北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 28-34. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.01.006
胶原静电纺纳米纤维膜对人牙髓细胞生物学行为的影响
张倩莉1,袁重阳1,刘力2,温世鹏2,△( ),王晓燕1,△(
),王晓燕1,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,牙体牙髓科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2. 北京化工大学,北京市先进弹性体工程技术研究中心, 北京 100029
Effects of electrospun collagen nanofibrous matrix on the biological behavior of human dental pulp cells
Qian-li ZHANG1,Chong-yang YUAN1,Li LIU2,Shi-peng WEN2,△( ),Xiao-yan WANG1,△(
),Xiao-yan WANG1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Cariology and Endodontology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Beijing Engineering Research Centre of Advanced Elastomers, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing 100029, China
摘要:
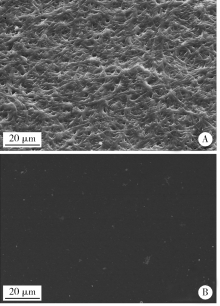
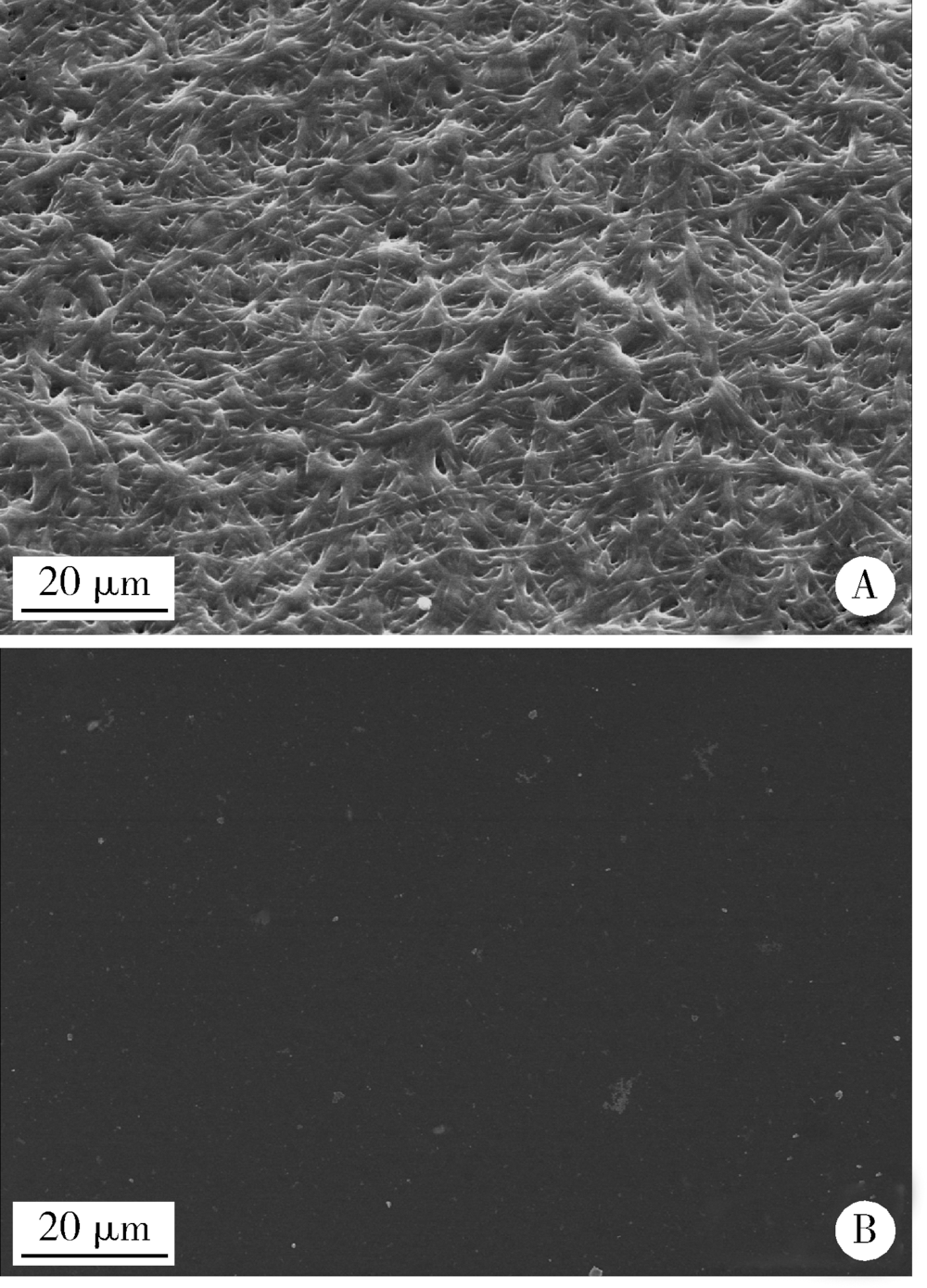
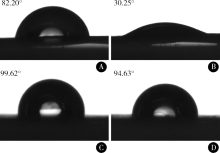
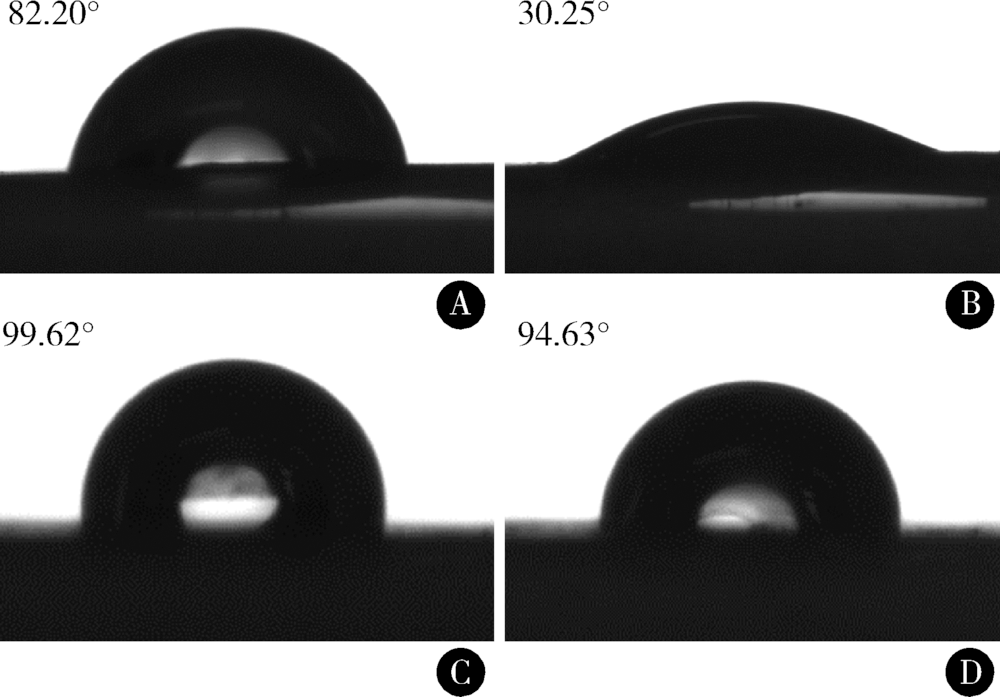
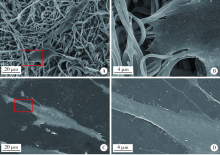
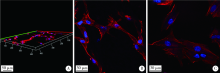
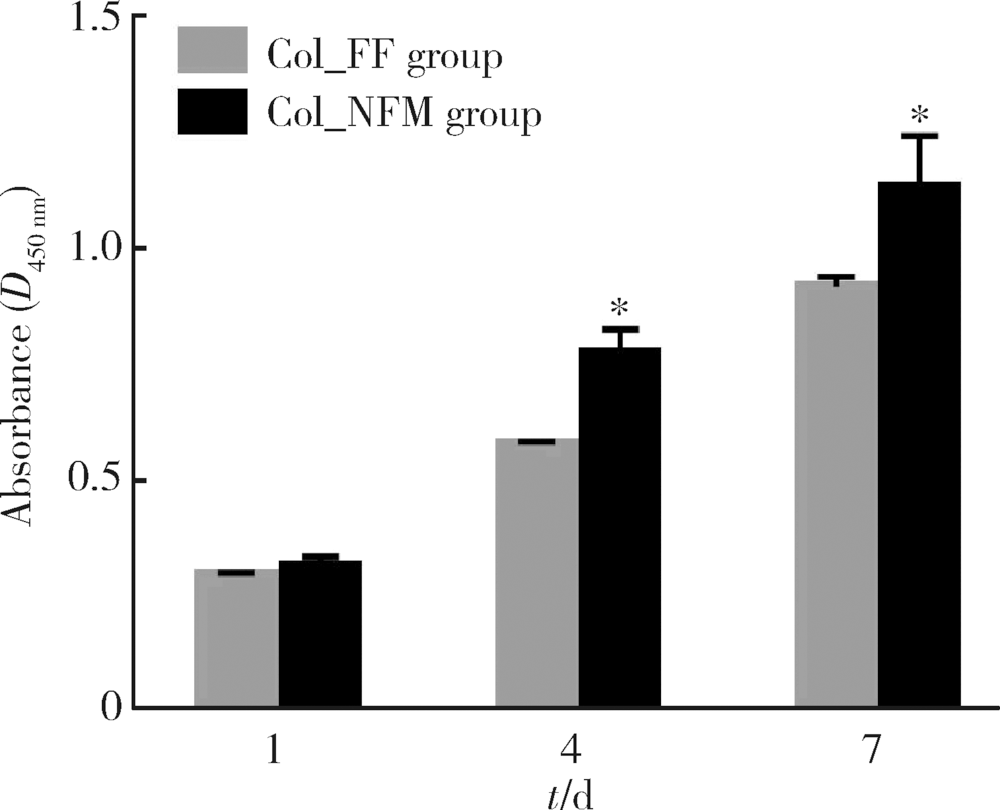
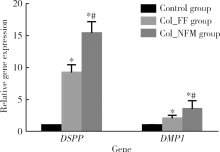
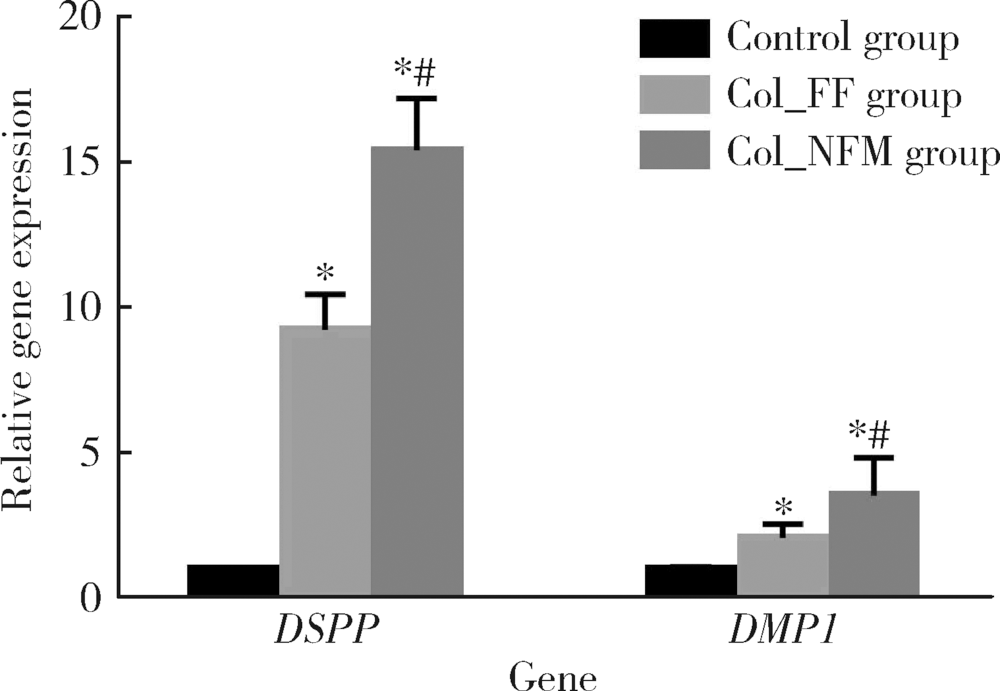
目的:比较人牙髓细胞(human dental pulp cells,hDPCs)在胶原静电纺纳米纤维膜(collagen nanofibrous matrix,Col_NFM)与直接沉积胶原膜(collagen flat film,Col_FF)上的黏附、增殖和分化情况,探究胶原纳米纤维支架对hDPCs生物学行为的影响。方法:采用扫描电镜(scanning electron microscopy, SEM)观察两种胶原膜的表面形貌,并比较其表面接触角和溶胀性能。将hDPCs分别接种于两种胶原膜表面共培养,SEM和激光共聚焦显微镜(laser scanning microscope,LSM)观察hDPCs在支架表面的生长形态,并用CCK-8法测定hDPCs的增殖情况。在诱导14 d后,比较成牙本质分化相关基因的表达变化,茜素红染色观察矿化结节的形成情况。结果:SEM图可见Col_NFM组纤维直径为(884±159) nm,纤维之间存在大量三维连通的孔隙结构,而Col_FF组表面平坦,未见孔隙结构。Col_NFM组瞬间表面接触角为85.03°±4.45°,溶胀度为3,Col_FF组瞬间表面接触角为98.98°±5.81°,溶胀度为1,Col_NFM组的亲水性和溶胀性能更佳。SEM和LSM结果显示,Col_NFM组hDPCs表现为不规则多角形,呈三维生长,Col_FF组细胞在二维平面上呈纺锤形生长。CCK-8结果显示,hDPCs在Col_NFM支架上增殖活性更高。在诱导14 d后,Col_NFM组成牙本质分化相关基因表达水平较Col_FF组显著升高(P<0.05),茜素红染色也更深。结论:Col_NFM具有纳米尺度的微观结构,并具备良好的亲水性和溶胀性能,相较于Col_FF,hDPCs在Col_NFM表面表现出更好的黏附、增殖和分化性能。
中图分类号:
- R781.3
| [1] |
Lysaght MJ, Reyes J . The growth of tissue engineering[J]. Tissue Eng, 2001,7(5):485-493.
doi: 10.1089/107632701753213110 pmid: 11694183 |
| [2] |
Malhotra N, Kundabala M, Acharya S. Current strategies and applications of tissue engineering in dentistry: a review part 1 [J]. Dent Update, 2009, 36(9): 577- 579, 581-582.
pmid: 20099610 |
| [3] |
Wiesmann HP, Meyer U, Plate U , et al. Aspects of collagen mineralization in hard tissue formation[J]. Int Rev Cytol, 2005,242:121-156.
doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(04)42003-8 pmid: 15598468 |
| [4] |
Sumita Y, Honda MJ, Ohara T , et al. Performance of collagen sponge as a 3-D scaffold for tooth-tissue engineering[J]. Biomaterials, 2006,27(17):3238-3248.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.01.055 pmid: 16504285 |
| [5] |
Prescott RS, Alsanea R, Fayad MI , et al. In vivo generation of dental pulp-like tissue by using dental pulp stem cells, a collagen scaffold, and dentin matrix protein 1 after subcutaneous transplantation in mice[J]. J Endod, 2008,34(4):421-426.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2008.02.005 pmid: 18358888 |
| [6] |
Kim NR, Lee DH, Chung PH , et al. Distinct differentiation pro-perties of human dental pulp cells on collagen, gelatin, and chitosan scaffolds[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2009,108(5):94-100.
doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.07.031 pmid: 19836718 |
| [7] |
Strom SC, Michalopoulos G . Collagen as a substrate for cell growth and differentiation[J]. Methods Enzymol, 1982,82(Pt A):544-555.
doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82086-7 |
| [8] |
Grinnell F, Bennett MH . Ultrastructural studies of cell: collagen interactions[J]. Methods Enzymol, 1982,82(Pt A):535-544.
doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82085-5 |
| [9] |
Elsdale T, Bard J . Collagen substrata for studies on cell behavior[J]. J Cell Biol, 1972,54(3):626-637.
doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.3.626 |
| [10] |
Woo KM, Chen VJ, Ma PX . Nano-fibrous scaffolding architecture selectively enhances protein adsorption contributing to cell attachment[J]. J Biomed Mater Res A, 2003,67(2):531-537.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.10098 pmid: 14566795 |
| [11] |
Wang J, Ma H, Jin X , et al. The effect of scaffold architecture on odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells[J]. Biomaterials, 2011,32(31):7822-7830.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.04.034 pmid: 3159766 |
| [12] |
Kuang R, Zhang Z, Jin X , et al. Nanofibrous spongy microspheres enhance odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells[J]. Adv Healthc Mater, 2015,4(13):1993-2000.
doi: 10.1002/adhm.201500308 pmid: 26138254 |
| [13] |
Kwon YS, Lee SH, Hwang YC , et al. Behaviour of human dental pulp cells cultured in a collagen hydrogel scaffold cross-linked with cinnamaldehyde[J]. Int Endod J,2017,50(1):58-66.
doi: 10.1111/iej.12592 pmid: 26650820 |
| [14] |
Coyac BR, Chicatun F, Hoac B , et al. Mineralization of dense collagen hydrogel scaffolds by human pulp cells[J]. J Dent Res, 2013,92(7):648-654.
doi: 10.1177/0022034513488599 pmid: 23632809 |
| [15] |
Pan S, Dangaria S, Gopinathan G , et al. SCF promotes dental pulp progenitor migration, neovascularization, and collagen remo-deling: potential applications as a homing factor in dental pulp regeneration[J]. Stem Cell Rev, 2013,9(5):655-667.
doi: 10.1007/s12015-013-9442-7 pmid: 23703692 |
| [16] |
Kim JJ, Bae WJ, Kim JM , et al. Mineralized polycaprolactone nanofibrous matrix for odontogenesis of human dental pulp cells[J]. J Biomater Appl, 2014,28(7):1069-1078.
doi: 10.1177/0885328213495903 |
| [17] |
Liu H, Ding X, Zhou G , et al. Electrospinning of nanofibers for tissue engineering applications[J]. J Nanomater, 2013,47(2013):63-72.
doi: 10.1155/2013/495708 |
| [18] |
Huang GT, Gronthos S, Shi S . Mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental tissues vs. those from other sources: their biology and role in regenerative medicine[J]. J Dent Res, 2009,88(9):792-806.
doi: 10.1177/0022034509340867 pmid: 2830488 |
| [19] |
Kumar G, Tison CK, Chatterjee K , et al. The determination of stem cell fate by 3D scaffold structures through the control of cell shape[J]. Biomaterials, 2011,32(35):9188-9196.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.054 pmid: 3428125 |
| [20] |
Chen CS, Mrksich M, Huang S , et al. Geometric control of cell life and death[J]. Science, 1997,276(5317):1425-1428.
doi: 10.1126/science.276.5317.1425 |
| [21] | Folkman J, Moscona A . Role of cell shape in growth control[J]. Nature, 1978,273(5661):345-349. |
| [22] |
McBeath R, Pirone DM, Nelson CM , et al. Cell shape, cytoske-letal tension, and RhoA regulate stem cell lineage commitment[J]. Developmental Cell, 2004,6(4):483-495.
doi: 10.1016/S1534-5807(04)00075-9 |
| [23] |
Lee JH, Lee JW, Khang G , et al. Interaction of cells on chargeable functional group gradient surfaces[J]. Biomaterials, 1997,18(4):351-358.
doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(96)00128-7 |
| [24] |
Khorasani MT, Mirzadeh H, Irani S . Plasma surface modification of poly (-lactic acid) and poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) films for improvement of nerve cells adhesion[J]. Radiat Phys Chem, 2008,77(3):280-287.
doi: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2007.05.013 |
| [1] | 王明瑞, 王起, 胡浩, 赖金惠, 唐鑫伟, 万春艳, 许克新, 徐涛. 覆膜金属输尿管支架治疗盆腔脂肪增多症所致肾积水的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 919-922. |
| [2] | 杨文博,余磊,张维宇,徐涛,王强. 带线输尿管支架自排技术在肾移植受者中的效果及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 656-660. |
| [3] | 段登辉,WANGHom-Lay,王恩博. 可吸收胶原膜在颊侧袋形瓣引导性骨再生手术中的作用: 一项回顾性影像学队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1097-1104. |
| [4] | 赖金惠,王起,姬家祥,王明瑞,唐鑫伟,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情期间延迟拔除输尿管支架对泌尿系结石术后患者生活质量和心理状态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [5] | 王磊,金香淑,董慧君,欧国敏,赖鑫源,庄辉,李彤,向宽辉. 基于COL1A1启动子和增强型绿色荧光蛋白基因建立人肝星状细胞活化的细胞模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 876-885. |
| [6] | 韩金涛,张宇翔,贾子昌,姜除寒,刘恋,栾景源,梁飞,赵彦清. Neuroform Atlas支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞未破裂性颅内宽颈动脉瘤[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 139-143. |
| [7] | 李雨柯,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华,陈晓颖. 不同pH值对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层海绵支架螯合锶离子的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 44-51. |
| [8] | 张春龙,王明瑞,王起,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 覆膜金属输尿管支架维持性治疗输尿管镜碎石术后难治性输尿管狭窄的远期疗效评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 674-679. |
| [9] | 邓艺,张一,李博文,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华. 不同交联剂处理对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层多孔支架的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 557-564. |
| [10] | 马欣蓉,朱晓鸣,李静,李德利,李和平,谭建国. 新型大气压冷等离子体射流处理对牙本质胶原纤维交联化的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 83-88. |
| [11] | 朱正达,高岩,何汶秀,方鑫,刘洋,魏攀,闫志敏,华红. 红色诺卡氏菌细胞壁骨架治疗糜烂型口腔扁平苔藓的疗效及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 964-969. |
| [12] | 庄金满,李天润,李选,栾景源,王昌明,冯琦琛,韩金涛. Rotarex 旋切导管在下肢动脉硬化闭塞症支架内再狭窄中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 740-743. |
| [13] | 董文敏,王明瑞,胡浩,王起,许克新,徐涛. Allium覆膜金属输尿管支架长期留置治疗输尿管-回肠吻合口狭窄的初期临床经验及随访结果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 637-641. |
| [14] | 曹春玲,杨聪翀,屈小中,韩冰,王晓燕. 可注射羟乙基壳聚糖基水凝胶理化性能及其对人牙髓细胞增殖和成牙本质向分化的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 10-17. |
| [15] | 贾子昌,李选,郑梅,栾景源,王昌明,韩金涛. 复合手术治疗无残端的症状性长段颈内动脉慢性闭塞[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 177-180. |
|
||