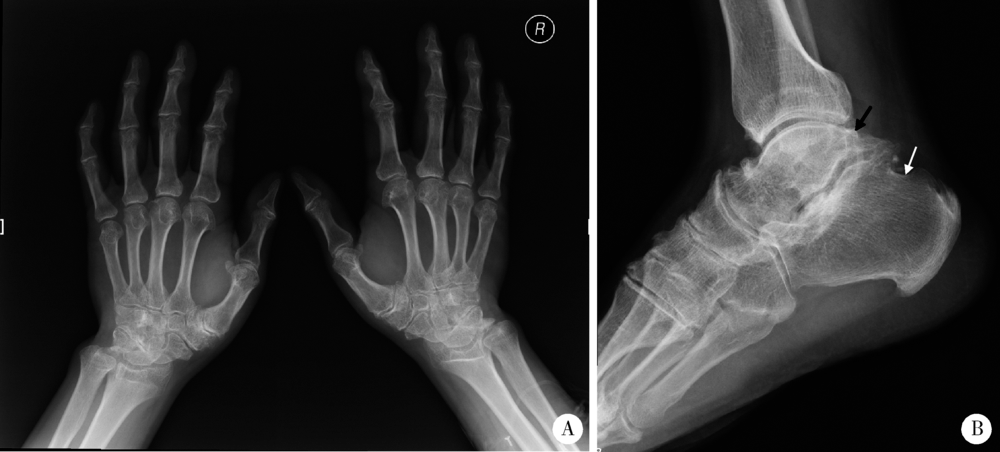
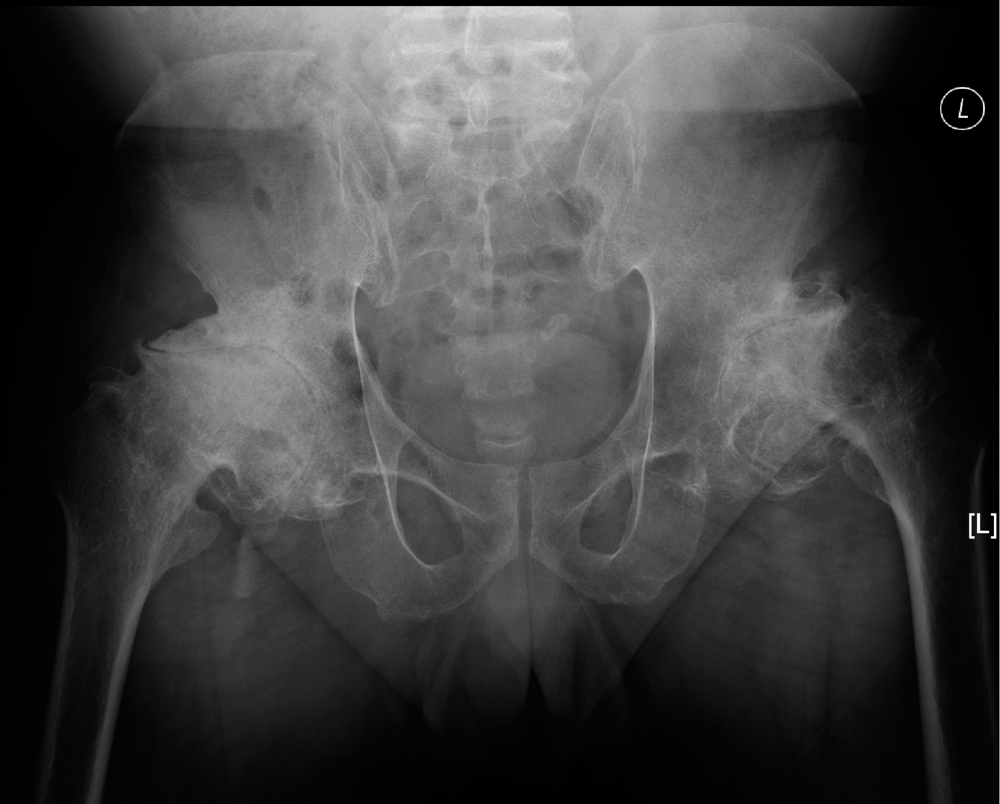
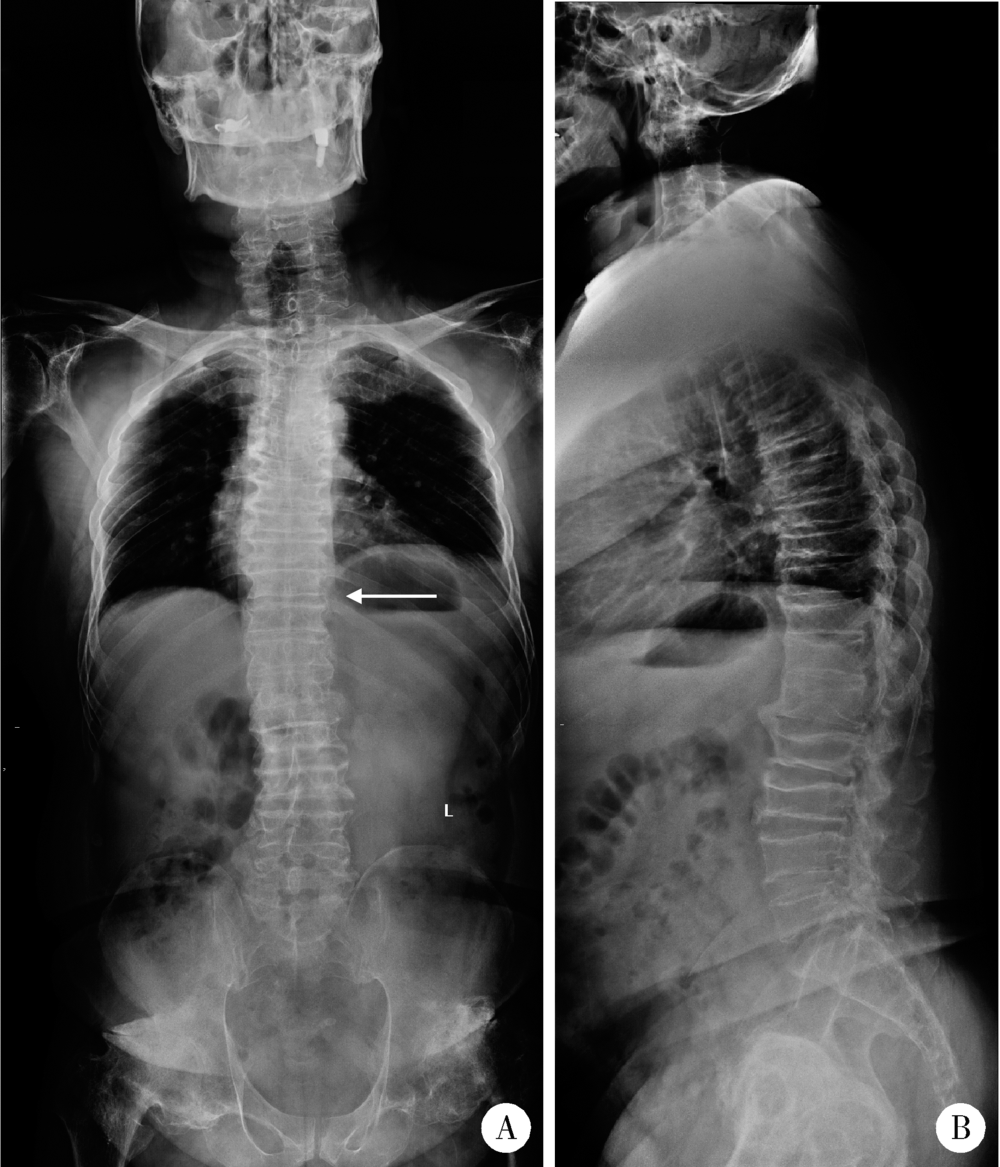
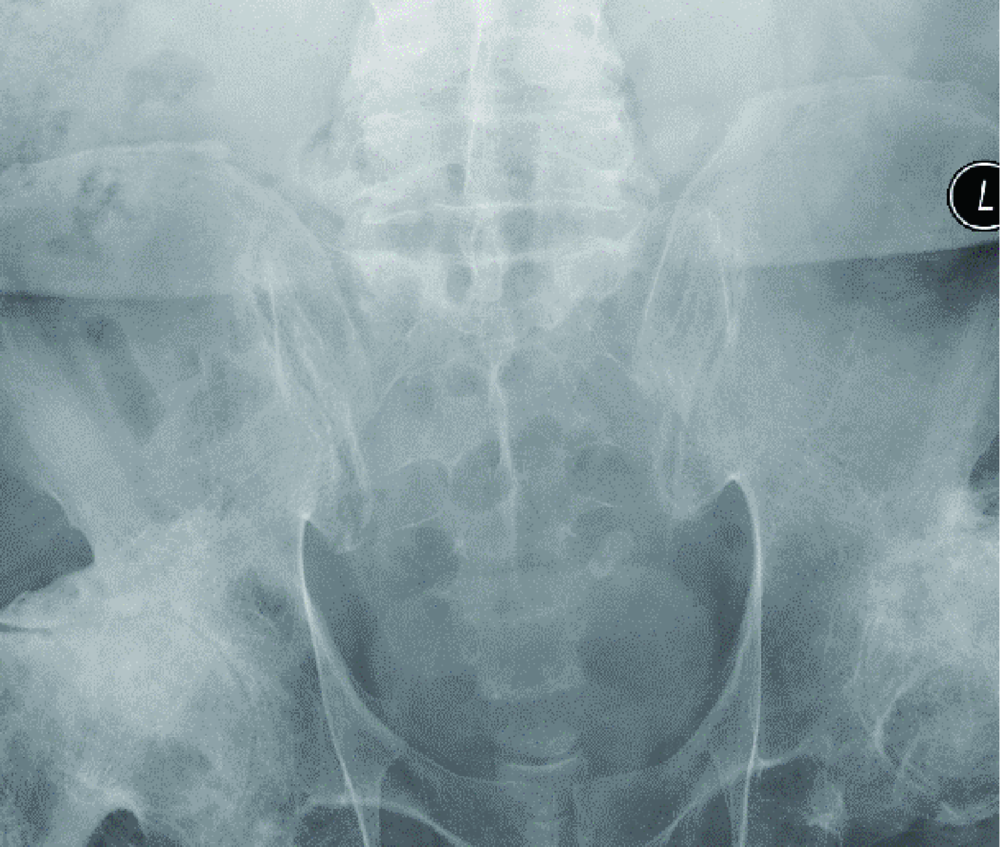
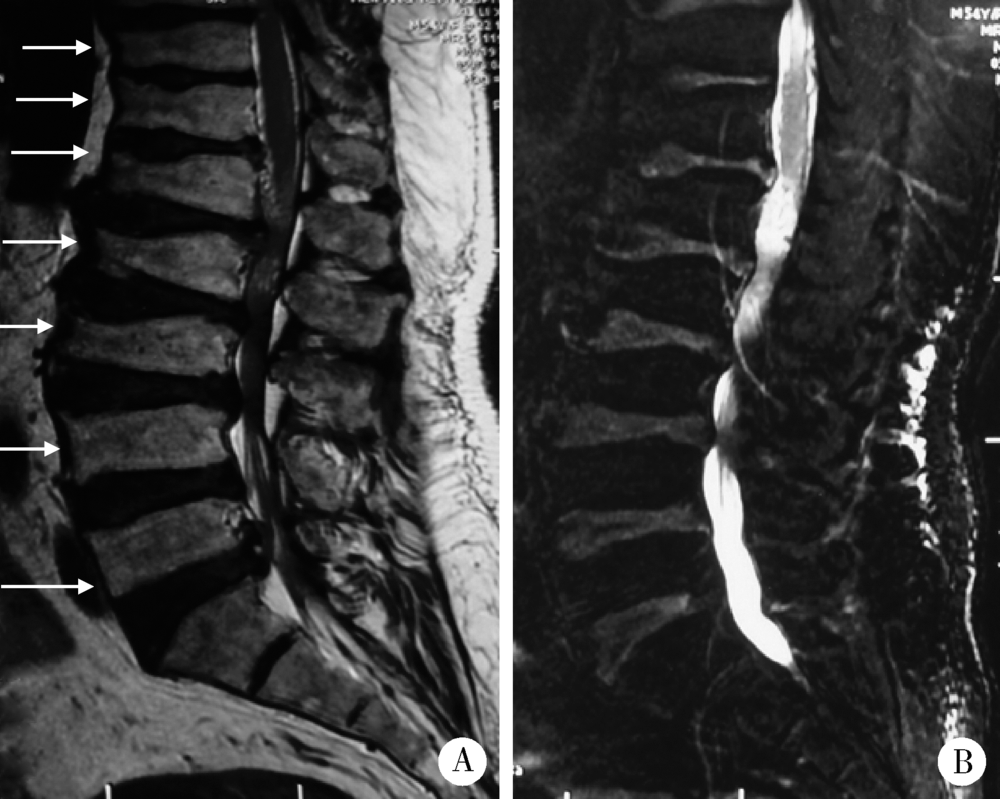
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1112-1116. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.031
误诊为强直性脊柱炎的进行性假性类风湿发育不良1例
- 北京大学第三医院风湿免疫科,北京 100191
Progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia misdiagnosed asankylosing spondylitis: a case report
Rui LIU,Jia-yu ZHAI,Xiang-yuan LIU,Zhong-qiang YAO( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
中图分类号:
- R596
| [1] |
邓小虎, 黄烽, 张江林 , 等. 进行性假性类风湿发育不良症的临床分析[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2006,31(4):351-353.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-7402.2006.04.025 |
| [2] |
叶军, 张惠文, 王彤 , 等. 进行性假性类风湿性发育不良症的临床诊断及WISP3基因突变分析[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2010,48(3):194-198.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2010.03.009 |
| [3] | Wynne-Davies R, Hall C, Ansell BM . Spondylo-epiphysial dysplasia tarda with progressive arthropathy. A “new” disorder of autosomal recessive inheritance[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1982,64(4):442-445. |
| [4] |
Hurvitz JR, Suwairi WM, Van Hul W , et al. Mutations in the CCN gene family member WISP3 cause progressive pseudorheu-matoid dysplasia[J]. Nat Genet, 1999,23(1):94-98.
doi: 10.1038/12699 pmid: 10471507 |
| [5] | Delague V, Chouery E, Corbani S , et al. Molecular study of WISP3 in nine families originating from the Middle-East and presenting with progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia: identification of two novel mutations, description of a founder effect [J]. Am J Med Genet, 2005, 138 A( 2):118-126. |
| [6] |
Bennani L, Amine B, Ichchou L , et al. Progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia: three cases in one family[J]. Joint Bone Spine, 2007,74(4):393-395.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2006.11.014 pmid: 17596985 |
| [7] |
Yue H, Zhang ZL, He JW . Identification of novel mutations in WISP3 gene in two unrelated Chinese families with progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia[J]. Bone, 2009,44(4):547-554.
doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2008.11.005 pmid: 19064006 |
| [8] |
Sailani MR, Chappell J, Jingga I , et al. WISP3 mutation associated with pseudorheumatoid dysplasia[J]. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud, 2018,4(1):1-11.
doi: 10.1101/mcs.a001990 pmid: 29092958 |
| [9] |
Hu Q, Liu J, Wang Y , et al. Delayed-onset of progressive pseudo-rheumatoid dysplasia in a Chinese adult with a novel compound WISP3 mutation: a case report[J]. BMC Medical Genetics, 2017,18(1):149.
doi: 10.1186/s12881-017-0507-3 pmid: 5732398 |
| [10] |
Ye J, Zhang HW, Qiu WJ , et al. Patients with progressive pseudo-rheumatoid dysplasia: from clinical diagnosis to molecular studies[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2012,5(1):190-195.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2011.619 pmid: 21993478 |
| [11] |
Zhou HD, Bu YH, Peng YQ , et al. Cellular and molecular responses in progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia articular cartilage associated with compound heterozygous WISP3 gene mutation[J]. J Mol Med (Berl), 2007,85(9):985-996.
doi: 10.1007/s00109-007-0193-2 pmid: 17483925 |
| [12] |
Sun J, Xia W, He S , et al. Novel and recurrent mutations of WISP3 in two Chinese families with progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia[J]. PLoS One. 2012,7(6):e38643.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038643 pmid: 3369844 |
| [13] |
Yu Y, Hu M, Xing X , et al. Identification of a mutation in the WISP3 gene in three unrelated families with progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2015,12(1):419-425.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3430 pmid: 25738435 |
| [14] |
Liu L, Li N, Zhao Z , et al. Novel WISP3 mutations causing spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda with progressive arthropathy in two unrelated Chinese families[J]. Joint Bone Spine, 2015,82(2):125-128.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2014.10.005 pmid: 25553839 |
| [15] |
Yan W, Dai J, Xu Z , et al. Novel WISP3 mutations causing progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia in two Chinese families[J]. Hum Genome Var, 2016(3):16041.
doi: 10.1038/hgv.2016.41 pmid: 5143363 |
| [16] |
Luo H, Shi C, Mao C , et al. A novel compound WISP3 mutation in a Chinese family with progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia[J]. Gene, 2015,564(1):35-38.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.03.029 pmid: 25794430 |
| [17] |
EI-Shant HE, Omari HZ, Qubain HL . Progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia:report of a family and review[J]. J Med Genet, 1997,34(7):559-563.
doi: 10.1136/jmg.34.7.559 pmid: 9222963 |
| [18] |
曹春霞, 郭雄, 张永忠 . 青少年大骨节病诊断指标筛选和模型的构建[J]. 中国地方病学杂志, 2011,30(6):687-690.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-4955.2011.06.026 |
| [19] |
史晓薇, 郭雄 . COL9A1基因多态性与儿童大骨节病的关联分析[J]. 中国妇幼健康研究, 2016,27(5):556-557, 646.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5293.2016.05.002 |
| [20] | 马民, 刘红光, 王其军 . 大骨节病的X线及CT诊断[J]. 实用医学影像杂志, 2003,4(2):83-85 |
| [21] |
钱向东, 赵云辉 . 非病区成人大骨节病的X线诊断及鉴别诊断[J]. 新疆医学, 2013,43(7):110-113.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5183.2013.07.046 |
| [1] | 时云飞,王豪杰,刘卫平,米岚,龙孟平,刘雁飞,赖玉梅,周立新,刁新婷,李向红. 血管免疫母细胞性T细胞淋巴瘤临床与分子病理学特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
| [2] | 熊焰,张波,聂立功,吴世凯,赵虎,李东,邸吉廷. 胸部SMARCA4缺失性未分化肿瘤的病理诊断与联合免疫检测点抑制剂治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 351-356. |
| [3] | 周秋君,龚潘,焦莶如,杨志仙. 1例Angelman综合征合并眼皮肤白化病2型患者的临床和遗传学分析及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 181-185. |
| [4] | 程晓静,蒋栋,张连海,王江华,李雅真,翟佳慧,闫宝琪,张露露,谢兴旺,李子禹,季加孚. KRAS G12V特异性T细胞受体治疗恶性肿瘤的临床前研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 884-895. |
| [5] | 秦彩朋,宋宇轩,丁梦婷,王飞,林佳兴,杨文博,杜依青,李清,刘士军,徐涛. 肾癌免疫治疗疗效评估突变预测模型的建立[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 663-668. |
| [6] | 陈曦,王斯悦,薛恩慈,王雪珩,彭和香,范梦,王梦莹,武轶群,秦雪英,李劲,吴涛,朱洪平,李静,周治波,陈大方,胡永华. 基于核心家系全外显子组测序数据探索新生突变与非综合征型唇腭裂的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 387-393. |
| [7] | 曹泽,王乐童,刘振明. 严重急性呼吸综合征冠状病毒2的Spike蛋白点突变后与受体蛋白质及潜在抗病毒药物结合能力的同源建模分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 150-158. |
| [8] | 吴君怡,余淼,孙仕晨,樊壮壮,郑静蕾,张刘陶,冯海兰,刘洋,韩冬. 少汗性外胚层发育不良患者EDA基因突变检测及表型分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 24-33. |
| [9] | 鲍轶,莫娟芬. 同时性多原发肺腺癌组织编码转录因子ERG基因相同位点突变1例报告[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 971-974. |
| [10] | 张宽根,周雨禾,邵雅昆,梅放,由江峰,刘北英,裴斐. 肿瘤转移抑制基因LASS2/TMSG1 S248A突变体通过增加ATP6V0C表达促进前列腺癌的侵袭[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 210-220. |
| [11] | 王皓,刘洋,刘浩辰,韩冬,冯海兰. 先天性缺牙患者中BMP2基因突变检测及功能分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 9-15. |
| [12] | 尤柱,徐丽莉,李雪芬,张建运,杜菁,孙丽莎. 成釉细胞纤维瘤中BRAF突变基因的检测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 4-5. |
| [13] | 张晓东,刘德若. 肺腺癌新分类与表皮生长因子受体基因突变之间的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 640-644. |
| [14] | 朱燕,石永进,赵玉亮,朱平. 拓扑异构酶抑制剂通过ATM/ATR和NF-κB途径上调乳腺癌细胞MICA/B 的表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 318-325. |
| [15] | 杨夕樱,朱灵平,刘雪芹,张春雨,姚勇,吴晔. 基因诊断Caroli综合征合并常染色体隐性遗传性多囊肾1例及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 335-339. |
|
||