北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 69-75. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.01.011
数字化评估CAD/CAM个性化基台与成品基台影响粘接剂残留的体外研究
- 1.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,牙周科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,修复科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Comparison of residual cement between CAD/CAM customized abutments and stock abutments via digital measurement in vitro
YUE Zhao-guo1,ZHANG Hai-dong1,YANG Jing-wen2,HOU Jian-xia1,Δ( )
)
- 1. Department of Periodontology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Prosthetics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
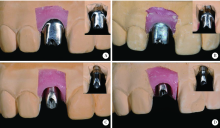
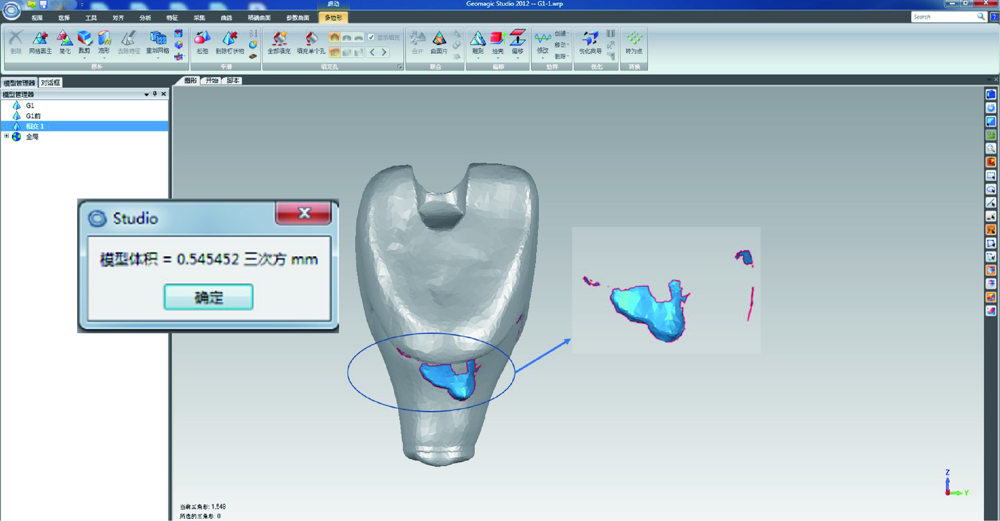
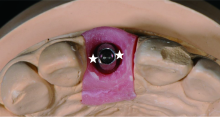
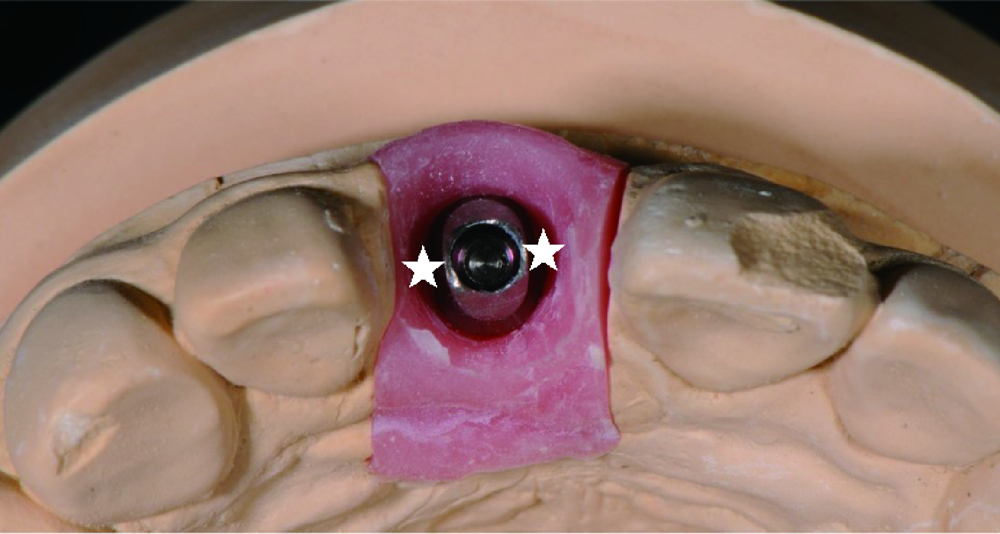
目的: 通过体外模型比较计算机辅助设计/计算机辅助制造个性化基台(computer aided design/computer aided manufacturing customized abutments,CCA)与成品基台(stock abutments,SA)对粘接剂残留的影响,同时初步评价数字化三维扫描技术定量评估残留粘接剂的可行性。方法: 本研究所需20个工作模型皆取自同一例已在北京大学口腔医院牙周科接受了右上中切牙种植手术的患者。通过个性化愈合基台成形植体周软组织后,测得植体平台位于颊侧黏膜下5 mm。利用个性化转移杆取模后灌制20副工作模型,并根据基台种类及粘接边缘位置将工作模型分为四组,每组5个:CCA1(穿黏膜高度5 mm,即平齐黏膜粘接边缘)、CCA2(穿黏膜高度4 mm,即黏膜下1 mm粘接边缘)、SA1(穿黏膜高度3 mm,即黏膜下2 mm粘接边缘)和SA2(穿黏膜高度1 mm,即黏膜下4 mm粘接边缘)。在工作模型上模拟临床粘接过程并清除多余粘接剂后,利用三维扫描技术获得残留粘接剂的体积,利用数码相机拍摄二维图像获得残留粘接剂面积百分比,利用称量的方式获得残留粘接剂的质量,并分析三维扫描方法获取的体积与传统评价方法所得的面积百分比及质量的相关性。结果: 所有冠-基台复合体粘接边缘均有粘接剂残留。其中,CCA组残留粘接剂的体积明显小于SA组[(0.635 3±0.535 4) mm3 vs. (2.293 8±0.943 8) mm 3,P<0.001], 面积百分比及质量也显著低于SA组[面积百分比:7.57%±2.99% vs. 22.68%±10.06%,P<0.001;质量:(0.001 5±0.001 0) g vs. (0.003 7±0.001 4) g,P<0.001],而三者在CCA组及SA组内差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。三维扫描所得残留粘接剂的体积与传统评价方法所得残留粘接剂的面积百分比及残留粘接剂的质量间均具强相关性(r>0.75,P<0.001)。结论: 与SA相比,CCA能更有效地减少粘接剂的残留。基于三维扫描技术数字化评估残留粘接剂的方法切实可行,但其效度和信度还需进一步研究。
中图分类号:
- R783
| [1] |
Jung RE, Pjetursson BE, Glauser R, et al. A systematic review of the 5-year survival and complication rates of implant-supported single crowns[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2008,19(2):119-130.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2007.01453.x pmid: 18067597 |
| [2] |
Chee W, Felton DA, Johnson PF, et al. Cemented versus screw-retained implant prostheses: Which is better?[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 1999,14(1):137-141.
pmid: 10074764 |
| [3] |
Linkevicius T, Vindasiute E, Puisys A, et al. The influence of margin location on the amount of undetected cement excess after delivery of cement-retained implant restorations[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2011,22(12):1379-1384.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2010.02119.x pmid: 21382089 |
| [4] |
Staubli N, Walter C, Schmidt JC, et al. Excess cement and the risk of peri-implant disease: A systematic review[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2017,28(10):1278-1290.
doi: 10.1111/clr.12954 pmid: 27647536 |
| [5] |
Korsch M, Obst U, Walther W. Cement-associated peri-implantitis: A retrospective clinical observational study of fixed implant-supported restorations using a methacrylate cement[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2014,25(7):797-802.
doi: 10.1111/clr.12173 pmid: 23600620 |
| [6] |
Wilson TG Jr. The positive relationship between excess cement and peri-implant disease: A prospective clinical endoscopic study[J]. J Periodontol, 2009,80(9):1388-1392.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090115 pmid: 19722787 |
| [7] |
Linkevicius T, Puisys A, Vindasiute E, et al. Does residual cement around implant-supported restorations cause peri-implant disease? A retrospective case analysis[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2013,24(11):1179-1184.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02570.x pmid: 22882700 |
| [8] |
Ichikawa T, Ishida O, Watanabe M, et al. A new retrieval system for cement-retained implant superstructures: A technical report[J]. J Prosthodont, 2008,17(6):487-489.
doi: 10.1111/j.1532-849X.2008.00329.x pmid: 18544129 |
| [9] |
Galván G, Kois JC, Chaiyabutr Y, et al. Cemented implant restoration: A technique for minimizing adverse biologic consequences[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2015,114(4):482-485.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2014.10.017 pmid: 26119018 |
| [10] |
Seo CW, Seo JM. A technique for minimizing subgingival residual cement by using rubber dam for cement-retained implant crowns[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2017,117(2):327-328.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2016.08.024 pmid: 27771147 |
| [11] | Linkevicius T. Zero bone loss concepts [M]. Illinois: Quintessence Publishing Co, 2019. |
| [12] |
Lewis S, Beumer J 3rd, Hornburg W, et al. The “UCLA” abutment[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 1988,3(3):183-189.
pmid: 3074050 |
| [13] | 戴文雍, 汤春波. 种植体修复个性化基台研究现状及展望[J]. 口腔医学, 2012,32(11):685-687. |
| [14] | 宿玉成. 口腔种植学[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2014: 403-404. |
| [15] |
Shapoff CA, Lahey BJ. Crestal bone loss and the consequences of retained excess cement around dental implants[J]. Compend Contin Educ Dent, 2012,33(2):94-101.
pmid: 22545427 |
| [16] |
Schwarz F, Derks J, Monje A, et al. Peri-implantitis[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2018,45(Suppl 20):S246-S266.
doi: 10.1111/jcpe.2018.45.issue-S20 |
| [17] |
Andersson B, Odman P, Lindvall AM, et al. Cemented single crowns on osseointegrated implants after 5 years: Results from a prospective study on CeraOne[J]. Int J Prosthodont, 1998,11(3):212-218.
pmid: 9728114 |
| [18] |
Linkevicius T, Vindasiute E, Puisys A, et al. The influence of the cementation margin position on the amount of undetected cement. A prospective clinical study[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2013,24(1):71-76.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02453.x pmid: 22487018 |
| [19] |
Kappel S, Eiffler C, Lorenzo-Bermejo J, et al. Undetected resi-dual cement on standard or individualized all-ceramic abutments with cemented zirconia single crowns: A prospective randomized pilot trial[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2016,27(9):1065-1071.
doi: 10.1111/clr.12691 pmid: 26381392 |
| [20] |
Kotsakis GA, Zhang L, Gaillard P, et al. Investigation of the association between cement retention and prevalent peri-implant diseases: A cross-sectional study[J]. J Periodontol, 2016,87(3):212-220.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2015.150450 pmid: 26537368 |
| [21] |
Daubert DM, Weinstein BF, Bordin S, et al. Prevalence and predictive factors for peri-implant disease and implant failure: A cross-sectional analysis[J]. J Periodontol, 2015,86(3):337-347.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2014.140438 pmid: 25415249 |
| [22] | Fuchigami K, Munakata M, Kitazume T, et al. A diversity of peri-implant mucosal thickness by site[J]. Clin Oral Impl Res, 2017,28(2):171-176. |
| [23] | 张众, 孟焕新, 韩劼, 等. 软组织垂直厚度对牙周炎患者种植修复临床效果的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020,52(2):332-338. |
| [24] |
Dumbrigue HB, Abanomi AA, Cheng LL. Techniques to minimize excess luting agent in cement-retained implant restorations[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2002,87(1):112-114.
doi: 10.1067/mpr.2002.119418 pmid: 11807495 |
| [25] |
Vindasiute E, Puisys A, Maslova N, et al. Clinical factors influencing removal of the cement excess in implant-supported restorations[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2015,17(4):771-778.
doi: 10.1111/cid.12170 pmid: 24224895 |
| [26] |
Andersson B, Odman P, Lindvall AM, et al. Single-tooth restorations supported by osseointegrated implants: results and experiences from a prospective study after 2 to 3 years[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 1995,10(6):702-711.
pmid: 8530173 |
| [27] | Higginbottom F, Belser U, Jones JD, et al. Prosthetic management of implants in the esthetic zone[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 2004,19(Suppl.):62-72. |
| [28] |
Berglundh T, Lindhe J, Marinello C, et al. Soft tissue reaction to de novo plaque formation on implants and teeth. An experimental study in the dog[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 1992,3(1):1-8.
doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.1992.030101.x pmid: 1420721 |
| [29] | 高鹏程, 谢理哲, 严斌. 牙颌模型三维数字化技术及其在口腔正畸学中的应用进展[J]. 口腔生物医学, 2014,5(3):152-157. |
| [1] | 邢念增,王明帅,杨飞亚,尹路,韩苏军. 前列腺免活检创新理念的临床实践及其应用前景[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 565-566. |
| [2] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [3] | 唐祖南,胡耒豪,陈震,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 增强现实技术在口腔颌面颈部解剖识别中的应用评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 541-545. |
| [4] | 吕梁,张铭津,温奧楠,赵一姣,王勇,李晶,杨庚辰,柳大为. 应用三维软组织空间线角模板法评价颏部对称性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 106-110. |
| [5] | 毛渤淳,田雅婧,王雪东,李晶,周彦恒. 骨性Ⅱ类高角患者拔牙矫治前后的面部软硬组织变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [6] | 凌晓彤,屈留洋,郑丹妮,杨静,闫雪冰,柳登高,高岩. 牙源性钙化囊肿与牙源性钙化上皮瘤的三维影像特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [7] | 徐心雨,吴灵,宋凤岐,李自力,张益,刘筱菁. 基于下颌运动轨迹的正颌外科术中下颌骨髁突定位方法及初步精度验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [8] | 李穗,马雯洁,王时敏,丁茜,孙瑶,张磊. 上前牙种植单冠修复体切导的数字化设计正确度[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 81-87. |
| [9] | 刘毅,袁昌巍,吴静云,沈棋,肖江喜,赵峥,王霄英,李学松,何志嵩,周利群. 靶向穿刺+6针系统穿刺对PI-RADS 5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [10] | 袁昌巍,李德润,李志华,刘毅,山刚志,李学松,周利群. 多参数磁共振成像中动态对比增强状态在诊断PI-RADS 4分前列腺癌中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [11] | 刘颖,霍然,徐慧敏,王筝,王涛,袁慧书. 磁共振血管壁成像评估颈动脉中重度狭窄患者斑块特征与脑血流灌注的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [12] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [13] | 刘想,谢辉辉,许玉峰,张晓东,陶晓峰,柳林,王霄英. 人工智能对提高放射科住院医生诊断胸部肋骨骨折一致性的价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 670-675. |
| [14] | 黄莹,吴志远,周行红,蔡志刚,张杰. 股前外侧皮瓣修复上颌骨缺损术后面部软组织对称性感观分级[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 708-715. |
| [15] | 张雯,刘筱菁,李自力,张益. 基于解剖标志的鼻翼基底缩窄缝合术对正颌患者术后鼻唇部形态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
|
||