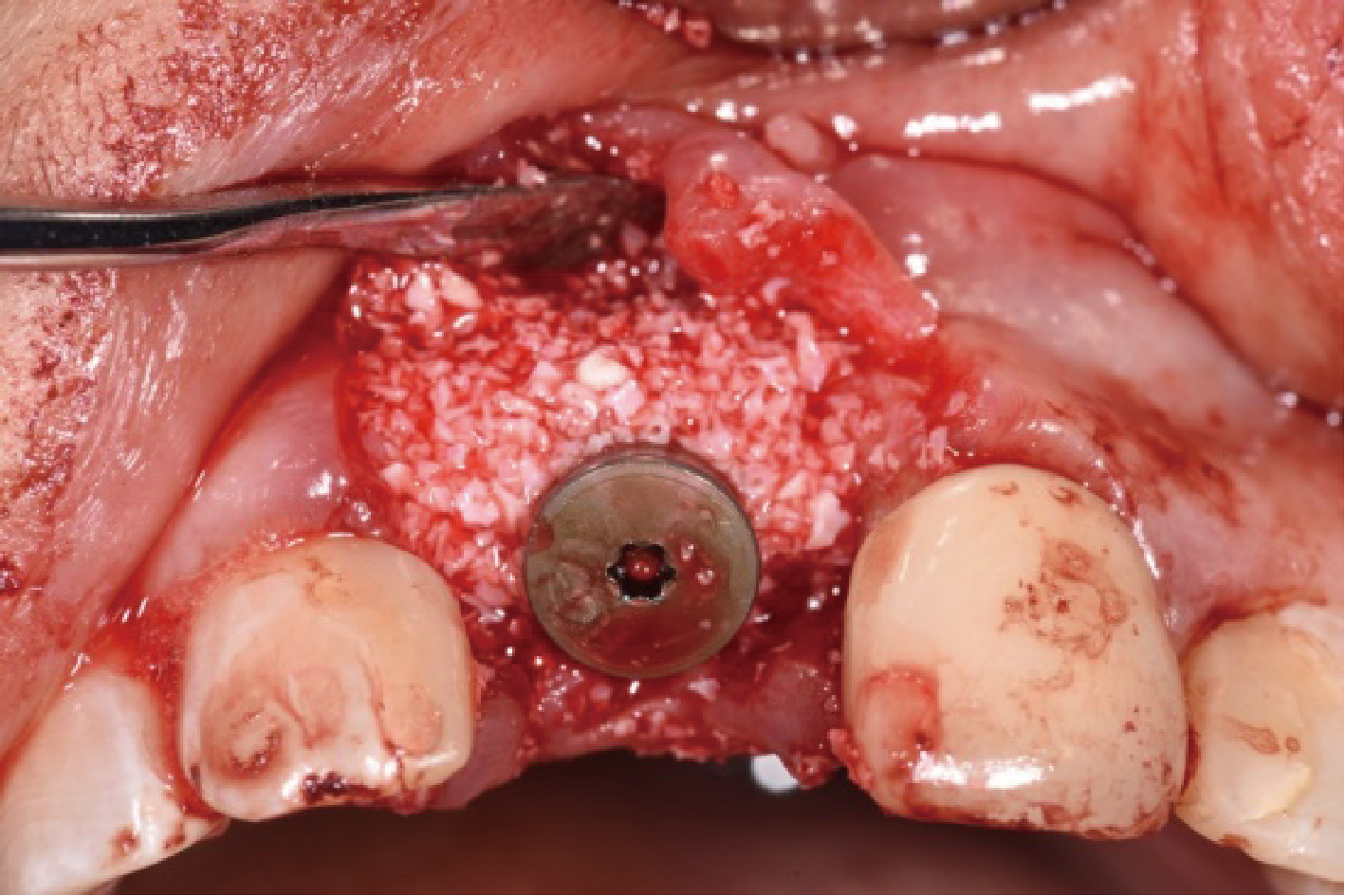
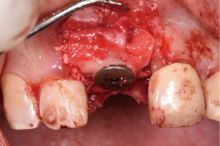
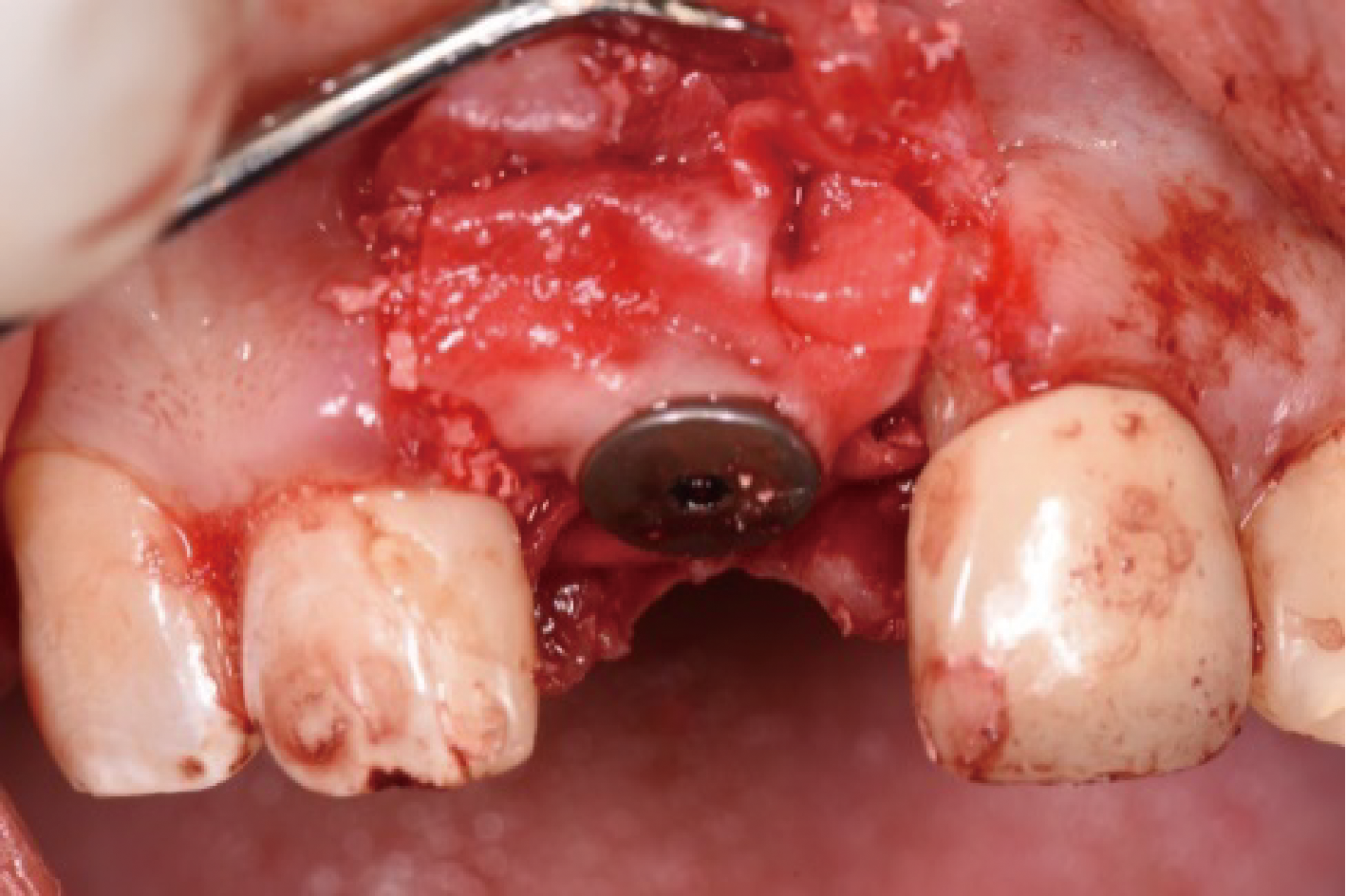
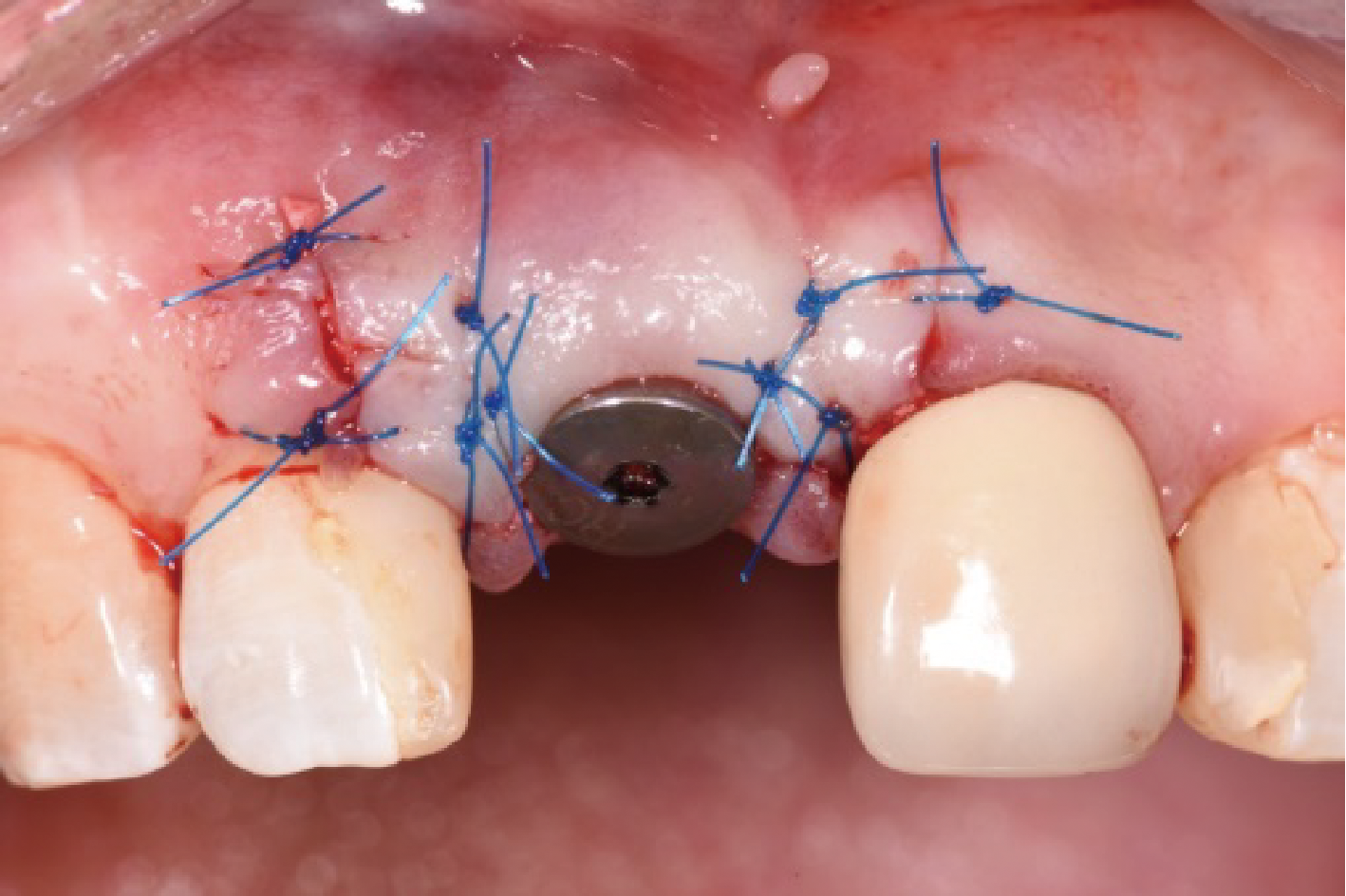
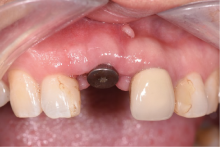
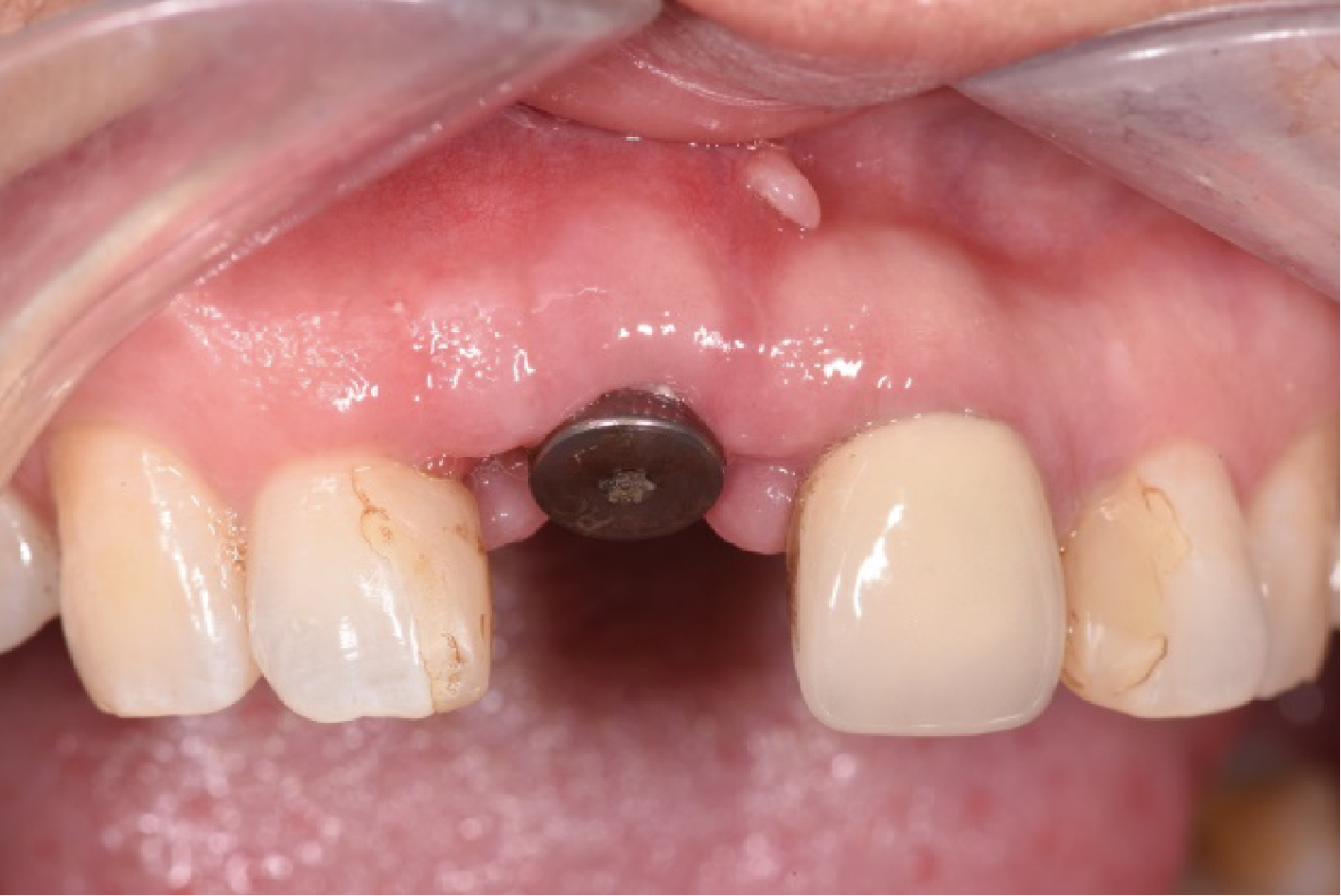
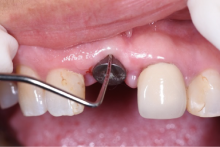
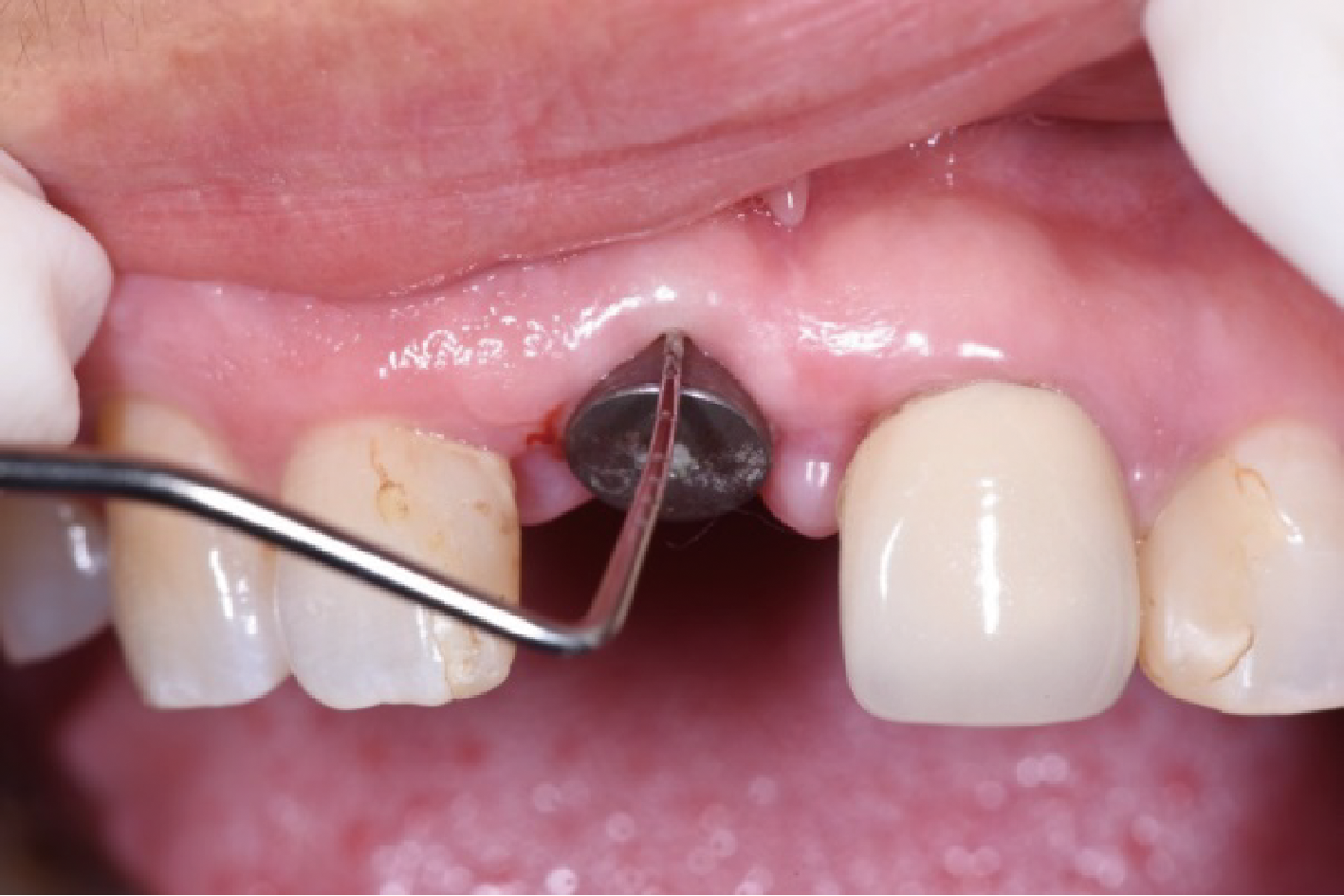
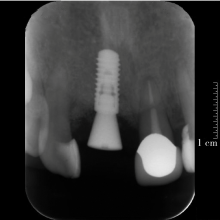
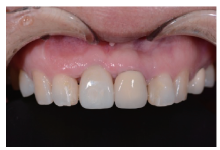
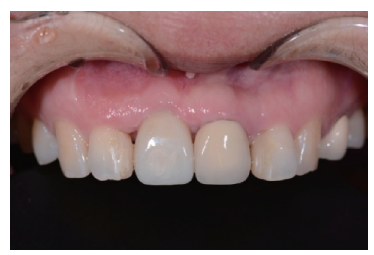
目的:评价植体周炎相关骨缺损进行再生性手术的短期疗效。方法:纳入2018年3月至2019年1月就诊的植体周炎患者9例,受累植体共计10枚,所有纳入植体经影像学检查均有3 mm以上垂直骨缺损,存留2个或以上骨壁,其中3枚植体因修复体存在缺陷,治疗前拆除修复体,更换为愈合基台。常规牙周及植体周非手术治疗后,进行植体周引导性骨再生手术,植体周翻瓣后进行机械清创,彻底清除炎症肉芽组织,用3%过氧化氢溶液充分擦洗植体表面,生理盐水冲洗后,骨缺损内植入骨替代材料,覆盖胶原屏障膜,采用非埋入愈合方式,术后追踪观察6个月,分别比较治疗前和术后6个月的植体周探诊深度(probing depth,PD,植体周袋底与黏膜边缘之间的距离)和骨水平(bone level, BL,植体周骨缺损最根方与植体颈部平台之间的距离)。结果:所有受累植体基线时最深PD范围6~10 mm,最大BL范围3.2~8.3 mm。相比基线水平, 术后6个月植体周平均PD从(6.2±1.4) mm降低为(3.1±0.6) mm, BL平均改善为(3.0±1.5) mm,治疗前后PD和BL的差异均有统计学意义,P<0.01。如果将术后6个月无PD≥6 mm位点及探诊出血,且实现1 mm以上骨高度增加作为再生治疗成功的标准,8例患者的9枚植体治疗成功,另有一枚植体因术后6个月PD仍达6 mm,且有明显探诊出血,未达到治疗成功标准。结论:引导性骨再生技术应用于植体周炎骨缺损的再生治疗,可获得较好的短期疗效,长期疗效有待继续观察。
中图分类号:
- R781.4
| [1] | Berglundh T, Armitage G, Araujo MG , et al. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions[J]. J Periodontol, 2018,89(Suppl 1):313-318. |
| [2] | Khoury F, Keeve PL, Ramanauskaite A , et al. Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: Consensus report of working group 4[J]. Int Dent J, 2019,69(Suppl 2):18-22. |
| [3] | Tomasi C, Regidor E, Ortiz-Vigón A , et al. Efficacy of reconstructive surgical therapy at peri-implantitis related bone defects. A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2019,46(Supppl 21):340-356. |
| [4] | Clem D, Gunsolley JC . Peri-implantitis treatment using Er:YAG laser and bone grafting. A prospective consecutive case series evaluation: 1 year post therapy[J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 2019,39(4):479-489. |
| [5] | de Tapia B, Valles C, Ribeiro-Amaral T , et al. The adjunctive effect of a titanium brush in implant surface decontamination at peri-implantitis surgical regenerative interventions: A randomized controlled clinical trial[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2019,46(5):586-596. |
| [6] | 释栋 . 种植体周围炎再生治疗五年观察一例[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2018,53(4):271-274. |
| [7] | Schwarz F, Herten M, Sager M , et al. Comparison of naturally occurring and ligature-induced peri-implantiti bone defects in humans and dogs[J]. Clin Oral Impl Res, 2007,18(2):167-170. |
| [8] | Renvert S, Persson GR, Pirih FQ , et al. Peri-implant health, peri-implant mucositis, and peri-implantitis: Case definitions and diagnostic considerations[J]. J Periodonto, 2018,89(Suppl 1):304-312. |
| [9] | Roos-Jansåker AM, Renvert H, Lindahl C , et al. Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis using a bone substitute with or without a resorbable membrane: A prospective cohort study[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2007,34:625-632. |
| [10] | Hämmerle CH, Fourmousis I, Winkler JR , et al. Successful bone fill in late peri-implant defects using guided tissue regeneration. A short communication[J]. J Periodontol, 1995,66(4):303-308. |
| [11] | Almohandes A, Carcuac O, Abrahamsson I , et al. Re-osseointegration following reconstructive surgical therapy of experimental peri-implantitis. A pre-clinical in vivo study[J]. Clin Oral Impl Res, 2019,30(5):447-456. |
| [12] | Roos-Jansåker AM, Renvert H, Lindahl C , et al. Submerged healing following surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: A case series[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2007,34:723-727. |
| [13] | Schwarz F, Sahm N, Schwarz K , et al. Impact of defect configuration on the clinical outcome following surgical regenerative therapy of peri-implantitis[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2010,37(5):449-455. |
| [14] | Schwarz F, Sahm N, Becker J . Combined surgical therapy of advanced peri-implantitis lesions with concomitant soft tissue volume augmentation. A case series[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2014,25(1):132-136. |
| [15] | Aghazadeh A, Rutger PG, Renvert S . A single-centre randomized controlled clinical trial on the adjunt treatment of intra-bony defects with autogenous bone or a xenograft: Results after 12 months[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2012,39(7):666-673. |
| [16] | Roccuzzo M, Pittoni D, Roccuzzo A , et al. Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis intrabony lesions by means of deproteinized bovine bone mineral with 10% collagen: 7-year-results[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2017,28(12):1577-1583. |
| [1] | 王聪伟,高敏,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 游离腓骨瓣修复下颌骨缺损术后义齿修复的临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
| [2] | 丁茜,李文锦,孙丰博,谷景华,林元华,张磊. 表面处理对氧化钇和氧化镁稳定的氧化锆种植体晶相及断裂强度的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 721-728. |
| [3] | 孟令玮,李雪,高胜寒,李悦,曹瑞涛,张毅,潘韶霞. 三种方法建立大鼠种植体周炎模型的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 22-29. |
| [4] | 孙菲,刘建,李思琪,危伊萍,胡文杰,王翠. 种植体黏膜下微生物在健康种植体和种植体周炎中的构成与差异:一项横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 30-37. |
| [5] | 孙菲,李思琪,危伊萍,钟金晟,王翠,胡文杰. 种植体周病非手术治疗中联合应用甘氨酸粉喷砂的临床效果评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 119-125. |
| [6] | 梁峰,吴敏节,邹立东. 后牙区单牙种植修复5年后的临床修复疗效观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 970-976. |
| [7] | 尤鹏越,刘玉华,王新知,王思雯,唐琳. 脱细胞猪心包膜生物相容性及成骨性能的体内外评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 776-784. |
| [8] | 王思雯,尤鹏越,刘玉华,王新知,唐琳,王梅. 两种可吸收生物膜联合去蛋白牛骨基质植入犬拔牙窝成骨的影像学评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 364-370. |
| [9] | 张众,孟焕新,韩劼,张立,释栋. 软组织垂直厚度对牙周炎患者种植修复临床效果的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 332-338. |
| [10] | 林春平,卢松鹤,朱浚鑫,胡洪成,岳兆国,唐志辉. 个性化根形种植体的螺纹形态对周围牙槽骨应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1130-1137. |
| [11] | 刘潇倩,陈秋雯,冯海兰,王兵,屈健,孙振,衡墨迪,潘韶霞. 无牙颌患者locator附着体种植覆盖义齿修复后口腔卫生维护的纵向研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 136-144. |
| [12] | 吴敏节,邹立东,梁峰. 上前牙即刻种植即刻修复负载3年后软、硬组织变化的临床观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 694-699. |
| [13] | 刘婧寅,陈飞,葛严军,魏菱,潘韶霞,冯海兰. 选择性激光熔化种植体对早期骨矿化沉积率的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 117-122. |
| [14] | 梁乃文,石磊,黄颖,邓旭亮. 不同形貌纯钛表面对人脐静脉内皮细胞生物学行为的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 43-048. |
| [15] | 李贝贝, 林野, 崔宏燕, 郝强, 胥加斌, 邸萍. 碳纤维增强“All-on-4”即刻修复体的临床评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(1): 133-137. |
|
||