北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 16-23. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.01.004
广泛型侵袭性牙周炎患者牙根形态异常与相关致病基因的关联
刘建,王宪娥,吕达,乔敏,张立,孟焕新( ),徐莉(
),徐莉( ),毛铭馨
),毛铭馨
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,牙周科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Association between root abnormalities and related pathogenic genes in patients with generalized aggressive periodontitis
LIU Jian,WANG Xian-e,LV Da,QIAO Min,ZHANG Li,MENG Huan-xin( ),XU Li(
),XU Li( ),MAO Ming-xin
),MAO Ming-xin
- Department of Periodontology,Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
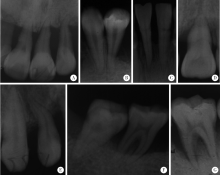
目的: 探索广泛型侵袭性牙周炎(generalized aggressive periodontitis,GAgP)患者牙根形态异常与骨代谢或牙根发育相关基因多态性的关联。方法: 纳入179例GAgP患者,平均(27.23±5.19)岁,男 ∶女=67 ∶112,平均存留牙数(26.80±1.84)颗。采用基于基质辅助激光解吸电离飞行时间质谱技术进行 9个与骨代谢和牙根发育相关基因的13个单核苷酸多态性位点(single nucleotide polymorphisms,SNPs)的基因型检测。采用全口根尖片评判牙根形态异常,包括锥根、细长根、冠根比例失调、弯曲根、融合根、后牙根形态异常,分析13个SNPs位点不同基因型根形态异常牙的数量及发生率。结果: GAgP患者根形态异常牙构成比为14.49%(695/4 798颗),平均(3.88±3.84)颗。维生素D受体(vitamin D receptor,VDR)基因rs2228570位点的CC、CT、TT基因型患者根形态异常牙数量分别为(4.66±4.10)、(3.71±3.93)和(2.68±2.68)颗,CC基因型和TT基因型之间差异有统计学意义(t=2.62,P=0.01)。降钙素受体(calcitotin receptor,CTR)基因rs2283002位点CC、CT、TT基因型患者根形态异常数分别为(5.02±3.70)、(3.43±3.95)、(3.05±3.12)颗,CC基因型的根形态异常发病率高于CT和TT基因型(87.86% vs. 65.26%和63.64%,P=0.006,adjusted OR=3.71,95%CI:1.45~9.50)。结论: VDR rs2228570及CTR rs2283002位点可能与广泛型侵袭性牙周炎患者牙根形态异常的发生有关,值得进一步研究。
中图分类号:
- R394.3
| [1] | Stabholz A, Soskolne WA, Shapira L. Genetic and environmental risk factors for chronic periodontitis and aggressive periodontitis[J]. Periodontology, 2010,53(1):138-153. |
| [2] |
Park KS, Nam JH, Choi J. The short vitamin D receptor is associated with increased risk for generalized aggressive periodontitis[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2006,33(8):524-528.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2006.00944.x pmid: 16899094 |
| [3] |
Li S, Yang MH, Zeng CA, et al. Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms in Chinese patients with generalized aggressive periodontitis[J]. J Periodontal Res, 2008,43(3):360-363.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2007.01044.x pmid: 18205735 |
| [4] |
McNamara CM, Garvey MT, Winter GB. Root abnormalities, talon cusps, dens invaginati with reduced alveolar bone levels: case report[J]. Int J Paediatr Dent, 1998,8(1):41-45.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-263x.1998.00060.x pmid: 9558545 |
| [5] | 梁鑫. 人类牙根发育异常疾病概述[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2019,54(11):783-787. |
| [6] | 徐莉, 孟焕新, 田雨, 等. 侵袭性牙周炎患者牙根形态异常的观察[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2009,44(5):266-269. |
| [7] | 乔敏, 徐莉, 孟焕新, 等. 侵袭性牙周炎核心家系牙槽骨吸收和牙根形态的遗传度分析[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2013,48(10):577-580. |
| [8] | 孟焕新, 曹采方, 和璐, 等. 临床牙周病学[M].2版. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2014: 95-99. |
| [9] | Puthiyaveetil JSV, Kota K, Chakkarayan R, et al. Epithelial mesenchymal interactions in tooth development and the significant role of growth factors and genes with emphasis on mesenchyme: a review[J]. J Clin Diagn Res, 2016,10(9):5-9. |
| [10] |
Huang XF, Chai Y. Molecular regulatory mechanism of tooth root development[J]. Int J Oral Sci, 2012,4(4):177-181.
doi: 10.1038/ijos.2012.61 pmid: 23222990 |
| [11] |
Li JY, Parada G, Yang G. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of tooth root development[J]. Development, 2017,144(3):374-384.
doi: 10.1242/dev.137216 pmid: 28143844 |
| [12] |
Jia SH, Edward KHJ, Lan Y, et al. Bmp4-Msx1 signaling and Osr2 control tooth organogenesis through antagonistic regulation of secreted Wnt antagonists[J]. Developmental Biology, 2016,420(1):110-119.
pmid: 27713059 |
| [13] |
Vaahtokari A, Aberg T, Thesleff I. Apoptosis in the developing tooth: association with an embryonic signaling center and suppression by EGF and FGF-4[J]. Development, 1996,122(1):121-129.
pmid: 8565823 |
| [14] | Guo T, Cao G, Liu BY, et al. Cbfα1 hinders autophagy by DSPP upregulation in odontoblast differentiation[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2019,115(10):78-89. |
| [15] |
Balic A, Thesleff I. Tissue interactions regulating tooth development and renewal[J]. Curr Top Dev Biol, 2015,115:157-186.
doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.07.006 pmid: 26589925 |
| [16] | Hanna AE, Sanjad S, Andary R, et al. Tooth development associated with mutations in hereditary vitamin D-resistant rickets[J]. Clin Trans Res, 2018,3(1):28-34. |
| [17] |
Mallek HM, Nakamoto T, Nuchtern E, et al. The effect of calcitonin in vitro on tooth germs in protein-energy malnourished rats[J]. J Dent Res, 1979,58(9):1921-1925.
doi: 10.1177/00220345790580091901 pmid: 114562 |
| [18] |
Sakakura Y, Iida S, Ishizeki K, et al. Ultrastructure of the effects of calcitonin on the development of mouse tooth germs in vitro[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 1984,29(7):507-512.
doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(84)90071-2 pmid: 6591883 |
| [19] | 张瑞, 黄晓峰, 张方明, 等. Nfic在牙根发育中作用的研究[J]. 北京口腔医学, 2013,21(3):121-124. |
| [20] |
Steele-Perkins G, Butz KG, Lyons GE, et al. Essential role for NFI-C/CTF transcription-replication factor in tooth root development.[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2003,23(3):1075-1084.
doi: 10.1128/mcb.23.3.1075-1084.2003 pmid: 12529411 |
| [21] |
Huang H, Wang J, Zhang Y, et al. Bone resorption deficiency affects tooth root development in RANKL mutant mice due to attenuated IGF-1 signaling in radicular odontoblasts[J]. Bone, 2018,114:161-171.
doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2017.12.026 pmid: 29292230 |
| [22] |
Zhang R, Yang G, Wu X, et al. Disruption of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in odontoblasts and cementoblasts arrests tooth root development in postnatal mouse teeth[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2013,9(3):228-236.
doi: 10.7150/ijbs.5476 pmid: 23494738 |
| [23] |
Chen HM, Guo SY, Xia Y, et al. The role of Rho-GEF Trio in regulating tooth root development through the p38 MAPK pathway[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2018,372(2):158-167.
pmid: 30268758 |
| [24] | 张宇凝, 王骏周, 陈晨. 牙根发育调控机制的研究进展[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2020,55(8):591-594. |
| [25] |
LV D, Meng HX, Xu L, et al. Root abnormalities and nonsurgical management of generalized, aggressive periodontitis[J]. J Oral Sci, 2017,59(1):1-8.
doi: 10.2334/josnusd.16-0027 pmid: 27725369 |
| [26] | 田雨, 徐莉, 孟焕新, 等. 单根牙牙根表面积的测量与估算[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009,44(1):32-35. |
| [27] |
Berdal A, Hotton D, Pike JW, et al. Cell- and stage-specific expression of vitamin D receptor and calbindin genes in rat incisor: regulation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3[J]. Dev Biol, 1993,155(1):172-179.
doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1016 pmid: 8380146 |
| [28] | Papagerakis P. Differential epithelial and mesenchymal regulation of tooth-specific matrix protein sexpression by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in vivo[J]. Connect Tissue Res, 2002,43(2/3):372-375. |
| [29] |
Onishi T. Relationship of vitamin D with calbindin D9k and D28k expression in ameloblasts.[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2008,53(2):117-123.
doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2007.09.009 pmid: 17981260 |
| [30] | Bailleul-Forestier I, Davideau JL, Papagerakis P, et al. Immunolocalization of vitamin D receptor and calbindin-D28k in human tooth germ[J]. Pediatr Res, 1996,39(4):636-642. |
| [31] | Botelho J, Machado V, Proença L, et al. Vitamin D deficiency and oral health: a comprehensive review[J]. Nutrients, 2020,12(5):1471-1487. |
| [32] | 李媛媛, 崔凌凌, 李鑫, 等. 中国汉族男性原发性痛风与维生素D受体基因rs2228570多态性的遗传易感性研究[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2015,31(4):316-319. |
| [33] |
Gross C, Eccleshall TR, Malloy PJ, et al. The presence of a polymorphism at the translation initiation site of the vitamin D receptor gene is associated with low bone mineral density in postmenopausal Mexican-American women[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 1996,11(12):1850-1855.
doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650111204 pmid: 8970885 |
| [34] |
Gross C, Krishnan AV, Malloy PJ, et al. The vitamin D receptor gene start codon polymorphism: A functional analysis of FokI variants[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 1998,13(11):1691-1699.
doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1998.13.11.1691 pmid: 9797477 |
| [35] | Egan JB, Thompson PA, Vitanov MV, et al. Vitamin D receptor ligands, adenomatous polyposis coli, and the vitamin D receptor FokI polymorphism collectively modulate beta-catenin activity in colon cancer cells[J]. Mol Carcinogen, 2010,49(4):337-352. |
| [36] |
Alimirah F, Peng XJ, Murillo G, et al. Functional significance of vitamin D receptor FokI polymorphismin human breast cancer cells[J]. PLoS One, 2011,6(1):e16024.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016024 pmid: 21283672 |
| [37] | Liu K, Han B, Meng HX, et al. Influence of rs2228570 on transcriptional activation by the vitamin D receptor in human gingival fibroblasts and periodontal ligament cells[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2017,88(9):1-19. |
| [38] |
Li S, Yang MH, Zeng CA, et al. Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms in Chinese patients with generalized aggressive periodontitis[J]. J Periodontal Res, 2008,43(3):360-363.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2007.01044.x pmid: 18205735 |
| [39] |
Xiong DH, Shen H, Zhao LJ, et al. Robust and comprehensive analysis of 20 osteoporosis candidate genes by very high-density single-nucleotide polymorphism screen among 405 white nuclear families identified significant association and gene-gene interaction[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2006,21(11):1678-1695.
doi: 10.1359/jbmr.060808 pmid: 17002564 |
| [40] |
Lawrence AW, Mary EF, Zheng YX, et al. In vitro characterization of a human calcitonin receptor gene polymorphism[J]. Mutat Res Fund Mol M, 2003,522(1/2):93-105.
doi: 10.1016/S0027-5107(02)00282-8 |
| [41] |
Giroux S, Elfassihi L, Clément V, et al. High-density polymorphisms analysis of 23 candidate genes for association with bone mineral density[J]. Bone, 2010,47(5):975-981.
doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2010.06.030 |
| [42] |
Yanovich R, Friedman E, Milgrom R, et al. Candidate gene ana-lysis in israeli soldiers with stress fractures[J]. J Sports Sci Med, 2012,11(1):147-155.
pmid: 24149131 |
| [1] | 薛恩慈, 陈曦, 王雪珩, 王斯悦, 王梦莹, 李劲, 秦雪英, 武轶群, 李楠, 李静, 周治波, 朱洪平, 吴涛, 陈大方, 胡永华. 中国人群非综合征型唇裂伴或不伴腭裂的单核苷酸多态性遗传度[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 775-780. |
| [2] | 焦莶如, 龚潘, 牛悦, 徐兆, 周宗朴, 杨志仙. 以婴儿癫痫性痉挛综合征为表型的吡哆醇依赖性癫痫[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 781-787. |
| [3] | 武志慧, 胡明智, 赵巧英, 吕凤凤, 张晶莹, 张伟, 王永福, 孙晓林, 王慧. miR-125b-5p修饰脐带间充质干细胞对系统性红斑狼疮的免疫调控机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [4] | 郭煌达,彭和香,王斯悦,侯天姣,李奕昕,章涵宇,王梦莹,武轶群,秦雪英,唐迅,李劲,陈大方,胡永华,吴涛. 短期大气颗粒物暴露和MTNR1B基因多态性对甘油三酯-葡萄糖指数影响的家系研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 375-383. |
| [5] | 侯天姣,周治波,王竹青,王梦莹,王斯悦,彭和香,郭煌达,李奕昕,章涵宇,秦雪英,武轶群,郑鸿尘,李静,吴涛,朱洪平. 转化生长因子β信号通路与非综合征型唇腭裂发病风险的基因-基因及基因-环境交互作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 384-389. |
| [6] | 王鹏,杨子瑶,王萌,王巍,李爱芝. 2例罕见RhD变异型RHD*DEL37的分子生物学分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 352-356. |
| [7] | 刘欢锐,彭祥,李森林,苟欣. 基于HER-2相关基因构建风险模型用于膀胱癌生存预后评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [8] | 金银姬,孙琳,赵金霞,刘湘源. 血清IgA型抗鼠科肉瘤病毒癌基因同源物B1抗体在类风湿关节炎中的意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 631-635. |
| [9] | 谢尚,蔡志刚,单小峰. 全外显子测序及相关指标在口腔鳞状细胞癌精准治疗中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 697-701. |
| [10] | 许媛媛,孙志琳,张秀莲,刘子莲,刘维,关欣. 卡马西平致HLA-A * 3101基因阳性中国汉族人发生Stevens-Johnson综合征1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 755-757. |
| [11] | 史佳琪,马莺,张奕,陈章健,贾光. 纳米二氧化钛颗粒对人肝癌细胞HepG2中circRNA表达谱的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 392-399. |
| [12] | 王雪珩,王斯悦,彭和香,范梦,郭煌达,侯天姣,王梦莹,武轶群,秦雪英,唐迅,李劲,陈大方,胡永华,吴涛. 基因-环境交互作用对动脉僵硬度影响的家系研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 400-407. |
| [13] | 时云飞,王豪杰,刘卫平,米岚,龙孟平,刘雁飞,赖玉梅,周立新,刁新婷,李向红. 血管免疫母细胞性T细胞淋巴瘤临床与分子病理学特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
| [14] | 王微,李鑫,柳萍,董颖. 荧光原位杂交检测MDM2和DDIT3基因信号改变在诊断脂肪肉瘤中的价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 228-233. |
| [15] | 周秋君,龚潘,焦莶如,杨志仙. 1例Angelman综合征合并眼皮肤白化病2型患者的临床和遗传学分析及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 181-185. |
|
||