北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 1047-1051. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.06.016
全自动EasyNAT核酸快速检测系统检测石蜡包埋组织诊断结核病的临床价值
- 首都医科大学附属北京胸科医院/北京市结核病胸部肿瘤研究所病理科,耐药结核病研究北京市重点实验室,北京 101149
Clinical value of automated EasyNAT system for the diagnosis of tuberculosis in paraffin-embedded tissues
Jialu CHE, Zichen LIU, Kun LI, Chen ZHANG, Nanying CHE*( )
)
- Department of Pathology, Beijing Key Laboratory for Drug Resistant Tuberculosis Research, Beijing Chest Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing Tuberculosis and Thoracic Tumor Research Institute, Beijing 101149, China
摘要:
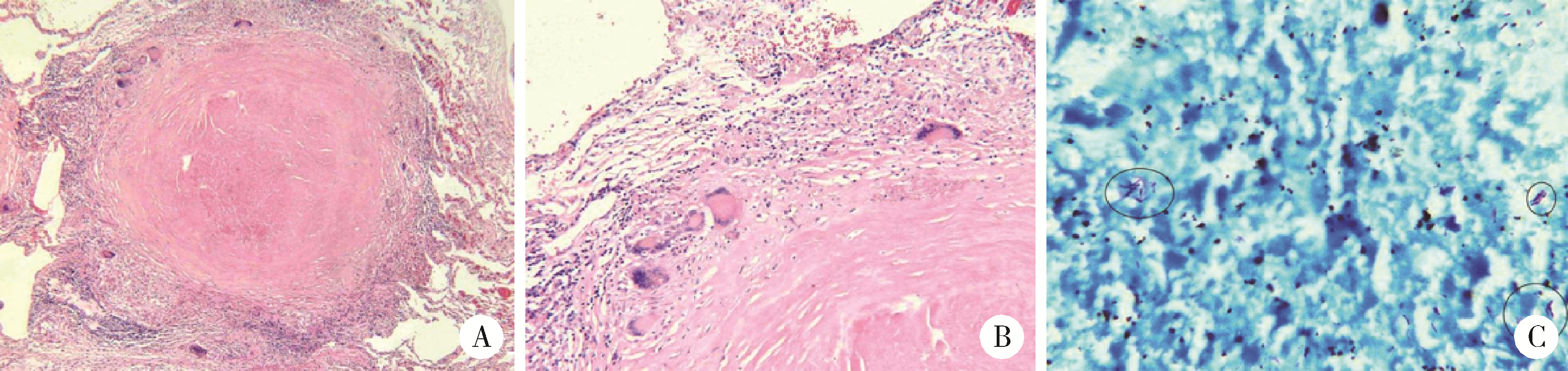
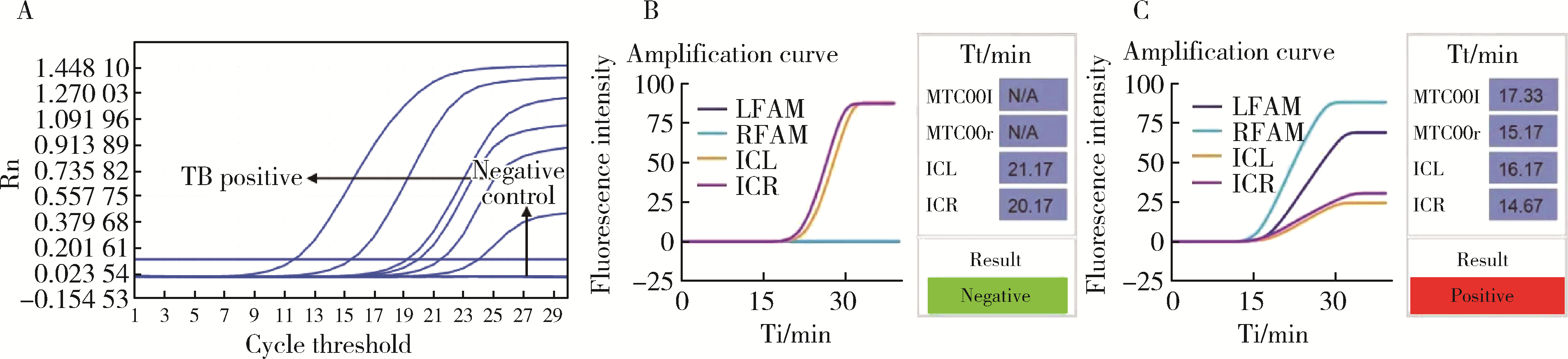
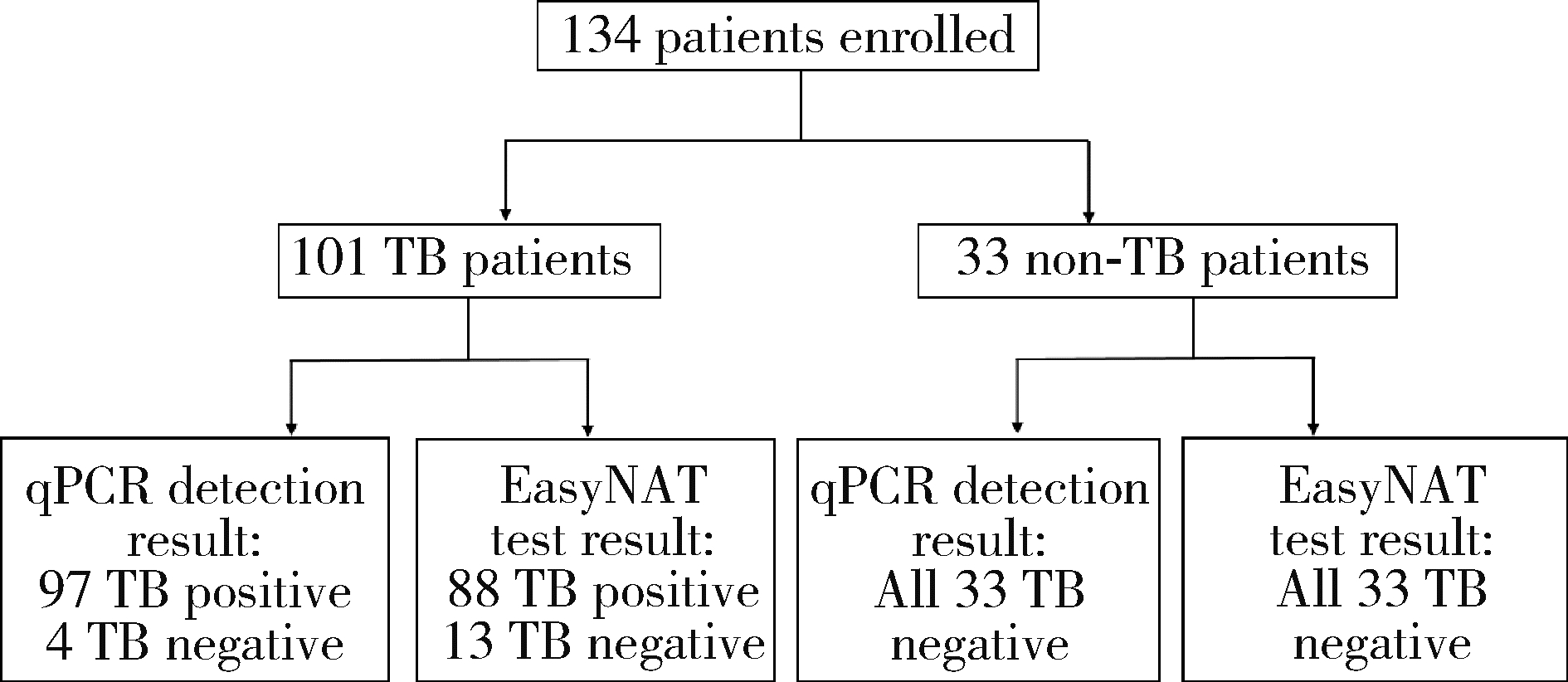
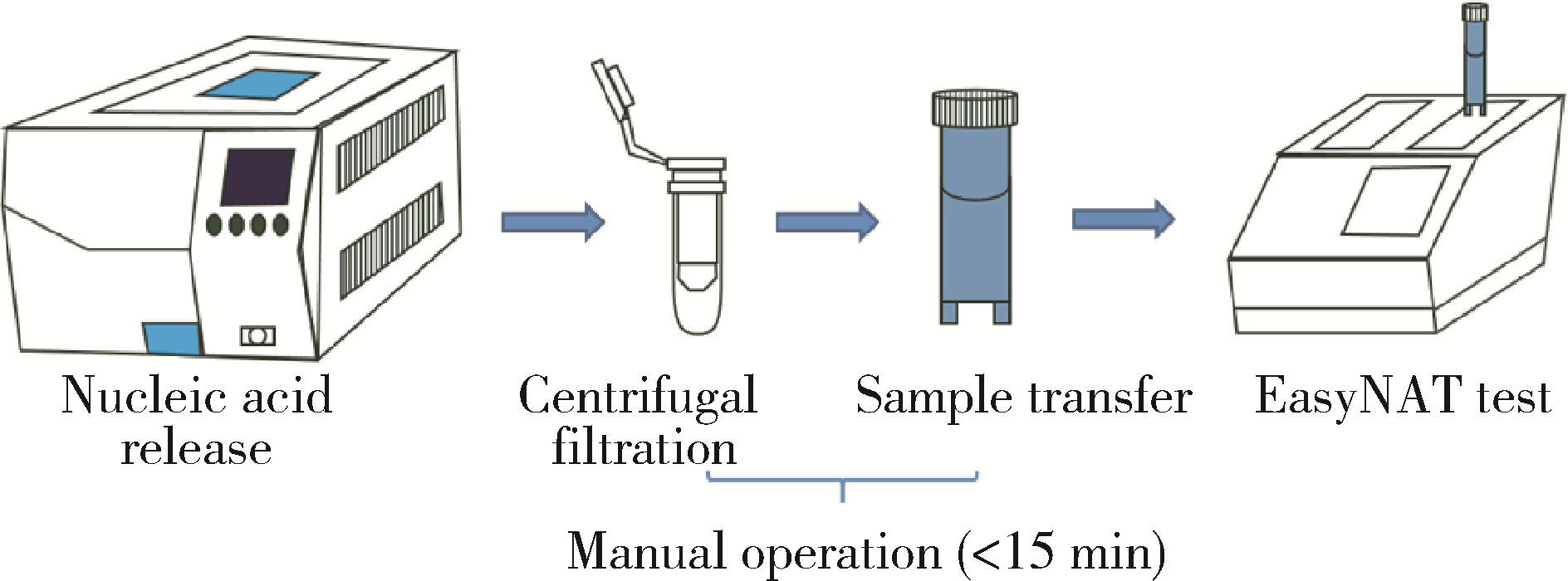
目的: 评估自动化EasyNAT核酸快速检测系统检测石蜡包埋组织诊断结核病的准确性。方法: 选择首都医科大学附属北京胸科医院2018年至2022年患者的病例资料进行回顾性分析,连续纳入134例患者,包括结核病确诊患者101例,非结核患者33例。以临床诊断结果为参考标准,分析EasyNAT核酸快速检测系统应用于石蜡包埋组织诊断结核病的敏感性、特异性、阳性预测值、阴性预测值和准确率。结果: EasyNAT核酸快速检测系统应用于石蜡包埋组织诊断结核病的敏感性为87.1%(88/101,95% CI:79.2%~92.3%),特异性为100.0%(33/33,95%CI:89.6%~100.0%),阳性预测值为100.0%(88/88,95%CI:95.8%~100.0%),阴性预测值为71.7%(33/46,95%CI:57.5%~82.7%),准确率为90.3%(121/134,95%CI:84.1%~94.2%)。与实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction,qPCR)技术检测结果的一致性检验Kappa值为0.84。对肺结核的检出率为86.4%(38/44,95%CI:73.3%~ 93.6%),肺外结核的检出率为87.7%(50/57,95% CI:76.8%~93.9%),与qPCR对应的检测结果比较差异均无统计学意义(P均>0.05)。而EasyNAT检测集核酸提取、扩增和分析于一体,与传统qPCR法相比,手工操作时间缩短了2 h,总检测时间缩短了3 h。结论: EasyNAT核酸快速检测系统可以快速、便捷、准确地检测出石蜡包埋组织中的结核分枝杆菌DNA,对于病理学诊断结核病具有良好的应用价值。
中图分类号:
- R52
| 1 | Global tuberculosis report 2021(EB/OL). [2022-08-01]. https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/t-reports/global-tuberculosis-report-2021. |
| 2 | 中国结核病病理学诊断专家共识[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2017, 40(6): 419-425. |
| 3 | Suárez I , Fnger SM , Kröger S , et al.The diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis[J].Dtsch Arztebl Int,2019,116(43):729-735. |
| 4 | 中华医学会结核病学分会临床检验专业委员会.结核病病原学分子诊断专家共识[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志,2018,41(9):8. |
| 5 | 中国医疗保健国际交流促进会临床微生物与感染分会, 中华医学会检验医学分会临床微生物学组, 中华医学会微生物学和免疫学分会临床微生物学组.综合医院结核分枝杆菌感染实验室检查共识[J].中华检验医学杂志,2022,45(4):343-353. |
| 6 | 罗春英, 王建东, 王璇, 等.荧光定量聚合酶链反应检测石蜡包埋组织结核杆菌的应用价值[J].中华病理学杂志,2012,41(8):562-563. |
| 7 | 郝颖华, 罗森源, 汤显斌.即时荧光定量PCR法对石蜡包埋组织中结核杆菌的检测价值探究[J].中华病理学杂志,2020,49(10):1068-1070. |
| 8 |
Zhang Z , Du J , Liu T , et al.EasyNAT MTC assay: A simple, rapid, and low-cost cross-priming amplification method for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis suitable for point-of-care testing[J].Emerg Microbes Infect,2021,10(1):1530-1535.
doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1959271 |
| 9 | Fang R , Li X , Hu L , et al.Cross-priming amplification for rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum specimens[J].J Clin Microbiol,2009,47(3):845-847. |
| 10 | 朱岩昆, 王宇, 靳晓伟, 等.交叉引物核酸恒温扩增技术在基层实验室诊断肺结核的应用价值[J].中国防痨杂志,2016,38(10):813-817. |
| 11 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 结核病分类: WS196—2017[S/OL]. (2017-12-04)[2022-09-01]. http://www.sohu.com/a/208488734.771405. |
| 12 | 肺结核诊断: WS 288—2017[J]. 中国感染控制杂志, 2018, 17(7): 642-652. |
| 13 | 叶丰, 陈昱, 何度, 等.应用荧光定量聚合酶链反应对疑似结核组织的DNA分析[J].中华病理学杂志,2013,42(8):534-537. |
| 14 | 方木通, 杨倩婷, 王仲元, 等.病理组织中的病原学检查对结核病的诊断价值[J].中华传染病杂志,2021,39(2):92-96. |
| [1] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | 钟华, 李原, 徐丽玲, 白明欣, 苏茵. 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [3] | 李正芳,罗采南,武丽君,吴雪,孟新艳,陈晓梅,石亚妹,钟岩. 抗氨基甲酰化蛋白抗体在诊断类风湿关节炎中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [4] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [5] | 李挺. 建设当代临床病理学科[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 197-200. |
| [6] | 熊焰,李鑫,梁丽,李东,鄢丽敏,李雪迎,邸吉廷,李挺. 甲状腺粗针穿刺活检病理诊断的准确性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 234-242. |
| [7] | 哈雪梅,姚永正,孙莉华,辛春杨,熊焰. 实性肺胎盘样变形1例及文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [8] | 宁博涵,张青霞,杨慧,董颖. 伴间质细胞增生、玻璃样变性及索状结构的子宫内膜样腺癌1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 366-369. |
| [9] | 陈适,刘田. 重视系统性血管炎的早期识别和个体化治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1065-1067. |
| [10] | 曹瑞洁,姚中强,焦朋清,崔立刚. 不同分类标准对中国大动脉炎的诊断效能比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1128-1133. |
| [11] | 徐朝焰,林长艺,叶达梅,吴培埕,宋明辉,刘有添,邓琼,黄雪艳,范忠晓,游雪兰. 感染性关节炎诊断分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1234-1237. |
| [12] | 郝哲,岳蜀华,周利群. 拉曼技术在泌尿系统肿瘤检测中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 779-784. |
| [13] | 于博,赵扬玉,张喆,王永清. 妊娠合并感染性心内膜炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 578-580. |
| [14] | 孟广艳,张筠肖,张渝昕,刘燕鹰. IgG4相关性疾病中枢神经系统受累的临床特点分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1043-1048. |
| [15] | 翟莉,邱楠,宋惠. 多中心网状组织细胞增生症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1183-1187. |
|
||