北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 126-132. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.01.019
下颌下腺质量和体积的实体体外检测
王怡平1,蔡志刚1,彭歆1,张杰1,孙志鹏2,李巍1,张雷1,Δ( ),俞光岩1,Δ(
),俞光岩1,Δ( )
)
- 1.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,颌面外科, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 10008
2.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,放射科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
Measurement of the weight and volume of submandibular gland in vitro
WANG Yi-ping1,CAI Zhi-gang1,PENG Xin1,ZHANG Jie1,SUN Zhi-peng2,LI Wei1,ZHANG Lei1,Δ( ),YU Guang-yan1,Δ(
),YU Guang-yan1,Δ( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Oral Radiology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
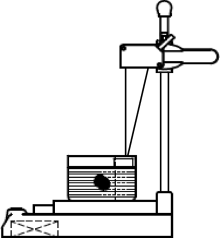
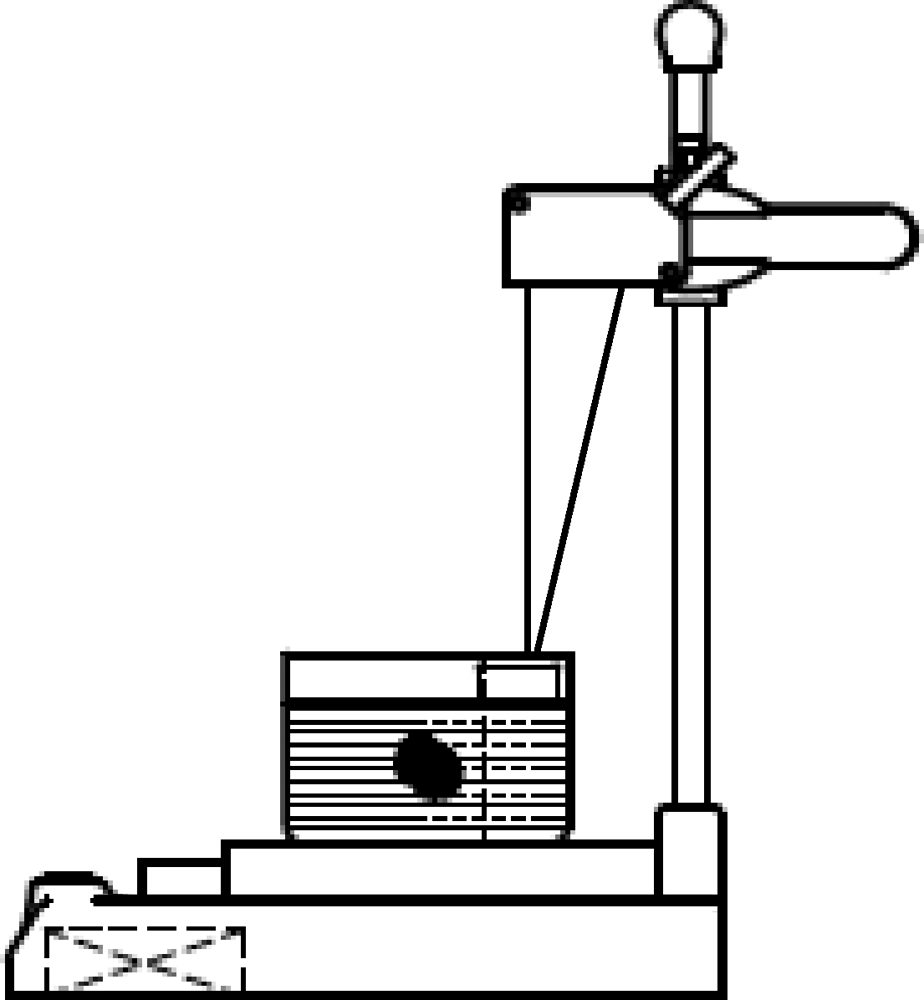
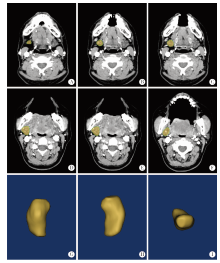
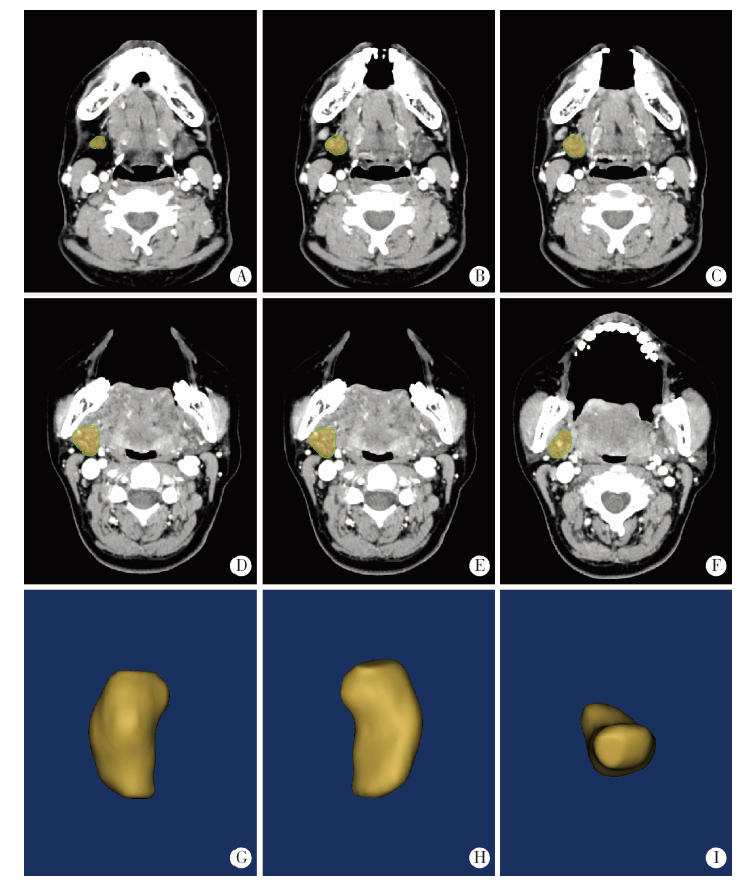
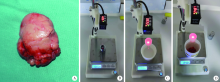
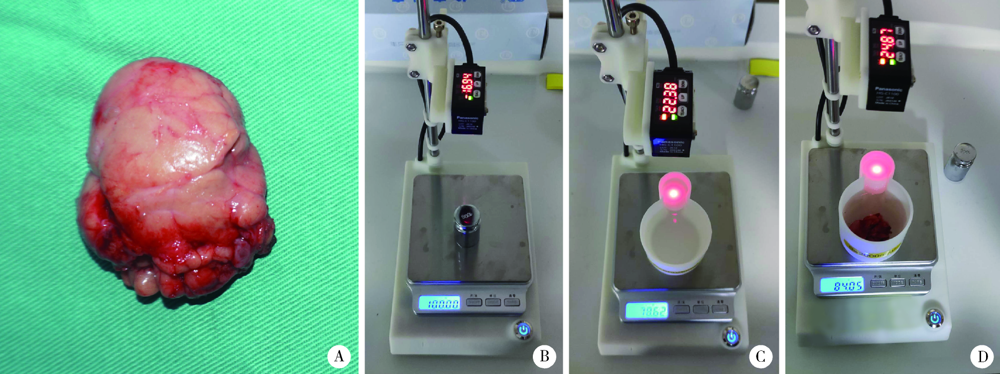
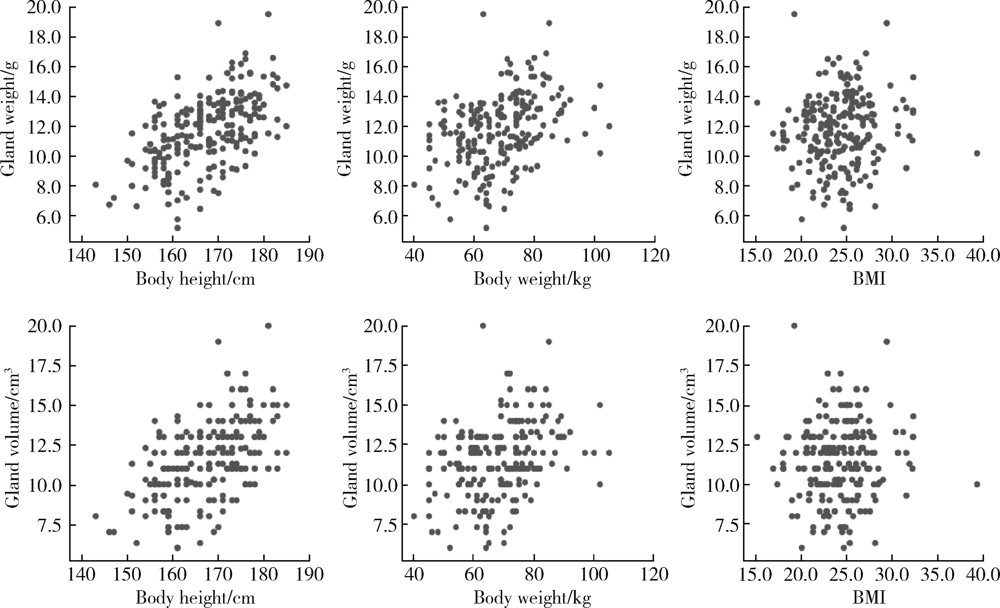
目的: 采用腺体实体体外检测法测量正常下颌下腺的质量和体积,探讨影响下颌下腺质量和体积可能的相关因素,并与CT容积重建法测量值做比较,评估两种检测方法的一致性。方法: 选择2019年5月至2020年1月在北京大学口腔医院因口腔癌接受选择性颈淋巴结清扫术且术后组织病理学证实下颌下腺正常的患者,术前CT扫描图像通过CT容积重建法测量下颌下腺体积;术中颈淋巴结清扫标本离体后沿包膜完整游离下颌下腺,使用一体式无菌测量装置测量下颌下腺的质量和体积,进行两种测量方法所得下颌下腺体积的比较。参照中华医学会老年医学会和世界卫生组织(2000年)标准对受试者进行年龄分组,测量不同性别和年龄组正常下颌下腺质量和体积,分析年龄、性别、身高、体质量、体重指数等因素与下颌下腺质量和体积的相关性。结果: 共完成220例受试者正常下颌下腺质量和体积的腺体实体体外检测,下颌下腺平均质量为(11.69±2.45) g,平均体积为(11.55±2.41) cm3。CT容积重建法测得的下颌下腺体积为实体体外检测法所得体积的70%~82%,两种方法测量结果的相关系数为0.976(P<0.05)。青年组、中年组、年轻老年及老年组中,男性下颌下腺的质量和体积明显高于女性(P<0.05),青少年组不同性别间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。下颌下腺的质量和体积与身高呈中等强度的正相关(P<0.05),与体质量呈弱正相关(P<0.05),与体重指数无关(P>0.05)。年轻老年及老年组女性的下颌下腺质量和体积显著低于其他三组(P<0.05)。结论: 腺体实体体外检测法可以精确检测下颌下腺的质量和体积,本研究建立了不同性别和年龄组正常下颌下腺质量和体积的参考值。CT容积重建法测量的下颌下腺体积为腺体实体体外检测法的70%~82%,两种方法测量结果趋势一致,拟合度好。下颌下腺的质量和体积与年龄、性别、身高和体质量具有相关性。
中图分类号:
- R782.7
| [1] | 张震康, 俞光岩. 口腔颌面外科学[M]. 2版. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2013: 301. |
| [2] | 赵士杰, 皮昕. 口腔颌面部解剖学[M]. 2版. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2014: 66. |
| [3] | 李巍, 孙志鹏, 刘筱菁, 等. 腮腺和颌下腺体积的测量[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014,46(2):288-293. |
| [4] | 潘天鹏, 石津生, 高和. 中华老年医学[M]. 北京: 华夏出版社, 2010: 1079. |
| [5] |
Ying M, Pang BS. Three-dimensional ultrasound measurement of cervical lymph node volume[J]. Br J Radiol, 2009,82(980):617-625.
doi: 10.1259/bjr/17611956 pmid: 19153188 |
| [6] |
Prionas ND, Ray S. Boone JM. Volume assessment accuracy in computed tomography: A phantom study[J]. J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2010,11(2):168-180.
doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v11i2.3037 |
| [7] | 张红丽, 徐亮, 许建铭, 等. 颌下腺增龄性改变的MRI定量分析[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2016,27(2):90-93. |
| [8] |
Lee MK, Sepahdari A, Cohen M. Radiologic measurement of submandibular gland ptosis[J]. Facial Plast Surg, 2013,29(4):316-320.
doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1349356 |
| [9] |
Heo MS, Lee SC, Lee SS, et al. Quantitative analysis of normal major salivary glands using computed tomography[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2001,92(2):240-244.
doi: 10.1067/moe.2001.114756 pmid: 11505274 |
| [10] | 李运成, 鲁际, 李丽亚, 等. 正常人下颌下腺的多层螺旋CT影像解剖研究[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2007,26(6):558-560. |
| [11] |
Stimec BV, Rakocevic Z, Ignjatovic D, et al. Planimetric correlation between the submandibular glands and the pancreas: A postmortem ductographic study[J]. Anat Sci Int, 2018,93(1):114-118.
doi: 10.1007/s12565-016-0382-6 pmid: 27832478 |
| [1] | 李成跃, 王浩, 阿力木江·依米提·塔尔肯. 1985——2019年新疆维吾尔族中小学生生长发育的长期趋势[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 802-808. |
| [2] | 黄伟,许庭珉,王天兵,姜保国. 创伤中心医疗质量控制指标专家共识[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 551-555. |
| [3] | 吴一凡,玉应香,谢岚,张志达,常翠青. 不同体重指数青年男性的静息能量消耗特点及预测方程评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 247-252. |
| [4] | 赖金惠,王起,姬家祥,王明瑞,唐鑫伟,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情期间延迟拔除输尿管支架对泌尿系结石术后患者生活质量和心理状态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [5] | 李志华,黄燕波,庞秋颖,于书慧,陈宇珂,李德润. 膀胱阴道瘘修补术后患者生存质量和心理状态调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 190-193. |
| [6] | 柳登高,郑丹妮,赵雅宁,张亚琼,叶欣,张丽琪,谢晓艳,张雷,张祖燕,俞光岩. 疑难唾液腺结石病的治疗研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 8-12. |
| [7] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 类风湿关节炎患者生活质量与疾病活动度的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1086-1093. |
| [8] | 俞光岩,苏家增,柳登高,吴立玲,丛馨. 下颌下腺保存治疗新技术体系的建立与应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 842-845. |
| [9] | 唐文豪,邓琛耀,高江曼,罗智超,吴寒,田森林,魏楠,李斌,赵乾程,宋建飞,张梁,马潞林,姜辉. 季节因素对北京地区捐精志愿者精液质量的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 658-662. |
| [10] | 陈阳阳,周玉博,杨静,花语蒙,原鹏波,刘爱萍,魏瑗. 双胎妊娠孕期体质量对血清高敏C反应蛋白与妊娠期糖尿病关联的影响:一项队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 427-433. |
| [11] | 李炳雨,唐祖南,胡耒豪,章文博,于尧,俞光岩,彭歆. 腮腺微小肿瘤的临床病理研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 335-339. |
| [12] | 俞光岩,柳登高,李巍,洪霞,张严妍,朱文瑄,张可夫,李潇,栗占国,刘燕鹰,陈艳,高岩,苏家增. 3类新型慢性唾液腺炎的诊断和治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 13-17. |
| [13] | 陈超伦,苏家增,俞光岩. 酸刺激对腮腺和下颌下腺唾液流率及成分的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 89-94. |
| [14] | 王佳文,刘敬超,孟令峰,张威,刘晓东,张耀光. 间质性膀胱炎/膀胱疼痛综合征患者生活质量及相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 653-658. |
| [15] | 朱忆颖,闵赛南,俞光岩. 局部注射环孢素A对非肥胖糖尿病小鼠下颌下腺分泌功能及炎症的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 750-757. |
|
||