北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1111-1117. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.024
伴神经精神系统病变的系统性红斑狼疮相关巨噬细胞活化综合征2例
- 华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院风湿免疫科, 武汉 430022
Systemic lupus erythematosus associated macrophage activation syndrome with neuropsychiatric symptoms: A report of 2 cases
Zhi-jun LUO,Jia-jia WU,You SONG,Chun-li MEI,Rong DU*( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China
摘要:
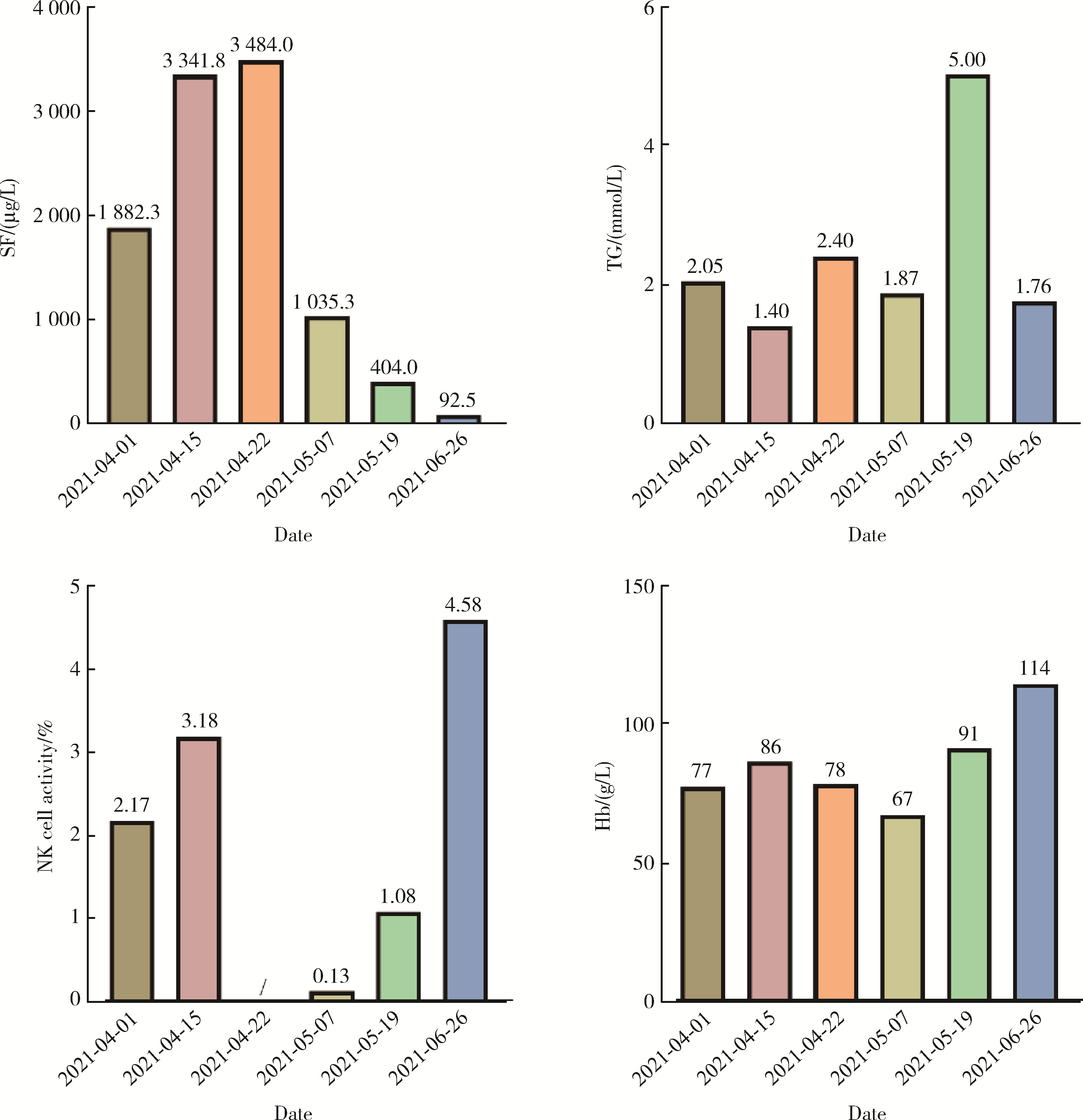
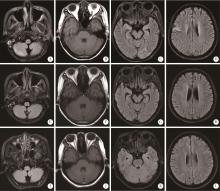
系统性红斑狼疮(systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE)相关巨噬细胞活化综合征(macrophage activation syndrome, MAS)属于临床重症疾病, 病死率较高, 伴发神经精神症状少见, 在诊治过程中, 需积极判断患者出现的神经精神症状是由狼疮脑病(neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus, NPSLE)还是由巨噬细胞活化综合征引起。本研究回顾性分析2例就诊于华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院风湿免疫科伴神经精神系统病变的系统性红斑狼疮相关巨噬细胞活化综合征患者的临床资料。病例1为30岁女性, 2019年无诱因出现明显脱发, 伴消瘦、乏力、口干, 2021年3月腿软无力摔倒, 随后无明显诱因出现发热伴寒战, 完善相关检查后诊断为"系统性红斑狼疮", 给予激素、抗感染等对症治疗, 患者仍发热, 完善检查提示中度贫血, 铁蛋白升高, 甘油三酯升高, NK淋巴细胞活性减低, 穿孔素阳性率为4.27%, 诊断"噬血细胞综合征前期"; 2021年5月患者出现精神恍惚, 胡言乱语, 完善相关检查后诊断为"系统性红斑狼疮合并巨噬细胞活化综合征", 予甲泼尼龙、抗感染、改善精神状态等治疗后, 患者体温正常, 神经精神症状好转。病例2为30岁女性, 2019年6月出现颜面部鼻翼两侧蝶形红斑, 颈部数个红斑, 伴脱发、口腔溃疡、发热, 完善相关检查后诊断为"系统性红斑狼疮", 给予甲泼尼龙、静脉滴注人免疫球蛋白等治疗后病情缓解, 2019年10月患者出现神清淡漠, 无嗜睡, 并再次出现发热, 同时伴有头晕、呕吐, 完善相关检查提示中度贫血、NK淋巴细胞活性减低、甘油三酯升高、铁蛋白升高, 考虑诊断为"系统性红斑狼疮、狼疮脑病、巨噬细胞活化综合征", 予激素、静脉滴注人免疫球蛋白、抗感染、利妥昔单抗(美罗华)治疗, 患者病情好转出院, 出院后规律口服甲泼尼龙片, 精神症状仍间断发作; 2019年11月出现发热、躁狂、谵妄等精神症状, 后转为淡漠状态, 给予甲泼尼龙静脉滴注, 奥氮平片(再普乐)口服, 精神症状好转后给予利妥昔单抗治疗, 后因反复感染更换为贝利尤单抗, 在2021年3月患者精神异常症状恢复。通过分析临床症状、影像学检查、实验室检查、治疗经过及其效果, 推测病例1的神经精神症状由巨噬细胞活化综合征引起可能性大, 病例2的神经精神症状由系统性红斑狼疮引起可能性大。目前对两者的鉴别还缺乏直接的实验室依据, 可以通过临床表现、影像学表现、脑脊液检测、患者对治疗的反应来综合判断出现神经精神症状的病因, 本研究的2个病例最终取得较好的预后, 与对本病的早期诊断、治疗、干预密切相关。
中图分类号:
- R593.241
| 1 |
中国医师协会血液科医师分会, 中华医学会儿科学分会血液学组, 噬血细胞综合征中国专家联盟. 中国噬血细胞综合征诊断与治疗指南(2022年版)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2022, 102 (20): 1492- 1499.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20220310-00488 |
| 2 | 王迁, 王旖旎, 王嫱, 等. 风湿性疾病相关噬血细胞综合征诊疗规范[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2023, 62 (1): 23- 30. |
| 3 |
Pastula DM , Burish M , Reis GF , et al. Adult-onset central nervous system hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: A case report[J]. BMC Neurol, 2015, 15 (1): 203.
doi: 10.1186/s12883-015-0470-6 |
| 4 |
Li J , Wang Q , Zheng W , et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Clinical analysis of 103 adult patients[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2014, 93 (2): 100- 105.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000022 |
| 5 |
Wang J , Tuo H , Wu L , et al. Neurological symptoms of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 2[J]. J Integr Neurosci, 2020, 19 (1): 131- 135.
doi: 10.31083/j.jin.2020.01.1250 |
| 6 |
Zhao YZ , Zhang Q , Li ZG , et al. Central nervous system involvement in 179 chinese children with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2018, 131 (15): 1786- 1792.
doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.237409 |
| 7 |
Shyu S , Luca D , Vandenbussche CJ , et al. Cytomorphologic features found in cerebrospinal fluid specimens of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis patients[J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 2021, 156 (3): 381- 390.
doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa248 |
| 8 |
孟广强, 王晶石, 吴林, 等. 干燥综合征相关噬血细胞性淋巴组织细胞增多症伴中枢神经系统病变一例[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2021, 25 (11): 758- 760.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn141217-20201113-00408 |
| 9 |
Popescu A , Kao AH . Neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Curr Neuropharmacol, 2011, 9 (3): 449- 457.
doi: 10.2174/157015911796557984 |
| 10 |
Hanly JG , Kozora E , Beyea SD , et al. Nervous system disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: Current status and future directions[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2019, 71 (1): 33- 42.
doi: 10.1002/art.40591 |
| 11 | The American College of Rheumatology nomenclature and case definitions for neuropsychiatric lupus syndromes [J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1999, 42(4): 599-608. |
| 12 |
Bertsias GK , Ioannidis JP , Aringer M , et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus with neuropsychiatric manifestations: Report of a task force of the EULAR standing committee for clinical affairs[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2010, 69 (12): 2074- 2082.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.130476 |
| 13 |
Fanouriakis A , Kostopoulou M , Alunno A , et al. 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2019, 78 (6): 736- 745.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215089 |
| 14 |
Farinha F , Abrol E , Isenberg DA . Biologic therapies in patients with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Lupus, 2016, 25 (11): 1278- 1279.
doi: 10.1177/0961203316631636 |
| 15 | 张清, 周惠琼, 郭娟, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮合并噬血细胞综合征、狼疮脑病、弥漫性肺泡出血及消化道出血一例救治体会[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98 (1): 63- 64. |
| 16 | 许书添, 董建华, 李世军. 系统性红斑狼疮合并噬血细胞综合征[J]. 肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志, 2019, 28 (3): 293- 297. |
| 17 | Yamaguchi M , Mizuno M , Kitamura F , et al. Case report: Thrombotic microangiopathy concomitant with macrophage activation syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus refractory to conventional treatment successfully treated with eculizumab[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2022, 9, 1097528. |
| [1] | 武志慧, 胡明智, 赵巧英, 吕凤凤, 张晶莹, 张伟, 王永福, 孙晓林, 王慧. miR-125b-5p修饰脐带间充质干细胞对系统性红斑狼疮的免疫调控机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [2] | 乔佳佳,田聪,黄晓波,刘军. 肾结石合并系统性红斑狼疮行经皮肾镜碎石取石术的安全性和有效性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 745-749. |
| [3] | 任立敏,赵楚楚,赵义,周惠琼,张莉芸,王友莲,沈凌汛,范文强,李洋,厉小梅,王吉波,程永静,彭嘉婧,赵晓珍,邵苗,李茹. 系统性红斑狼疮低疾病活动度及缓解状况的真实世界研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 273-278. |
| [4] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [5] | 赵祥格,刘佳庆,黄会娜,陆智敏,白自然,李霞,祁荆荆. 干扰素-α介导系统性红斑狼疮外周血CD56dimCD57+自然杀伤细胞功能的损伤[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 975-981. |
| [6] | 邢晓燕,张筠肖,朱冯赟智,王一帆,周新尧,李玉慧. 皮肌炎合并巨噬细胞活化综合征5例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1214-1218. |
| [7] | 邵苗,郭惠芳,雷玲彦,赵清,丁艳杰,林进,吴锐,于峰,李玉翠,苗华丽,张莉芸,杜燕,焦瑞英,庞丽霞,龙丽,栗占国,李茹. 短间期小剂量环磷酰胺治疗系统性红斑狼疮耐受性的多中心对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1112-1116. |
| [8] | 李敏,侯林卿,金月波,何菁. 系统性红斑狼疮合并视网膜病变的临床及免疫学特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1106-1111. |
| [9] | 张琳崎,赵静,王红彦,王宗沂,李英妮,汤稷旸,李思莹,曲进锋,赵明威. 抗ENO1抗体与狼疮性视网膜病变的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1099-1105. |
| [10] | 邹健梅,武丽君,罗采南,石亚妹,吴雪. 血清25-羟维生素D与系统性红斑狼疮活动的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 938-941. |
| [11] | 高伟波,石茂静,张海燕,吴春波,朱继红. 显著高铁蛋白血症与噬血细胞性淋巴组织细胞增多症的相互关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 921-927. |
| [12] | 夏芳芳,鲁芙爱,吕慧敏,杨国安,刘媛. 系统性红斑狼疮伴间质性肺炎的临床特点及相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 266-272. |
| [13] | 贾园,栗占国. 成人巨噬细胞活化综合征诊断困境和个体化治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 991-994. |
| [14] | 耿研,李伯睿,张卓莉. 系统性红斑狼疮患者有症状关节病变的肌肉骨骼超声特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 163-168. |
| [15] | 王玉华,张国华,张令令,罗俊丽,高兰. 系统性红斑狼疮合并自发性肾上腺出血1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1178-1181. |
|
||