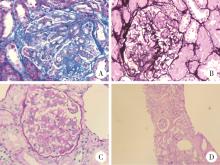
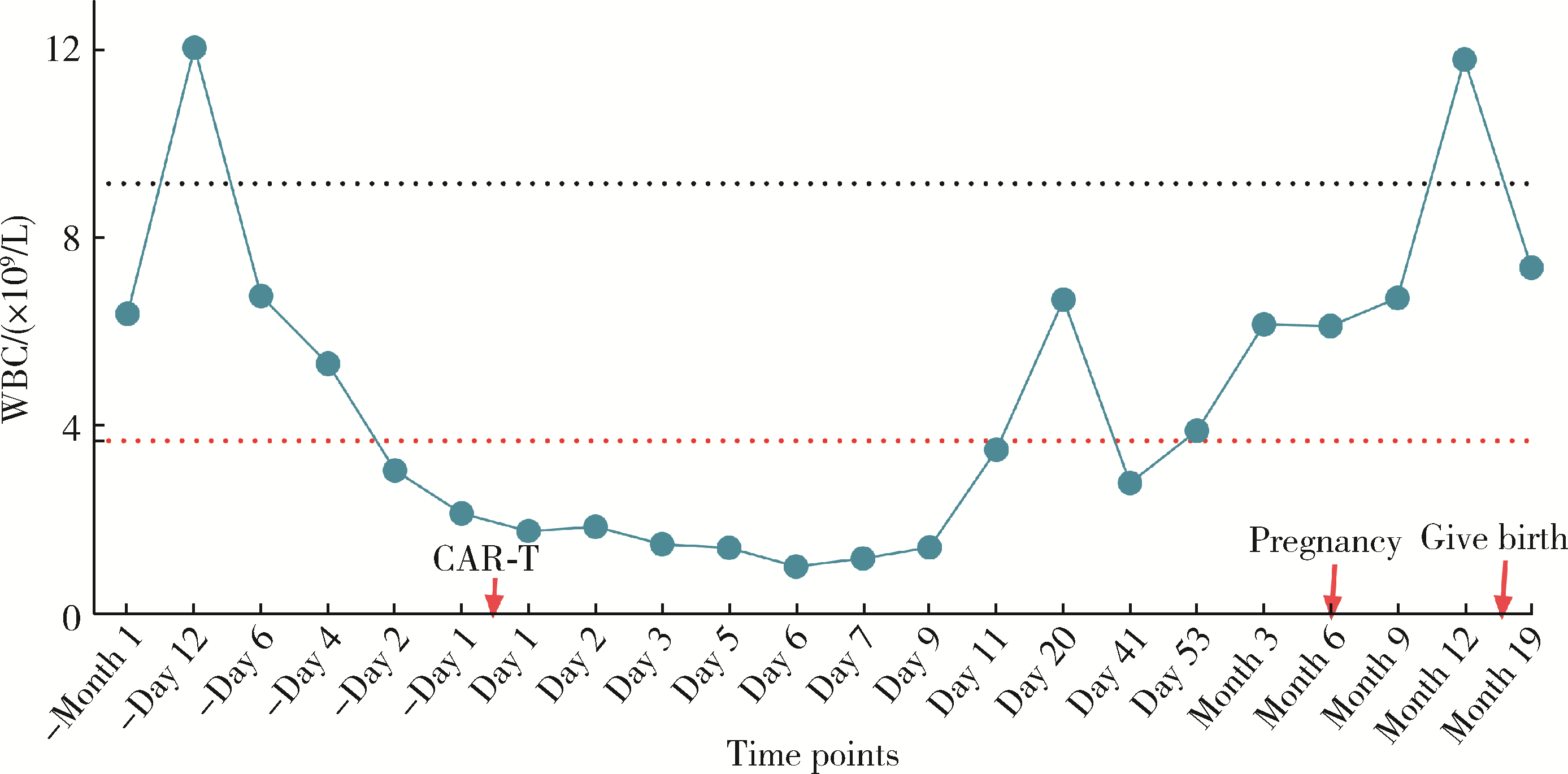
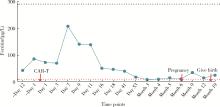
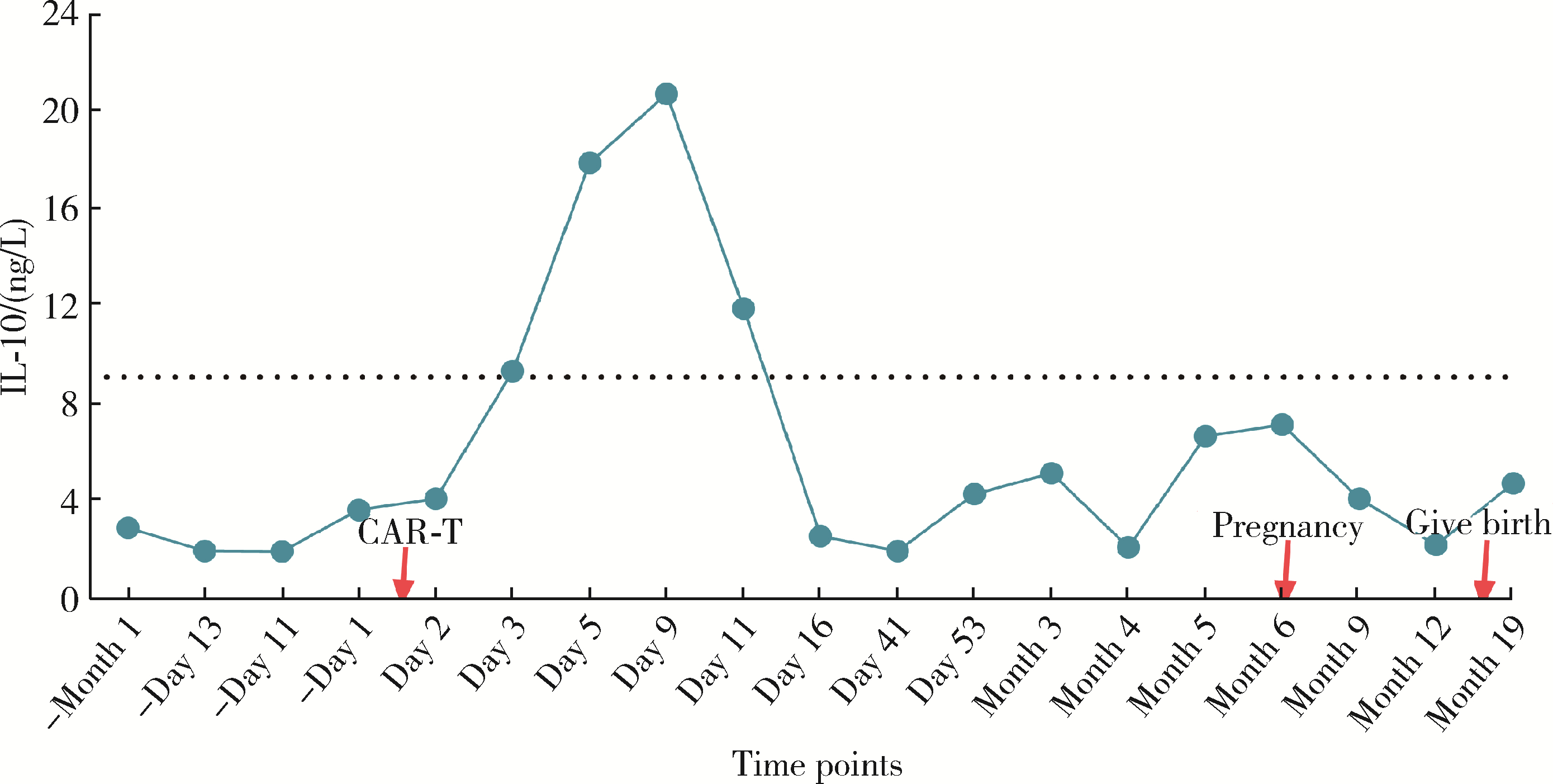
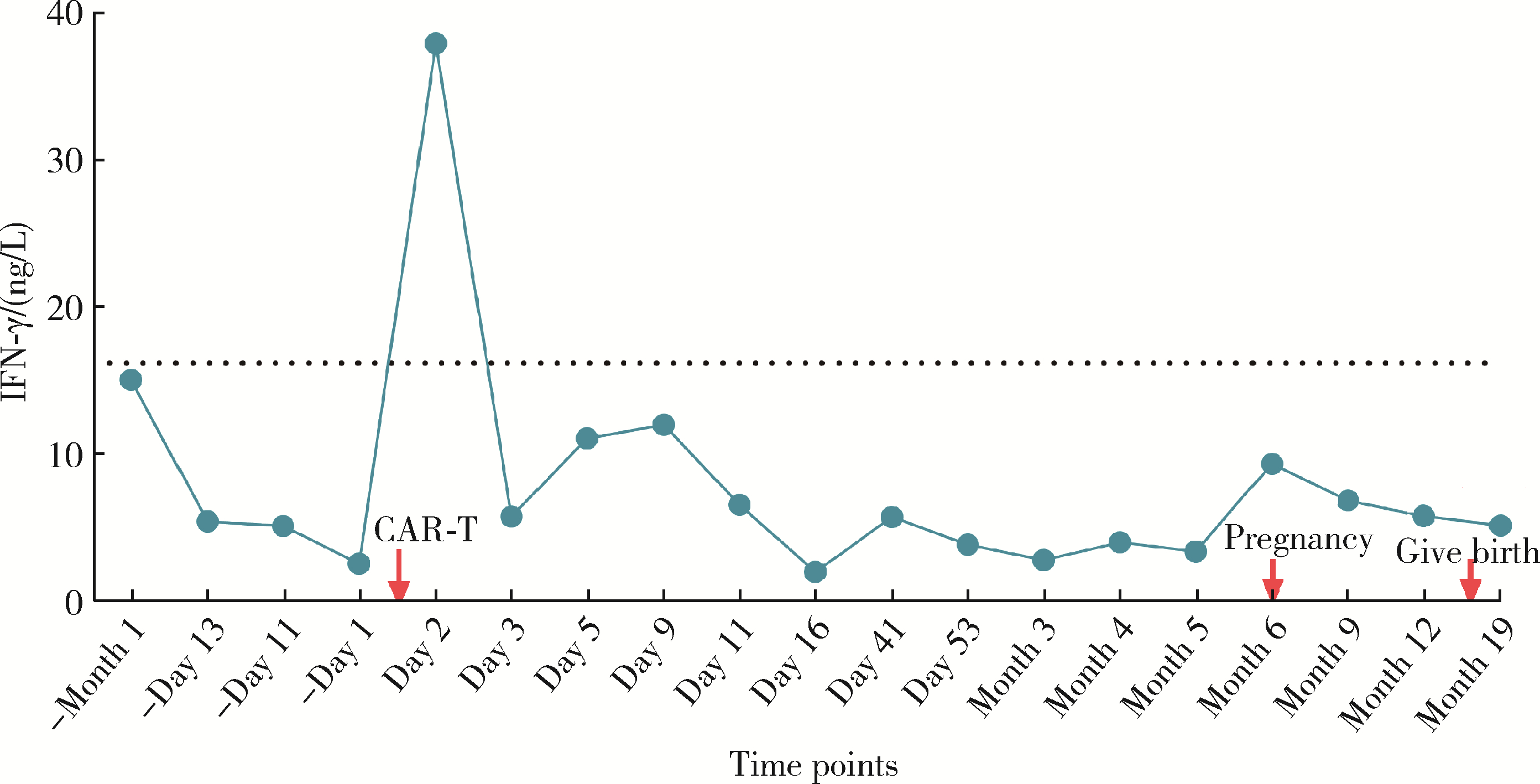
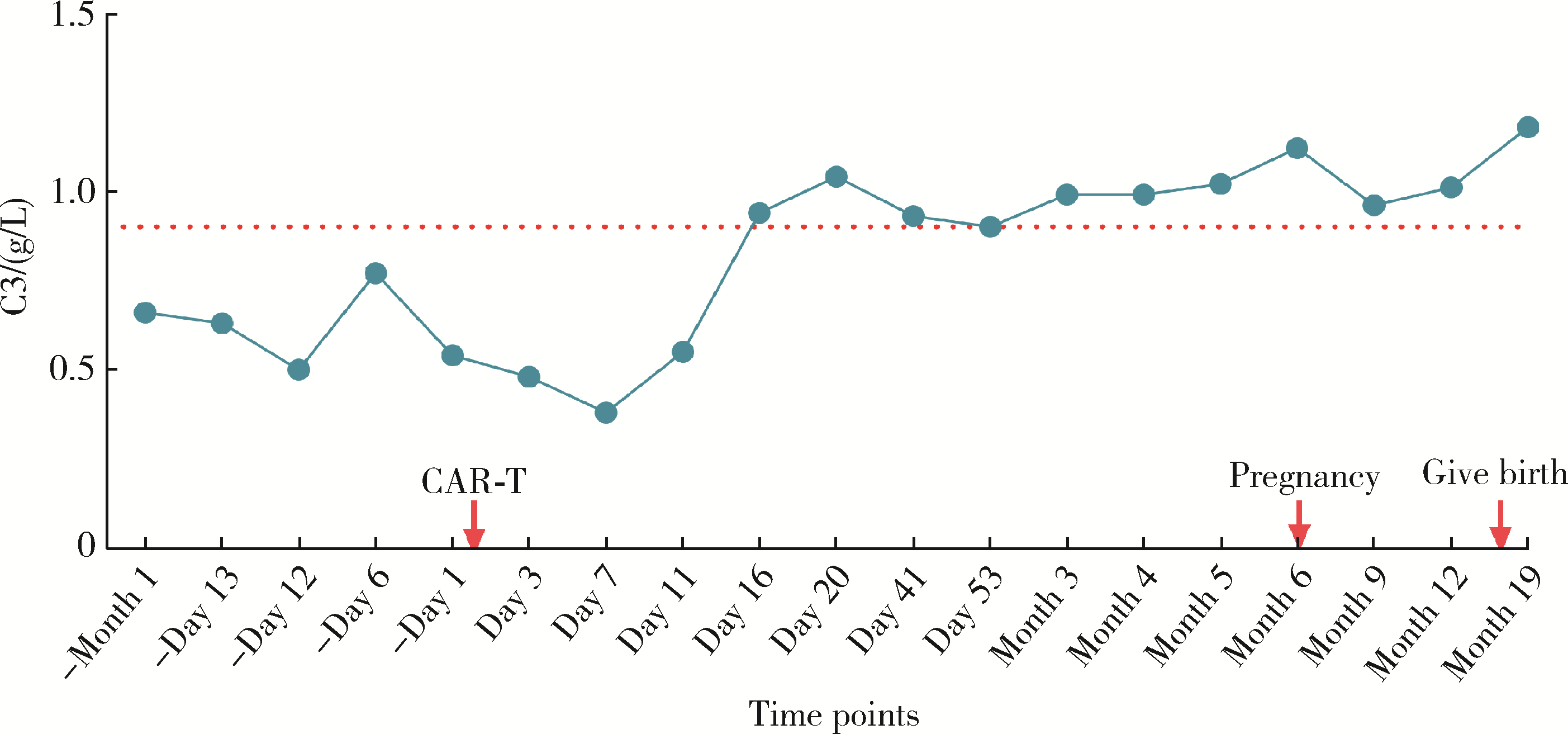
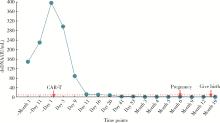
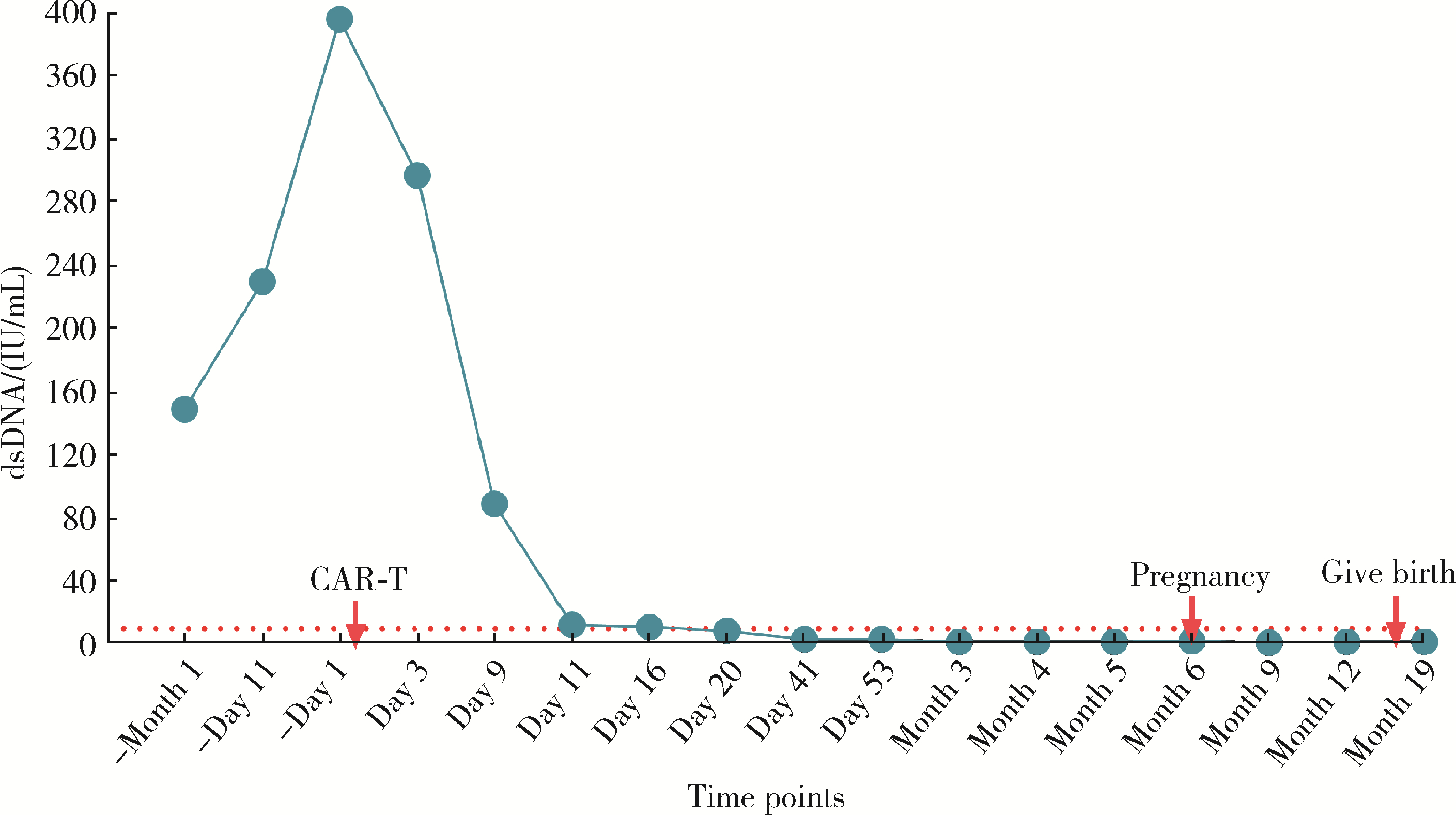
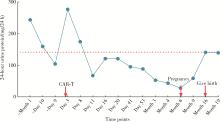
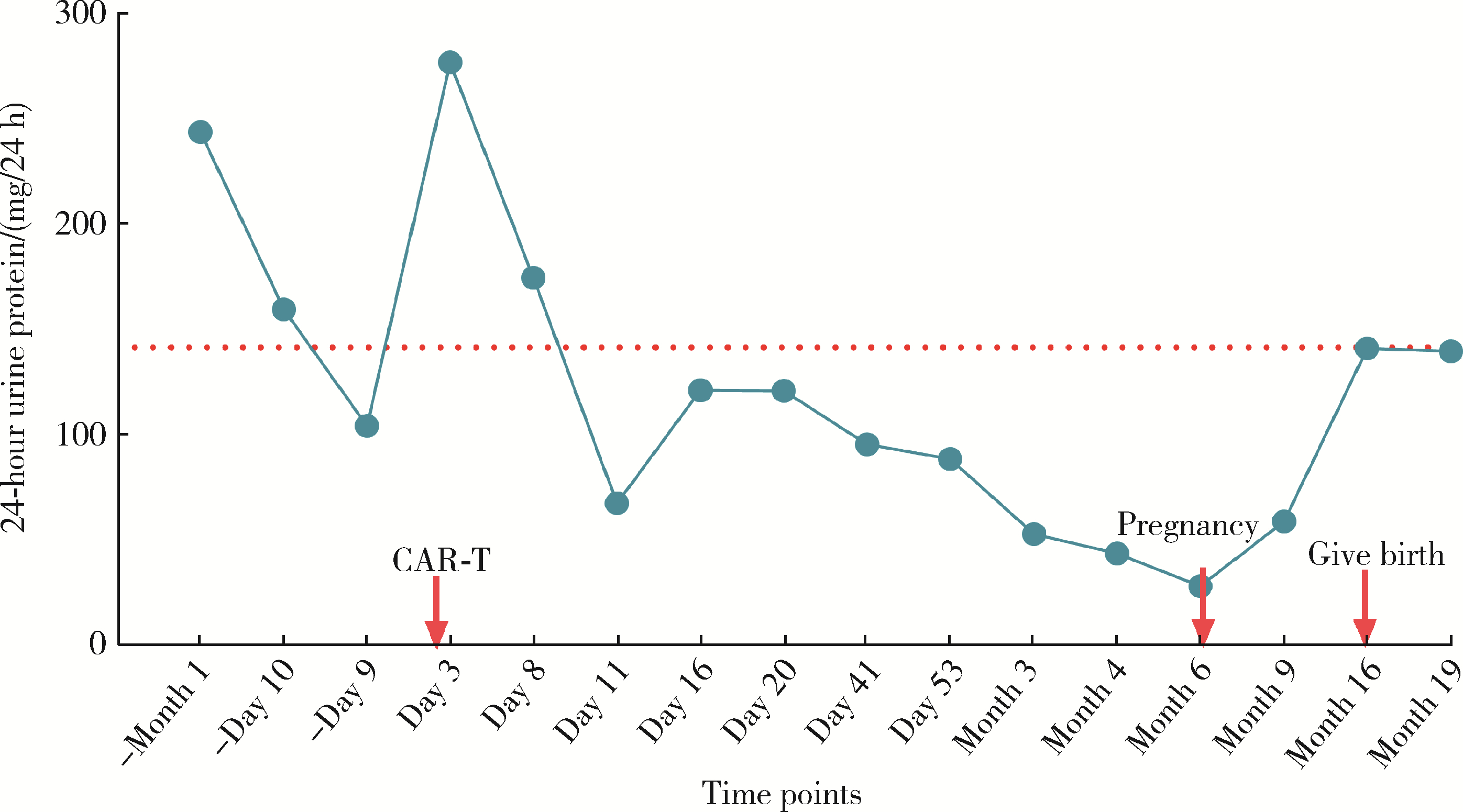
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 1119-1125. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.06.029
双靶点嵌合抗原受体T细胞治疗系统性红斑狼疮患者停药后安全孕产1例
王明霞1, 丁菱1, 王敏1, 邹婵娟1, 颜丝语1, 梁颖文2, 王伟佳2, 何善智1,*( )
)
- 1. 中山市人民医院风湿免疫科, 广东中山 528403
2. 中山市人民医院先进诊断与先进治疗临床研究中心, 广东中山 528403
Safe pregnancy and delivery in a female patient with systemic lupus erythematosus after discontinuation of dual-target chimeric antigen receptor T cells therapy
Mingxia WANG1, Ling DING1, Min WANG1, Chanjuan ZOU1, Siyu YAN1, Yingwen LIANG2, Weijia WANG2, Shanzhi HE1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Zhong-shan People' s Hospital, Zhongshan 528403, Guangdong, China
2. Department of Advanced Diagnostic and Clinical Medicine, Zhong-shan People' s Hospital, Zhongshan 528403, Guangdong, China
中图分类号:
- R593.241
| 1 |
Zen M , Gatto M , Depascale R , et al. Early and late response and glucocorticoid-sparing effect of belimumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with joint and skin manifestations: Results from the belimumab in real life setting study-joint and skin (BeRLiSS-JS)[J]. J Pers Med, 2023, 13 (4): 691.
doi: 10.3390/jpm13040691 |
| 2 |
Van Schaik M , Arends EJ , Soonawala D , et al. Efficacy of belimumab combined with rituximab in severe systemic lupus erythematosus: Study protocol for the phase 3, multicenter, randomized, open-label synbiose 2 trial[J]. Trials, 2022, 23 (1): 939.
doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06874-w |
| 3 |
Schuster SJ , Svoboda J , Chong EA , et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells in refractory B-cell lymphomas[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377 (26): 2545- 2554.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1708566 |
| 4 |
Müller F , Taubmann J , Bucci L , et al. CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in autoimmune disease: A case series with follow-up[J]. N Engl J Med, 2024, 390 (8): 687- 700.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2308917 |
| 5 |
Salazar-Camarena DC , Ortiz-Lazareno PC , Cruz A , et al. Asso-ciation of BAFF, APRIL serum levels, BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA expression on peripheral B-cell subsets with clinical manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Lupus, 2016, 25 (6): 582- 592.
doi: 10.1177/0961203315608254 |
| 6 |
Wang W , He S , Zhang W , et al. BCMA-CD19 compound CAR T cells for systemic lupus erythematosus: A phase 1 open-label clinical trial[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2024, 83 (10): 1304- 1314.
doi: 10.1136/ard-2024-225785 |
| 7 |
Wang JY , Wang L . CAR-T cell therapy: Where are we now, and where are we heading?[J]. Blood Sci, 2023, 5 (4): 237- 248.
doi: 10.1097/BS9.0000000000000173 |
| 8 |
Mackensen A , Müller F , Mougiakakos D , et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Nat Med, 2022, 28 (10): 2124- 2132.
doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-02017-5 |
| [1] | 王红彦, 李鑫铭, 房柯池, 朱华群, 贾汝琳, 王晶. 系统性红斑狼疮疾病活动度相关特征分析及评估模型的构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1017-1022. |
| [2] | 陈丹丹, 李云, 卢情怡, 相晓红, 孙峰, 李英妮, 赵静, 王红彦, 李春. 育龄期系统性红斑狼疮患者卵巢功能的评价及其影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1023-1028. |
| [3] | 王莉, 高超, 任欢欢, 沈艳平, 黄晓玮, 姚鸿, 韩丹丹. 系统性红斑狼疮患者自我管理能力现状及相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1029-1035. |
| [4] | 柴静, 王钥, 穆荣, 赵金霞. 系统性红斑狼疮累及穹窿柱导致低钠血症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1115-1118. |
| [5] | 武志慧, 胡明智, 赵巧英, 吕凤凤, 张晶莹, 张伟, 王永福, 孙晓林, 王慧. miR-125b-5p修饰脐带间充质干细胞对系统性红斑狼疮的免疫调控机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [6] | 乔佳佳,田聪,黄晓波,刘军. 肾结石合并系统性红斑狼疮行经皮肾镜碎石取石术的安全性和有效性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 745-749. |
| [7] | 任立敏,赵楚楚,赵义,周惠琼,张莉芸,王友莲,沈凌汛,范文强,李洋,厉小梅,王吉波,程永静,彭嘉婧,赵晓珍,邵苗,李茹. 系统性红斑狼疮低疾病活动度及缓解状况的真实世界研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 273-278. |
| [8] | 赵祥格,刘佳庆,黄会娜,陆智敏,白自然,李霞,祁荆荆. 干扰素-α介导系统性红斑狼疮外周血CD56dimCD57+自然杀伤细胞功能的损伤[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 975-981. |
| [9] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [10] | 罗芷筠,吴佳佳,宋优,梅春丽,杜戎. 伴神经精神系统病变的系统性红斑狼疮相关巨噬细胞活化综合征2例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1111-1117. |
| [11] | 邵苗,郭惠芳,雷玲彦,赵清,丁艳杰,林进,吴锐,于峰,李玉翠,苗华丽,张莉芸,杜燕,焦瑞英,庞丽霞,龙丽,栗占国,李茹. 短间期小剂量环磷酰胺治疗系统性红斑狼疮耐受性的多中心对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1112-1116. |
| [12] | 李敏,侯林卿,金月波,何菁. 系统性红斑狼疮合并视网膜病变的临床及免疫学特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1106-1111. |
| [13] | 张琳崎,赵静,王红彦,王宗沂,李英妮,汤稷旸,李思莹,曲进锋,赵明威. 抗ENO1抗体与狼疮性视网膜病变的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1099-1105. |
| [14] | 邹健梅,武丽君,罗采南,石亚妹,吴雪. 血清25-羟维生素D与系统性红斑狼疮活动的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 938-941. |
| [15] | 夏芳芳,鲁芙爱,吕慧敏,杨国安,刘媛. 系统性红斑狼疮伴间质性肺炎的临床特点及相关因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 266-272. |
|
||