北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 429-435. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.03.007
儿童青少年身体脂肪分布与抑郁和社交焦虑的关联:基于双能X线检测的横断面研究
袁雯1,张奕1,陈力1,蒋家诺1,陈曼曼1,刘婕妤1,马涛1,马奇1,崔孟杰1,郭桐君1,王鑫鑫2,董彦会1,马军1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学公共卫生学院,北京大学儿童青少年卫生研究所,北京 100191
2. 宁夏医科大学公共卫生与管理学院,银川 750004
Association of body fat distribution with depression and social anxiety in children and adolescents: A cross-sectional study based on dual-energy X-ray detection
Wen YUAN1,Yi ZHANG1,Li CHEN1,Jia-nuo JIANG1,Man-man CHEN1,Jie-yu LIU1,Tao MA1,Qi MA1,Meng-jie CUI1,Tong-jun GUO1,Xin-xin WANG2,Yan-hui DONG1,Jun MA1,*( )
)
- 1. Institute of Child and Adolescent Health, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. School of Public Health and Management, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, China
摘要:
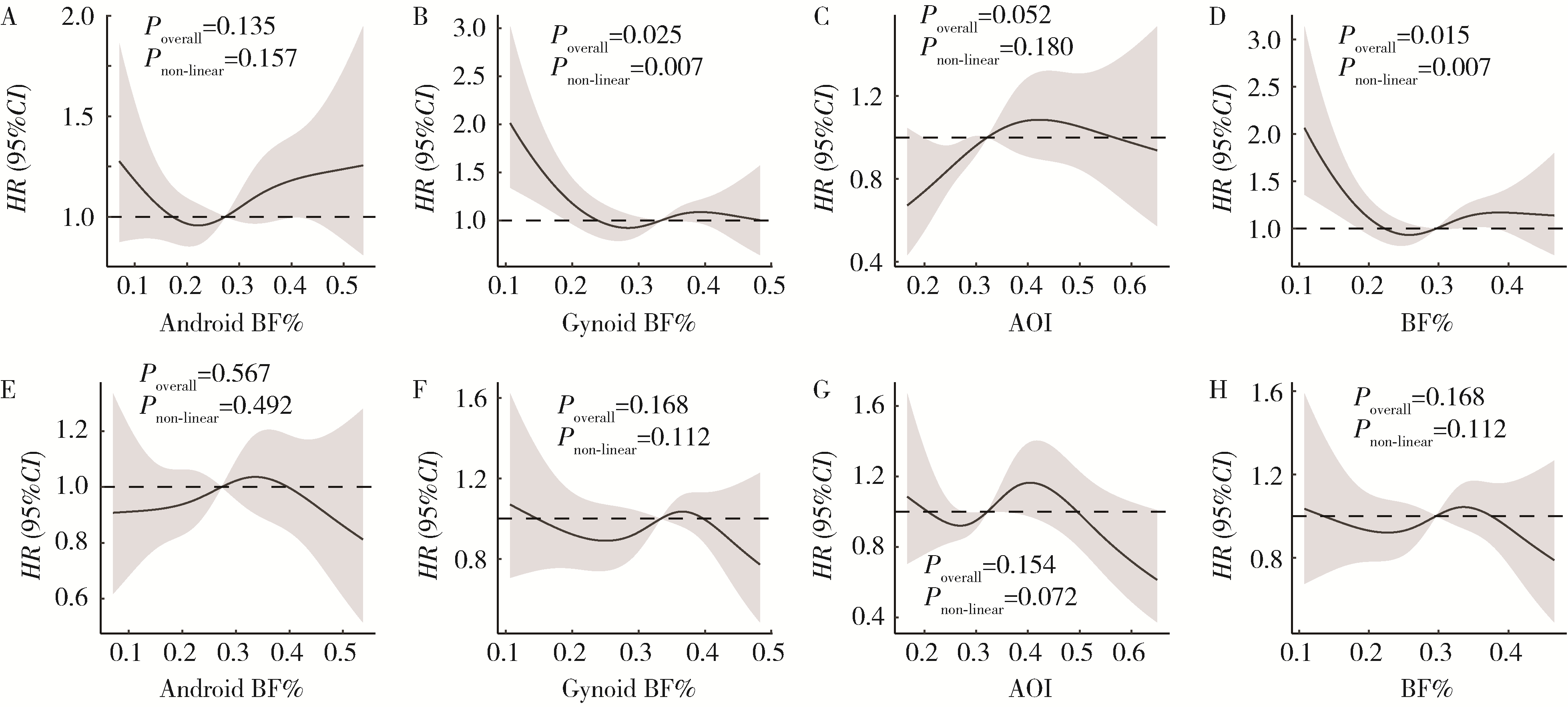
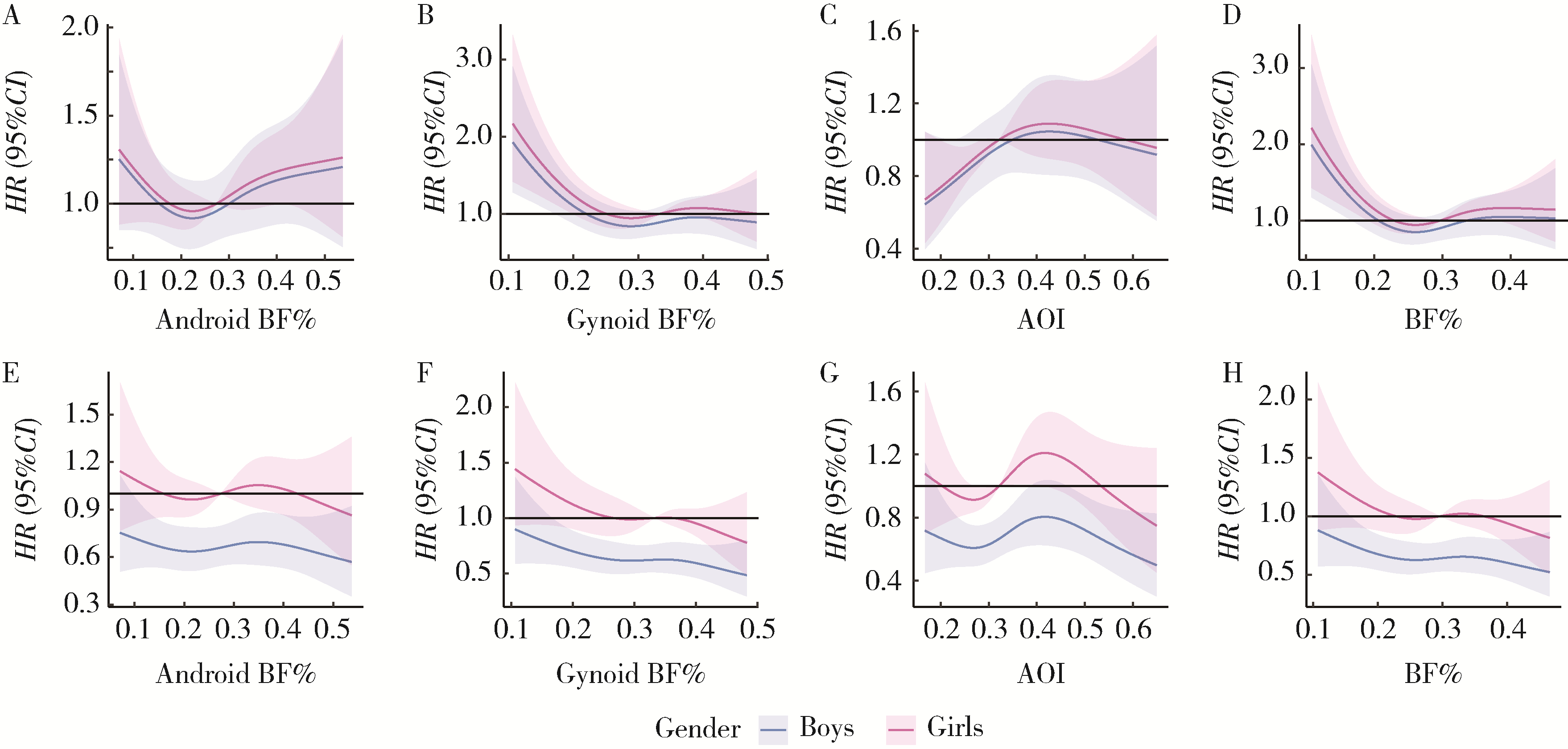
目的: 探讨儿童青少年抑郁、社交焦虑的现状,并分析儿童青少年脂肪分布与抑郁和社交焦虑的关联。方法: 采取分层整群随机抽样法纳入北京市7~18岁儿童青少年1 412名,使用双能X线吸收法获得其脂肪分布,使用儿童抑郁量表和儿童社交焦虑量表评价其抑郁和社交焦虑情况,采用多元线性回归和限制性立方样条分析估计儿童青少年脂肪分布与其抑郁、社交焦虑的线性与非线性关联。结果: 13.1%和31.1%的儿童青少年分别存在抑郁症状和社交焦虑症状,且男生、低年龄组的抑郁和社交焦虑检出率显著低于女生、高年龄组。儿童青少年的总脂肪率、Android脂肪率、Gynoid脂肪率、Android与Gynoid脂肪比(Android-to-Gynoid fat ratio,AOI)与抑郁和社交焦虑不存在显著性线性关联,但总脂肪率和Gynoid脂肪率与抑郁的非线性关联显著,表现为倒“U”型曲线关系,切点分别为26.8%和30.9%。脂肪分布与抑郁、社交焦虑的关联在不同性别和高低年龄组间差异不存在统计学意义。结论: 儿童青少年的脂肪分布与抑郁和社交焦虑不存在显著性线性关联; 脂肪分布与抑郁呈现倒“U”型曲线,主要表现在总脂肪率和Gynoid脂肪率上,且这种趋势在不同性别和不同年龄组上均表现出一致性。将儿童青少年的脂肪分布维持在一个合适的水平,是未来儿童青少年抑郁、社交焦虑防控关注的方向。
中图分类号:
- R179
| 1 |
Charlson F , van Ommeren M , Flaxman A , et al.New WHO pre-valence estimates of mental disorders in conflict settings: Asyste- matic review and meta-analysis[J].Lancet,2019,394(10194):240-248.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30934-1 |
| 2 |
Lu J , Xu XF , Huang YQ , et al.Prevalence of depressive disorders and treatment in China: A cross-sectional epidemiological study[J].Lancet Psychiat,2021,8(11):981-990.
doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00251-0 |
| 3 | Clarke DM , Currie KC .Depression, anxiety and their relationship with chronic diseases: A review of the epidemiology, risk and treatment evidence[J].Med J Australia,2009,190(7):S54-S60. |
| 4 |
Blaine B .Does depression cause obesity? A meta-analysis of longitudinal studies of depression and weight control[J].J Health Psychol,2008,13(8):1190-1197.
doi: 10.1177/1359105308095977 |
| 5 |
Dixon JB , Dixon ME , O'Brien PE .Depression in association with severe obesity: Changes with weight loss[J].Arch Intern Med,2003,163(17):2058-2065.
doi: 10.1001/archinte.163.17.2058 |
| 6 |
Quek YH , Tam WWS , Zhang MWB , et al.Exploring the association between childhood and adolescent obesity and depression: A meta-analysis[J].Obes Rev,2017,18(7):742-754.
doi: 10.1111/obr.12535 |
| 7 |
Rao WW , Zong QQ , Zhang JW , et al.Obesity increases the risk of depression in children and adolescents: Results from a systema-tic review and meta-analysis[J].J Affect Disorders,2020,267,78-85.
doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.01.154 |
| 8 |
Cole TJ , Bellizzi MC , Flegal KM , et al.Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: International survey[J].BMJ,2000,320(7244):1240-1243.
doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7244.1240 |
| 9 | 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 学龄儿童青少年超重与肥胖筛查[S]. (2018-08-01)[2023-01-05]. https://www.chinacdc.cn/jkzt/yyhspws/xzdc/201804/P020180418380884895984.pdf. |
| 10 |
Javed A , Jumean M , Murad MH , et al.Diagnostic performance of body mass index to identify obesity as defined by body adiposity in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Pediatr Obes,2015,10(3):234-244.
doi: 10.1111/ijpo.242 |
| 11 |
Romero-Corral A , Somers VK , Sierra-Johnson J , et al.Accuracy of body mass index in diagnosing obesity in the adult general population[J].Int J Obesity,2008,32(6):959-966.
doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.11 |
| 12 |
Zhou Y , Hoglund P , Clyne N .Comparison of DEXA and bioimpedance for body composition measurements in nondialysis patients with CKD[J].J Ren Nutr,2019,29(1):33-38.
doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2018.05.003 |
| 13 |
Liu XJ , Zhang DD , Liu Y , et al.Dose response association between physical activity and incident hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies[J].Hypertension,2017,69(5):813-820.
doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08994 |
| 14 |
Ye SY , Zhu CN , Wei C , et al.Associations of body composition with blood pressure and hypertension[J].Obesity,2018,26(10):1644-1650.
doi: 10.1002/oby.22291 |
| 15 | Kovacs M .The childrens depression inventory (CDI)[J].Psychopharmacol Bull,1985,21(4):995-998. |
| 16 |
Helsel WJ , Matson JL .The assessment of depression in children: The internal structure of the child depression inventory (CDI)[J].Behav Res Ther,1984,22(3):289-298.
doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(84)90009-3 |
| 17 |
Lagreca AM , Dandes SK , Wick P , et al.Development of the social anxiety scale for children: Reliability and concurrent validity[J].J Clin Child Psychol,1988,17(1):84-91.
doi: 10.1207/s15374424jccp1701_11 |
| 18 |
Zhao G , Ford ES , Dhingra S , et al.Depression and anxiety among US adults: Associations with body mass index[J].Int J Obesity,2009,33(2):257-266.
doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.268 |
| 19 | 陈曼曼, 马莹, 苏彬彬, 等.北京市7~18岁儿童青少年体成分百分位值变化特征[J].中国学校卫生,2021,42(11):1703-1707. |
| 20 |
He W , James S A , Merli MG , et al.An increasing socioeconomic gap in childhood overweight and obesity in China[J].Am J Public Health,2014,104(1):E14-E22.
doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2013.301669 |
| 21 |
Chung KH , Chiou HY , Chen YH .Psychological and physiological correlates of childhood obesity in Taiwan[J].Sci Rep,2015,5,17439.
doi: 10.1038/srep17439 |
| 22 |
Merikangas AK , Mendola P , Pastor PN , et al.The association between major depressive disorder and obesity in US adolescents: Results from the 2001-2004 National Health and Nutrition Exa-mination Survey[J].J Behav Med,2012,35(2):149-154.
doi: 10.1007/s10865-011-9340-x |
| 23 | 陆迪菲, 袁振芳, 杨丽华, 等.肥胖人群焦虑抑郁情况与肥胖程度相关性的调查分析[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2019,27(8):592-596. |
| 24 |
Chung S .Body composition analysis and references in children: Clinical usefulness and limitations[J].Eur J Clin Nutr,2019,73(2):236-242.
doi: 10.1038/s41430-018-0322-8 |
| 25 |
Rapuano KM , Laurent JS , Hagler DJ , et al.Nucleus accumbens cytoarchitecture predicts weight gain in children[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2020,117(43):26977-26984.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2007918117 |
| 26 |
Dionysopoulou S , Charmandari E , Bargiota A , et al.The role of hypothalamic inflammation in diet-induced obesity and its association with cognitive and mood disorders[J].Nutrients,2021,13(2):498.
doi: 10.3390/nu13020498 |
| 27 |
Zhang JH , Lam SP , Li SX , et al.A community-based study on the association between insomnia and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: Sex and pubertal influences[J].J Clin Endocr Metab,2014,99(6):2277-2287.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-3728 |
| 28 |
Kohler CA , Freitas TH , Maes M , et al.Peripheral cytokine and chemokine alterations in depression: A meta-analysis of 82 studies[J].Acta Psychiat Scand,2017,135(5):373-387.
doi: 10.1111/acps.12698 |
| 29 | Jantaratnotai N , Mosikanon K , Lee Y , et al.The interface of depression and obesity[J].Obes Res Clin Pract,2017,11(1):1-10. |
| 30 | Pierce GL , Kalil GZ , Ajibewa T , et al.Anxiety independently contributes to elevated inflammation in humans with obesity[J].Obesity,2017,25(2):286-289. |
| 31 | Dos Santos RRG , Forte GC , Mundstock E , et al.Body composition parameters can better predict body size dissatisfaction than body mass index in children and adolescents[J].Eat Weight Disord,2020,25(5):1197-1203. |
| [1] | 王敏, 李倩. 青少年抑郁症患者心理弹性影响因素的路径分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 809-814. |
| [2] | 陈敬,单蕊,肖伍才,张晓蕊,刘峥. 青春期和成年早期自制力与抑郁症状和超重肥胖共病风险的关联:基于全国调查的十年前瞻性队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 397-402. |
| [3] | 汤华萌,袁典琪,王明星,杨晗冰,郭超. 数字融入和健康生活方式对社会经济状况与老年人抑郁关系的序列中介作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 230-238. |
| [4] | 赖金惠,王起,姬家祥,王明瑞,唐鑫伟,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情期间延迟拔除输尿管支架对泌尿系结石术后患者生活质量和心理状态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [5] | 祝春素,连至炜,崔一民. 中国中老年人抑郁和慢性病的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 606-611. |
| [6] | 张紫薇,花语蒙,刘爱萍. 中国中老年人群抑郁症状、缺血性心血管疾病10年风险对心血管疾病的联合影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 465-470. |
| [7] | 汪雨欣,邓宇含,谭银亮,刘宝花. 应激性血糖升高对重症监护病房患者28 d全因死亡风险的预测价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 442-449. |
| [8] | 王婷,李乔晟,刘皓冉,简伟研. 人格特征、城乡差异与抑郁症状变化的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 385-391. |
| [9] | 陆林,刘晓星,袁凯. 中国脑科学计划进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 791-795. |
| [10] | 樊理诗,高敏,Edwin B.FISHER,孙昕霙. 北京市通州区和顺义区747例2型糖尿病患者生存质量影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 523-529. |
| [11] | 王一帆,范稹,成姚斌,金月波,霍阳,何菁. 原发性干燥综合征患者睡眠障碍的相关影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1063-1068. |
| [12] | 耿研,宋志博,张晓慧,邓雪蓉,王昱,张卓莉. 银屑病关节炎抑郁和焦虑患病情况及相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1048-1055. |
| [13] | 易端,朱薇,孟秀丽,刘晓光,李水清,祝斌,贾东林. 慢性腰腿痛患者微创术前焦虑,抑郁状态及相关影响因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 285-289. |
| [14] | 刘颖,曾祥柱,王筝,张函,王希林,袁慧书. 三维动脉自旋标记技术评价抑郁合并高血压患者脑血流灌注[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 260-264. |
| [15] | 雷杰,刘木清,傅开元. 睡眠问题、焦虑及压力是颞下颌关节紊乱病肌筋膜疼痛发病的风险指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 692-696. |
|
||