北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 51-57. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.01.008
大鼠咬合干扰致口颌面痛敏的自我赏罚实验行为学特点
白珊珊1,2,莫思怡1,2,徐啸翔1,2,刘云1,2,谢秋菲1,2,△( ),曹烨1,2,△(
),曹烨1,2,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院, 修复科, 北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,口颌功能诊疗研究中心 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
Characteristics of orofacial operant test for orofacial pain sensitivity caused by occlusal interference in rats
Shan-shan BAI1,2,Si-yi MO1,2,Xiao-xiang XU1,2,Yun LIU1,2,Qiu-fei XIE1,2,△( ),Ye CAO1,2,△(
),Ye CAO1,2,△( )
)
- 1. Center for Oral and Jaw Functional Diagnosis, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & Department of Prosthodontics, Beijing 100081, China
2. Center for Oral and Jaw Functional Diagnosis, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
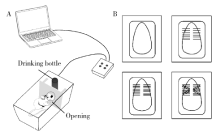
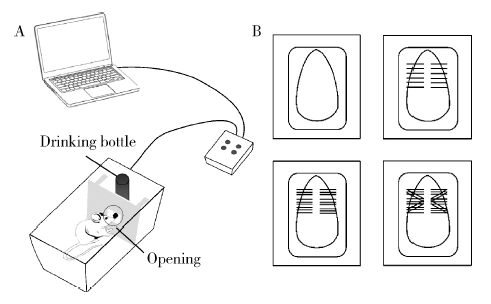
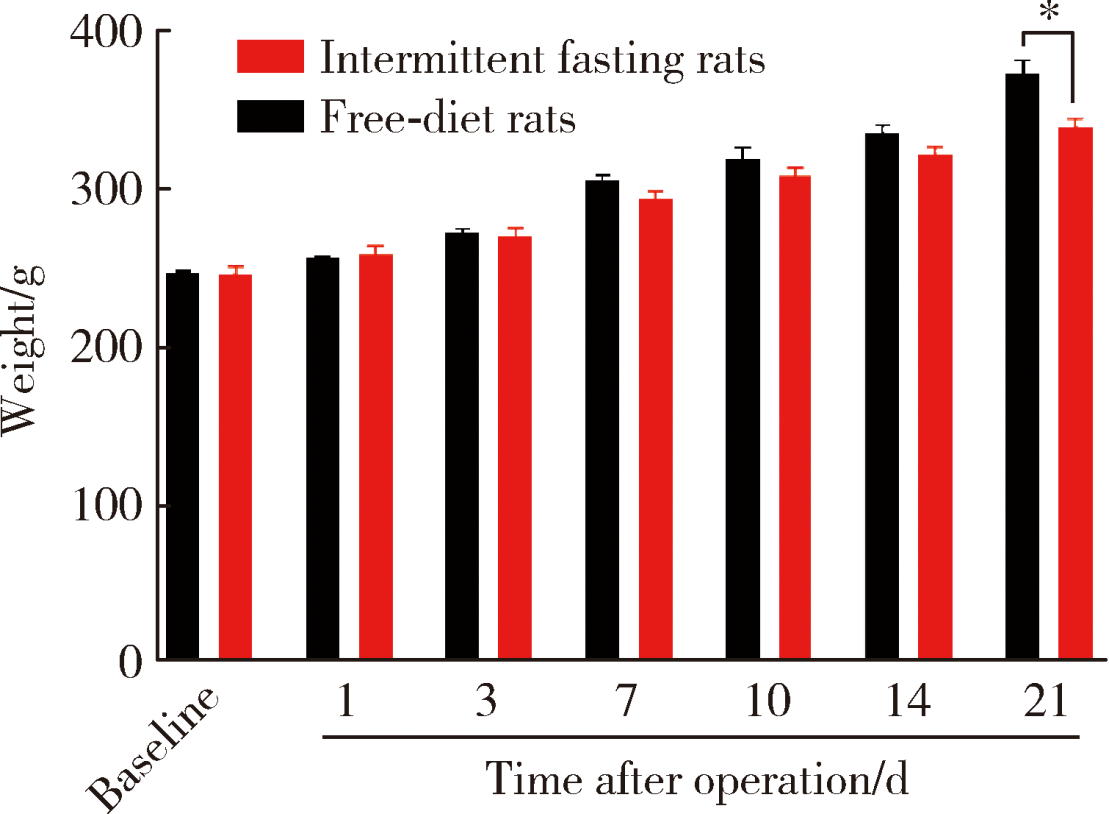
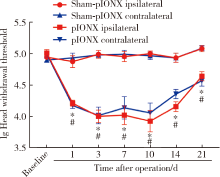
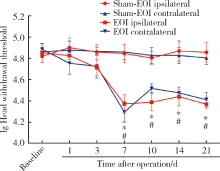
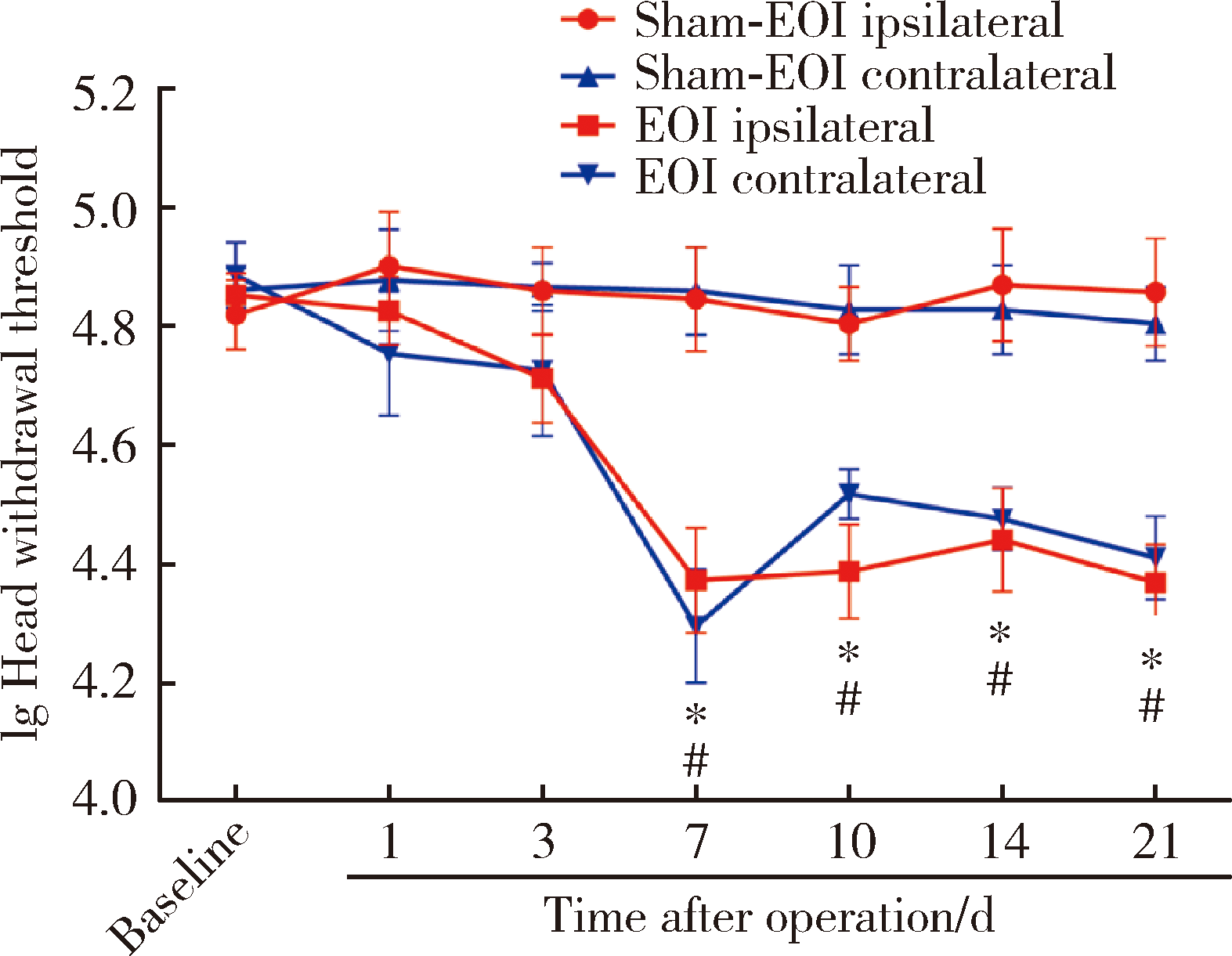
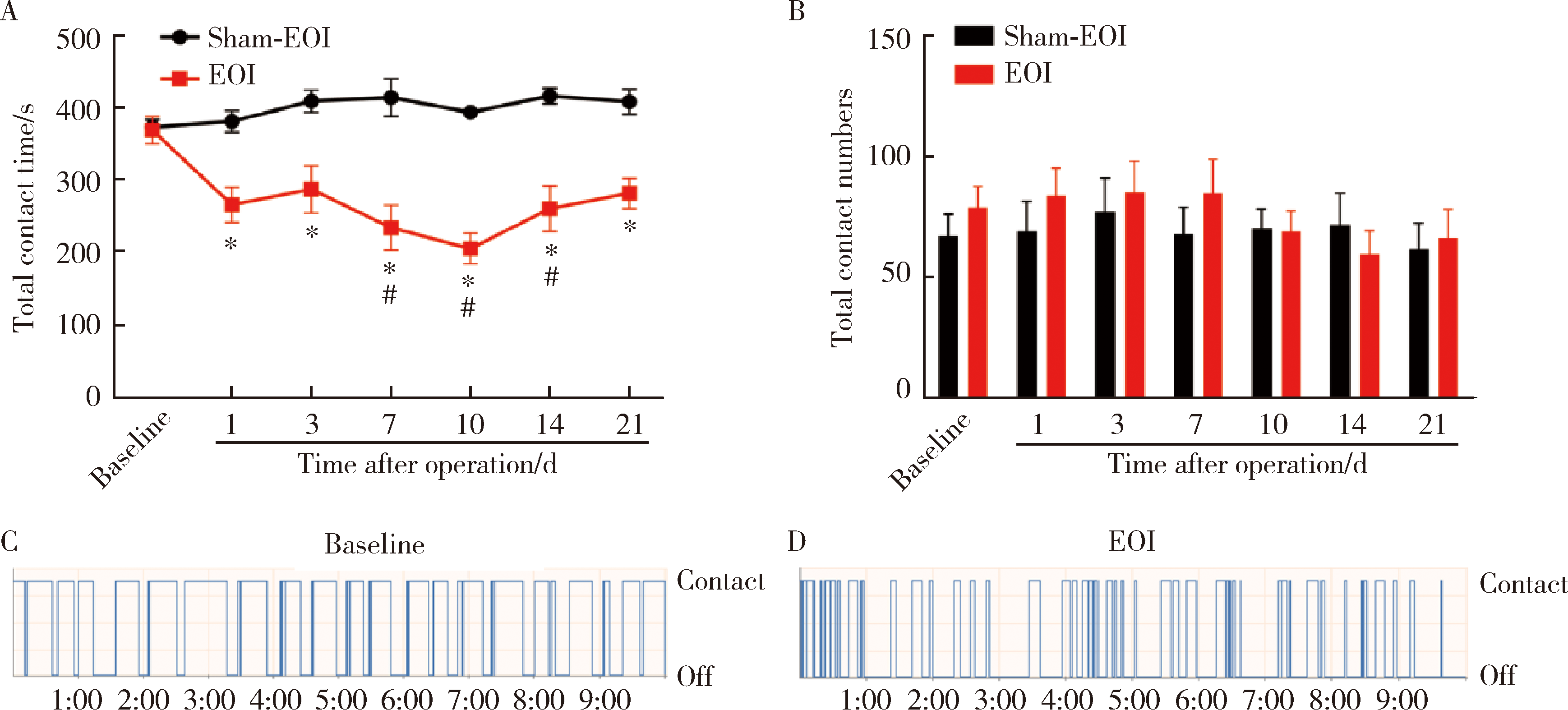
目的:测定咬合干扰模型(experimental occlusal interference, EOI)与部分眶下神经切断模型(partial infraorbital nerve transection,pIONX)两种口颌面疼痛模型大鼠的自我赏罚实验行为学表现及机械诱发反应痛敏,比较两种测痛方法所反映的不同疼痛模型的疼痛特点。方法:Sprague-Dawley大鼠随机分为8组,每组6只,分别为机械刺激诱发反应组(sham-EOI、EOI、sham-pIONX与pIONX组,sham为假手术组)与自我赏罚实验组(sham-EOI、EOI、sham-pIONX与pIONX组,sham为假手术组)。于建模前及建模后1、3、7、10、14、21 d测定各组大鼠机械刺激反应阈值与自我赏罚行为学表现。结果:机械刺激诱发反应组大鼠pIONX组von Frey纤维的机械刺激反应阈值于1~21 d出现显著下降(P<0.05),7~10 d达到最低;自我赏罚实验组大鼠pIONX组的总摄食时间于10~21 d出现显著下降(P<0.05),10~14 d达到最低。机械刺激诱发反应组大鼠EOI组von Frey纤维的机械刺激反应阈值于3~21 d出现显著下降(P<0.05),7 d达到最低;自我赏罚实验组大鼠EOI组的总摄食时间于1~21 d出现显著下降(P<0.05),7~10 d达到最低。结论:自我赏罚实验可以作为口颌面疼痛的行为学测定新方法,而且在神经病理性疼痛和咬合干扰所致口颌面疼痛的模型中均可稳定应用。两种模型中,自我赏罚实验与机械刺激诱发反应均表现出了不同的痛敏时程,两种方法互为补充可以更全面地揭示不同模型的疼痛行为学特点。
中图分类号:
- R782
| [1] | Alrashdan M, Alkhader M . Psychological factors in oral mucosal and orofacial pain conditions[J]. Eur J Dent, 2017,11(4):548-552. |
| [2] | Haviv Y, Zini A, Etzioni Y , et al. The impact of chronic orofacial pain on daily life: the vulnerable patient and the disruptive pain[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2016,123(1):58-66. |
| [3] | Deuis JR, Dvorakova LS, Irina V . Methods used to evaluate pain behaviors in rodents[J]. Front Mol Neurosci, 2017,10:284. |
| [4] | Tappe-Theodor A, King T, Morgan MM . Pros and cons of clinically relevant methods to assess pain in rodents[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2019,100(5):335-343. |
| [5] | Martinez-Garcia MA, Miguelanez-Medran BC, Goicoechea C . Animal models in the study and treatment of orofacial pain[J]. J Clin Exp Dent, 2019,11(4):e382-e390. |
| [6] | Barrot M . Tests and models of nociception and pain in rodents[J]. Neuroscience, 2012,211(11):39-50. |
| [7] | Woolf CJ . Long term alterations in the excitability of the flexion reflex produced by peripheral tissue injury in the chronic decerebrate rat[J]. Pain, 1984,18(4):325-343. |
| [8] | Cha M, Kohan KJ, Zuo X , et al. Assessment of chronic trigeminal neuropathic pain by the orofacial operant test in rats[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2012,234(1):82-90. |
| [9] | Neubert JK, Widmer CG, Malphurs W , et al. Use of a novel thermal operant behavioral assay for characterization of orofacial pain sensitivity[J]. Pain, 2005,116(3):386-395. |
| [10] | Rohrs EL, Kloefkorn HE, Lakes EH , et al. A novel operant-based behavioral assay of mechanical allodynia in the orofacial region of rats[J]. J Neurosci Methods, 2015,248(13):1-6. |
| [11] | Ramirez HE, Queeney TJ, Dunbar ML , et al. Assessment of an orofacial operant pain assay as a preclinical tool for evaluating analgesic efficacy in rodents[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2015,54(4):426-432. |
| [12] | Araujo-Filho HG, Pereira EWM, Campos AR , et al. Chronic orofacial pain animal models-progress and challenges[J]. Expert Opin Drug Discov, 2018,13(10):949-964. |
| [13] | Kaan TK, Ohara PT, Jasmin L , et al. Orofacial pain models and behavior assessment[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2012,851:159-170. |
| [14] | Deseure K, Hans GH . Differential drug effects on spontaneous and evoked pain behavior in a model of trigeminal neuropathic pain[J]. J Pain Res, 2017,10:279-286. |
| [15] | Romero-Reyes M, Akerman S, Nguyen E , et al. Spontaneous behavioral responses in the orofacial region: a model of trigeminal pain in mouse[J]. Headache, 2013,53(1):137-151. |
| [16] | Zhang Q, Cao DL, Zhang ZJ , et al. Chemokine CXCL13 mediates orofacial neuropathic pain via CXCR5/ERK pathway in the trigeminal ganglion of mice[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2016,13(1):183. |
| [17] | Cao Y, Xie QF, Li K , et al. Experimental occlusal interference induces long-term masticatory muscle hyperalgesia in rats[J]. Pain, 2009,144(3):287-293. |
| [18] | Cao Y, Wang H, Chiang CY , et al. Pregabalin suppresses nociceptive behavior and central sensitization in a rat trigeminal neuropathic pain model[J]. J Pain, 2013,14(2):193-204. |
| [19] | 韩济生 . 疼痛学[M]. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2012: 46. |
| [20] | Chapman CR, Casey KL, Dubner R , et al. Pain measurement: an overview[J]. Pain, 1985,22(1):1-31. |
| [21] | Chesler EJ, Wilson SG, Lariviere WR , et al. Identification and ranking of genetic and laboratory environment factors influencing a behavioral trait, thermal nociception, via computational analysis of a large data archive[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2002,26(8):907-923. |
| [22] | Chung JM . Animal models and experimental tests to study nociception and pain[M] // Gebhart GF, Schmidt RF. Encyclopedia of pain. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2013: 154-157. |
| [23] | Kauppila T, Kontinen VK, Pertovaara A . Influence of spinalization on spinal withdrawal reflex responses varies depending on the submodality of the test stimulus and the experimental pathophysiological condition in the rat[J]. Brain Res, 1998,797(2):234-242. |
| [24] | Ling J, Erol F, Gu JG . Role of KCNQ2 channels in orofacial cold sensitivity: KCNQ2 upregulation in trigeminal ganglion neurons after infraorbital nerve chronic constrictive injury[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2018,664(3):84-90. |
| [25] | Budtz-Jørgensen E . Occlusal dysfunction and stress. An experimental study in Macaque monkeys[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2010,8(1):1-9. |
| [26] | Wang C, Yin X . Occlusal risk factors associated with temporomandibular disorders in young adults with normal occlusions[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2012,114(4):419-423. |
| [27] | Raphael KG, Marbach JJ . Widespread pain and the effectiveness of oral splints in myofascial face pain[J]. J Am Dent Assoc, 2001,132(3):305-316. |
| [28] | Ding TT, Xu XX, Cao Y , et al. Inflammatory pain memory facilitates occlusal interference-induced masticatory muscle hyperalgesia in rats[J]. Eur J Pain, 2016,20(3):353-364. |
| [29] | Xu XX, Cao Y, Mo SY , et al. ACC plasticity maintains masseter hyperalgesia caused by occlusal interference[J]. J Dent Res, 2019,98(5):589-596. |
| [30] | Nag S, Mokha SS . Activation of the trigeminal α2-adrenoceptor produces sex-specific, estrogen dependent thermal antinociception and antihyperalgesia using an operant pain assay in the rat[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2016,314(19):152-158. |
| [31] | Rohrs EL, Neubert JK, Caudle RM , et al. Behavioral characteristics of capsaicin mediated cutaneous, myogenic, and arthrogenic orofacial nociception in rats[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2018,92(8):18-24. |
| [32] | Zimmermann M . Pathobiology of neuropathic pain[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2001,429(1-3):23-37. |
| [33] | Melo LT, Panchalingam V, Cherkas P , et al.( -)-α-Bisabolol reduces nociception and trigeminal central sensitisation in acute orofacial neuropathic pain induced by infraorbital nerve injury[J]. Life Sci, 2019,227(12):122-128. |
| [34] | Meacham K, Shepherd A, Mohapatra DP , et al. Neuropathic pain: central vs. peripheral mechanisms[J]. Curr Pain Headache Rep, 2017,21(6):28. |
| [35] | Cao Y, Li K, Fu KY , et al. Central sensitization and MAPKs are involved in occlusal interference-Induced facial pain in rats[J]. J Pain, 2013,14(8):793-807. |
| [1] | 金江, 陈雪, 赵琰, 贾军, 张建中. 卵清蛋白诱导的特应性皮炎小鼠模型中白细胞介素-25的作用及其调控意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 756-762. |
| [2] | 张展奕,张帆,颜野,曹财广,李长剑,邓绍晖,孙悦皓,黄天亮,管允鹤,李楠,陆敏,胡振华,张树栋. 近红外荧光靶向探针用于前列腺神经血管束术中成像[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 843-850. |
| [3] | 袁婷婷,李燊,吴燕,吴海涛. 长期自由选择饮酒小鼠模型的建立及其行为学评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 315-323. |
| [4] | 孟令玮,李雪,高胜寒,李悦,曹瑞涛,张毅,潘韶霞. 三种方法建立大鼠种植体周炎模型的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 22-29. |
| [5] | 何伟,杨思雯,陈娟,朱晓俊,陈志忠,马文军. 275 nm和310 nm紫外线对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 236-243. |
| [6] | 陈章健,韩硕,郑湃,贾光. 锐钛矿型纳米二氧化钛经口暴露90天对Sprague-Dawley大鼠血常规指标的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1205-1208. |
| [7] | 王贵红,左婷,李然,左正才. 瑞巴派特在大鼠痛风性关节炎急性发作中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 716-720. |
| [8] | 尹雪倩, 张晓玄, 文婧, 刘思奇, 刘欣然, 周若宇, 王军波. 荞麦、燕麦、豌豆复配对糖尿病大鼠血糖的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 447-452. |
| [9] | 白枫,何倚帆,牛亚楠,杨若娟,曹静. 超细颗粒物对大鼠离体灌注心脏功能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 240-245. |
| [10] | 周迪,陈章健,胡贵平,阎腾龙,龙昌茂,冯慧敏,贾光. 纳米二氧化钛亚急性经口暴露对大鼠氧化/抗氧化生物标志和炎性因子的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 821-827. |
| [11] | 陈章健,韩硕,郑湃,周淑佩,贾光. 纳米二氧化钛与葡萄糖亚慢性联合经口暴露对幼年大鼠血清叶酸和维生素B12水平的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 451-456. |
| [12] | 韩硕,陈章健,周迪,郑湃,张家赫,贾光. 纳米二氧化钛经口暴露90天对大鼠粪便代谢组的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 457-463. |
| [13] | 何姣,袁戈恒,张俊清,郭晓蕙. 早期糖尿病周围神经病变大鼠模型的建立[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1150-1154. |
| [14] | 王伟,侯进,黄文强. 运动导致兴奋脑区组织液流动一过性加速[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 206-209. |
| [15] | 闫树东,杨广聚,莫思怡,刘云,谢秋菲. 大鼠后肢长期抗阻训练对慢性咬肌机械痛觉敏感性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 21-27. |
|
||