北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 575-581. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.04.005
靶向穿刺联合区域系统穿刺对PI-RADS 4~5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能
- 北京大学第一医院泌尿外科,北京大学泌尿外科研究所,泌尿生殖系疾病(男)分子诊治北京市重点实验室,国家泌尿男生殖系肿瘤中心,北京 100034
Diagnostic efficacy of targeted biopsy combined with regional systematic biopsy in prostate cancer in patients with PI-RADS 4-5
Kaifeng YAO,Mingjian RUAN,Derun LI,Yuxuan TIAN,Yuke CHEN,Yu FAN,Yi LIU*( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital; Institution of Urology, Peking University; Beijing Key Laboratory of Urogenital Diseases (Male) Molecular Diagnosis and Treatment Center; National Urological Cancer Center, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
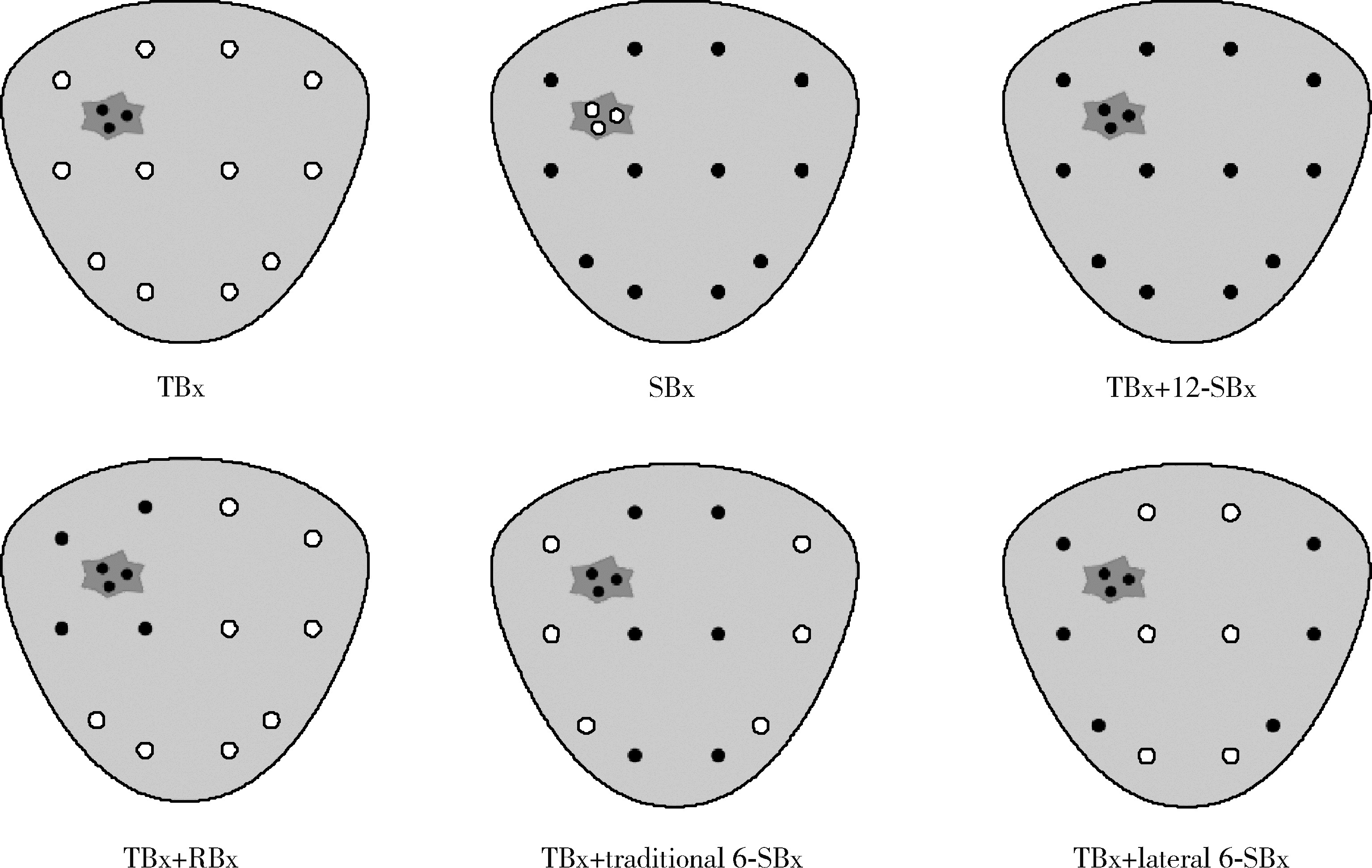
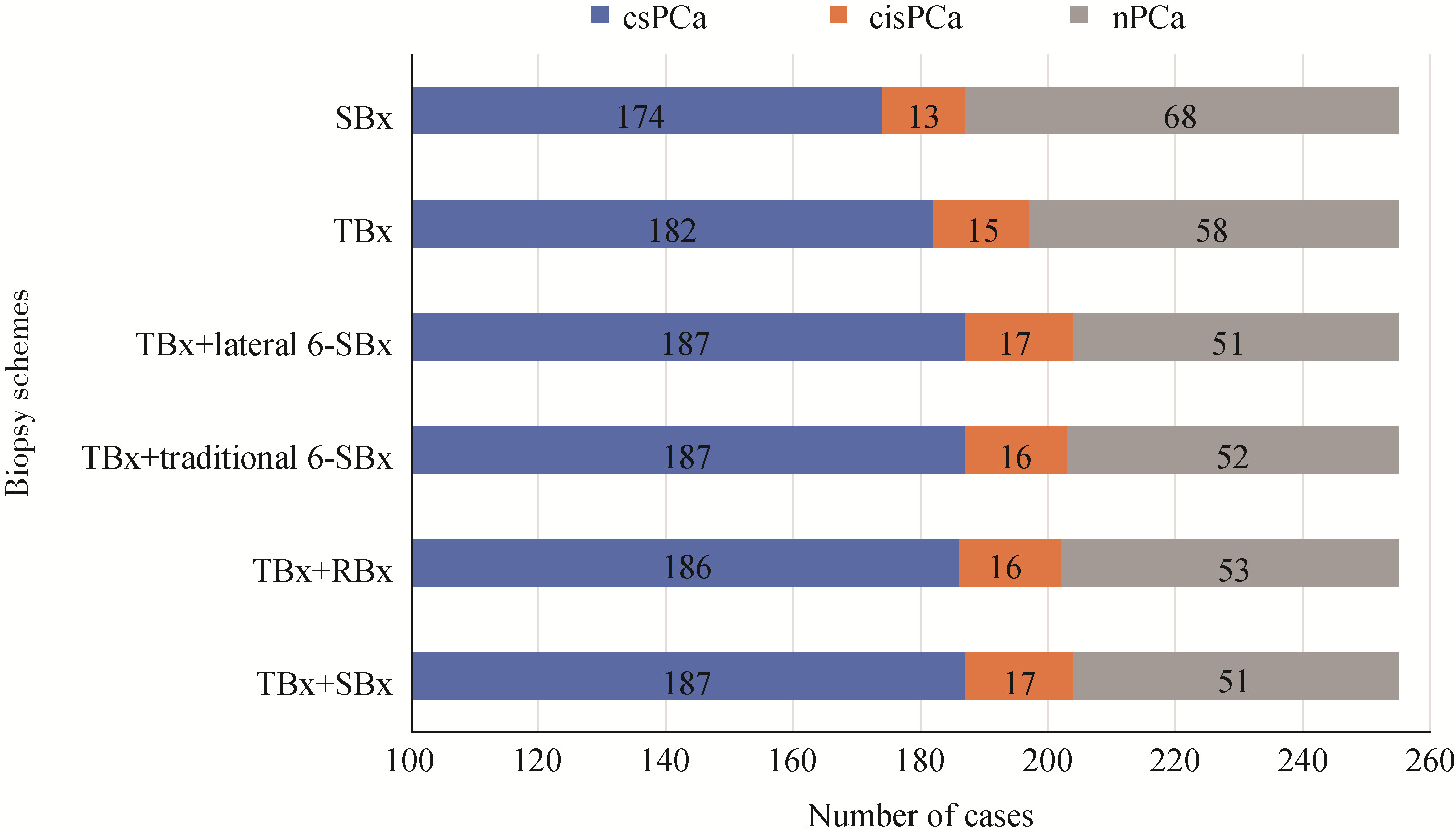
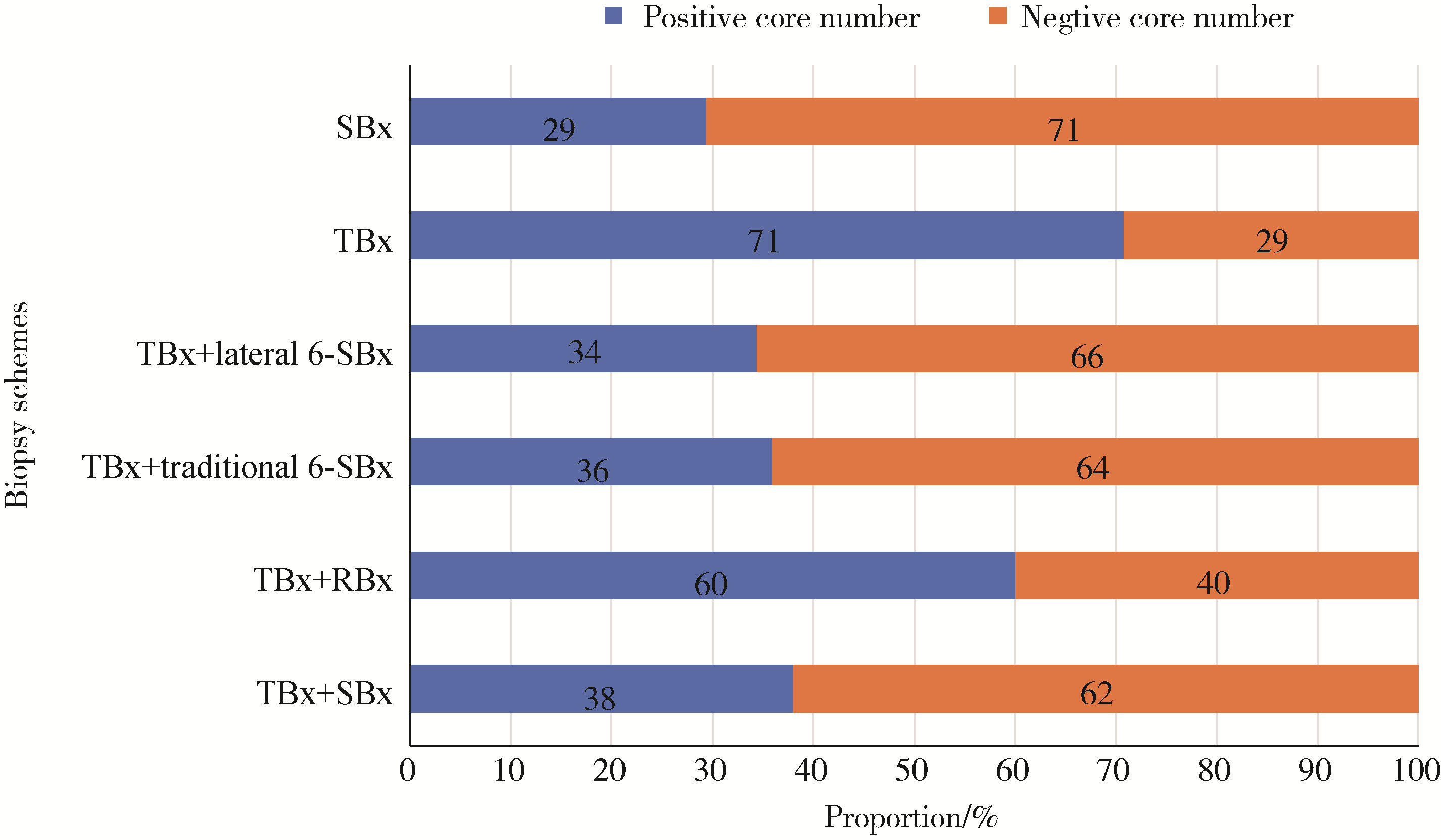
目的: 探讨靶向穿刺联合区域系统穿刺对前列腺影像和数据评分系统2.1版本(prostate imaging reporting and data system,PI-RADS v2.1)4~5分患者的前列腺癌(prostate cancer,PCa)诊断效能。方法: 前瞻性收集2023年1—10月于北京大学第一医院初次行前列腺穿刺活检, 总前列腺特异性抗原(total prostate specific antigen,tPSA)≤20 ng/mL且磁共振检查PI-RADS 4~5分的患者,行经直肠认知融合靶向穿刺(3针)和系统穿刺(12针),选取不同穿刺位点定义多种假设穿刺方案, 比较靶向穿刺联合区域系统穿刺与其他穿刺方案对PCa检出效果的差异。结果: 共纳入255例患者,其中检出前列腺腺癌204例(80.0%),临床有意义前列腺癌(clinically significant prostate cancer,csPCa)187例(73.3%)。靶向穿刺的PCa检出率显著低于靶向穿刺联合12针系统穿刺(77.3% vs. 80.0%,P=0.016),漏诊患者中71.4%(5/7)为csPCa;靶向穿刺联合4针区域系统穿刺与联合12针系统穿刺相比,检出率差异无统计学意义(P>0.999),漏诊csPCa及临床无意义前列腺癌(clinically insignificant prostate can-cer,cisPCa)各1例。靶向穿刺联合区域系统穿刺与联合外侧或传统6分区系统穿刺相比具有更少穿刺针数及更高的阳性针数占比。靶向穿刺漏诊与病灶最大径相关(OR=0.086,95%CI:0.013~0.562,P=0.010)。对于PI-RADS 5分患者,单纯靶向穿刺在122例中仅漏诊1例PCa;对于PI-RADS 4分患者,单纯靶向穿刺在133例中漏诊6例PCa,靶向穿刺联合区域系统穿刺漏诊csPCa及cisPCa各1例。结论: 靶向穿刺联合区域系统穿刺在PI-RADS评分为4~5分患者中具有较高诊断效能,可作为目前靶向穿刺联合12针系统穿刺的改良方案之一。对于PI-RADS 5分患者单纯靶向穿刺同样可行。
中图分类号:
- R737.25
| 1 | 黄健, 王建业, 孔垂泽. 中国泌尿外科和男科疾病诊断治疗指南(2019版)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020: 115- 131. |
| 2 |
Turkbey B , Rosenkrantz AB , Haider MA , et al. Prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2.1: 2019 update of prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2[J]. Eur Urol, 2019, 76 (3): 340- 351.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.02.033 |
| 3 |
Mottet N , van den Bergh RCN , Briers E , et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer: 2020 update. Part 1: Screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent[J]. Eur Urol, 2021, 79 (2): 243- 262.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.09.042 |
| 4 |
Hagens MJ , Noordzij MA , Mazel JW , et al. An magnetic resonance imaging-directed targeted-plus-perilesional biopsy approach for prostate cancer diagnosis: "Less is more"[J]. Eur Urol Open Sci, 2022, 43, 68- 73.
doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2022.07.006 |
| 5 | Freifeld Y , Xi Y , Passoni N , et al. Optimal sampling scheme in men with abnormal multiparametric MRI undergoing MRI-TRUS fusion prostate biopsy[J]. Urol Oncol, 2018, 37 (1): 57- 62. |
| 6 |
Raman AG , Sarma KV , Raman SS , et al. Optimizing spatial biopsy sampling for the detection of prostate cancer[J]. J Urol, 2021, 206 (3): 595- 603.
doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001832 |
| 7 |
Hagens MJ , Salamanca MF , Padhani AR , et al. Diagnostic performance of a magnetic resonance imaging-directed targeted plus regional biopsy approach in prostate cancer diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Euro Urol Open Sci, 2022, 40, 95- 103.
doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2022.04.001 |
| 8 |
Caverly TJ , Hayward RA , Reamer E , et al. Presentation of benefits and harms in US cancer screening and prevention guidelines: Systematic review[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2016, 108 (6): djv436.
doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv436 |
| 9 |
何为, 全晶, 张琦, 等. 影像融合靶向穿刺、系统穿刺以及联合穿刺诊断前列腺癌的差异[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 42 (8): 581- 585.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20210628-00346 |
| 10 |
刘禹, 高杰, 汪维, 等. 靶向穿刺与靶向联合系统穿刺对前列腺PI-RADS评分4~5分患者的诊断效能比较[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 42 (3): 192- 196.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20200722-00553 |
| 11 |
Kasivisvanathan V , Rannikko AS , Borghi M , et al. MRI-targeted or standard biopsy for prostate-cancer diagnosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 378 (19): 1767- 1777.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1801993 |
| 12 |
Rouvière O , Puech P , Renard-Penna R , et al. Use of prostate systematic and targeted biopsy on the basis of multiparametric MRI in biopsy-naive patients (MRI-FIRST): A prospective, multicentre, paired diagnostic study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2019, 20 (1): 100- 109.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30569-2 |
| 13 |
Schoots IG , Roobol MJ , Nieboer D , et al. Magnetic resonance imaging-targeted biopsy may enhance the diagnostic accuracy of significant prostate cancer detection compared to standard trans-rectal ultrasound-guided biopsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur Urol, 2015, 68 (3): 438- 450.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.11.037 |
| 14 |
梁玲辉, 承逸飞, 夏炜, 等. MRI-TRUS融合靶向前列腺活检中的靶区针数最优化研究[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 43 (11): 850- 854.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20210108-00012 |
| 15 |
涂祥, 熊性宇, 张驰宸, 等. 6针系统穿刺联合3针磁共振引导靶向穿刺对前列腺癌的检出效果[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 43 (12): 914- 919.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20211005-00526 |
| 16 |
Bryk DJ , Llukani E , Taneja S , et al. The role of ipsilateral and contralateral transrectal ultrasound-guided systematic prostate biopsy in men with unilateral magnetic resonance imaging lesion undergoing magnetic resonance imaging-ultrasound fusion-targeted prostate biopsy[J]. Urology, 2017, 102, 178- 182.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2016.11.017 |
| 17 | 刘毅, 袁昌巍, 吴静云, 等. 靶向穿刺+6针系统穿刺对PI-RADS 5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55 (5): 812- 817. |
| 18 | Cornford P, Tilki D, van den Bergh RCN, et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-ISUP-SIOG Guidelines on prostate cancer: Diagnostic evaluation [R/OL]. (2024-04) [2024-05-06]. https://uroweb.org/guidelines/prostate-cancer/chapter/diagnostic-evaluation. |
| 19 |
Klingebiel M , Arsov C , Ullrich T , et al. Reasons for missing cli-nically significant prostate cancer by targeted magnetic resonance imaging/ultrasound fusion-guided biopsy[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2021, 137, 109587.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.109587 |
| 20 |
Feuer Z , Meng X , Rosenkrantz AB , et al. Application of the PRECISION trial biopsy strategy to a contemporary magnetic resonance imaging-targeted biopsy cohort: How many clinically significant prostate cancers are missed?[J]. J Urol, 2021, 205 (3): 740- 747.
doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001406 |
| 21 | Le Nobin J , Orczyk C , Deng FM , et al. Prostate tumour volumes: Evaluation of the agreement between magnetic resonance imaging and histology using novel co-registration software[J]. BJU Int, 2014, 114 (6b): E105- E112. |
| 22 | Franklin A , Gianduzzo T , Yaxley J , et al. Use of a trizonal schema to assess targeting accuracy in prostatic fusion biopsy[J]. BJU Int, 2020, 126 (Suppl 1): 6- 11. |
| 23 |
Aslim EJ , Law YXT , Fook-Chong SMC , et al. Defining prostate cancer size and treatment margin for focal therapy: Does intra-lesional heterogeneity impact the performance of multiparametric MRI?[J]. BJU Int, 2021, 128 (2): 178- 186.
doi: 10.1111/bju.15355 |
| 24 |
Priester A , Natarajan S , Khoshnoodi P , et al. Magnetic resonance imaging underestimation of prostate cancer geometry: Use of patient specific molds to correlate images with whole mount pathology[J]. J Urol, 2017, 197 (2): 320- 326.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2016.07.084 |
| 25 |
Brisbane WG , Priester AM , Ballon J , et al. Targeted prostate biopsy: Umbra, penumbra, and value of perilesional sampling[J]. Eur Urol, 2022, 82 (3): 303- 310.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2022.01.008 |
| 26 |
Novara G , Zattoni F , Zecchini G , et al. Role of targeted biopsy, perilesional biopsy, and random biopsy in prostate cancer diagnosis by mpMRI/transrectal ultrasonography fusion biopsy[J]. World J Urol, 2023, 41 (11): 3239- 3247.
doi: 10.1007/s00345-023-04382-3 |
| 27 | Jiang X, Chen M, Tian J, et al. Comparison of regional saturation biopsy, targeted biopsy, and systematic biopsy in patients with prostate-specific antigen levels of 4-20 ng/mL: A prospective, single-center, randomized controlled trial [J/OL]. Eur Urol Oncol, (2023-12-28) [2024-01-19]. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2023.12.002. |
| [1] | 李志存, 吴天俣, 梁磊, 范宇, 孟一森, 张骞. 穿刺活检单针阳性前列腺癌术后病理升级的危险因素分析及列线图模型构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | 田宇轩,阮明健,刘毅,李德润,吴静云,沈棋,范宇,金杰. 双参数MRI改良PI-RADS评分4分和5分病灶的最大径对临床有意义前列腺癌的预测效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [3] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [4] | 薛蔚,董樑,钱宏阳,费笑晨. 前列腺癌新辅助治疗与辅助治疗的现状及进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 775-780. |
| [5] | 刘毅,袁昌巍,吴静云,沈棋,肖江喜,赵峥,王霄英,李学松,何志嵩,周利群. 靶向穿刺+6针系统穿刺对PI-RADS 5分患者的前列腺癌诊断效能[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [6] | 毛海,张帆,张展奕,颜野,郝一昌,黄毅,马潞林,褚红玲,张树栋. 基于MRI前列腺腺体相关参数构建腹腔镜前列腺癌术后尿失禁的预测模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 818-824. |
| [7] | 袁昌巍,李德润,李志华,刘毅,山刚志,李学松,周利群. 多参数磁共振成像中动态对比增强状态在诊断PI-RADS 4分前列腺癌中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [8] | 田聪,刘军,杨波,乔佳佳,黄晓波,许清泉. 经皮肾镜取石术中异常肾盂黏膜活检结果分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 948-952. |
| [9] | 郑丹枫,李君禹,李佳曦,张英爽,钟延丰,于淼. 青少年特发性脊柱侧凸椎旁肌的病理特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 283-291. |
| [10] | 刘毅,刘志坚,沈棋,吴静云,范宇,李德润,虞巍,何志嵩. 14例恶性潜能未定的前列腺间质肿瘤病例分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 621-624. |
| [11] | 郝一昌,颜野,张帆,邱敏,周朗,刘可,卢剑,肖春雷,黄毅,刘承,马潞林. 穿刺活检单针阳性的前列腺癌手术策略选择及经验总结[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 625-631. |
| [12] | 颜野,夏海缀,李旭升,何为,朱学华,张智荧,肖春雷,刘余庆,黄华,何良华,卢剑. 基于U型卷积神经网络学习的前列腺癌影像重建模型在手术导航中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(3): 596-601. |
| [13] | 张帆,肖春雷,张树栋,黄毅,马潞林. 前列腺体积及前列腺突入膀胱长度与腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术后控尿功能恢复的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 621-625. |
| [14] | 毕永祥,肖民辉,张宁南,李晓云,毛晓鹏,张科,章卓睿,赵良运. 小鼠不同部位体内前列腺癌骨转移模型的建立及方法改进[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 590-596. |
| [15] | 张玉祥,蒙学兵,姚林,张崔建,宋刚,蔡林,张争,李学松,龚侃,李淑清,山刚志,何群,杨新宇,何志嵩,周利群. 单中心14年B超引导下经皮肾肿物穿刺活检经验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 617-621. |
|
||