北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 796-802. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.027
机器人辅助腹腔镜下腔静脉节段性切除术治疗肾肿瘤瘤栓侵犯血管壁
刘帅*, 刘茁*, 管允鹤, 王国良, 田晓军, 张洪宪, 刘磊, 马潞林, 张树栋*( )
)
- 北京大学第三医院泌尿外科,北京 100191
Robot-assisted laparoscopic inferior vena cava segmental resection for renal tumor with tumor thrombus invading the vascular wall
Shuai LIU, Zhuo LIU, Yunhe GUAN, Guoliang WANG, Xiaojun TIAN, Hongxian ZHANG, Lei LIU, Lulin MA, Shudong ZHANG*( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
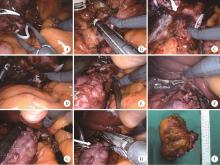
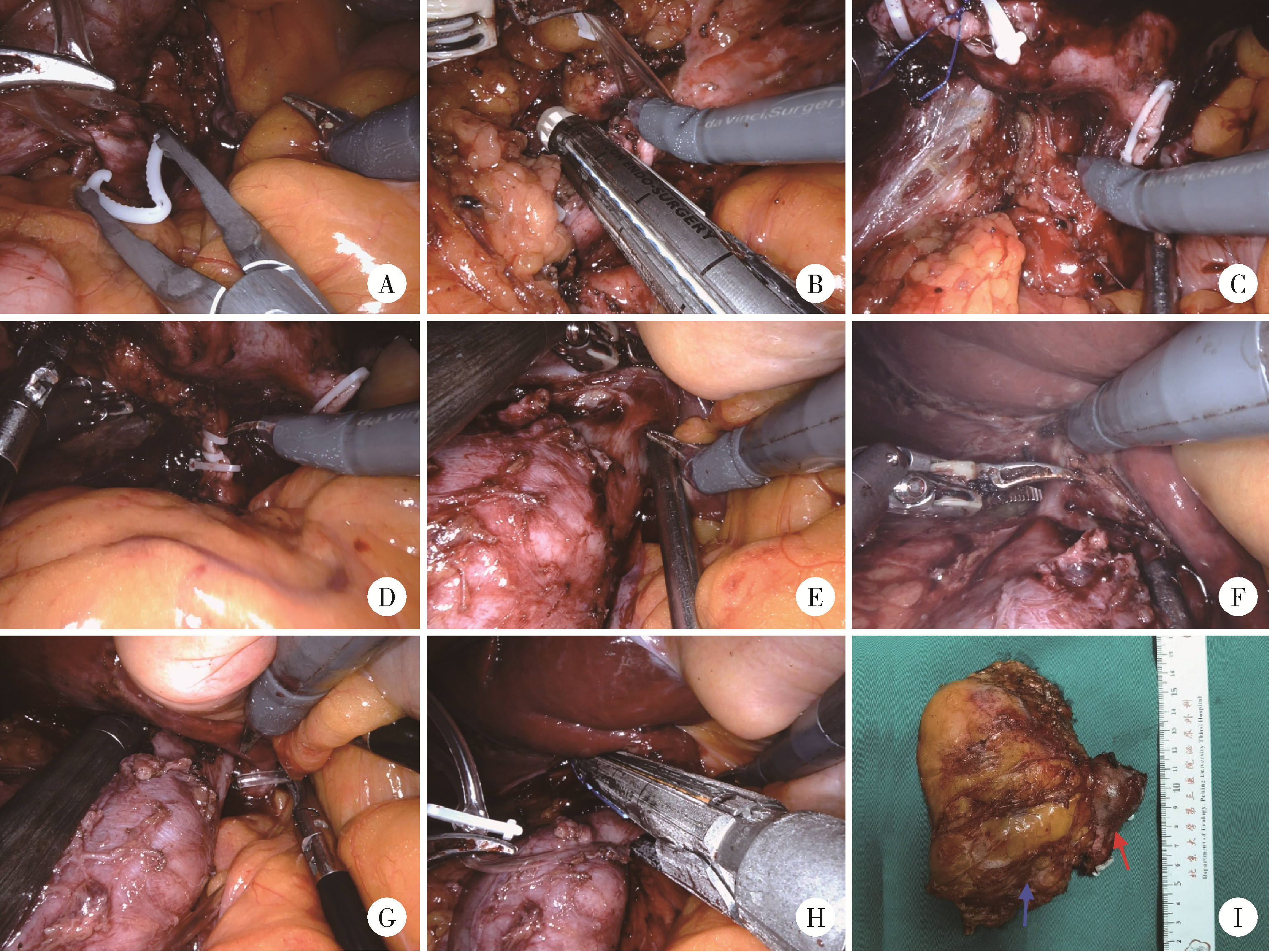
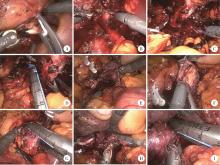
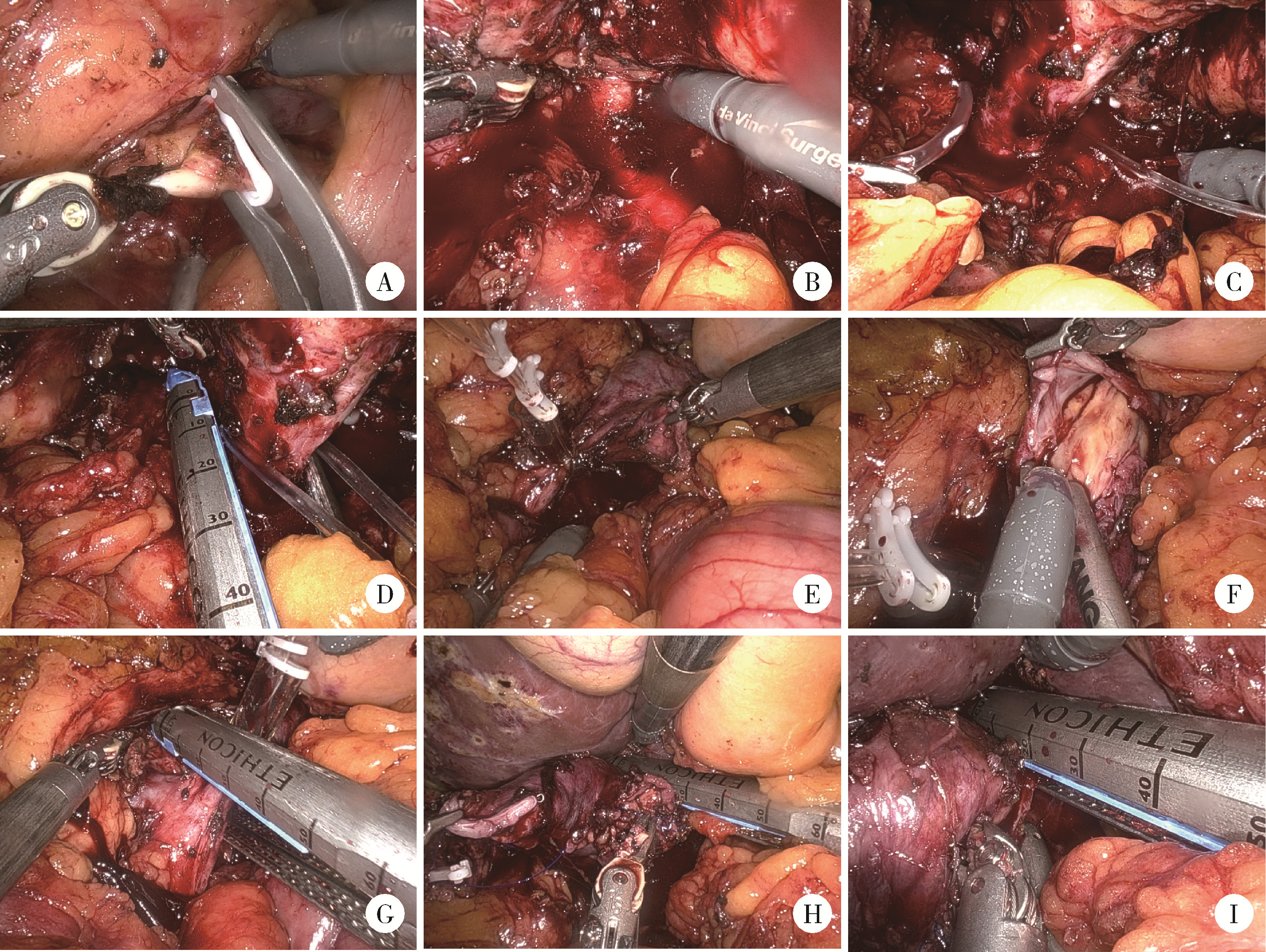
目的: 系统评估机器人辅助腹腔镜下腔静脉节段性切除术在肾肿瘤合并下腔静脉瘤栓治疗中的安全性及肿瘤控制效果。方法: 回顾性分析2021年1月至2025年2月北京大学第三医院泌尿外科收治的,行机器人辅助腹腔镜下腔静脉节段性切除术的肾肿瘤患者临床资料,采集患者基本信息、肿瘤参数、围术期指标及随访信息,通过电子病历系统提取手术记录及病理报告。连续变量以中位数(P25,P75)描述,分类变量以频数(百分比)呈现。结果: 共44例患者纳入本研究,中位年龄62(55,68)岁,男性31例、女性13例,右侧肿瘤39例、左侧5例,中位肿瘤直径8.1(6.1,10.1) cm,Mayo分级Ⅱ级37例、Ⅲ级6例、Ⅳ级1例,23例患者接受了新辅助治疗,17例患者合并下腔静脉血栓。中位手术时间224.0(167.3,303.8) min,术中失血量500.0(300.0,850.0) mL,19例患者接受输血,悬浮红细胞中位输注量800.0(400.0,1 200.0) mL。术后并发症发生率56.8%(25/44),Clavien-Dindo分级Ⅰ级8例、Ⅱ级17例;手术相关并发症包括下肢深静脉血栓6例、贫血需输血治疗5例、下肢水肿2例、肺栓塞2例,无手术相关死亡事件发生;术后中位肌酐116.0(86.5,157.5) μmol/L。病理组织学分析显示,肾透明细胞癌占大多数,为34例(77.3%);术后肾肿瘤病理分期T3b期12例、T3c期29例、T4期3例,N1期8例,M1期17例。中位随访时间为10个月(范围1~49个月),3例患者发生肿瘤特异性死亡,1例患者因其他原因死亡,5例患者随访期间发生肺转移,4例发生肝转移,4例发生局部复发。9例患者术后接受靶向和免疫联合辅助治疗,18例患者仅接受靶向辅助治疗。结论: 机器人辅助腹腔镜下腔静脉节段性切除术可实现复杂静脉瘤栓的精准切除,短期疗效确切,但需警惕血管相关并发症风险。
中图分类号:
- R737.11
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
叶剑飞, 马潞林, 赵磊, 等. 腔静脉节段切除术在处理侵犯腔静脉的肾肿瘤瘤栓中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50 (1): 183- 187.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.01.031 |
| 7 |
刘茁, 王国良, 田晓军, 等. 下腔静脉节段性切除术在肾癌伴下腔静脉癌栓中的应用[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2018, 23 (9): 677- 681.
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
赵勋, 颜野, 黄晓娟, 等. 癌栓粘连血管壁对非转移性肾细胞癌合并下腔静脉癌栓患者手术及预后的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53 (4): 665- 670.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.04.007 |
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| [1] | 李宗瀚, 黄洋阅, 李宁, 李明磊, 宋宏程, 张潍平, 刘超. 国产单孔蛇形臂机器人手术系统在儿童肾盂成形术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 662-665. |
| [2] | 张启鸣, 陈泽波, 田雨, 潘大猛, 刘磊, 张洪宪, 赵磊, 张树栋, 马潞林, 侯小飞. 机器人辅助腹腔镜移植肾切除术经验总结[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 666-669. |
| [3] | 刘世豪, 徐丽清, 李新飞, 杨昆霖, 李兆莹, 张子博, 王祥, 傅炜骁, 李志华, 李学松. 国产模块化手术机器人系统辅助肾盂成形术的可行性和安全性评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 779-783. |
| [4] | 王焕瑞, 赖世聪, 胡浩浦, 丁泽华, 徐涛, 胡浩. 腹腔镜与输尿管软镜联合定位治疗复杂输尿管狭窄的疗效分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 784-788. |
| [5] | 张树栋,谢睿扬. 机器人手术时代的肾癌合并腔静脉瘤栓治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 562-564. |
| [6] | 陈克伟,刘茁,邓绍晖,张帆,叶剑飞,王国良,张树栋. 肾血管平滑肌脂肪瘤伴下腔静脉瘤栓的临床诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 617-623. |
| [7] | 杨捷,冯杰莉,张树栋,马潞林,郑清. 经食管超声心动图在肾切除术联合Mayo Ⅲ~Ⅳ级静脉瘤栓取栓术不同手术方式中的临床作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 631-635. |
| [8] | 王滨帅,邱敏,张前进,田茂锋,刘磊,王国良,陆敏,田晓军,张树栋. 6例肾尤文肉瘤伴静脉瘤栓的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 636-639. |
| [9] | 应沂岑,杜毅聪,李志华,张一鸣,李新飞,王冰,张鹏,朱宏建,周利群,杨昆霖,李学松. 机器人辅助腹腔镜下颊黏膜补片输尿管成形术治疗复杂输尿管狭窄[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 640-645. |
| [10] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [11] | 薛子璇,唐世英,邱敏,刘承,田晓军,陆敏,董靖晗,马潞林,张树栋. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [12] | 邱敏,宗有龙,王滨帅,杨斌,徐楚潇,孙争辉,陆敏,赵磊,卢剑,刘承,田晓军,马潞林. 腹腔镜肾部分切除术治疗中高复杂程度肾肿瘤的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [13] | 周利群,徐纯如. 机器人时代中央型肾肿瘤的手术治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 587-591. |
| [14] | 左炜,高菲,袁昌巍,熊盛炜,李志华,张雷,杨昆霖,李新飞,刘靓,魏来,张鹏,王冰,谷亚明,朱宏建,赵峥,李学松. 基于多中心数据库的10年上尿路修复手术术式及术型变化趋势[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 692-698. |
| [15] | 刘茁,朱国栋,唐世英,洪鹏,赵勋,张启鸣,李丽伟,彭冉,陈志刚,王滨帅,张丽,杨飞龙,葛力源,孙争辉,张树栋,王国良,田晓军,张洪宪,马潞林. 外科手术治疗年龄≥75岁的高龄肾细胞癌合并静脉癌栓患者的临床经验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 774-778. |
|
||