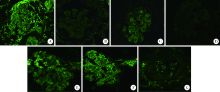
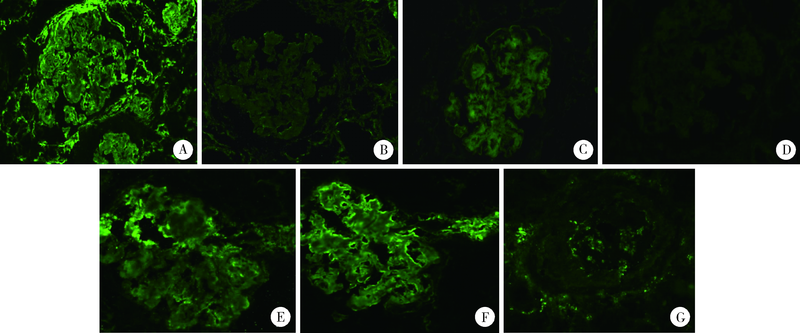
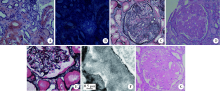
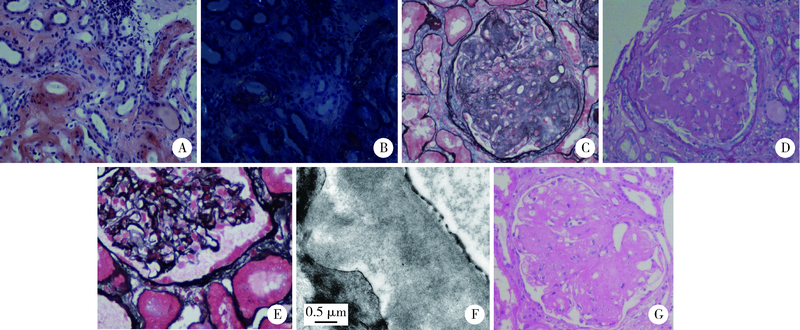
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1162-1165. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.06.031
4例重链或轻重链肾淀粉样变性患者的临床病理特点
赵冬慧1,李丹阳1,张帆1,屈磊1,张颖1,王素霞2,刘刚1,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第一医院 肾内科 北京大学肾脏病研究所 卫生部重点实验室 教育部慢性肾脏病防治重点实验室
2. 北京大学第一医院 病理中心电镜室, 北京 100034
摘要:
中图分类号:
- R597+.2
| [1] |
Jean DS, Merrill DB, Joel NB, et al. Amyloid fibril proteins and amyloidosis: chemical identification and clinical classification international society of amyloidosis 2016 nomenclature guidelines[J]. Amyloid, 2016,23(4):209-213.
doi: 10.1080/13506129.2016.1257986 pmid: 27884064 |
| [2] |
Nasr SH, Said SM, Valeri AM, et al. The diagnosis and characteristics of renal heavy-chain and heavy/light-chain amyloidosis and their comparison with renal light-chain amyloidosis[J]. Kidney Int, 2013,83(3):463-470.
doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.414 pmid: 23302715 |
| [3] | Sethi S, Theis JD, Leung N, et al. Mass spectrometry-based proteomic diagnosis of renal immunoglobulin heavy chain amyloidosis[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephral, 2010,5(12):2180-2187. |
| [4] |
杨林, 李娟, 王建荣, 等. 肾轻重链淀粉样变一例[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志, 2014,30(8):642.
doi: DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001?7097.2014.08.017 |
| [5] | 曾彩虹, 钟永忠, 刘志红. 肾脏重链淀粉样变性[J]. 肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志, 2013,22(3):282-287. |
| [6] | 张璐璐, 张晓雪, 权松霞, 等. 多发性骨髓瘤合并肾轻重链淀粉样变1例报道[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2016,30(10):1010-1011. |
| [7] |
Eulitz M, Weiss DT, Solomon A. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain-associated amyloidosis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1990,87(17):6542-6546.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6542 pmid: 2118650 |
| [8] |
Kaplan B, Martin BM, Boykov O, et al. Co-deposition of amyloidogenic immunoglobulin light and heavy chains in localized pulmonary amyloidosis[J]. Virchows Arch, 2005,447(4):756-761.
doi: 10.1007/s00428-005-0009-0 |
| [9] |
Rubinstein S, Cornell RF, Du L, et al. Novel pathologic scoring tools predict end-stage kidney disease in light chain (AL) amyloidosis[J]. Amyloid, 2017,24(3):205.
doi: 10.1080/13506129.2017.1360272 pmid: 28758811 |
| [10] |
Picken MM. Non-light-chain immunoglobulin amyloidosis: time to expand or refine the spectrum to include light+heavy chain amyloidosis[J]. Kidney Int, 2013,83(3):353-356.
doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.433 pmid: 23446254 |
| [11] |
Safadi S, Saad A, Quint PS, et al. Disappearance of immuno-globulins from persistent renal amyloid deposits following stem cell transplantation for heavy-and light-chain amyloidosis[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2015,30(7):1151-1155.
doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv018 pmid: 25796445 |
| [12] |
Hassoun Y, Kharfandabaja MA, Baz R. Bortezomib plus dexamethasone results in a late organ response in primary heavy-chain amyloidosis without a hematologic response[J]. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther, 2015,8(3):138-139.
doi: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2015.01.002 pmid: 25732670 |
| [13] |
Laura M. Dember amyloidosis-associated kidney disease[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2006,17(12):3458-3471.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006050460 pmid: 17093068 |
| [1] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | 钟华, 李原, 徐丽玲, 白明欣, 苏茵. 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [3] | 刘家骏, 刘国康, 朱玉虎. 免疫相关性重症肺炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 932-937. |
| [4] | 黄教悌,胡菁,韩博. 治疗相关神经内分泌前列腺癌机制研究与靶向治疗新进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 557-561. |
| [5] | 李正芳,罗采南,武丽君,吴雪,孟新艳,陈晓梅,石亚妹,钟岩. 抗氨基甲酰化蛋白抗体在诊断类风湿关节炎中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [6] | 侯婉音,董捷. 腹膜透析患者获得性肾囊肿出血3例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 546-550. |
| [7] | 李文菁,张保宙,李恒,赖良鹏,杜辉,孙宁,龚晓峰,李莹,王岩,武勇. 胫距跟融合治疗终末期踝和后足病变的中短期临床结果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 299-306. |
| [8] | 冯琦琛,盖铄,王昌明,李选. 经同侧大隐静脉入路髂静脉成型及支架植入术在日间治疗模式中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 322-325. |
| [9] | 彭圣嘉,祁雨,孙丽杰,李丹,王新宇,韩江莉,陈宝霞,张媛. 传入压力反射衰竭合并低钠血症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 357-361. |
| [10] | 陈晨,梁宇红. 复杂根管上颌磨牙的根管治疗3例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 190-195. |
| [11] | 任晓萌,李凯一,李春蕾. 基于转录组测序探索口腔扁平苔藓局部激素治疗敏感性相关分子特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 32-38. |
| [12] | 张晗,秦亦瑄,韦帝远,韩劼. 牙周炎患者种植修复维护治疗依从性的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 39-44. |
| [13] | 周颖,赵宁,黄竑远,李庆祥,郭传瑸,郭玉兴. 双层软组织缝合封闭技术在下颌骨中早期药物相关性颌骨骨坏死患者手术治疗中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 51-56. |
| [14] | 邹雪,白小娟,张丽卿. 艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [15] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
|
||