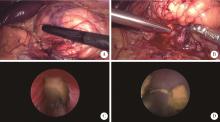
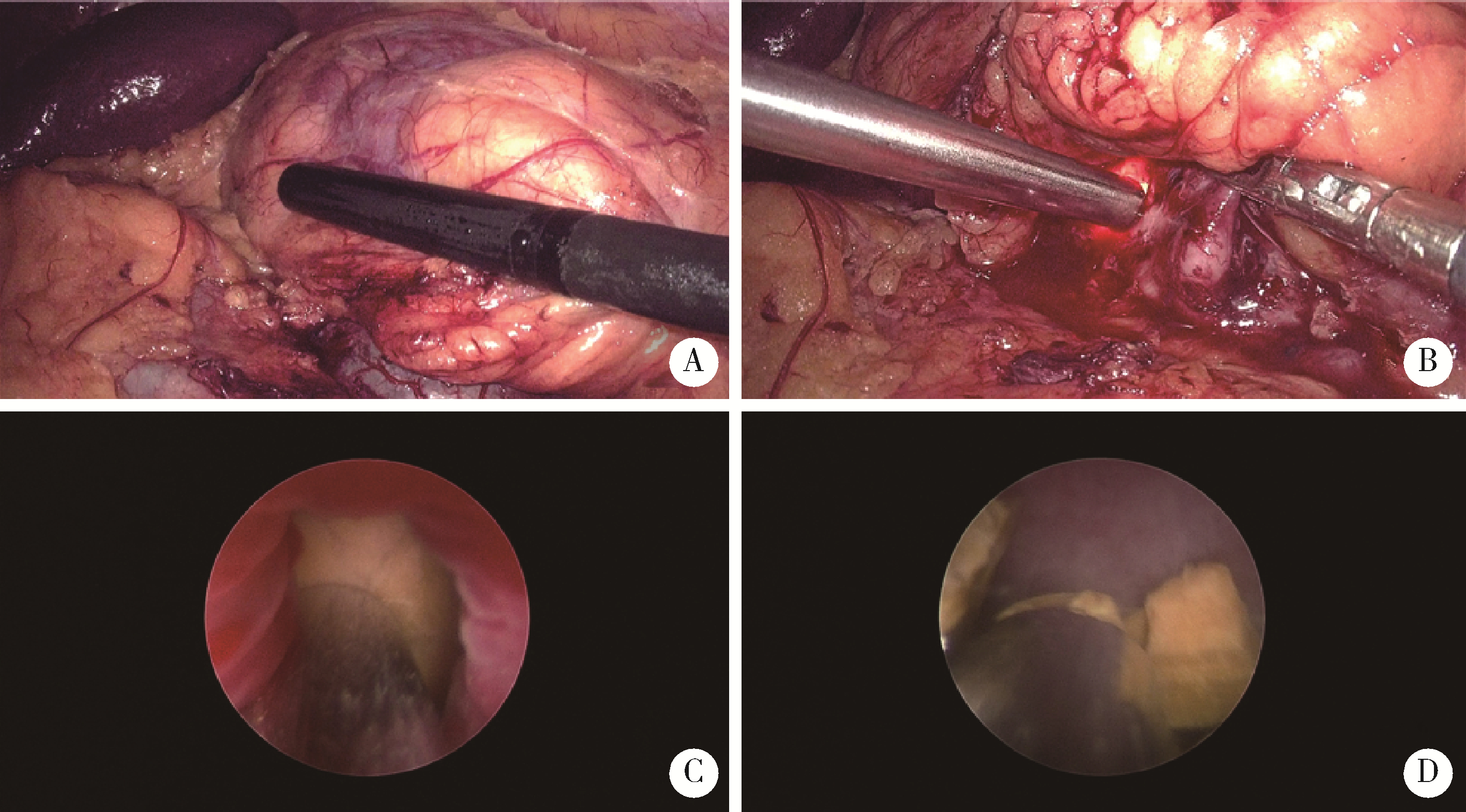
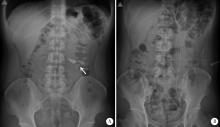
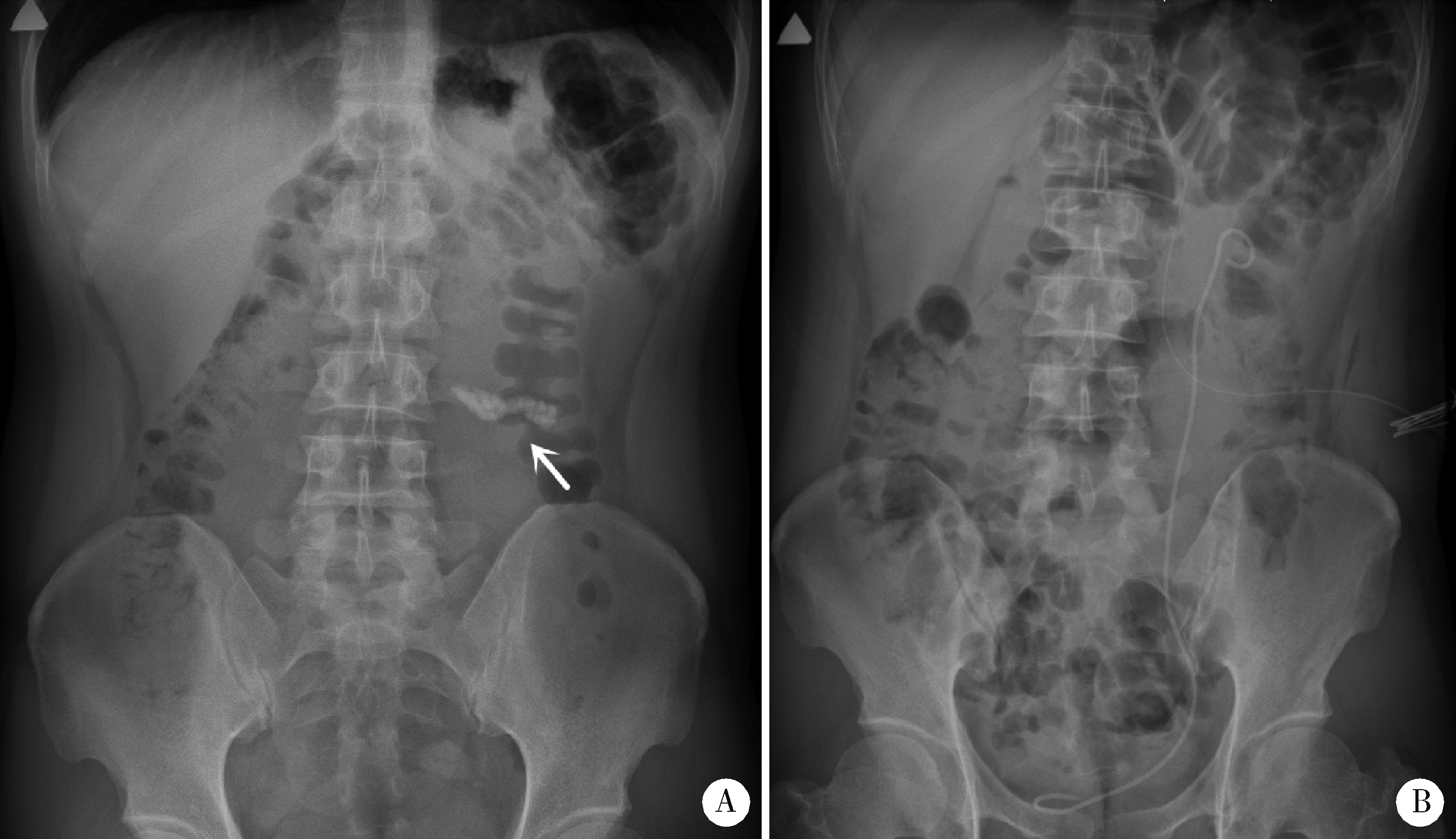
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 746-750. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.04.026
腹腔镜肾盂成形术联合肾盂镜超声碎石取石术治疗肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻合并肾结石
- 北京大学人民医院泌尿与碎石中心,北京大学应用碎石研究所,北京 100034
Laparoscopic pyeloplasty combined with ultrasonic lithotripsy via nephroscope for treatment of ureteropelvic junction obstruction with renal calculi
Li-zhe AN,Liu-lin XIONG*( ),Liang CHEN,Huan-rui WANG,Wei-nan CHEN,Xiao-bo HUANG
),Liang CHEN,Huan-rui WANG,Wei-nan CHEN,Xiao-bo HUANG
- Urology and Lithotripsy Center, Peking University People' s Hospital, Peking University Applied Lithotripsy Institute, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
目的: 探讨应用腹腔镜肾盂成形术联合肾盂镜超声碎石取石术治疗肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻(ureteropelvic junction obstruction,UPJO)合并肾结石的有效性和安全性。方法: 回顾性分析北京大学人民医院2016年6月至2022年1月接受该术式治疗的8例患者的临床资料,男性5例,女性3例,平均年龄40.5岁(23~51岁),平均体重指数(body mass index,BMI)27.0 kg/m2 (18.8~32.4 kg/m2);病变全部位于左侧,其中2例为孤立肾,1例为马蹄肾;单发结石1例,其余7例为多发结石,铸型结石2例;结石最大径平均为1.5 cm (0.6~2.5 cm);中度肾积水5例,重度肾积水3例。术中于肾盂前壁剪开约1.5 cm切口,经腹腔镜Trocar和肾盂切口置入19.5F(1F≈0.33 mm)肾镜于肾盂内,经肾镜置入3.3 mm超声碎石探针,利用超声探针将结石击碎并通过负压吸引将结石碎屑吸出,取石完毕后行改良经腹腹腔镜肾盂成形术。结果: 全部患者的手术均顺利完成,无中转开放手术,平均手术时间213 min (160~254 min),平均肾镜操作时间33 min (25~40 min)。术后第1天血红蛋白平均下降10.3 g/L (3~21 g/L)。术后净石率为75%(6/8例)。经改良Clavien分级系统(modified Clavien classification system,MCCS)评估,ⅢA级并发症1例,为肾盂内出血导致肾积水,予局部麻醉下行肾造瘘术后治愈。平均随访30个月(2~68个月),肾盂成形手术成功率为100%,1例患者因结石增多行经皮肾镜取石,其余患者未见结石复发或增多。结论: 腹腔镜肾盂成形术联合肾盂镜超声碎石取石术治疗UPJO合并肾结石安全、有效,操作性好,可作为现行取石方式的补充。
中图分类号:
- R691.2
| 1 |
Skolarikos A , Dellis A , Knoll T . Ureteropelvic obstruction and renal stones: etiology and treatment[J]. Urolithiasis, 2015, 43 (1): 5- 12.
doi: 10.1007/s00240-014-0736-2 |
| 2 |
Paik ML , Wainstein MA , Spirnak JP , et al. Current indications for open stone surgery in the treatment of renal and ureteral calculi[J]. J Urol, 1998, 159 (2): 374- 379.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(01)63922-3 |
| 3 |
Yanke BV , Lallas CD , Pagnani C , et al. The minimally invasive treatment of ureteropelvic junction obstruction: A review of our experience during the last decade[J]. J Urol, 2008, 180 (4): 1397- 1402.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.06.020 |
| 4 |
Klingler HC , Remzi M , Janetschek G , et al. Comparison of open versus laparoscopic pyeloplasty techniques in treatment of uretero-pelvic junction obstruction[J]. Eur Urol, 2003, 44 (3): 340- 345.
doi: 10.1016/S0302-2838(03)00297-5 |
| 5 |
Mufarrij PW , Woods M , Shah OD , et al. Robotic dismembered pyeloplasty: A 6-year, multi-institutional experience[J]. J Urol, 2008, 180 (4): 1391- 1396.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.06.024 |
| 6 |
Srivastava A , Singh P , Gupta M , et al. Laparoscopic pyeloplasty with concomitant pyelolithotomy: Is it an effective mode of treatment?[J]. Urol Int, 2008, 80 (3): 306- 309.
doi: 10.1159/000127347 |
| 7 |
Stein RJ , Turna B , Nguyen MM , et al. Laparoscopic pyeloplasty with concomitant pyelolithotomy: Technique and outcomes[J]. J Endourol, 2008, 22 (6): 1251- 1255.
doi: 10.1089/end.2008.0003 |
| 8 |
Atug F , Castle EP , Burgess SV , et al. Concomitant management of renal calculi and pelvi-ureteric junction obstruction with robotic laparoscopic surgery[J]. BJU Int, 2005, 96 (9): 1365- 1368.
doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05819.x |
| 9 |
Jensen PH , Berg KD , Azawi NH . Robot-assisted pyeloplasty and pyelolithotomy in patients with ureteropelvic junction stenosis[J]. Scand J Urol, 2017, 51 (4): 323- 328.
doi: 10.1080/21681805.2017.1300188 |
| 10 |
中华医学会泌尿外科学分会结石学组, 中国泌尿系结石联盟. 经皮肾镜取石术中国专家共识[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 41 (6): 401- 404.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20200530-00006 |
| 11 |
Yang K , Yao L , Li X , et al. A modified suture technique for transperitoneal laparoscopic dismembered pyeloplasty of pelviureteric junction obstruction[J]. Urology, 2015, 85 (1): 263- 267.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2014.09.031 |
| 12 |
Nayyar R , Gupta NP , Hemal AK . Robotic management of complicated ureteropelvic junction obstruction[J]. World J Urol, 2010, 28 (5): 599- 602.
doi: 10.1007/s00345-009-0469-y |
| 13 |
Yang C , Zhou J , Lu ZX , et al. Simultaneous treatment of ureteropelvic junction obstruction complicated by renal calculi with robotic laparoscopic surgery and flexible cystoscope[J]. World J Urol, 2019, 37 (10): 2217- 2223.
doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2608-9 |
| 14 | Meretyk I , Meretyk S , Clayman RV . Endopyelotomy: Comparison of ureteroscopic retrograde and antegrade percutaneous techniques[J]. J Urol, 1992, 148 (3): 775- 783. |
| 15 |
Knudsen BE , Cook AJ , Watterson JD , et al. Percutaneous antegrade endopyelotomy: Long-term results from one institution[J]. Urology, 2004, 63 (2): 230- 234.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2003.09.049 |
| 16 |
Minervini A , Davenport K , Keeley FJ , et al. Antegrade versus retrograde endopyelotomy for pelvi-ureteric junction (PUJ) obstruction[J]. Eur Urol, 2006, 49 (3): 536- 543.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2005.11.025 |
| 17 |
杨波, 胡浩, 王佳, 等. 经皮肾"三明治"腔内肾盂成形术治疗肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47 (4): 634- 637.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2015.04.017 |
| 18 |
Agarwal A , Varshney A , Bansal BS . Concomitant percutaneous nephrolithotomy and transperitoneal laparoscopic pyeloplasty for ureteropelvic junction obstruction complicated by stones[J]. J Endourol, 2008, 22 (10): 2251- 2255.
doi: 10.1089/end.2008.9726 |
| 19 |
Schuessler WW , Grune MT , Tecuanhuey LV , et al. Laparoscopic dismembered pyeloplasty[J]. J Urol, 1993, 150 (6): 1795- 1799.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)35898-6 |
| 20 |
Jarrett TW , Chan DY , Charambura TC , et al. Laparoscopic pyelo- plasty: The first 100 cases[J]. J Urol, 2002, 167 (3): 1253- 1256.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)65276-7 |
| 21 |
Moon DA , El-Shazly MA , Chang CM , et al. Laparoscopic pyeloplasty: Evolution of a new gold standard[J]. Urology, 2006, 67 (5): 932- 936.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2005.11.024 |
| 22 |
Ramakumar S , Lancini V , Chan DY , et al. Laparoscopic pyeloplasty with concomitant pyelolithotomy[J]. J Urol, 2002, 167 (3): 1378- 1380.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)65305-0 |
| 23 |
Hong P , Li Z , Zhu D , et al. A simple modification for the usage of flexible cystoscope in modified laparoscopic pyeloplasty for ureteropelvic junction obstruction with renal calculi: A flexible guiding tube[J]. Urol Int, 2019, 102 (3): 262- 268.
doi: 10.1159/000495569 |
| 24 |
丁光璞, 彭意吉, 杨昆霖, 等. 改良经腹腹腔镜肾盂成形术联合孙氏镜治疗UPJO合并肾结石的初步经验[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2019, 40 (9): 680- 684.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2019.09.008 |
| 25 | 郑蒙蒙, 丁光璞, 朱伟杰, 等. 术前三维影像重建在治疗肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52 (4): 705- 710. |
| [1] | 王明瑞,刘军,熊六林,于路平,胡浩,许克新,徐涛. 经皮微通道-微电子肾镜-微超声探针碎石术治疗1.5~2.5 cm肾结石的疗效和安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 605-609. |
| [2] | 郑生旗,花天池,殷桂草,张伟,姚曳,李一帆. 甘油三酯葡萄糖指数与男性肾结石风险的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 610-616. |
| [3] | 邱敏,宗有龙,王滨帅,杨斌,徐楚潇,孙争辉,陆敏,赵磊,卢剑,刘承,田晓军,马潞林. 腹腔镜肾部分切除术治疗中高复杂程度肾肿瘤的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [4] | 刘慧丽,吕彦函,王晓晓,李民. 老年患者腹腔镜泌尿系肿瘤根治术后慢性疼痛的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 851-856. |
| [5] | 田聪,刘军,杨波,乔佳佳,黄晓波,许清泉. 经皮肾镜取石术中异常肾盂黏膜活检结果分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 948-952. |
| [6] | 王昱,张慧敏,邓雪蓉,刘伟伟,陈璐,赵宁,张晓慧,宋志博,耿研,季兰岚,王玉,张卓莉. 尿枸橼酸定量检测在原发性痛风患者肾结石诊断中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1134-1140. |
| [7] | 张铃福,侯纯升,徐智,王立新,凌晓锋,王港,崔龙,修典荣. 腹腔镜下经胆囊管胆管引流联合胆总管探查取石术治疗复杂胆管结石的临床效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1185-1189. |
| [8] | 张帆,陈曲,郝一昌,颜野,刘承,黄毅,马潞林. 术前及术后膜性尿道长度与腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术后控尿功能恢复的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 299-303. |
| [9] | 张帆,黄晓娟,杨斌,颜野,刘承,张树栋,黄毅,马潞林. 前列腺尖部深度与腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术后早期控尿功能恢复的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 692-696. |
| [10] | 王明瑞,王起,胡浩,赖金惠,贺永新,熊杰,刘献辉,刘士军,许克新,徐涛. 标准通道经皮肾镜取石术治疗孤立肾肾结石的长期安全性和有效性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 663-666. |
| [11] | 康宁,蒋一航,蒋宇光,吴栗洋,张际青,牛亦农,张军晖. 内镜联合超声与单纯超声引导建立皮肾通道在多镜联合术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 692-696. |
| [12] | 郑蒙蒙,丁光璞,朱伟杰,杨昆霖,樊书菠,关豹,李新飞,蔡宇坤,张进生,李学松,周利群. 术前三维影像重建在治疗肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 705-710. |
| [13] | 熊盛炜,王杰,朱伟杰,程嗣达,张雷,李学松,周利群. 二次肾盂成形术在复发性肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻中的研究进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 794-798. |
| [14] | 朱学华,杨明钰,夏海缀,何为,张智荧,刘余庆,肖春雷,马潞林,卢剑. 机器学习模型在预测肾结石输尿管软镜碎石术后早期结石清除率中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 653-659. |
| [15] | 赵海岳,叶雄俊,陈伟男,安立哲,刘军,熊六林,黄晓波. 腹腔镜肾盂成型术中异位血管的处理方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 660-664. |
|
||