北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 966-974. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.003
系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标
姚海红1,杨帆1,2,唐素玫1,张霞1,何菁1,贾园1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科, 北京 100044
2. 首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院风湿内科, 北京 100050
Clinical characteristics and diagnostic indicators of macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still's disease
Hai-hong YAO1,Fan YANG1,2,Su-mei TANG1,Xia ZHANG1,Jing HE1,Yuan JIA1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Rheumatology, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China
摘要:
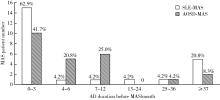
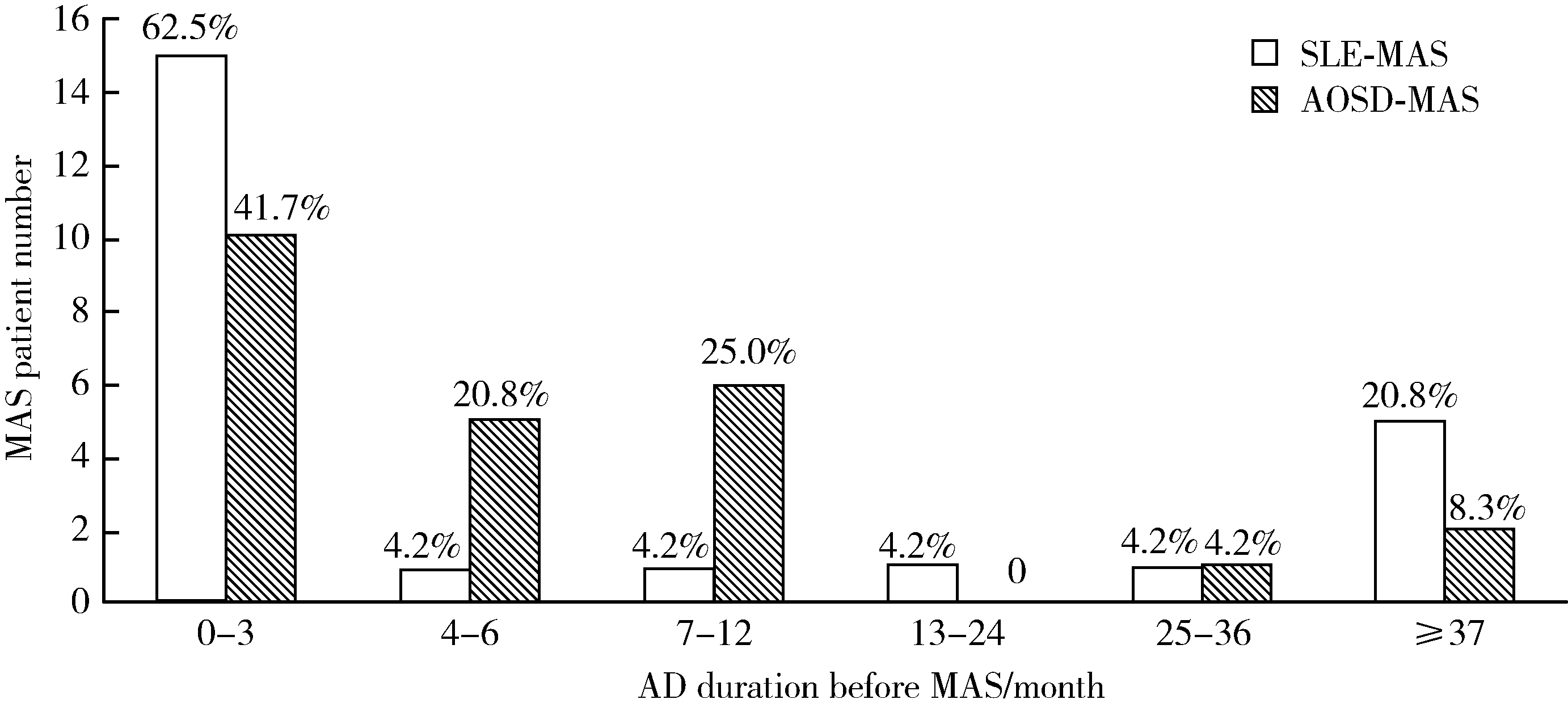
目的: 分析和比较系统性红斑狼疮(systemic lupus erythematosus,SLE)和成人Still病(adult-onset Still’s disease,AOSD)合并巨噬细胞活化综合征(macrophage activation syndrome,MAS)患者的临床及实验室指标特点,评估已有的2016年欧洲抗风湿病联盟/美国风湿病学会/儿童风湿病国际试验组织发布的全身型幼年特发性关节炎(systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis,sJIA)合并MAS(sJIA-MAS)分类标准在不同自身免疫病背景下的适用情况, 并提出新的诊断预测指标,为提高MAS早期诊断率、改善患者预后提供参考。方法: 回顾性分析2000—2018年在北京大学人民医院住院的24例SLE合并MAS患者和24例AOSD合并MAS患者的临床及实验室数据,分别与同期未发生MAS的50例SLE及50例AOSD患者进行比较,通过受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线确定预测MAS的实验室指标截断值。进一步使用实验室诊断预测值对2016年sJIA-MAS分类标准进行改进,探讨改进后的标准对于AOSD合并MAS的适用性。结果: 约60%的SLE合并MAS及40%的AOSD合并MAS患者发生在原发病确诊后的3个月内。发热是MAS最常见的临床表现。实验室指标除了2004年国际组织细胞学会修订的噬血细胞综合征诊断标准中的指标外,MAS患者的天冬氨酸转氨酶及乳酸脱氢酶也显著升高,白蛋白显著下降,噬血现象仅见于约50%的MAS患者。ROC曲线分析显示,当SLE患者铁蛋白≥1 010 μg/L、乳酸脱氢酶≥359 U/L,AOSD患者纤维蛋白原≤225.5 mg/dL、甘油三酯≥2.0 mmol/L时,对MAS诊断有最好的区分价值。将2016年sJIA-MAS分类标准应用于AOSD合并MAS,诊断的敏感性和特异性分别为100%和62%,对其中特异性低的铁蛋白和纤维蛋白原条目进行改进,诊断特异性可升高为86%。结论: SLE合并MAS及AOSD合并MAS最常发生于疾病确诊后的早期,不同疾病继发MAS因受自身免疫病特点的影响而在实验室指标方面存在明显差异,以同一标准进行MAS诊断可能导致误诊或漏诊。2016年sJIA-MAS分类标准在AOSD合并MAS诊断中敏感性高而特异性低,对之进行改进可提高特异性。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| 1 |
Ravelli A , Minoia F , Davi S , et al. 2016 classification criteria for macrophage activation syndrome complicating systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology/Paediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organisation Collaborative Initiative[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2016, 75 (3): 481- 489.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208982 |
| 2 |
Henter JI , Horne A , Arico M , et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis[J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2007, 48 (2): 124- 131.
doi: 10.1002/pbc.21039 |
| 3 | Hochberg MC . Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1997, 40 (9): 1725. |
| 4 |
Petri M , Orbai AM , Alarcon GS , et al. Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2012, 64 (8): 2677- 2686.
doi: 10.1002/art.34473 |
| 5 | Yamaguchi M , Ohta A , Tsunematsu T , et al. Preliminary criteria for classification of adult Still's disease[J]. J Rheumatol, 1992, 19 (3): 424- 430. |
| 6 |
Vardiman JW , Harris NL , Brunning RD . The World Health Organization (WHO) classification of the myeloid neoplasms[J]. Blood, 2002, 100 (7): 2292- 2302.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-04-1199 |
| 7 |
Swerdlow SH , Campo E , Pileri SA , et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms[J]. Blood, 2016, 127 (20): 2375- 2390.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-01-643569 |
| 8 |
Crayne CB , Albeituni S , Nichols KE , et al. The immunology of macrophage activation syndrome[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10, 119.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00119 |
| 9 |
Lenert A , Oh G , Ombrello MJ , et al. Clinical characteristics and comorbidities in adult-onset Still's disease using a large US administrative claims database[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2020, 59 (7): 1725- 1733.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez622 |
| 10 |
Ramos-Casals M , Brito-Zeron P , Lopez-Guillermo A , et al. Adult haemophagocytic syndrome[J]. Lancet, 2014, 383 (9927): 1503- 1516.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61048-X |
| 11 |
姚海红, 王旖旎, 张霞, 等. 67例成人巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特征及治疗转归[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51 (6): 996- 1002.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.003 |
| 12 |
Liu AC , Yang Y , Li MT , et al. Macrophage activation syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus: A multicenter, case-control study in China[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2018, 37 (1): 93- 100.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3625-6 |
| 13 |
Kumakura S , Murakawa Y . Clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes of autoimmune-associated hemophagocytic syndrome in adults[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2014, 66 (8): 2297- 2307.
doi: 10.1002/art.38672 |
| 14 |
Sen ES , Clarke SL , Ramanan AV . Macrophage activation syndrome[J]. Indian J Pediatr, 2016, 83 (3): 248- 253.
doi: 10.1007/s12098-015-1877-1 |
| 15 |
Knovich MA , Storey JA , Coffman LG , et al. Ferritin for the clinician[J]. Blood Rev, 2009, 23 (3): 95- 104.
doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2008.08.001 |
| 16 |
Ravelli A , Minoia F , Davi S , et al. Expert consensus on dynamics of laboratory tests for diagnosis of macrophage activation syndrome complicating systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis[J]. RMD Open, 2016, 2 (1): e000161.
doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2015-000161 |
| 17 |
Gao Q , Yuan Y , Wang Y , et al. Clinical characteristics of macrophage activation syndrome in adult-onset Still's disease[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2021, 39 (5): 59- 66.
doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/lp2u7g |
| 18 | Yang XP , Wang M , Li TF , et al. Predictive factors and prognosis of macrophage activation syndrome associated with adult-onset Still's disease[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2019, 37 (6): 83- 88. |
| 19 |
Wang R , Li T , Ye S , et al. Macrophage activation syndrome associated with adult-onset Still's disease: A multicenter retrospective analysis[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2020, 39 (8): 2379- 2386.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-04949-0 |
| 20 |
Di Benedetto P , Cipriani P , Iacono D , et al. Ferritin and C-reactive protein are predictive biomarkers of mortality and macrophage activation syndrome in adult onset Still's disease. Analysis of the multicentre Gruppo Italiano di Ricerca in Reumatologia Clinica e Sperimentale (GIRRCS) cohort[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15 (7): e0235326.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235326 |
| 21 |
Lehmberg K , McClain KL , Janka GE , et al. Determination of an appropriate cut-off value for ferritin in the diagnosis of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis[J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2014, 61 (11): 2101- 2103.
doi: 10.1002/pbc.25058 |
| 22 |
Minoia F , Davi S , Horne A , et al. Clinical features, treatment, and outcome of macrophage activation syndrome complicating systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A multinational, multicenter study of 362 patients[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2014, 66 (11): 3160- 3169.
doi: 10.1002/art.38802 |
| 23 |
Gauvin F , Toledano B , Champagne J , et al. Reactive hemophagocytic syndrome presenting as a component of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome[J]. Crit Care Med, 2000, 28 (9): 3341- 3345.
doi: 10.1097/00003246-200009000-00038 |
| 24 |
Wiwanitkit V . Bone marrow leishmaniasis: A review of situation in Thailand[J]. Asian Pac J Trop Med, 2011, 4 (10): 757- 759.
doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(11)60188-0 |
| 25 |
刘燕鹰, 周姝含, 张莉, 等. 噬血细胞综合征77例临床分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2015, 95 (9): 681- 684.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2015.09.011 |
| 26 |
Shimizu M , Mizuta M , Yasumi T , et al. Validation of classification criteria of macrophage activation syndrome in Japanese patients with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis[J]. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken), 2018, 70 (9): 1412- 1415.
doi: 10.1002/acr.23482 |
| 27 |
Tada Y , Inokuchi S , Maruyama A , et al. Are the 2016 EULAR/ACR/PRINTO classification criteria for macrophage activation syndrome applicable to patients with adult-onset Still's disease?[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2019, 39 (1): 97- 104.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-018-4114-1 |
| 28 |
Bae CB , Jung JY , Kim HA , et al. Reactive hemophagocytic syndrome in adult-onset Still disease clinical features, predictive factors, and prognosis in 21 patients[J]. Medicine, 2015, 94 (4): e451.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000451 |
| 29 |
Hot A , Toh ML , Coppere B , et al. Reactive hemophagocytic syndrome in adult-onset Still disease clinical features and long-term outcome: A case-control study of 8 patients[J]. Medicine, 2010, 89 (1): 37- 46.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0b013e3181caf100 |
| 30 |
Lin SJ , Chao HC , Yan DC . Different articular outcomes of Still's disease in Chinese children and adults[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2000, 19 (2): 127- 130.
doi: 10.1007/s100670050030 |
| [1] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | 钟华, 李原, 徐丽玲, 白明欣, 苏茵. 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [3] | 武志慧, 胡明智, 赵巧英, 吕凤凤, 张晶莹, 张伟, 王永福, 孙晓林, 王慧. miR-125b-5p修饰脐带间充质干细胞对系统性红斑狼疮的免疫调控机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [4] | 李正芳,罗采南,武丽君,吴雪,孟新艳,陈晓梅,石亚妹,钟岩. 抗氨基甲酰化蛋白抗体在诊断类风湿关节炎中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [5] | 乔佳佳,田聪,黄晓波,刘军. 肾结石合并系统性红斑狼疮行经皮肾镜碎石取石术的安全性和有效性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 745-749. |
| [6] | 任立敏,赵楚楚,赵义,周惠琼,张莉芸,王友莲,沈凌汛,范文强,李洋,厉小梅,王吉波,程永静,彭嘉婧,赵晓珍,邵苗,李茹. 系统性红斑狼疮低疾病活动度及缓解状况的真实世界研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 273-278. |
| [7] | 罗芷筠,吴佳佳,宋优,梅春丽,杜戎. 伴神经精神系统病变的系统性红斑狼疮相关巨噬细胞活化综合征2例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1111-1117. |
| [8] | 赵祥格,刘佳庆,黄会娜,陆智敏,白自然,李霞,祁荆荆. 干扰素-α介导系统性红斑狼疮外周血CD56dimCD57+自然杀伤细胞功能的损伤[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 975-981. |
| [9] | 熊焰,李鑫,梁丽,李东,鄢丽敏,李雪迎,邸吉廷,李挺. 甲状腺粗针穿刺活检病理诊断的准确性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 234-242. |
| [10] | 哈雪梅,姚永正,孙莉华,辛春杨,熊焰. 实性肺胎盘样变形1例及文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [11] | 宁博涵,张青霞,杨慧,董颖. 伴间质细胞增生、玻璃样变性及索状结构的子宫内膜样腺癌1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 366-369. |
| [12] | 陈适,刘田. 重视系统性血管炎的早期识别和个体化治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1065-1067. |
| [13] | 张琳崎,赵静,王红彦,王宗沂,李英妮,汤稷旸,李思莹,曲进锋,赵明威. 抗ENO1抗体与狼疮性视网膜病变的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1099-1105. |
| [14] | 李敏,侯林卿,金月波,何菁. 系统性红斑狼疮合并视网膜病变的临床及免疫学特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1106-1111. |
| [15] | 邵苗,郭惠芳,雷玲彦,赵清,丁艳杰,林进,吴锐,于峰,李玉翠,苗华丽,张莉芸,杜燕,焦瑞英,庞丽霞,龙丽,栗占国,李茹. 短间期小剂量环磷酰胺治疗系统性红斑狼疮耐受性的多中心对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1112-1116. |
|
||