北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 1089-1096. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.06.023
2型糖尿病对口腔鳞状细胞癌患者预后的影响
毛雅晴1, 陈震1, 于尧1, 章文博1, 刘洋2,*( ), 彭歆1,*(
), 彭歆1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔颌面外科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔黏膜科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on the prognosis of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma
Yaqing MAO1, Zhen CHEN1, Yao YU1, Wenbo ZHANG1, Yang LIU2,*( ), Xin PENG1,*(
), Xin PENG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Oral Medicine, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
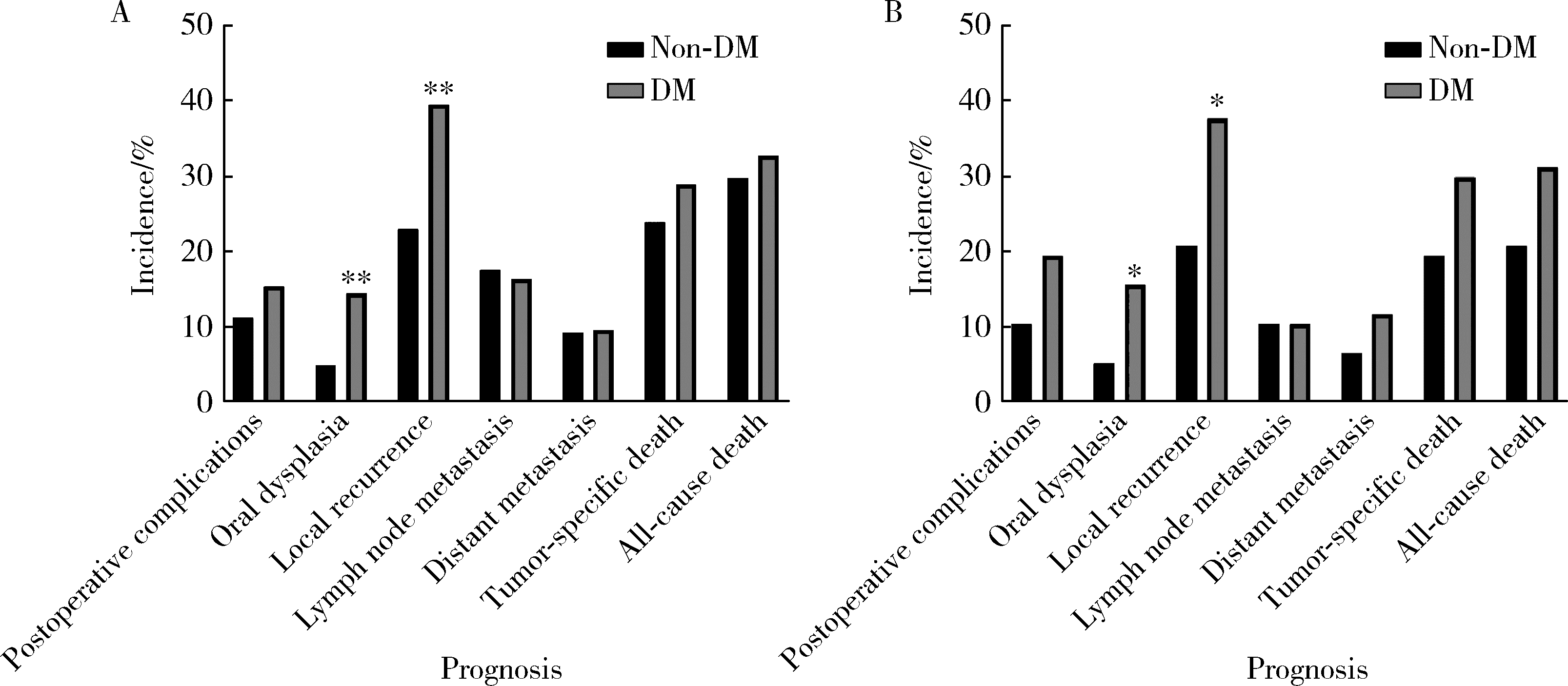
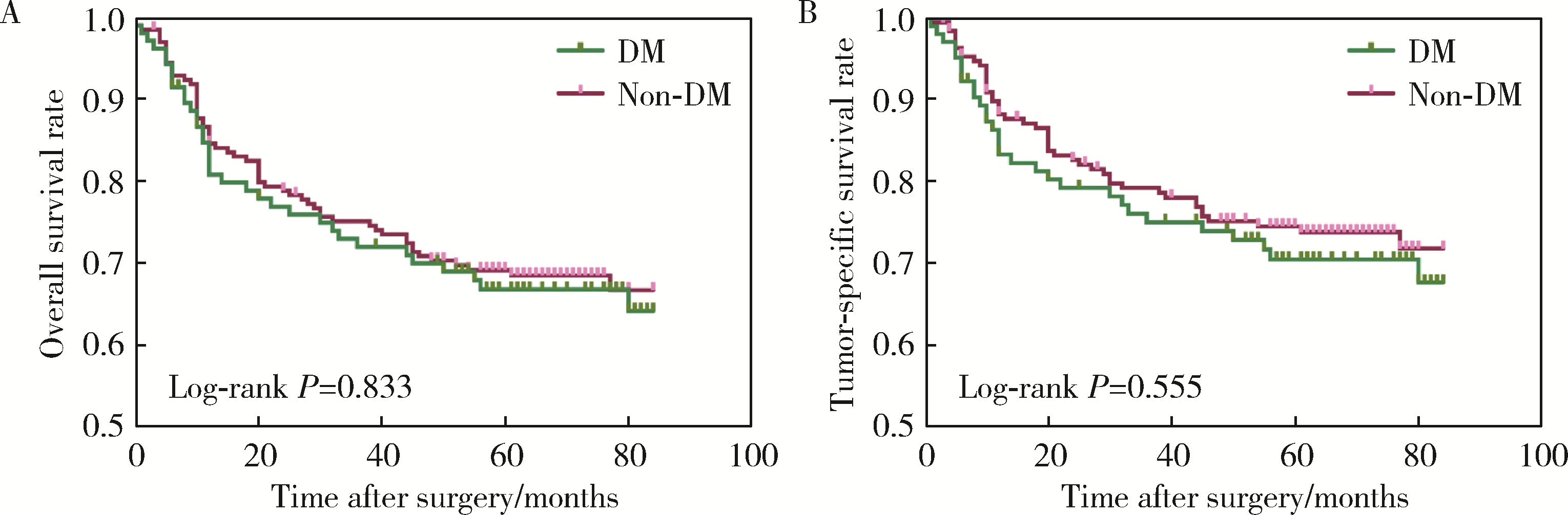
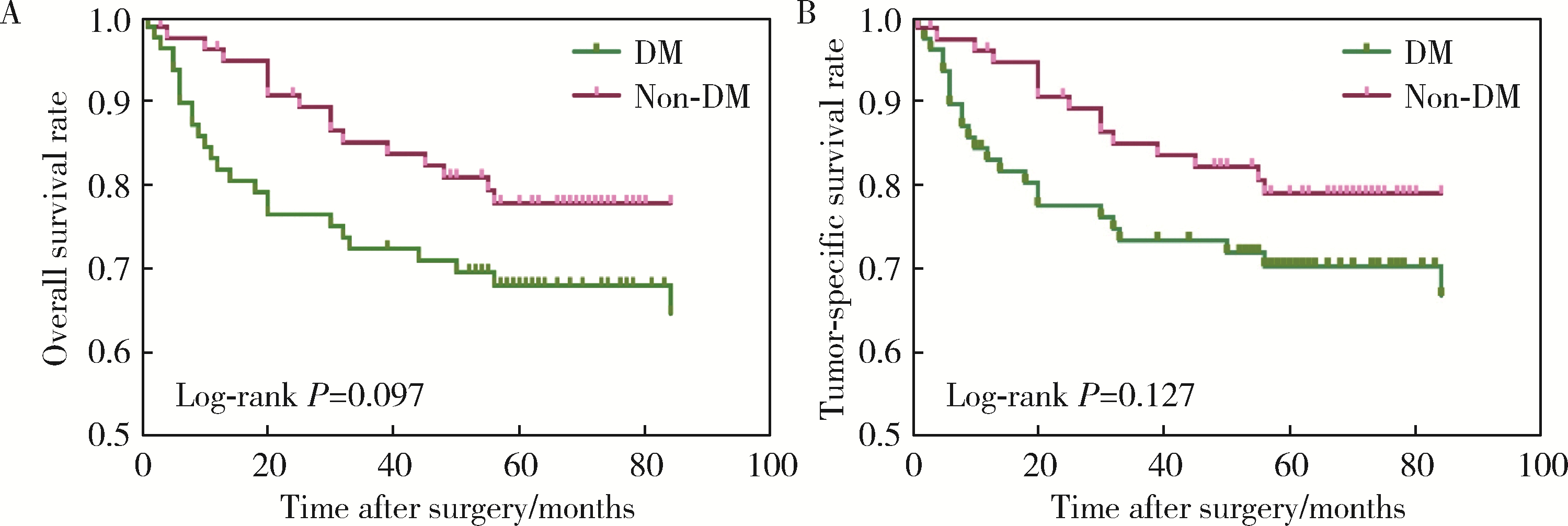
目的: 分析合并2型糖尿病(diabetes mellitus, DM)对罹患口腔鳞状细胞癌(oral squamous cell carcinoma, OSCC)的患者预后的影响。方法: 回顾性分析2014年1月至2017年12月间北京大学口腔医院口腔颌面外科收治的309例OSCC患者的临床病理资料,其中DM组104例,无DM组205例,对患者的基本临床资料和预后情况进行总结分析,利用倾向评分匹配(propensity score matching, PSM)方法均衡两组的组间协变量,采用Kaplan-Meier方法计算两组患者的生存率,采用Cox回归分析影响预后的风险因素,并分析DM组血糖控制情况对生存结果的影响。结果: 经过PSM,两组共有77对匹配成功,组间协变量达到均衡。两组患者术后出现黏膜癌前病变以及局部复发的比例差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。两组患者的生存分析结果差异无统计学意义,但经过匹配后,DM组的生存率有低于无DM组的趋势。单因素及多因素分析显示,肿瘤分期是OSCC患者总生存率及肿瘤特异性生存率的独立影响因素(P < 0.05),而有无DM对OSCC患者的生存影响差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。针对DM组的多因素分析发现,肿瘤分期、甘油三酯水平、术前平均末梢血糖(空腹)、术后平均末梢血糖(餐后2 h)是DM组患者术后总生存情况的独立危险因素;肿瘤分期和术后平均末梢血糖(餐后2 h)是DM组患者术后肿瘤特异性生存率的独立危险因素。DM组内的血糖控制欠佳组出现术后并发症及远处转移的风险有高于血糖控制良好组的趋势。结论: 有无DM对患者的总生存率及肿瘤特异性生存率的影响差异无统计学意义,但DM组术后出现黏膜癌前病变或局部肿瘤复发的可能性高于无DM组;糖尿病患者的肿瘤分期、甘油三酯水平、血糖控制情况可能影响其预后。
中图分类号:
- R739.8
| 1 |
Campbell PT , Newton CC , Patel AV , et al.Diabetes and cause-specific mortality in a prospective cohort of one million U.S. adults[J].Diabetes Care,2012,35(9):1835-1844.
doi: 10.2337/dc12-0002 |
| 2 | 赵佳, 韩雪, 谢梦, 等.2型糖尿病并发恶性肿瘤患者的流行病学分析[J].中国慢性病预防与控制,2018,26(7):514-516. |
| 3 |
Tsilidis KK , Kasimis JC , Lopez DS , et al.Type 2 diabetes and cancer: Umbrella review of meta-analyses of observational studies[J].BMJ,2015,350,g7607.
doi: 10.1136/bmj.g7607 |
| 4 | Vairaktaris E , Spyridonidou S , Goutzanis L , et al.Diabetes and oral oncogenesis[J].Anticancer Res,2007,27(6B):4185-4193. |
| 5 |
Wu CH , Wu TY , Li CC , et al.Impact of diabetes mellitus on the prognosis of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study[J].Ann Surg Oncol,2010,17(8):2175-2183.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-010-0996-1 |
| 6 |
Stott-Miller M , Chen C , Schwartz SM .Type Ⅱ diabetes and metabolic syndrome in relation to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma risk: A SEER-Medicare database study[J].Cancer Epidemiol,2013,37(4):428-433.
doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2013.03.006 |
| 7 |
Tseng CH .Oral cancer in Taiwan: Is diabetes a risk factor?[J].Clin Oral Investig,2013,17(5):1357-1364.
doi: 10.1007/s00784-012-0820-3 |
| 8 |
中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2021,37(4):311-398.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311282-20210304-00142 |
| 9 |
Pfister DG , Spencer S , Adelstein D , et al.Head and neck cancers, version 2.2020, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology[J].J Natl Compr Canc Netw,2020,18(7):873-898.
doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2020.0031 |
| 10 | Amin MB , Edge SB , Greene FL , et al.AJCC cancer staging manual[M].8th ed. New York: Springer,2017. |
| 11 |
高柳, 毛驰, 俞光岩, 等.成人并存疾病评价指数27条目中文简体版引进的授权、翻译回译和语义调适[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2016,51(10):623-627.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2016.10.010 |
| 12 |
Austin PC .An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies[J].Multivariate Behav Res,2011,46(3):399-424.
doi: 10.1080/00273171.2011.568786 |
| 13 | Ling S , Brown K , Miksza JK , et al.Risk of cancer incidence and mortality associated with diabetes: A systematic review with trend analysis of 203 cohorts[J].Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis,2020,31(1):14-22. |
| 14 |
Pearson-Stuttard J , Bennett J , Cheng YJ , et al.Trends in predominant causes of death in individuals with and without diabetes in England from 2001 to 2018: An epidemiological analysis of linked primary care records[J].Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol,2021,9(3):165-173.
doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30431-9 |
| 15 | 周维, 何明艳, 沈婉莹, 等.2005—2015年中国口腔癌发病及死亡趋势分析[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2020,49(6):58-63. |
| 16 | Végh D , Bányai D , Ujpál M .Change in the incidence of diabetes mellitus in oral cancer patients based on a long-term comparative study[J].Fogorv Sz,2015,108(1):9-12. |
| 17 |
Yan P , Wang Y , Yu X , et al.Type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of head and neck cancer subtypes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies[J].Acta Diabetol,2021,58(5):549-565.
doi: 10.1007/s00592-020-01643-0 |
| 18 | 王新革. 舌鳞癌与肿瘤侵袭模式、2型糖尿病的相关性研究[D]. 西安: 第四军医大学, 2017: 42. |
| 19 |
Supabphol S , Seubwai W , Wongkham S , et al.High glucose: An emerging association between diabetes mellitus and cancer progression[J].J Mol Med (Berl),2021,99(9):1175-1193.
doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02096-w |
| 20 |
Cignarelli A , Annamaria Genchi V , Caruso I , et al.Diabetes and cancer: Pathophysiological fundamentals of a "dangerous affair"[J].Diabetes Res Clin Pract,2018,143,378-388.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.04.002 |
| 21 | Liu CJ , Chang WJ , Chen CY , et al.Dynamic cellular and mole-cular modulations of diabetes mediated head and neck carcinogenesis[J].Oncotarget,2015,30(6):29268-29284. |
| 22 | 张东升, 郑家伟, 张陈平, 等.口腔癌合并全身系统性疾病患者的多学科协作诊疗模式专家共识[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2020,38(6):603-615. |
| 23 | 李金, 华红. 口腔癌中国流行病学趋势及口腔白斑癌变危险因素分析[D]. 北京: 北京大学, 2019. |
| 24 |
Villa A , Woo SB .Leukoplakia: A diagnostic and management algorithm[J].J Oral Maxillofac Surg,2017,75(4):723-734.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2016.10.012 |
| 25 |
Li G , Da M , Zhang W , et al.Alteration of serum lipid profile and its prognostic value in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J].J Oral Pathol Med,2016,45(3):167-172.
doi: 10.1111/jop.12344 |
| 26 |
Shalapour S , Karin M .Immunity, inflammation, and cancer: An eternal fight between good and evil[J].J Clin Invest,2015,125(9):3347-3355.
doi: 10.1172/JCI80007 |
| 27 | Lu A , Li H , Zheng Y , et al.Prognostic significance of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, lymphocyte to monocyte ratio, and platelet to lymphocyte ratio in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J].Biomed Res Int,2017,2017,3047802. |
| [1] | 张培恒, 高莹, 吴红花, 张健, 张俊清. 暴发性1型糖尿病合并急性胰腺炎1例及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 923-927. |
| [2] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [3] | 刘帅,刘磊,刘茁,张帆,马潞林,田晓军,侯小飞,王国良,赵磊,张树栋. 伴静脉癌栓的肾上腺皮质癌的临床治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [4] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [5] | 周泽臻,邓绍晖,颜野,张帆,郝一昌,葛力源,张洪宪,王国良,张树栋. 非转移性T3a肾细胞癌患者3年肿瘤特异性生存期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [6] | 方杨毅,李强,黄志高,陆敏,洪锴,张树栋. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮肿瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [7] | 曾媛媛,谢云,陈道南,王瑞兰. 脓毒症患者发生正常甲状腺性病态综合征的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [8] | 苏俊琪,王晓颖,孙志强. 舌鳞状细胞癌根治性切除术后患者预后预测列线图的构建与验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 120-130. |
| [9] | 马雨佳,卢燃藜,周泽宸,李晓怡,闫泽玉,武轶群,陈大方. 基于两样本孟德尔随机化的失眠与2型糖尿病关联研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 174-178. |
| [10] | 李建斌,吕梦娜,池强,彭一琳,刘鹏程,吴锐. 干燥综合征患者发生重症新型冠状病毒肺炎的早期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [11] | 刘欢锐,彭祥,李森林,苟欣. 基于HER-2相关基因构建风险模型用于膀胱癌生存预后评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [12] | 薛子璇,唐世英,邱敏,刘承,田晓军,陆敏,董靖晗,马潞林,张树栋. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [13] | 鲍雷,蔡夏夏,张明远,任磊磊. 维生素D3对2型糖尿病小鼠轻度认知障碍的改善作用及机制研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 587-592. |
| [14] | 卢汉,张建运,杨榕,徐乐,李庆祥,郭玉兴,郭传瑸. 下颌牙龈鳞状细胞癌患者预后的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [15] | 张晓悦,林雨欣,蒋莹,张蓝超,董芒艳,池海谊,董浩宇,马利军,李智婧,常春. 自我效能在2型糖尿病患者自我管理能力和自我管理行为间的中介效应[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 450-455. |
|
||