北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 835-839. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.05.008
Neuroform EZ支架在治疗复杂症状性颅内动脉重度狭窄中的应用
贾子昌1,卞焕菊2,李选1,栾景源1,王昌明1,刘启佳1,韩金涛1,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第三医院介入血管外科,北京 100191
2. 冠县人民医院神经内科,山东聊城 252500
Application of Neuroform EZ stent in the treatment of severe intracranial arterial stenosis with complex symptomatic
Zi-chang JIA1,Huan-ju BIAN2,Xuan LI1,Jing-yuan LUAN1,Chang-ming WANG1,Qi-jia LIU1,Jin-tao HAN1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Interventional Radiology and Vascular Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, ChinaDepartment of Neurology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Neurology, Guanxian People’s Hospital, Liaocheng 252500, Shandong, China
摘要:
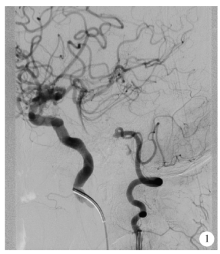
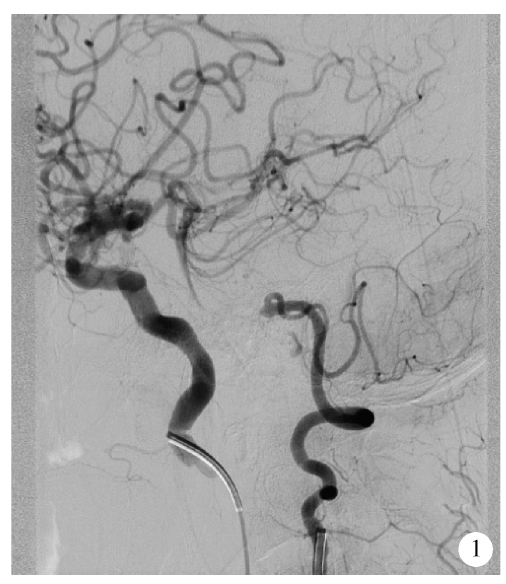
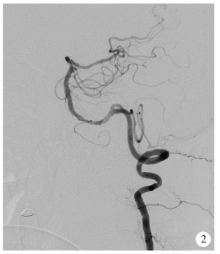
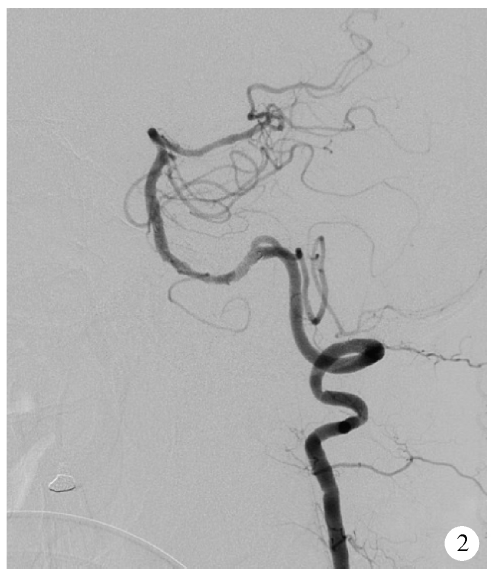
目的:评估Neuroform EZ支架治疗复杂症状性重度颅内动脉粥样硬化性狭窄(intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis,ICAS)的安全性和有效性。方法:回顾性分析2016年1月至2017年12月于北京大学第三医院介入血管外科选用经微导管释放的Neuroform EZ支架治疗的18例复杂症状性ICAS(手术路径严重迂曲、病变>10 mm或闭塞、病变接近分叉、狭窄附近合并动脉瘤等)的患者资料。主要终点事件定义为术后30 d内任何脑卒中事件(含缺血性和出血性)或任何原因引起的死亡,次要终点事件为支架治疗成功以及随访期间支架内再狭窄(狭窄率>50%)。结果:18例均获得技术成功,血管狭窄率从85%±7%降为18%±6%,主要终点事件发生率为5.6%(1/18),为左椎动脉串联病变患者术后出现基底节区梗塞。无出血性脑卒中及死亡并发症,1例合并狭窄附近动脉瘤患者予二期栓塞治疗。12例获得数字减影血管造影(digital subtraction angiography,DSA)随访,随访 8~26个月,平均随访时间(16±8)个月,有2例患者(2/12,16.7%)出现支架内再狭窄,其中1例为症状性再狭窄,予支架内球囊扩张治疗。结论:Neuroform EZ支架治疗经严格选择的复杂症状性重度ICAS是安全有效的,较传统支架有其优势。
中图分类号:
- R743.3
| [1] | Wang Y, Zhao X, Liu L , et al. Prevalence and outcomes of symptomatic intracranial large artery stenoses and occlusions in China: the Chinese Intracranial Atherosclerosis (CICAS) Study[J]. Stroke, 2014,45(3):663-669. |
| [2] | Wong LK . Global burden of intracranial atherosclerosis[J]. Int J Stroke, 2006,1(3):158-159. |
| [3] | Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Howlett-Smith H , et al. Comparison of warfarin and aspirin for symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2005,352(13):1305-1316. |
| [4] | Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Derdeyn CP , et al. Stenting versus aggressive medical therapy for intracranial arterial stenosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2011,365(11):993-1003. |
| [5] | Zaidat OO, Fitzsimmons BF, Woodward BK , et al. Effect of a balloon-expandable intracranial stent vs. medical therapy on risk of stroke in patients with symptomatic intracranial stenosis: the VISSIT randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA, 2015,313(12):1240-1248. |
| [6] | Miao Z, Zhang Y, Shuai J . Study Group of registry study of sten-ting for symptomatic intracranial artery stenosis in China: Thirty-day outcome of a multicenter registry study of stenting for sympto-matic intracranial artery stenosis in China[J]. Stroke, 2015,46(10):2822-2829. |
| [7] | Wang Y, Miao Z, Wang Y , et al. Protocol for a prospective, multicenter registry study of stenting for symptomatic intracranial artery stenosis in China[J]. BMJ Open, 2014,4(8):e005175. |
| [8] | Sacco RL, Kargman DE, Gu Q , et al. Race-ethnicity and determinants of intracranial atherosclerotic cerebral infarction. The Northern Manhattan Stroke Study[J]. Stroke, 1995,26(1):14-20. |
| [9] | Cheng XQ, Tian JM, Zuo CJ , et al. Hemodynamic alterations in unilateral chronic middle cerebral artery stenosis patients and the effect of percutaneous transluminal angioplasty and stenting: A perfusion-computed tomography study[J]. Acta Radiol, 2015,56(6):754-760. |
| [10] | Duan G, Feng Z, Zhang L , et al. Solitaire stents for the treatment of complex symptomatic intracranial stenosis after antithrombotic failure: Safety and efficacy evaluation[J]. Neurointerv Surg, 2016,8(7):680-684. |
| [11] | Marks MP . Is there a future for endovascular treatment of intracranial atherosclerotic disease after stenting and aggressive medical management for preventing recurrent stroke and intracranial stenosis (SAMMPRIS)?[J]. Stroke, 2012,43(2):580-584. |
| [12] | Vajda Z, Guthe T, Perez MA , et al. Prevention of intracranial in-stent restenosis: Predilatation with a drug eluting balloon, followed by the deployment of a self-expanding stent[J]. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2013,36(2):346-352. |
| [13] | Hahnel S, Ringleb P, Hartmann M . Treatment of intracranial stenosis using the Neuroform stent system: Initial experience in five cases[J]. Neuroradiology, 2016,48(7):479-485. |
| [14] | Liu L, Ma N, Mo DP , et al. Enterprise stent in treatment of symptomatic complex intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis[J]. Chin J Stroke, 2017,12(7):592-597. |
| [15] | Liu L, Zhao X, Mo D , et al. Stenting for symptomatic intracranial vertebrobasilar artery stenosis: 30-day results in a high-volume stroke center[J]. Clin Neurol Neurosurg, 2016,4(143):132-138. |
| [16] | Krischek Ö, Miloslavski E, Fischer S , et al. A comparison of functional and physical properties of self-expanding intracranial stents[J]. Minim Invasive Neurosurg, 2011,54(1):21-28. |
| [17] | Shin YS, Kim BM, Suh SH , et al. Wingspan stenting for intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis: Clinical outcomes and risk factors for in-stent restenosis[J]. Neurosurgery, 2013,72(4):596-604. |
| [18] | Vajda Z, Schmid E, Guthe T , et al. The modified Bose method for the endovascular treatment of intracranial atherosclerotic arterial stenoses using the Enterprise stent[J]. Neurosurgery, 2012,70(1):91-101. |
| [1] | 王明瑞, 王起, 胡浩, 赖金惠, 唐鑫伟, 万春艳, 许克新, 徐涛. 覆膜金属输尿管支架治疗盆腔脂肪增多症所致肾积水的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 919-922. |
| [2] | 杨文博,余磊,张维宇,徐涛,王强. 带线输尿管支架自排技术在肾移植受者中的效果及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 656-660. |
| [3] | 赖金惠,王起,姬家祥,王明瑞,唐鑫伟,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情期间延迟拔除输尿管支架对泌尿系结石术后患者生活质量和心理状态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [4] | 于欢,杨若彤,王斯悦,吴俊慧,王梦莹,秦雪英,吴涛,陈大方,武轶群,胡永华. 2型糖尿病患者使用二甲双胍与缺血性脑卒中发病风险的队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 456-464. |
| [5] | 韩金涛,张宇翔,贾子昌,姜除寒,刘恋,栾景源,梁飞,赵彦清. Neuroform Atlas支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞未破裂性颅内宽颈动脉瘤[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 139-143. |
| [6] | 李雨柯,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华,陈晓颖. 不同pH值对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层海绵支架螯合锶离子的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 44-51. |
| [7] | 张春龙,王明瑞,王起,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 覆膜金属输尿管支架维持性治疗输尿管镜碎石术后难治性输尿管狭窄的远期疗效评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 674-679. |
| [8] | 杨若彤,王梦莹,李春男,于欢,王小文,吴俊慧,王斯悦,王伽婷,陈大方,吴涛,胡永华. 缺血性脑卒中全基因组关联研究提示阳性基因位点与睡眠行为的交互作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 412-420. |
| [9] | 邓宇含,姜勇,王子尧,刘爽,汪雨欣,刘宝花. 基于长短期记忆网络和Logistic回归的重症监护病房脑卒中患者院内死亡风险预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 458-467. |
| [10] | 邓艺,张一,李博文,王梅,唐琳,刘玉华. 不同交联剂处理对脱细胞小肠黏膜下层多孔支架的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 557-564. |
| [11] | 吴俊慧,武轶群,吴瑶,王紫荆,吴涛,秦雪英,王梦莹,王小文,王伽婷,胡永华. 北京城镇职工2型糖尿病患者缺血性脑卒中发病率及主要危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 249-254. |
| [12] | 任国勇,吴雪梅,李颖,李婕妤,孙伟平,黄一宁. 大血管闭塞性脑卒中亚急性期磁敏感血管征的表现[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1133-1138. |
| [13] | 朱正达,高岩,何汶秀,方鑫,刘洋,魏攀,闫志敏,华红. 红色诺卡氏菌细胞壁骨架治疗糜烂型口腔扁平苔藓的疗效及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 964-969. |
| [14] | 庄金满,李天润,李选,栾景源,王昌明,冯琦琛,韩金涛. Rotarex 旋切导管在下肢动脉硬化闭塞症支架内再狭窄中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 740-743. |
| [15] | 候越,赵旭彤,谢志颖,袁云,王朝霞. 线粒体DNA 8344 A>G突变导致的MELAS/MERRF/Leigh重叠综合征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 851-855. |
|
||