北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1124-1129. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.026
利用近场微波系统检测不同方法干燥根管的效果
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,牙体牙髓科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
2. 北京大学工学院力学与工程科学系,湍流与复杂系统国家重点实验室, 北京 100871
3. 北京大学国际医院口腔科, 北京 102206
Effects of different methods on drying root canal by near-field microwave detection system
Jia-sha WANG1,Pei-yu WANG2,Yu-hong LIANG1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Cariology and Endodontology,Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. State Key Laboratory for Turbulence and Complex Systems, College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
3. Department of Stomatology, Peking University International Hospital, Beijing 102206, China
摘要:
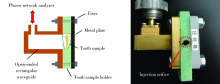
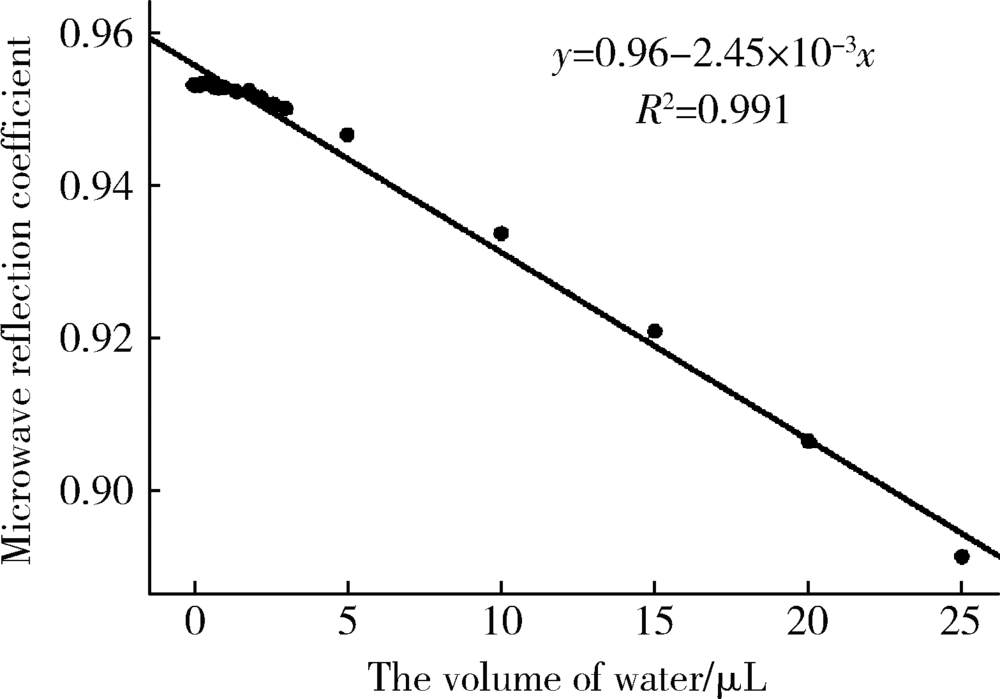
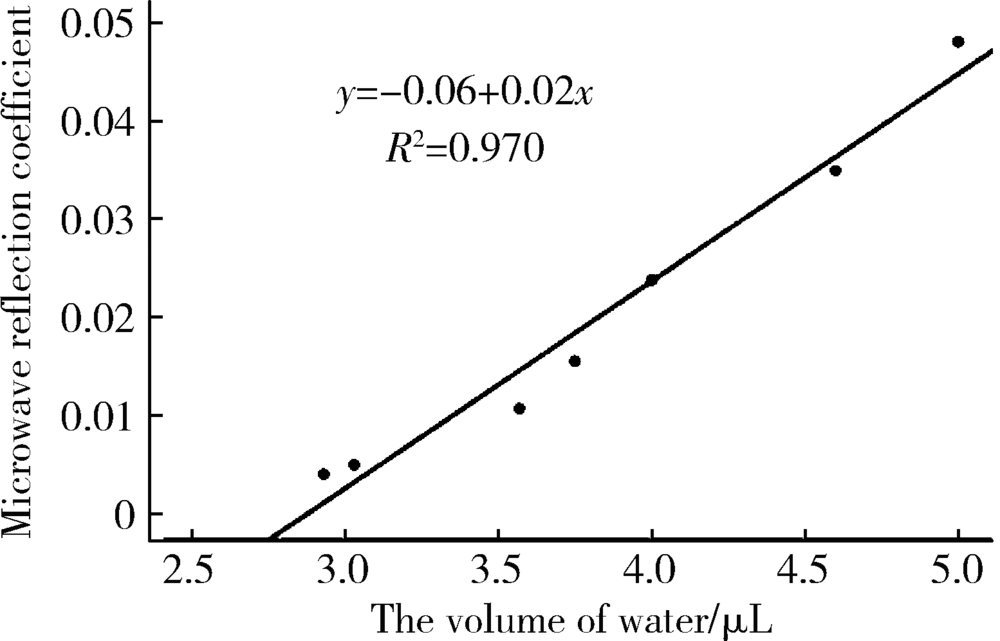
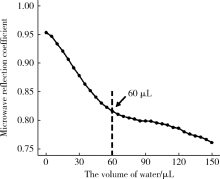
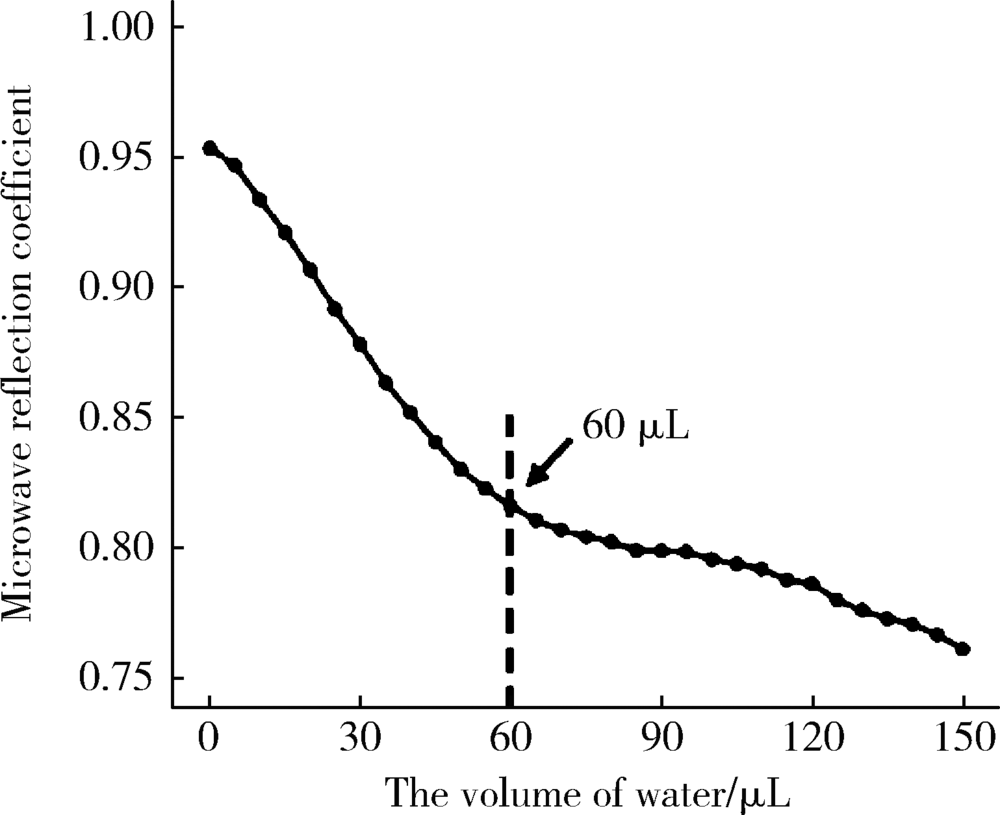
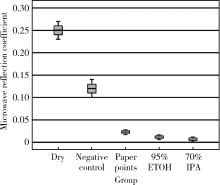
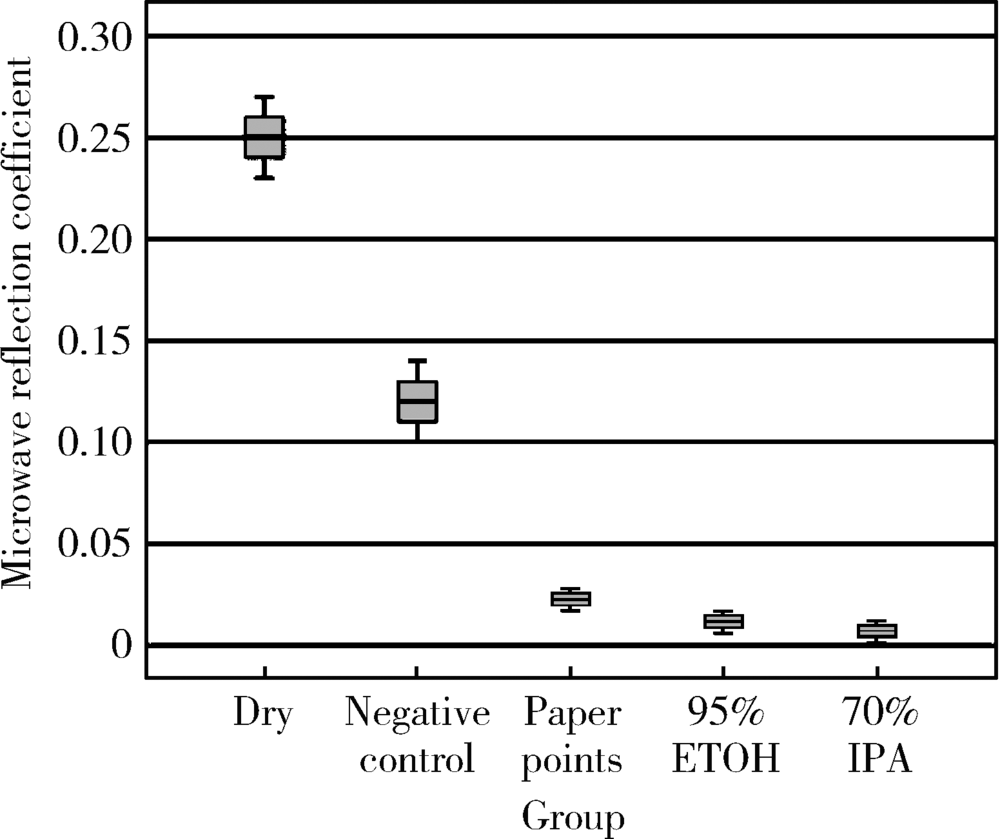
目的 建立近场微波检测系统,并评价其测量含水量的准确性,观察不同方法干燥根管的效果。方法 构建近场微波反射检测系统,检测Eppendorf管中、离体牙根管内已知定量的蒸馏水并记录微波反射系数,评价近场微波系统测量含水量的准确性。将12颗牙根发育完全、根管弯曲度小于10°的单根管下颌前磨牙截冠后保留14 mm牙根,机械预备至F3后烘干,向根管内注入10 μL蒸馏水,按照不同干燥方法分为4组(n=12),采用近场微波系统检测烘干后和干燥完成后含水量的变化,评价其干燥效果:(1)阴性对照组,根管内注入10 μL蒸馏水,不采用任何干燥方法;(2)纸尖干燥实验组,用4根 #60纸尖依次插入根管中上1/3至有阻力,再用#40纸尖插入根管内至工作长度,重复至立体显微镜下纸尖尖端无水痕视为干燥完成;(3)95%(体积分数)乙醇干燥实验组,使用纸尖干燥根管(干燥方法同纸尖实验组)后,向根管内注入10 μL 95%乙醇,静置10 s后,再用纸尖干燥;(4)70%(体积分数)异丙醇干燥实验组,使用纸尖干燥根管(干燥方法同纸尖实验组)后,向根管内注入10 μL 70%异丙醇,静置10 s后,再用纸尖干燥。采用线性回归分析比较近场微波法和物理测量法检测含水量的相关性,计算Pearson相关系数。采用卡方检验比较不同方法干燥根管的差异,并进行两两比较。结果 Eppendorf管及离体根管内含水量的近场微波反射系数和含水量的物理测量值呈线性关系,R 2分别为0.991和0.970。不同干燥方法的实验组之间的微波反射系数差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。纸尖干燥后根管内残余的含水量最多,微波反射系数最大,为 0.023。70%异丙醇进行根管干燥,残余的含水量最少,微波反射系数为0.006,干燥效果最佳。结论 近场微波系统可以用来检测根管内含水量的变化,70%异丙醇干燥根管的效果优于95%乙醇和纸尖干燥法。
中图分类号:
- R781.3
| [1] | 高学军, 岳林, 董艳梅 , 等. 牙体牙髓病学[M]. 2版. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2013: 387. |
| [2] | Wong Y, Spencer P . Continuing etching of an all-in-one adhesive in wet dentin tubules[J]. J Dent Res, 2005,84(4):350-354. |
| [3] | Hasselgren G . The prognosis for endodontic treatment of obliterated root canals[J]. J Endod, 1988,14(11):565-567. |
| [4] | Bence RW . Handbook of clinical endodontics[M]. London: Mosby, 1980. |
| [5] | Nagas E, Uyanik MO, Eymirli A , et al. Dentin moisture conditions affect the adhesion of root canal sealers[J]. J Endod, 2012,38(2):240-244. |
| [6] | Stevens RW, Strother JM, Mcclanahan SB . Leakage and sealer penetration in smear-free dentin after a final rinse with 95% ethanol[J]. J Endod, 2006,32(8):785-788. |
| [7] | Gibby SG, Wong Y, Kulild JC , et al. Novel methodology to eva-luate the effect of residual moisture on epoxy resin sealer/dentine interface: a pilot study[J]. Int Endod J, 2011,44(3):236-244. |
| [8] | Roggendorf MJ, Ebert J, Petschelt A , et al. Influence of moisture on the apical seal of root canal fillings with five different types of sealer[J]. J Endod, 2007,33(1):31-33. |
| [9] | 黎粤华, 李靖宇 . 基于微波技术的温室作物含水量检测[J]. 森林工程, 2013(3):90-92. |
| [10] | 杨厚荣, 罗友哲, 陈小英 . 微波雷达水分传感器应用于有耗介质水分测量研究[J]. 计测技术, 2010(S1):52-56. |
| [11] | Takeyama T, Nikawa Y. Diagnosis of dental caries using millimeter wave reflection[C]// Asia Pacific Microwave Conference. Europe: Microwave Conference, 2009: 1196-1199. |
| [12] | Komabayashi T, Zhu Q, Jiang J , et al. A rapid nondestructive method for root dentin moisture measurements: in vitro pilot study[J]. Oral Surg Oral Medo, 2009,107(3):e107-e111. |
| [13] | Pane ES, Palamara JEA, Messer HH . Critical evaluation of the push-out test for root canal filling materials[J]. J Endod, 2013,39(5):669-673. |
| [14] | Tay FR, Pashley DH, Yoshiyama M . Two modes of nanoleakage expression in single-step adhesives[J]. J Dent Res, 2002,81(7):472-476. |
| [15] | Zoughi R . Microwave non-destructive testing and evaluation principles[M]. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media, 2012. |
| [16] | Pozar DM . Microwave engineering[M]. USA: John Wiley & Sons, 2009. |
| [17] | 周在杞 . 微波检测技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008. |
| [18] | Sacilik K, Tarimci C, Colak A . Moisture content and bulk density dependence of dielectric properties of safflower seed in the radio frequency range[J]. J Food Eng, 2007,78(4):1111-1116. |
| [19] | Krupka J . Frequency domain complex permittivity measurements at microwave frequencies[J]. Meas Sci Technol, 2006,17(6):R55. |
| [20] | McKeown MS, Trabelsi S, Tollner EW , et al. Dielectric spectroscopy measurements for moisture prediction in Vidalia onions[J]. J Food Eng, 2012,111(3):505-510. |
| [21] | Wang PY, Zhou L . Near-field microwave identification and quantitative evaluation of liquid ingress in honeycomb sandwich structures[J]. NDT & E Int, 2016(83):32-37. |
| [22] | Gao M, Tang J, Johnson JA , et al. Dielectric properties of ground almond shells in the development of radio frequency and microwave pasteurization[J]. J Food Eng, 2012,112(4):282-287. |
| [23] | Stuchly SS . Dielectric properties of some granular solids containing water[J]. J Microwave Power, 1970,5(2):62-68. |
| [24] | Engel GT, Goodell GG , McClanahan SB. Sealer penetration and apical microleakage in smear-free dentin after a final rinse with either 70% isopropyl alcohol or Peridex[J]. J Endod, 2005,31(8):620-623. |
| [25] | 邢其毅, 徐瑞秋, 裴伟伟 , 等. 基础有机化学[M]. 4版. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2016: 7. |
| [1] | 陈思鹭, 王海菊, 吴宇财, 李志华, 黄燕波, 何宇辉, 许洋洋, 李学松, 贯华. 成人肾积水病因分析:一项单中心横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 913-918. |
| [2] | 王明瑞, 王起, 胡浩, 赖金惠, 唐鑫伟, 万春艳, 许克新, 徐涛. 覆膜金属输尿管支架治疗盆腔脂肪增多症所致肾积水的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 919-922. |
| [3] | 何佩瑶,包旭东. 常温流动牙胶封闭剂GuttaFlow2单尖充填弯曲根管的封闭效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 99-105. |
| [4] | 辛鹏,张昊,姜振明. 膀胱内灌注电灼联合水扩张法治疗女性间质性膀胱炎[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 865-870. |
| [5] | 秦彩朋,王飞,杜依青,张晓威,李清,刘士军,徐涛. 无症状无积水输尿管结石4例患者的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 939-942. |
| [6] | 李志华,徐纯如,刘颖,贯华,张萌,车新艳,唐琦,黄燕波,李学松,周利群. 饮水习惯与上尿路尿路上皮癌病理特征的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 621-627. |
| [7] | 李玭,赵艾,武薇,张健,王培玉,蓝航莲,张玉梅. 北京市和湖南省郴州市4~8月龄婴儿蔬菜水果添加情况的追踪性调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 526-531. |
| [8] | 闫文娟,钟洁,林碧琛,丁美丽,陈小贤. 常温流动牙胶应用于根尖诱导成形术后根管充填[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 77-82. |
| [9] | 杜莹珏,刘维超,陈茜,程永静. 秋水仙碱致慢性肾脏病患者肌肉病变1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1188-1190. |
| [10] | 于妍斐,何世明,吴宇财,熊盛炜,沈棋,李妍妍,杨风,何群,李学松. 延胡索酸水合酶缺陷型肾细胞癌的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 640-646. |
| [11] | 王京旗,王霄. 掺锶磷酸钙骨水泥材料生物学性能的动物实验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 378-383. |
| [12] | 王昱,邓雪蓉,季兰岚,张晓慧,耿研,张卓莉. 超声检测痛风患者肌腱受累的危险因素和诊断价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 143-149. |
| [13] | 刘世博,高辉,冯元春,李静,张彤,万利,刘燕鹰,李胜光,罗成华,张学武. 腹膜后纤维化致肾盂积水的临床分析:附17例报道[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1069-1074. |
| [14] | 陈文新,包旭东,岳林. 固化方式对树脂水门汀氧阻聚层形成的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1117-1123. |
| [15] | 钟剑球,曾沛英,王庆文. 类风湿关节炎合并淋巴水肿2例及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1157-1161. |
|
||