北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1150-1152. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.06.028
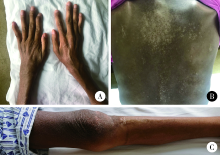
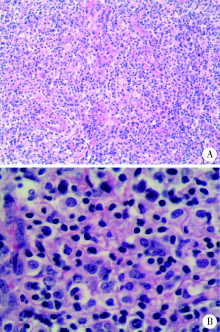
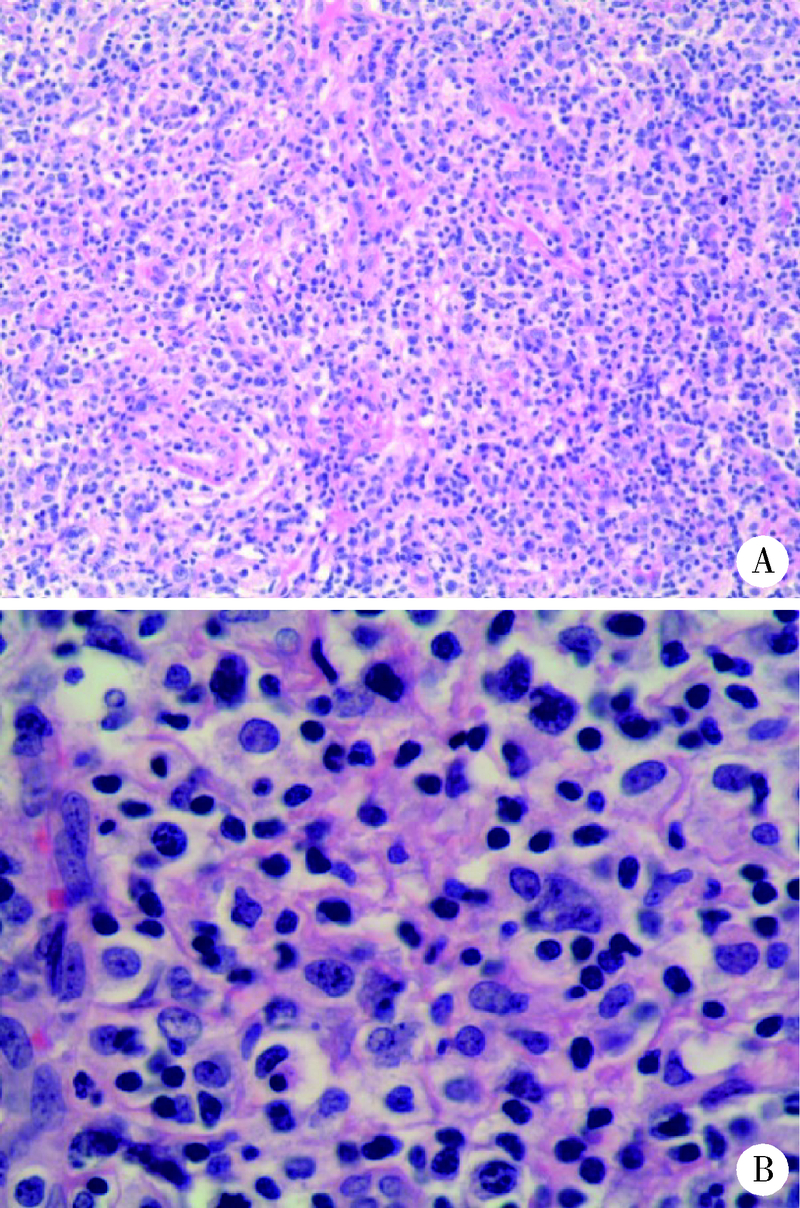
以发热、关节炎、皮肤色素沉着为主要表现的血管免疫母细胞性T细胞淋巴瘤1例
- 1. 北京大学人民医院 风湿免疫科
2. 北京大学人民医院 病理科
3. 北京大学人民医院 内分泌科,北京 100044
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma with fever, arthritis and skin pigmentation: A case report
Gong CHENG1,Xia ZHANG1,Fei YANG2,Jia-yu CHENG3,Yan-ying LIU1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology & Immunology
2. Department of Department of Pathology
3. Department of Endocrinology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
中图分类号:
- R733
| [1] |
Yabe M, Dogan A, Horwitz SM, et al. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma[J]. Cancer Treat Res, 2019,176:99-126.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-99716-2_5 pmid: 30596215 |
| [2] |
Eng V, Kulkarni SK, Kaplan MS, et al. Hypereosinophilia with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2020,124(5):513-515.
doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2020.01.028 pmid: 32044452 |
| [3] | 于慧, 杜玉薪, 李玲, 等. 血管免疫母细胞性T细胞淋巴瘤的临床特点和预后分析[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2020,55(3):414-418. |
| [4] |
Lunning MA, Vose JM. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: the many-faced lymphoma[J]. Blood, 2017,129(9):1095-1102.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-692541 pmid: 28115369 |
| [5] | Chiba S, Sakata-Yanagimoto M. Advances in understanding of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma[J/OL]. Leukemia, 2020(2020-07-23) [2020-07-29]. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41375-020-0990-y. |
| [6] |
Broccoli A, Zinzani PL. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma[J]. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am, 2017,31(2):223-238.
doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2016.12.001 pmid: 28340875 |
| [1] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | 钟华, 李原, 徐丽玲, 白明欣, 苏茵. 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [3] | 李正芳,罗采南,武丽君,吴雪,孟新艳,陈晓梅,石亚妹,钟岩. 抗氨基甲酰化蛋白抗体在诊断类风湿关节炎中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [4] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [5] | 马利加,胡攀攀,刘晓光. 脊柱转移癌伴软脊膜转移1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 563-566. |
| [6] | 熊焰,李鑫,梁丽,李东,鄢丽敏,李雪迎,邸吉廷,李挺. 甲状腺粗针穿刺活检病理诊断的准确性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 234-242. |
| [7] | 哈雪梅,姚永正,孙莉华,辛春杨,熊焰. 实性肺胎盘样变形1例及文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [8] | 宁博涵,张青霞,杨慧,董颖. 伴间质细胞增生、玻璃样变性及索状结构的子宫内膜样腺癌1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 366-369. |
| [9] | 陈适,刘田. 重视系统性血管炎的早期识别和个体化治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1065-1067. |
| [10] | 曹瑞洁,姚中强,焦朋清,崔立刚. 不同分类标准对中国大动脉炎的诊断效能比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1128-1133. |
| [11] | 徐朝焰,林长艺,叶达梅,吴培埕,宋明辉,刘有添,邓琼,黄雪艳,范忠晓,游雪兰. 感染性关节炎诊断分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1234-1237. |
| [12] | 郝哲,岳蜀华,周利群. 拉曼技术在泌尿系统肿瘤检测中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 779-784. |
| [13] | 于博,赵扬玉,张喆,王永清. 妊娠合并感染性心内膜炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 578-580. |
| [14] | 孟广艳,张筠肖,张渝昕,刘燕鹰. IgG4相关性疾病中枢神经系统受累的临床特点分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1043-1048. |
| [15] | 翟莉,邱楠,宋惠. 多中心网状组织细胞增生症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1183-1187. |
|
||