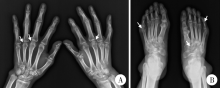
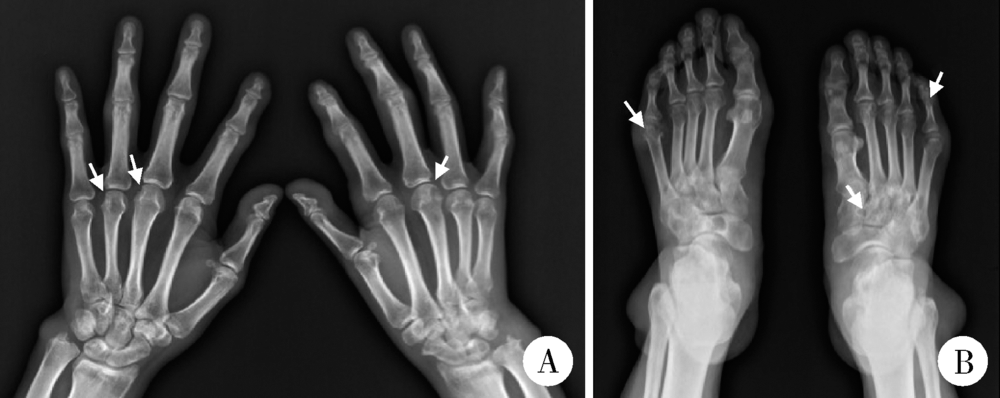
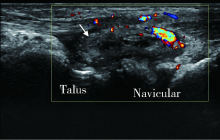
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1117-1119. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.032
原发性骨髓纤维化引起的继发性痛风1例
- 北京大学第一医院风湿免疫科,北京 100034
A case of gout secondary to primary myelofibrosis
Lan-lan JI,Yan-jie HAO,Zhuo-li ZHANG( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology,Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
中图分类号:
- R593
| [1] | 中华医学会风湿病学分会. 2016中国痛风诊疗指南[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2016,55(11):892-899. |
| [2] |
Neogi T, Jansen TLTA, Dalbeth N , et al. 2015 Gout classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2015,74(10):1789-1798.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208237 pmid: 4602275 |
| [3] |
Yü TF . Secondary gout associated with myeloproliferative diseases[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1965,8(5):765-771.
doi: 10.1002/art.1780080439 pmid: 5216775 |
| [4] |
Gutman AB . The past four decades of progress in the knowledge of gout, with an assessment of the present status[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1973,16(4):431-445.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1529-0131 |
| [5] |
Takahashi H, Hattori A, Shibata A . Profile of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis in chronic myeloproliferative disorders[J]. Tohoku J Exp Med, 1982,138(1):71-80.
doi: 10.1620/tjem.138.71 pmid: 6959382 |
| [6] |
Barbui T, Carobbio A, Cervantes F , et al. Thrombosis in primary myelofibrosis: incidence and risk factors[J]. Blood, 2010,115(4):778-782.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-08-238956 pmid: 19965680 |
| [7] |
Liu TT, Chen JB, Chen WJ , et al. Idiopathic myelofibrosis associated with renal extramedullary hematopoiesis and nephrotic syndrome: case report[J]. Chang Gung Med J, 2000,23(3):169-174.
pmid: 15641221 |
| [1] | 田佳宜, 郭一学, 张霞, 孙晓麟, 何菁. 中国健康成人外周血自然杀伤细胞及其亚群的正常值范围流式细胞学分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 839-844. |
| [2] | 杨玉淑, 齐晅, 丁萌, 王炜, 郭惠芳, 高丽霞. 抗唾液腺蛋白1抗体联合抗腮腺分泌蛋白抗体对干燥综合征的诊断价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 845-852. |
| [3] | 钟华, 李原, 徐丽玲, 白明欣, 苏茵. 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [4] | 武志慧, 胡明智, 赵巧英, 吕凤凤, 张晶莹, 张伟, 王永福, 孙晓林, 王慧. miR-125b-5p修饰脐带间充质干细胞对系统性红斑狼疮的免疫调控机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [5] | 刘东武, 陈杰, 高明利, 于静. 类风湿关节炎伴发淋巴结Castleman样病理改变1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [6] | 李正芳,罗采南,武丽君,吴雪,孟新艳,陈晓梅,石亚妹,钟岩. 抗氨基甲酰化蛋白抗体在诊断类风湿关节炎中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [7] | 乔佳佳,田聪,黄晓波,刘军. 肾结石合并系统性红斑狼疮行经皮肾镜碎石取石术的安全性和有效性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 745-749. |
| [8] | 黄会娜,赵静,赵祥格,白自然,李霞,王冠. 乳酸对类风湿关节炎患者外周血CD4+T细胞亚群的调控作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [9] | 任立敏,赵楚楚,赵义,周惠琼,张莉芸,王友莲,沈凌汛,范文强,李洋,厉小梅,王吉波,程永静,彭嘉婧,赵晓珍,邵苗,李茹. 系统性红斑狼疮低疾病活动度及缓解状况的真实世界研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 273-278. |
| [10] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [11] | 赖展鸿,李嘉辰,贠泽霖,张永刚,张昊,邢晓燕,邵苗,金月波,王乃迪,李依敏,李玉慧,栗占国. 特发性炎性肌病完全临床应答相关因素的单中心真实世界研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 284-292. |
| [12] | 韩艺钧,李常虹,陈秀英,赵金霞. 抗SSB抗体阳性和阴性的原发性干燥综合征患者临床及免疫学特征的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1000-1006. |
| [13] | 李建斌,吕梦娜,池强,彭一琳,刘鹏程,吴锐. 干燥综合征患者发生重症新型冠状病毒肺炎的早期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [14] | 邹雪,白小娟,张丽卿. 艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [15] | 李文根,古晓东,翁锐强,刘苏东,陈超. 血浆外泌体miR-34-5p和miR-142-3p在系统性硬化症中的表达及临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1022-1027. |
|
||