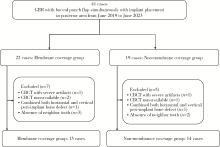
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1097-1104. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.022
可吸收胶原膜在颊侧袋形瓣引导性骨再生手术中的作用: 一项回顾性影像学队列研究
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔颌面外科, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
2. Department of Periodontics and Oral Medicine, School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, 48109, USA
Role of collagen membrane in modified guided bone regeneration surgery using buccal punch flap approach: A retrospective and radiographical cohort study
Deng-hui DUAN1,Hom-Lay WANG2,En-bo WANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Periodontics and Oral Medicine, School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, 48109, USA
摘要:
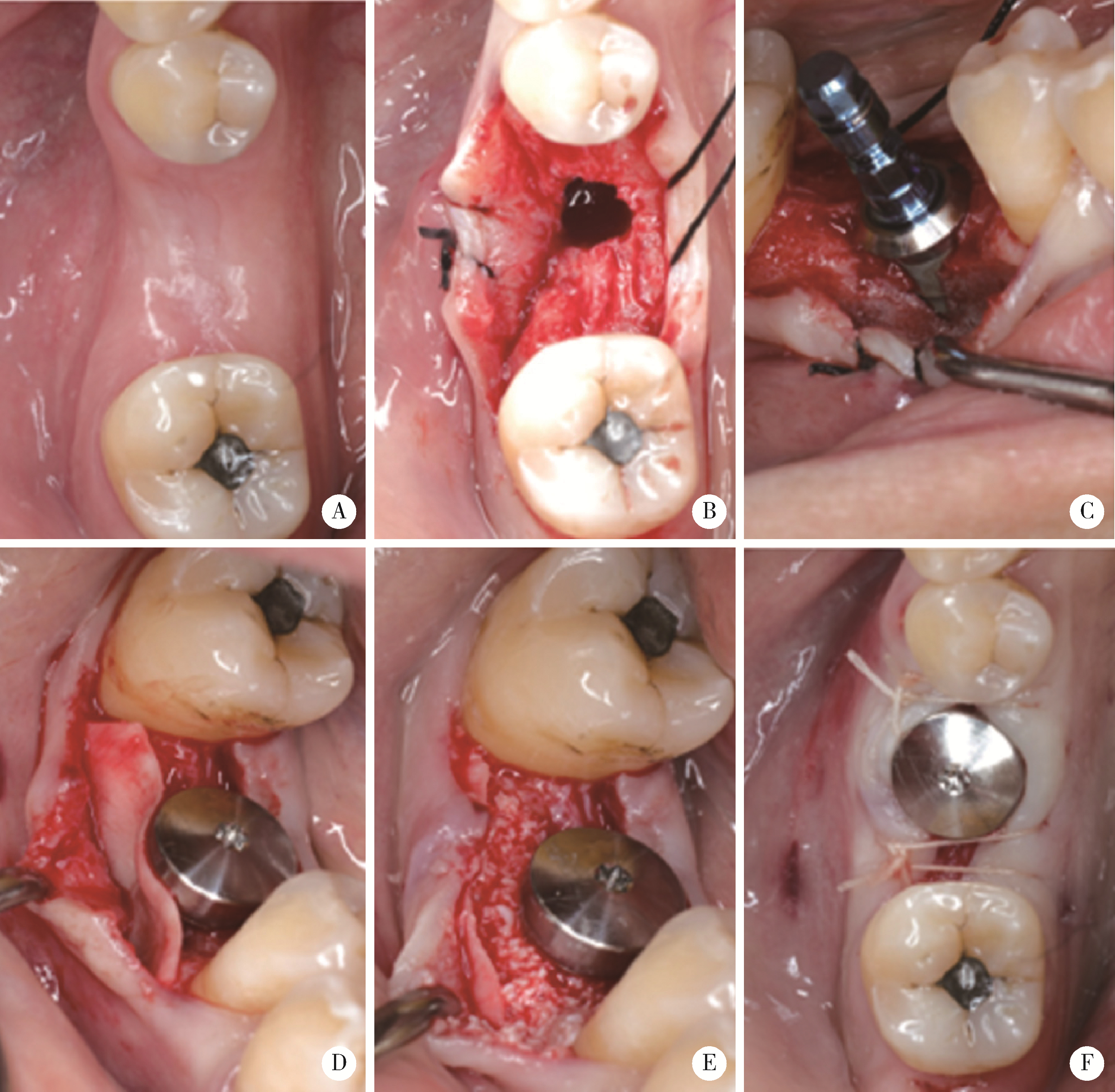
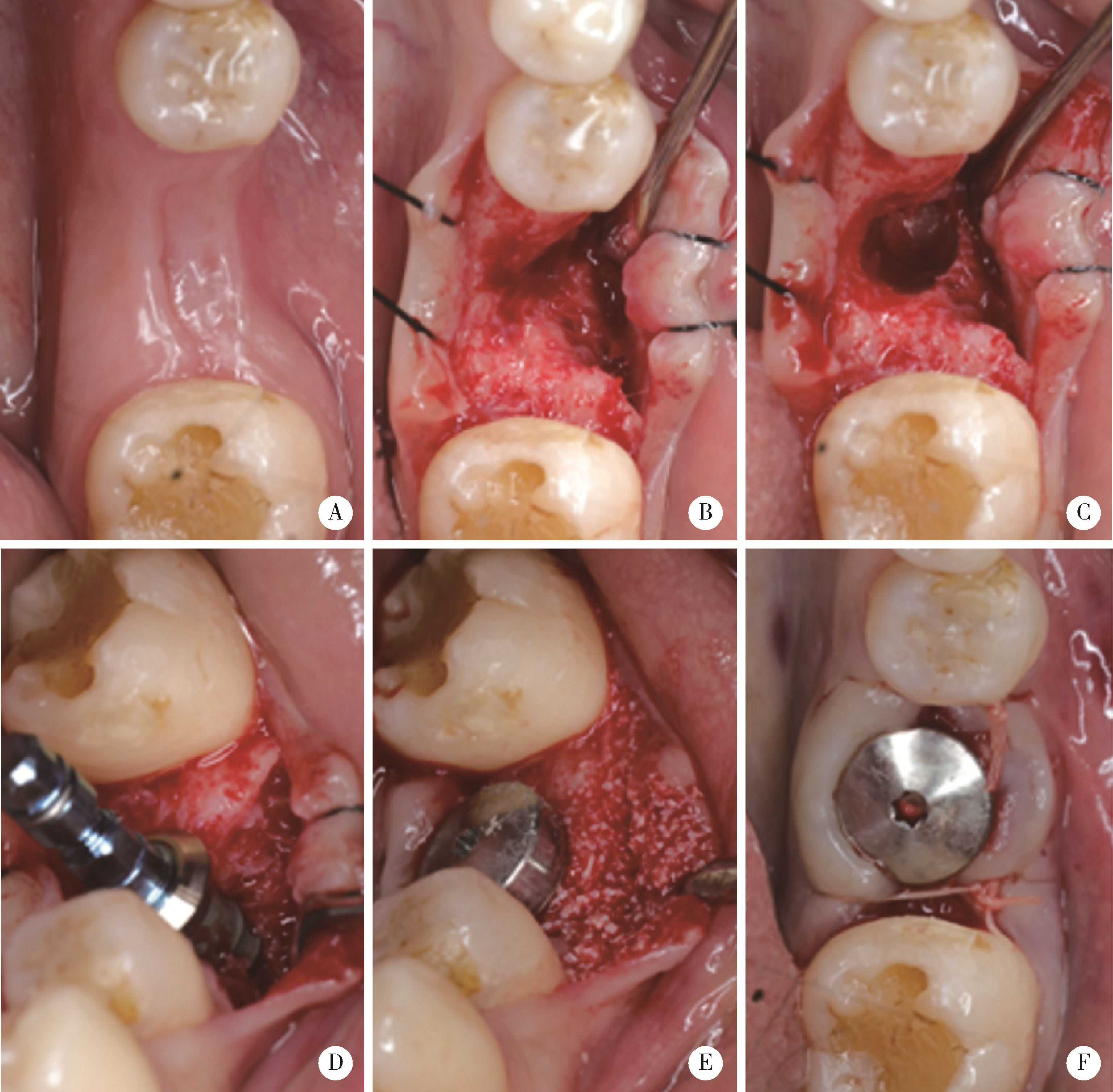
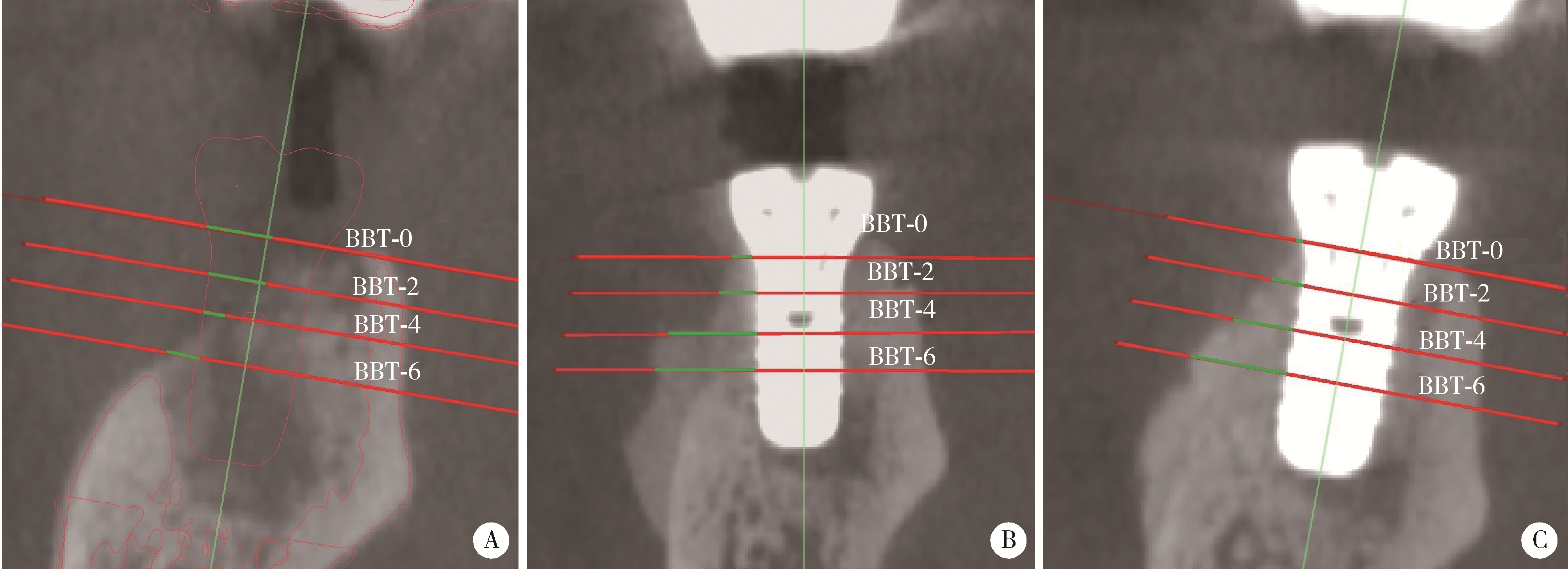
目的: 在颊侧袋形瓣引导性骨再生手术基础上, 探讨放置可吸收胶原膜是否有利于维持术后牙槽嵴轮廓稳定。方法: 收集2019年6月至2023年6月因单颗后牙缺失采用种植体植入同期进行颊侧袋形瓣引导性骨再生手术患者, 根据骨粉表面是否覆盖胶原膜分为胶原膜覆盖组和无覆盖组。术前(T0)、术后即刻(T1)和术后3~7个月(T2)拍摄锥形束CT, 利用Mimics软件测量种植体光滑-粗糙交界面下不同水平(0、2、4和6 mm)处颊侧骨板厚度(thickness of the buccal bone plate, BBT, 分别表示为BBT-0、-2、-4、-6)。结果: 收集胶原膜覆盖组15例, 无胶原膜覆盖组14例, 共计29例患者进行统计分析。在T0、T1和T2三个时间点, 不同水平的BBT在两组间差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。T2时, BBT-0在胶原膜覆盖组和无覆盖组分别为(1.22±0.55) mm和(1.70±0.97) mm, 相应的BBT-2分别为(2.32±0.94) mm和(2.57±1.26) mm。T1~T2愈合阶段不同水平处颊侧骨板吸收的绝对值[(0.47±0.54)~(1.33±0.75) mm]和百分数[(10.04%±24.81%)~(48.43%±18.32%)], 以及T0~T2阶段颊侧骨板新骨形成厚度[(1.27±1.09)~(2.75±2.15) mm]在两组间差异均无统计学意义。结论: 颊侧袋形瓣引导骨再生手术无论是否使用胶原膜均可有效修复种植体颈部颊侧骨缺损。与无胶原膜覆盖相比, 胶原膜覆盖植骨材料不能提高术后牙槽嵴轮廓的稳定性。
中图分类号:
- R782.13
| 1 | Hammerle CH , Jung RE , Feloutzis A . A systematic review of the survival of implants in bone sites augmented with barrier membranes (guided bone regeneration) in partially edentulous patients[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2002, 29 (Suppl 3): 226- 231. |
| 2 | Thoma DS , Bienz SP , Figuero E , et al. Efficacy of lateral bone augmentation performed simultaneously with dental implant placement: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Perio-dontol, 2019, 46 (Suppl 21): 257- 276. |
| 3 |
Jung RE , Fenner N , Hämmerle CH , et al. Long-term outcome of implants placed with guided bone regeneration (GBR) using resorbable and non-resorbable membranes after 12-14 years[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2013, 24 (10): 1065- 1073.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02522.x |
| 4 | Benic GI , Thoma DS , Jung RE , et al. Guided bone regeneration with particulate vs. block xenogenic bone substitutes: A pilot cone beam computed tomographic investigation[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2017, 28 (11): e262- e270. |
| 5 |
Fu JH , Oh TJ , Benavides E , et al. A randomized clinical trial evaluating the efficacy of the sandwich bone augmentation technique in increasing buccal bone thickness during implant placement surgery: Ⅰ. Clinical and radiographic parameters[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2014, 25 (4): 458- 467.
doi: 10.1111/clr.12171 |
| 6 | Ye GH , Duan DH , Wang EB . Ridge volume stability of maxillary anterior implants placed with simultaneous lateral guided bone regeneration during healing: A radiographic analysis[J]. Chin J Dent Res, 2021, 24 (4): 251- 256. |
| 7 |
Wang HL , Boyapati L . "PASS" principles for predictable bone regeneration[J]. Implant Dent, 2006, 15 (1): 8- 17.
doi: 10.1097/01.id.0000204762.39826.0f |
| 8 |
César Neto JB , Cavalcanti MC , Sapata VM , et al. The positive effect of tenting screws for primary horizontal guided bone regeneration: A retrospective study based on cone-beam computed tomography data[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2020, 31 (9): 846- 855.
doi: 10.1111/clr.13630 |
| 9 |
Farias D , Caceres F , Sanz A , et al. Horizontal bone augmentation in the posterior atrophic mandible and dental implant stability using the tenting screw technique[J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 2021, 41 (4): e147- e155.
doi: 10.11607/prd.5137 |
| 10 |
Duan DH , Wang HL , Xiao WC , et al. Bone regeneration using titanium plate stabilization for the treatment of peri-implant bone defects: A retrospective radiologic pilot study[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2022, 24 (6): 792- 800.
doi: 10.1111/cid.13139 |
| 11 |
Ciocca L , Lizio G , Baldissara P , et al. Prosthetically CAD-CAM-guided bone augmentation of atrophic jaws using customized tita-nium mesh: Preliminary results of an open prospective study[J]. J Oral Implantol, 2018, 44 (2): 131- 137.
doi: 10.1563/aaid-joi-D-17-00125 |
| 12 |
Her S , Kang T , Fien MJ . Titanium mesh as an alternative to a membrane for ridge augmentation[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2012, 70 (4): 803- 810.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2011.11.017 |
| 13 |
Lee SR , Jang TS , Seo CS , et al. Hard tissue volume stability effect beyond the bony envelope of a three-dimensional preformed titanium mesh with two different collagen barrier membranes on peri-implant dehiscence defects in the anterior maxilla: A rando-mized clinical trial[J]. Materials (Basel), 2021, 14 (19): 5618.
doi: 10.3390/ma14195618 |
| 14 |
Sumida T , Otawa N , Kamata YU , et al. Custom-made titanium devices as membranes for bone augmentation in implant treatment: Clinical application and the comparison with conventional titanium mesh[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2015, 43 (10): 2183- 2188.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2015.10.020 |
| 15 |
Lin Z , Fateh A , Salem DM , et al. Periosteum: Biology and applications in craniofacial bone regeneration[J]. J Dent Res, 2014, 93 (2): 109- 116.
doi: 10.1177/0022034513506445 |
| 16 | Duan DH , Wang HL , Wang EB . Effect of intact periosteum on alveolar ridge contour stability after horizontal guided bone regene-ration in posterior region: A retrospective and radiographical cohort study[J]. Chin J Dent Res, 2023, 26 (4): 229- 236. |
| 17 |
Deng C , Yi Z , Xiong C , et al. Using the intact periosteum for horizontal bone augmentation of peri-implant defects: A retrospective cohort study[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2022, 60 (10): 1325- 1331.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2022.09.012 |
| 18 |
Dahlin C , Linde A , Gottlow J , et al. Healing of bone defects by guided tissue regeneration[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1988, 81 (5): 672- 676.
doi: 10.1097/00006534-198805000-00004 |
| 19 | Dahlin C , Sennerby L , Lekholm U , et al. Generation of new bone around titanium implants using a membrane technique: An experimental study in rabbits[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 1989, 4 (1): 19- 25. |
| 20 | Becker W , Becker BE , Handlesman M , et al. Bone formation at dehisced dental implant sites treated with implant augmentation material: A pilot study in dogs[J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 1990, 10 (2): 92- 101. |
| 21 |
Louis PJ , Gutta R , Said-Al-Naief N , et al. Reconstruction of the maxilla and mandible with particulate bone graft and titanium mesh for implant placement[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2008, 66 (2): 235- 245.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2007.08.022 |
| 22 |
Atef M , Tarek A , Shaheen M , et al. Horizontal ridge augmentation using native collagen membrane vs titanium mesh in atrophic maxillary ridges: Randomized clinical trial[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2020, 22 (2): 156- 166.
doi: 10.1111/cid.12892 |
| 23 |
Urban IA , Saleh MHA , Ravidà A , et al. Vertical bone augmentation utilizing a titanium-reinforced PTFE mesh: A multi-variate analysis of influencing factors[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2021, 32 (7): 828- 839.
doi: 10.1111/clr.13755 |
| 24 |
Benic GI , Bienz SP , Song YW , et al. Randomized controlled clinical trial comparing guided bone regeneration of peri-implant defects with soft-type block versus particulate bone substitutes: Six-month results of hard-tissue changes[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2022, 49 (5): 480- 495.
doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13606 |
| 25 |
Park SH , Lee KW , Oh TJ , et al. Effect of absorbable membranes on sandwich bone augmentation[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2008, 19 (1): 32- 41.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2007.01408.x |
| 26 |
Spray JR , Black CG , Morris HF , et al. The influence of bone thickness on facial marginal bone response: Stage 1 placement through stage 2 uncovering[J]. Ann Periodontol, 2000, 5 (1): 119- 128.
doi: 10.1902/annals.2000.5.1.119 |
| 27 |
Botticelli D , Berglundh T , Lindhe J . Hard-tissue alterations following immediate implant placement in extraction sites[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2004, 31 (10): 820- 828.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2004.00565.x |
| 28 |
Severi M , Simonelli A , Farina R , et al. Effect of lateral bone augmentation procedures in correcting peri-implant bone dehiscence and fenestration defects: A systematic review and network meta-analysis[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2022, 24 (2): 251- 264.
doi: 10.1111/cid.13078 |
| 29 |
Park JC , Kim CS , Choi SH , et al. Flap extension attained by vertical and periosteal-releasing incisions: A prospective cohort study[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2012, 23 (8): 993- 998.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02244.x |
| 30 |
Monje A , Pons R , Vilarrasa J , et al. Significance of barrier membrane on the reconstructive therapy of peri-implantitis: A rando-mized controlled trial[J]. J Periodontol, 2023, 94 (3): 323- 335.
doi: 10.1002/JPER.22-0511 |
| [1] | 凌晓彤,屈留洋,郑丹妮,杨静,闫雪冰,柳登高,高岩. 牙源性钙化囊肿与牙源性钙化上皮瘤的三维影像特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [2] | 刘晓强,周寅. 牙种植同期植骨术围术期高血压的相关危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 93-98. |
| [3] | 杨刚,胡文杰,曹洁,柳登高. 牙周健康的上颌前牙唇侧嵴顶上牙龈的三维形态分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 990-994. |
| [4] | 尤鹏越,刘玉华,王新知,王思雯,唐琳. 脱细胞猪心包膜生物相容性及成骨性能的体内外评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 776-784. |
| [5] | 王思雯,尤鹏越,刘玉华,王新知,唐琳,王梅. 两种可吸收生物膜联合去蛋白牛骨基质植入犬拔牙窝成骨的影像学评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 364-370. |
| [6] | 高璐,谷岩. 中国人群腭中缝形态特点分期与Demirjian牙龄的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 133-138. |
| [7] | 释栋,曹婕,戴世爱,孟焕新. 植体周炎再生治疗短期疗效观察[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 58-63. |
| [8] | 宫玮玉,刘绍清,董艳梅,高学军,陈晓峰. 纳米生物活性玻璃促进兔颅骨临界骨缺损修复[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 42-48. |
| [9] | 贾鹏程,杨刚,胡文杰,赵一姣,刘木清. 根尖片评估单根牙骨内牙根表面积的准确性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 91-97. |
| [10] | 马静,江久汇. 骨性Ⅱ类和Ⅲ类高角错牙合患者下切牙区的牙槽骨形态分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 98-103. |
| [11] | 徐筱,徐莉,江久汇,吴佳琪,李小彤,靖无迪. 锥形束CT评判安氏Ⅲ类错牙合上前牙骨开裂与骨开窗的准确性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 104-109. |
| [12] | 曹婕1,孟焕新. 锥形束CT用于评估牙槽骨骨缺损的情况和骨再生区域骨密度的变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 110-116. |
| [13] | 常大桐,周彦恒,刘伟涛. 上颌反复快速扩缩对上气道影响的锥束CT研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 685-690. |
| [14] | 陈全,张晓1张智勇,高巍,刘文曙,孟甜,陈宇寰,王慧丽. 上颌窦前外侧壁骨内血管孔道位置锥形束CT影像判断分析及其临床应对措施[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(3): 540-546. |
| [15] | 赵一姣,王斯维,刘怡,王勇. 基于影像学牙周膜解剖特征快速提取活体牙三维牙根形态的方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 54-059. |
|
||