北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 829-834. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.05.007
重度颈内动脉狭窄伴未破裂动脉瘤的治疗策略
- 1. 北京大学第三医院 神经内科, 北京 100191
2. 北京大学第三医院 介入血管外科,北京 100191
Management of severe internal carotid stenosis with unruptured intracranial aneurysm
Hai-yan ZHAO1,Dong-sheng FAN1,Jin-tao HAN2,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Neurology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Interventional Radiology and Vascular Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
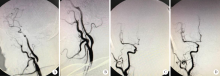
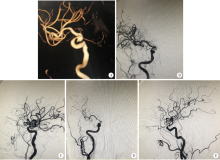
目的:探讨重度颈内动脉狭窄(≥70%)合并颅内未破裂动脉瘤的血管内治疗的安全性和可行性。方法:收集2012年1月至2015年7月在北京大学第三医院就诊的重度颈内动脉狭窄或闭塞患者共213例,其中伴有颅内未破裂动脉瘤的患者14例(6.6%),对其临床、影像学资料、治疗措施及预后进行分析。结果:14例重度颈内动脉狭窄或闭塞的患者中,动脉瘤共15个,11个位于狭窄后,1个位于狭窄前,3个位于非同流域。14例患者中1例实施颈内动脉剥脱术,11例成功置入颈内动脉支架(残留狭窄0~30%,平均6.4%),2例颈内动脉狭窄未处理。合并的15个动脉瘤大小1.0~7.0 mm,平均(2.8±1.5)mm,3例患者在处理狭窄同时处理动脉瘤,均行支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞,其中1例先处理动脉瘤;1例患者拒绝手术治疗,10例患者动脉瘤<5.0 mm,均未处理动脉瘤。围手术期均无手术并发症;3例患者失访,其他11例患者随访15~55个月,中位数37个月,均预后良好。结论:重度颈内动脉狭窄合并未破裂动脉瘤患者,需根据动脉瘤部位、大小等情况制定个体化方案治疗,而颅内小动脉瘤(<5.0 mm)不增加重度颈内动脉狭窄患者血管内治疗狭窄的手术风险。
中图分类号:
- R743
| [1] | Pappada G, Fiori L, Marina R , et al. Management of symptomatic carotid stenoses with coincidental intracranial aneurysms[J]. Acta Neurochir (Wien), 1996,138(12):1386-1390. |
| [2] | Ballotta E, Da GG, Manara R , et al. Extracranial severe carotid stenosis and incidental intracranial aneurysms[J]. Ann Vasc Surg, 2006,20(1):5-8. |
| [3] | Kim T, Lee H, Ahn S , et al. Incidence and risk factors of intracranial aneurysm: A national cohort study in Korea[J]. Int J Stroke, 2016,11(8):917-927. |
| [4] | Vlak MH, Algra A, Brandenburg R , et al. Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms, with emphasis on sex, age, comorbidity, country, and time period: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2011,10(7):626-636. |
| [5] | Kappelle LJ, Eliasziw M, Fox AJ , et al. Small, unruptured intracranial aneurysms and management of symptomatic carotid artery stenosis. North Am Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Group[J]. Neurology, 2000,55(2):307-309. |
| [6] | Griffiths PD, Worthy S, Gholkar A . Incidental intracranial vascular pathology in patients investigated for carotid stenosis[J]. Neuroradiology, 1996,38(1):25-30. |
| [7] | Héman LM, Jongen LM, van der Worp HB, et al. Incidental intracranial aneurysms in patients with internal carotid artery stenosis: A CT angiography study and a metaanalysis[J]. Stroke, 2009,40(4):1341-1346. |
| [8] | Kann BR, Matsumoto T, Kerstein MD . Safety of carotid end-arterectomy associated with small intracranial aneurysms[J]. South Med J, 1997,90(12):1213-1216. |
| [9] | Kim JH, Suh SH, Chung J , et al. Prevalence and characteristics of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in ischemic stroke patients[J]. Stroke, 2016,18(3):321-327. |
| [10] | 中华医学会神经外科学分会神经介入学组. 颅内动脉瘤血管内介入治疗中国专家共识(2013)[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2013,10(11):606-616. |
| [11] | Wiebers DO, Whisnant JP, Huston JR , et al. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: Natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment[J]. Lancet, 2003,362(9378):103-110. |
| [12] |
韩金涛, 赵海燕, 李选 . 颈动脉支架成形术血流动力学损害的相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015,47(5):804-808.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671167X.2015.05.014 |
| [13] | Ohta T, Nakahara I, Matsumoto S . Prediction of cerebral hyperperfusion after carotid artery stenting by cerebral angiography and single-photon emission computed tomography without acetazolamide challenge[J]. Neurosurgery, 2017,81(3):512-519. |
| [14] | Ferguson GG . Turbulence in human intracranial saccular aneurysms[J]. J Neurosurg, 1970,33(5):485-497. |
| [15] | Ballotta E, Da Giau G, Piccoli A , et al. Durability of carotid endarterectomy for treatment of symptomatic and asymptomatic stenosis[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2004,40(2):270-278. |
| [1] | 王明瑞, 王起, 胡浩, 赖金惠, 唐鑫伟, 万春艳, 许克新, 徐涛. 覆膜金属输尿管支架治疗盆腔脂肪增多症所致肾积水的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 919-922. |
| [2] | 万利, 张周沧, 丁嘉祥, 王梅. 中心静脉导管拔除后静脉空气栓塞1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 938-941. |
| [3] | 杨文博,余磊,张维宇,徐涛,王强. 带线输尿管支架自排技术在肾移植受者中的效果及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 656-660. |
| [4] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [5] | 张陈光,陈旭岩,吴圣,冯莉莉,王琰,陈妤,段敏,王科,宋琳琳. 咽旁脓肿致颈内动脉假性动脉瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1135-1138. |
| [6] | 赖金惠,王起,姬家祥,王明瑞,唐鑫伟,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情期间延迟拔除输尿管支架对泌尿系结石术后患者生活质量和心理状态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [7] | 彭清,刘佳君,刘焱,尚华,唐果,韩雅欣,龙丽. Padua预测评分和血清白蛋白水平在评估风湿病住院患者静脉血栓栓塞中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 625-630. |
| [8] | 刘颖,霍然,徐慧敏,王筝,王涛,袁慧书. 磁共振血管壁成像评估颈动脉中重度狭窄患者斑块特征与脑血流灌注的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [9] | 韩金涛,张宇翔,贾子昌,姜除寒,刘恋,栾景源,梁飞,赵彦清. Neuroform Atlas支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞未破裂性颅内宽颈动脉瘤[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 139-143. |
| [10] | 李雨柯,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华,陈晓颖. 不同pH值对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层海绵支架螯合锶离子的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 44-51. |
| [11] | 李芷晴,俞冰,蔡泽宇,王迎宝,张煦,周彪,方晓红,于芳,付毅,孙金鹏,李伟,孔炜. 柚皮素抑制马凡综合征小鼠胸主动脉瘤的形成[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 896-906. |
| [12] | 张春龙,王明瑞,王起,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 覆膜金属输尿管支架维持性治疗输尿管镜碎石术后难治性输尿管狭窄的远期疗效评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 674-679. |
| [13] | 邓艺,张一,李博文,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华. 不同交联剂处理对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层多孔支架的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 557-564. |
| [14] | 袁昌巍,王盈进,张书杰,沈胜利,段鸿洲. 显微外科手术与血管内栓塞治疗硬脊膜动静脉瘘临床疗效比较的meta分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 304-314. |
| [15] | 李伟浩,李伟,张学民,李清乐,焦洋,张韬,蒋京军,张小明. 去分支杂交手术和传统手术治疗胸腹主动脉瘤的结果比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 177-181. |
|
||