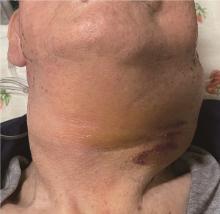
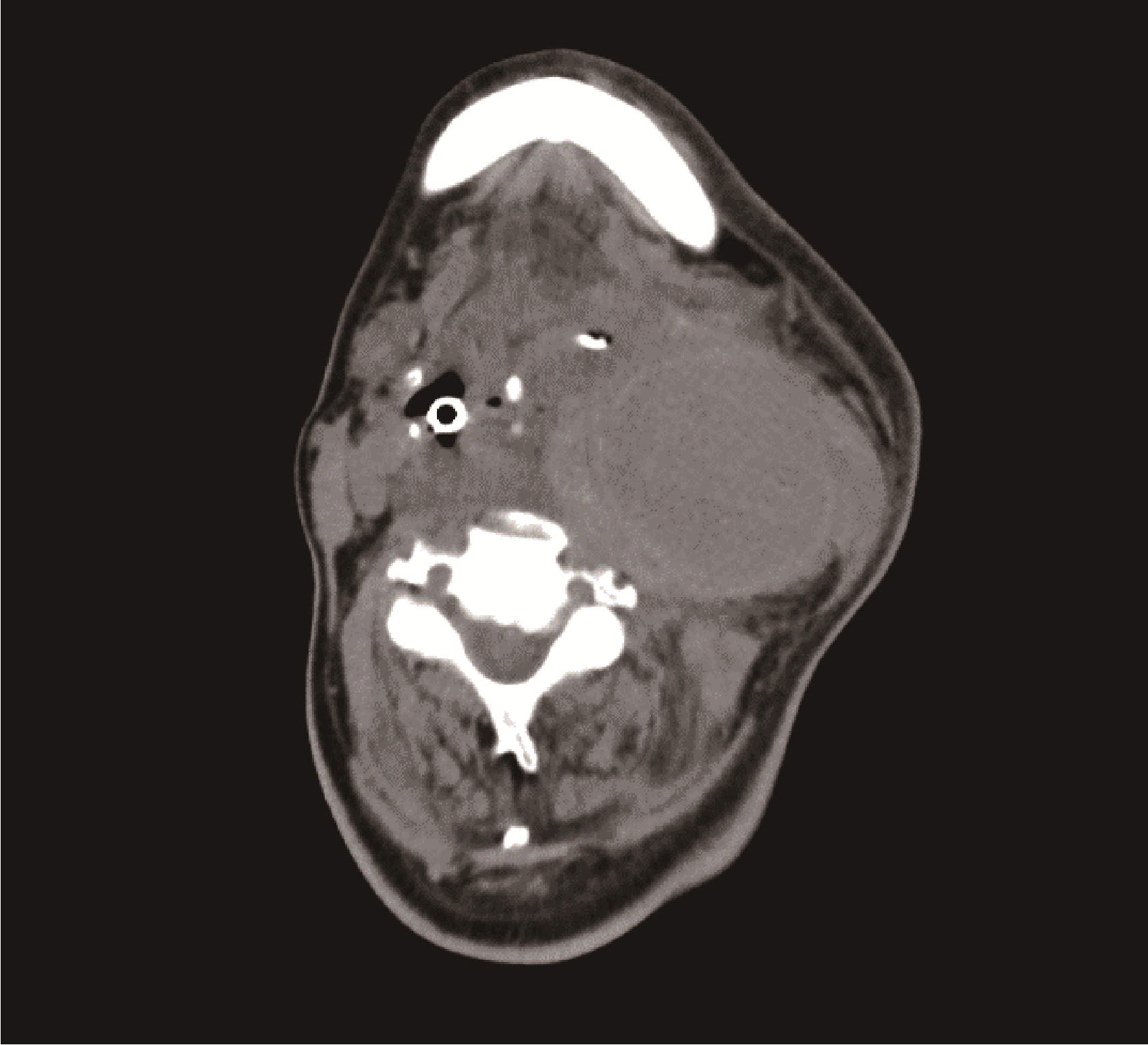
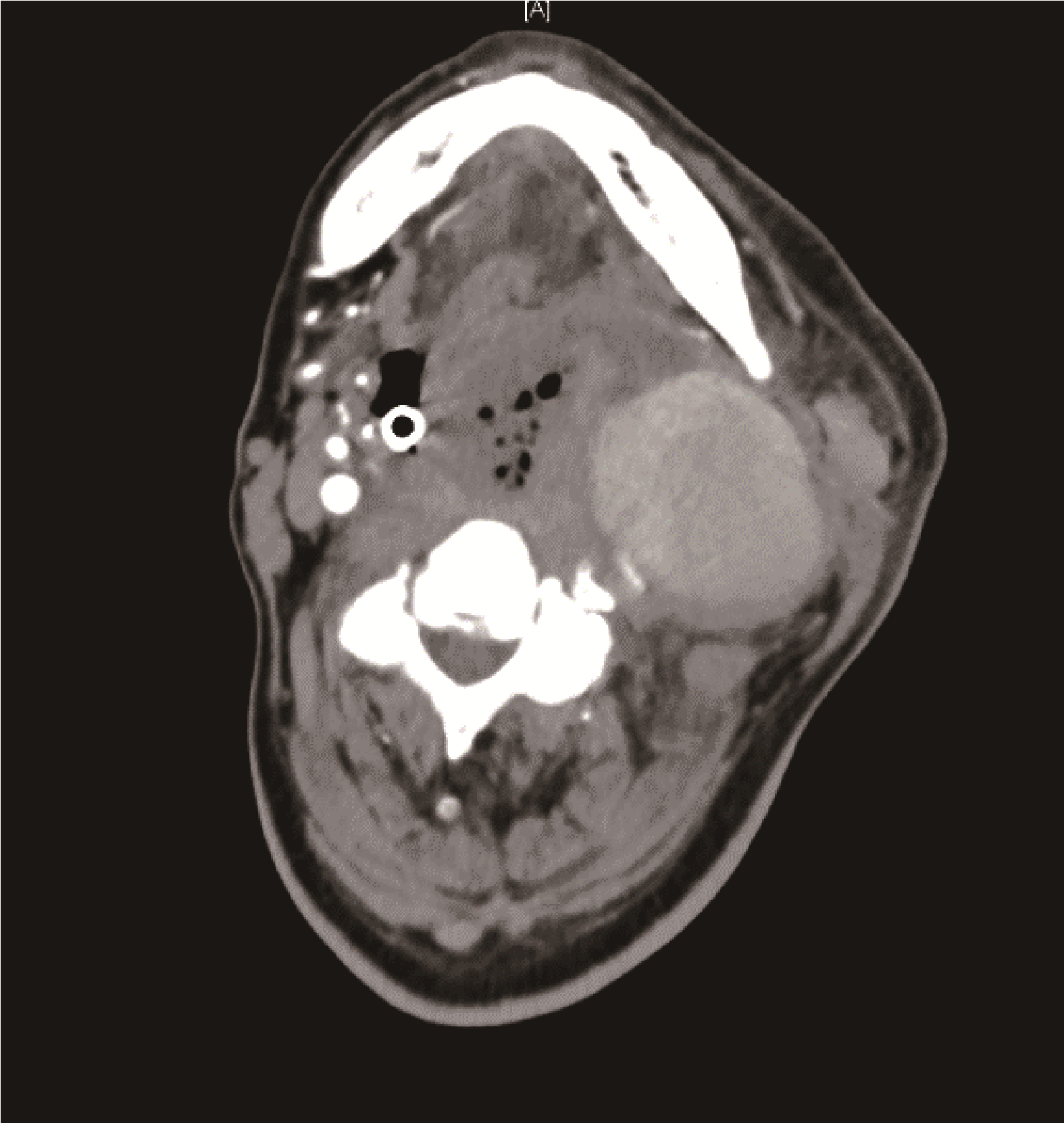
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1135-1138. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.028
咽旁脓肿致颈内动脉假性动脉瘤1例
张陈光,陈旭岩,吴圣,冯莉莉,王琰,陈妤,段敏,王科,宋琳琳*( )
)
- 清华大学附属北京清华长庚医院急诊科, 清华大学临床医学院, 北京 102218
Internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm caused by parapharyngeal abscess: A case report
Chen-guang ZHANG,Xu-yan CHEN,Sheng WU,Li-li FENG,Yan WANG,Yu CHEN,Min DUAN,Ke WANG,Lin-lin SONG*( )
)
- Department of Emergency, Beijing Tsinghua Changgung Hospital; School of Clinical Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing 102218, China
中图分类号:
- R766.4
| 1 |
Peters S , Braun-Dullaeus R , Herold J . Pseudoaneurysm[J]. Hamostaseologie, 2018, 38 (3): 166- 172.
doi: 10.5482/HAMO-17-01-0006 |
| 2 |
Pinzón M , Lobelo NO , Rodríguez MC , et al. Endovascular management of iatrogenic cervical internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm in a 9-year-old child: Case report and literature review[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 95, 29- 33.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2017.01.031 |
| 3 |
Patel S , Sharma AK , Meena D , et al. Extracranial carotid artery pseudoaneurysm due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis[J]. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann, 2020, 28 (5): 279- 281.
doi: 10.1177/0218492320932758 |
| 4 |
Gupta R , Patro SK , Chauhan N , et al. A giant pseudoaneurysm mimicking retropharyngeal abscess in a child[J]. Pediatr Emerg Care, 2019, 35 (5): e79- e83.
doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000001100 |
| 5 |
Lam EC , Palacios E , Neitzschman H . Carotid pseudoaneurysm of the neck[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2011, 90 (11): 512- 514.
doi: 10.1177/014556131109001103 |
| 6 |
Çiçek MT , Yildirim IO , Gündüz E . Endovascular treatment of caro-tid pseudoaneurysm bleeding due to parapharyngeal abscess[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2020, 31 (4): e324- e326.
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000006204 |
| 7 |
da Silva PS , Waisberg DR . Internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm with life-threatening epistaxis as a complication of deep neck space infection[J]. Pediatr Emerg Care, 2011, 27 (5): 422- 424.
doi: 10.1097/PEC.0b013e3182187539 |
| 8 |
Davidson C , Holihan C , Lee K , et al. Infectious pseudoaneurysm of the internal carotid artery in a child secondary to parapharyngeal abscess[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2023, 102 (1): 31- 34.
doi: 10.1177/0145561320984582 |
| 9 |
Bannazadeh M , Sattari AR , Skripochnik E , et al. Endovascular repair of infected carotid pseudoaneurysm: A case report[J]. Int J Surg Case Rep, 2020, 72, 163- 165.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.05.005 |
| 10 | Lau JSK , Wong JCY , Ng RYT , et al. Malignant otitis externa complicated by multiple cervical-petrous internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysms: A case report[J]. Hong Kong Med J, 2019, 25 (2): 152- 155. |
| 11 |
Pearson SE , Choi SS . Pseudoaneurysm of the internal carotid artery: A case report and review of the literature[J]. Arch Oto-laryngol Head Neck Surg, 2005, 131 (5): 454- 456.
doi: 10.1001/archotol.131.5.454 |
| 12 |
Kenyon O , Tanna R , Sharma V , et al. Mycotic pseudoaneurysm of the common carotid artery: An unusual neck lump[J]. BMJ Case Rep, 2020, 13 (11): e239921.
doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-239921 |
| 13 | Ozono Y , Nishiike S , Ishihara M , et al. Rupture of internal caro-tid artery pseudoaneurysm in the sphenoid sinus as a complication of deep neck space infection[J]. J Med Invest, 2019, 66 (1/2): 188- 189. |
| 14 |
Zhang CG , Duan M , Zhang XY , et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae infection secondary to spontaneous renal rupture that presents only as fever: A case report[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2021, 9 (11): 2602- 2610.
doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i11.2602 |
| 15 | 张欣, 陈佰义. 高毒力肺炎克雷伯菌感染研究进展[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2020, 43 (10): 870- 874. |
| [1] | 乔佳佳,田聪,黄晓波,刘军. 肾结石合并系统性红斑狼疮行经皮肾镜碎石取石术的安全性和有效性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 745-749. |
| [2] | 朱金荣,赵亚娜,黄巍,赵微微,王悦,王松,苏春燕. 感染新型冠状病毒的血液透析患者的临床特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 267-272. |
| [3] | 刘鑫,石雪迎,李军. 新型冠状病毒感染相关缺血性结肠炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 362-365. |
| [4] | 王丽芳,石连杰,宁武,高乃姝,王宽婷. 干燥综合征合并冷凝集素病1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1130-1134. |
| [5] | 乔婕,芦丽霞,何玉婷,门春翠,楚新新,武蓓,赵慧萍,王梅. 真菌性腹膜透析导管出口感染合并隧道感染1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 748-754. |
| [6] | 林浩,李菁华,杨潇,陈晓婷,史宇晖,常春,郝元涛,曹望楠. 中国成都男男性行为人群HIV暴露前预防用药行为-认知偏差现状及其影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 511-520. |
| [7] | 王哲,孙伟,杨雪,宋颖,姬爱平,白洁. 口腔急诊颌面部感染患者临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 543-547. |
| [8] | 叶一林,刘恒,潘利平,柴卫兵. 全膝关节置换术后假体周围痛风发作误诊1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 362-365. |
| [9] | 曹芳,钟明,刘从容. 宫体POLE突变型内膜样癌合并HPV感染相关性宫颈腺癌1例报道及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 370-374. |
| [10] | 邢晓燕,张筠肖,朱冯赟智,王一帆,周新尧,李玉慧. 皮肌炎合并巨噬细胞活化综合征5例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1214-1218. |
| [11] | 徐朝焰,林长艺,叶达梅,吴培埕,宋明辉,刘有添,邓琼,黄雪艳,范忠晓,游雪兰. 感染性关节炎诊断分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1234-1237. |
| [12] | 康志宇,王磊磊,韩永正,郭向阳. 北京冬季奥林匹克运动会运动员手术的麻醉管理[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 770-773. |
| [13] | 于博,赵扬玉,张喆,王永清. 妊娠合并感染性心内膜炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 578-580. |
| [14] | 张朴丽,杨红霞,张立宁,葛勇鹏,彭清林,王国春,卢昕. 血清YKL-40在诊断抗黑色素瘤分化相关基因5阳性皮肌炎合并严重肺损伤中的价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1055-1060. |
| [15] | 王成,孟令宇,陈拿云,李玳,王健全,敖英芳. 前交叉韧带重建术后膝关节感染的诊断和治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 850-856. |
|
||