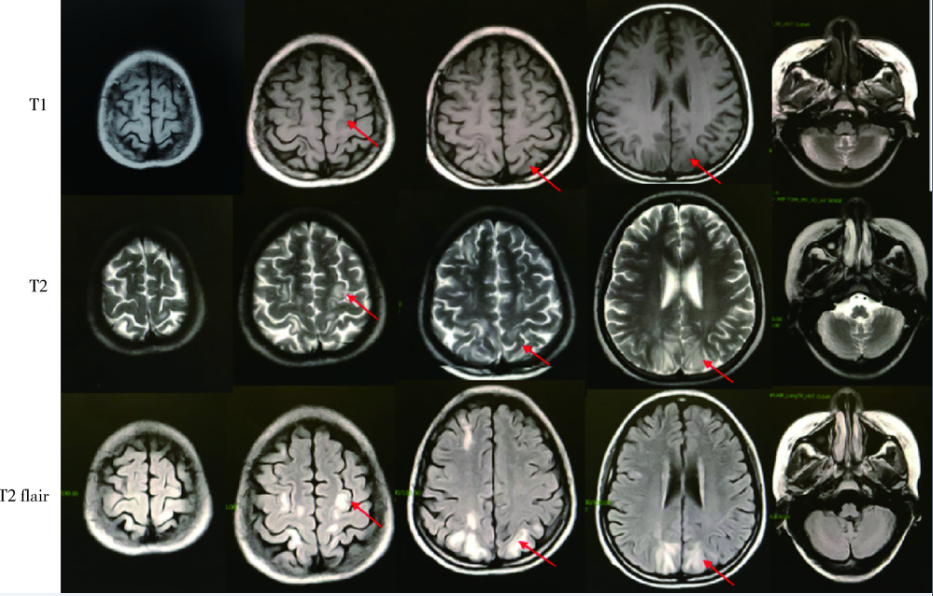
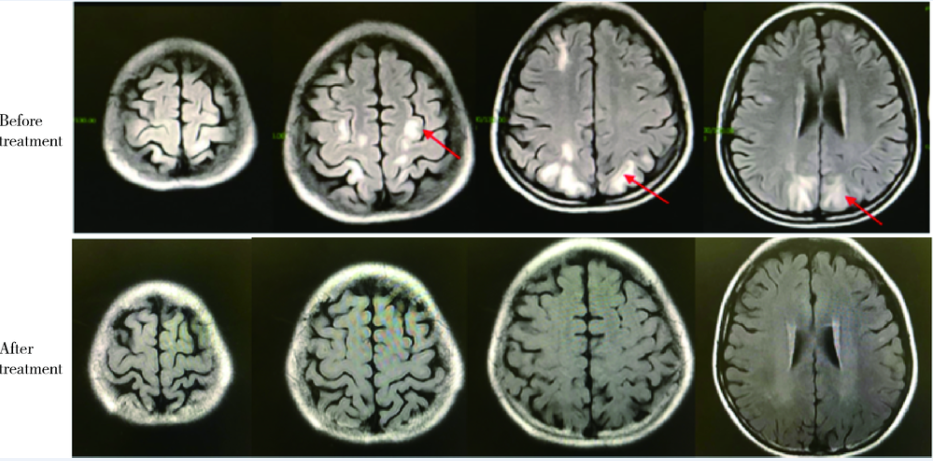
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1102-1107. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.029
系统性红斑狼疮合并可逆性后部脑病综合征1例
- 1. 风湿免疫科 北京大学第一医院 北京 100034
2. 神经内科 北京大学第一医院 北京 100034
3. 影像科 北京大学第一医院 北京 100034
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report
Xiao-hui ZHANG1,Xue-rong DENG1,Fan Li2,Ying ZHU3,Zhuo-li ZHANG1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology
2. Department of Neurology
3. Department of Radiology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
中图分类号:
- R593.24 +1
| [1] |
Tay SH, Mak A . Diagnosing and attributing neuropsychiatric events to systemic lupus erythematosus:time to untie the Gordian knot[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2017,56(Suppl1):i14-i23.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex017 pmid: 28339930 |
| [2] |
Shankar J, Banfield J . Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a review[J]. Can Assoc Radiol J, 2017,68(2):147-153.
doi: 10.1016/j.carj.2016.08.005 pmid: 28131335 |
| [3] |
Toledano M, Fugate JE . Posterior reversible encephalopathy in the intensive care unit[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2017,141:467-483.
doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63599-0.00026-0 |
| [4] |
Fugate JE, Rabinstein AA . Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: clinical and radiological manifestations, pathophysiology, and outstanding questions[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2015,14(9):914-925.
doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00111-8 pmid: 26184985 |
| [5] |
Datar S, Singh TD, Fugate JE , et al. Albuminocytologic dissociation in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome[J]. Mayo Clin Proc, 2015,90(10):1366-1371.
doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.07.018 pmid: 26349950 |
| [6] |
Lee VH, Wijdicks EF, Manno EM , et al. Clinical spectrum of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome[J]. Arch Neurol, 2008,65(2):205-210.
doi: 10.1016/S0887-8994(01)00265-X pmid: 18268188 |
| [7] |
Varaprasad IR, Agrawal S, Prabu VN , et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. J Rheumatol, 2011,38(8):1607-1611.
doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e3182a21ffd pmid: 23965484 |
| [8] | Casey SO, Sampaio RC, Michel E , et al Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: utility of fluid-attenuated inversion re-covery MR imaging in the detection of cortical and subcortical lesions[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2000,21(7):1199-1206. |
| [9] |
Magnano MD, Bush TM, Herrera I , et al. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2006,35(6):396-402.
doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2006.01.002 pmid: 16765717 |
| [10] |
Brady E, Parikh NS, Navi BB , et al. The imaging spectrum of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a pictorial review[J]. Clin Imaging, 2018,47:80-89.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2017.08.008 pmid: 28910681 |
| [11] |
Bartynski WS, Boardman JF . Distinct imaging patterns and lesion distribution in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2007,28(7):1320-1327.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A0549 |
| [12] |
McKinney AM, Short J, Truwit CL , et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: incidence of atypical regions of involvement and imaging findings[J]. Am J Roentgenol, 2007,189(4):904-912.
doi: 10.2214/AJR.07.2024 pmid: 17885064 |
| [13] |
Gao B, Lyu C, Lerner A , et al. Controversy of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: what have we learnt in the last 20 years[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2018,89(1):14-20.
doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2017-316225 pmid: 28794149 |
| [14] |
Gatla N, Annapureddy N, Sequeira W , et al Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. J Clin Rheumatol, 2013,19(6):334-340.
doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e3182a21ffd pmid: 23965484 |
| [15] |
Junewar V, Verma R, Sankhwar PL , et al. Neuroimaging features and predictors of outcome in eclamptic encephalopathy: a prospective observational study[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2014,35(9):1728-1734.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A3923 pmid: 24722310 |
| [16] |
Karia SJ, Rykken JB , McKinney ZJ, et al. Utility and significance of gadolinium-based contrast enhancement in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2016,37(3):415-422.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4563 pmid: 26564441 |
| [17] |
Covarrubias DJ, Luetmer PH, Campeau NG . Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: prognostic utility of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR images[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2002,23(6):1038-1048.
doi: 10.1055/s-2002-32034 pmid: 12063238 |
| [18] |
Schweitzer AD, Parikh NS, Askin G , et al. Imaging characteristics associated with clinical outcomes in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome[J]. Neuroradiology, 2017,59(4):379-386.
doi: 10.1007/s00234-017-1815-1 pmid: 28289809 |
| [19] |
Rabinstein AA, Mandrekar J, Merrell R , et al. Blood pressure fluctuations in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2012,21(4):254-258.
doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2011.03.011 pmid: 21536456 |
| [20] |
van Beek AH, Claassen JA, Rikkert MG , et al. Cerebral auto-regulation: an overview of current concepts and methodology with special focus on the elderly[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2008,28(6):1071-1085.
doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2008.13 pmid: 18349877 |
| [21] |
Gao B, Lerner A, Law M . The Clinical outcome of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2016,37(9):E55-E56.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4853 |
| [22] |
Sha Z, Moran BP , McKinney AMT, et al. Seizure outcomes of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and correlations with electroencephalographic changes[J]. Epilepsy Behav, 2015,48:70-74.
doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.05.027 pmid: 26071927 |
| [23] |
Legriel S, Schraub O, Azoulay E , et al. Determinants of recovery from severe posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome[J]. PLoS One, 2012,7(9):e44534.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044534 pmid: 23024751 |
| [24] |
Shaharir SS, Remli R, Marwan AA , et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus: pooled analysis of the literature reviews and report of six new cases[J]. Lupus, 2013,22(5):492-496.
doi: 10.1177/0961203313478303 pmid: 23435619 |
| [25] |
Damrongpipatkul U, Oranratanachai K, Kasitanon N , et al. Clinical features, outcome, and associated factors for posterior reversible encephalopathy in Thai patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case-control study[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2018,37(3):691-702.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3892-2 pmid: 29103182 |
| [26] |
Jung SM, Moon SJ, Kwok SK , et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in Korean patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: risk factors and clinical outcome[J]. Lupus, 2013,22(9):885-891.
doi: 10.1177/0961203313496341 pmid: 23846231 |
| [27] |
Lai CC, Chen WS, Chang YS , et al. Clinical features and outcomes of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken), 2013,65(11):1766-1774.
doi: 10.1002/acr.22047 pmid: 23687067 |
| [28] |
Budhoo A, Mody GM . The spectrum of posterior reversible encephalopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2015,34(12):2127-2134.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-3055-2 pmid: 26298534 |
| [29] |
Ferreira TS, Reis F, Appenzeller S . Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and association with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Lupus, 2016,25(12):1369-1376.
doi: 10.1177/0961203316643598 pmid: 27084028 |
| [30] |
Merayo-Chalico J, Apodaca E, Barrera-Vargas A , et al. Clinical outcomes and risk factors for posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus: a multicentric case-control study[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2016,87(3):287-294.
doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2014-310145 pmid: 25804426 |
| [31] |
Ishimori ML, Pressman BD, Wallace DJ , et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: another manifestation of CNS SLE[J]. Lupus, 2007,16(6):436-443.
doi: 10.1177/0961203307078682 pmid: 17664235 |
| [32] |
Barber CE, Leclerc R, Gladman DD , et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: an emerging disease manifestation in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2011,41(3):353-363.
doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2011.07.001 pmid: 21868061 |
| [1] | 焦莶如, 龚潘, 牛悦, 徐兆, 周宗朴, 杨志仙. 以婴儿癫痫性痉挛综合征为表型的吡哆醇依赖性癫痫[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 781-787. |
| [2] | 武志慧, 胡明智, 赵巧英, 吕凤凤, 张晶莹, 张伟, 王永福, 孙晓林, 王慧. miR-125b-5p修饰脐带间充质干细胞对系统性红斑狼疮的免疫调控机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [3] | 乔佳佳,田聪,黄晓波,刘军. 肾结石合并系统性红斑狼疮行经皮肾镜碎石取石术的安全性和有效性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 745-749. |
| [4] | 任立敏,赵楚楚,赵义,周惠琼,张莉芸,王友莲,沈凌汛,范文强,李洋,厉小梅,王吉波,程永静,彭嘉婧,赵晓珍,邵苗,李茹. 系统性红斑狼疮低疾病活动度及缓解状况的真实世界研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 273-278. |
| [5] | 罗芷筠,吴佳佳,宋优,梅春丽,杜戎. 伴神经精神系统病变的系统性红斑狼疮相关巨噬细胞活化综合征2例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1111-1117. |
| [6] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [7] | 赵祥格,刘佳庆,黄会娜,陆智敏,白自然,李霞,祁荆荆. 干扰素-α介导系统性红斑狼疮外周血CD56dimCD57+自然杀伤细胞功能的损伤[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 975-981. |
| [8] | 张琳崎,赵静,王红彦,王宗沂,李英妮,汤稷旸,李思莹,曲进锋,赵明威. 抗ENO1抗体与狼疮性视网膜病变的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1099-1105. |
| [9] | 李敏,侯林卿,金月波,何菁. 系统性红斑狼疮合并视网膜病变的临床及免疫学特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1106-1111. |
| [10] | 邵苗,郭惠芳,雷玲彦,赵清,丁艳杰,林进,吴锐,于峰,李玉翠,苗华丽,张莉芸,杜燕,焦瑞英,庞丽霞,龙丽,栗占国,李茹. 短间期小剂量环磷酰胺治疗系统性红斑狼疮耐受性的多中心对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1112-1116. |
| [11] | 刘京,陆爱东,左英熹,吴珺,黄志卓,贾月萍,丁明明,张乐萍,秦炯. 儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病合并癫痫发作75例临床特征和预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 948-953. |
| [12] | 杜燕燕,王健,贺兰,季丽娜,徐樨巍. 儿童川崎病合并轻微脑炎/脑病伴可逆性胼胝体压部病变综合征1例并文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 756-761. |
| [13] | 田佳宜,张霞,程功,刘庆红,王世阳,何菁. 系统性红斑狼疮患者血清白细胞介素-2受体α水平及其临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1083-1087. |
| [14] | 李正芳,吴雪,武丽君,罗采南,石亚妹,钟岩,陈晓梅,孟新艳. Rhupus综合征的临床特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 933-937. |
| [15] | 邹健梅,武丽君,罗采南,石亚妹,吴雪. 血清25-羟维生素D与系统性红斑狼疮活动的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 938-941. |
|
||