北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 779-783. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.024
国产模块化手术机器人系统辅助肾盂成形术的可行性和安全性评价
刘世豪1,*, 徐丽清1,*, 李新飞1, 杨昆霖1, 李兆莹1,2, 张子博1,2, 王祥1, 傅炜骁1, 李志华1,2,*( ), 李学松1,*(
), 李学松1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第一医院泌尿外科,北京大学泌尿外科研究所,国家泌尿男生殖系肿瘤中心,北京 100034
2. 北京大学第一医院护理部,北京 100034
Evaluation of the feasibility and safety of a Chinese developed modular surgical robotic system for robot-assisted pyeloplasty
Shihao LIU1, Liqing XU1, Xinfei LI1, Kunlin YANG1, Zhaoying LI1,2, Zibo ZHANG1,2, Xiang WANG1, Wei-xiao FU1, Zhihua LI1,2,*( ), Xuesong LI1,*(
), Xuesong LI1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital; Institute of Urology, Peking University; National Urological Cancer Center, Beijing 100034, China
2. Nursing Department, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
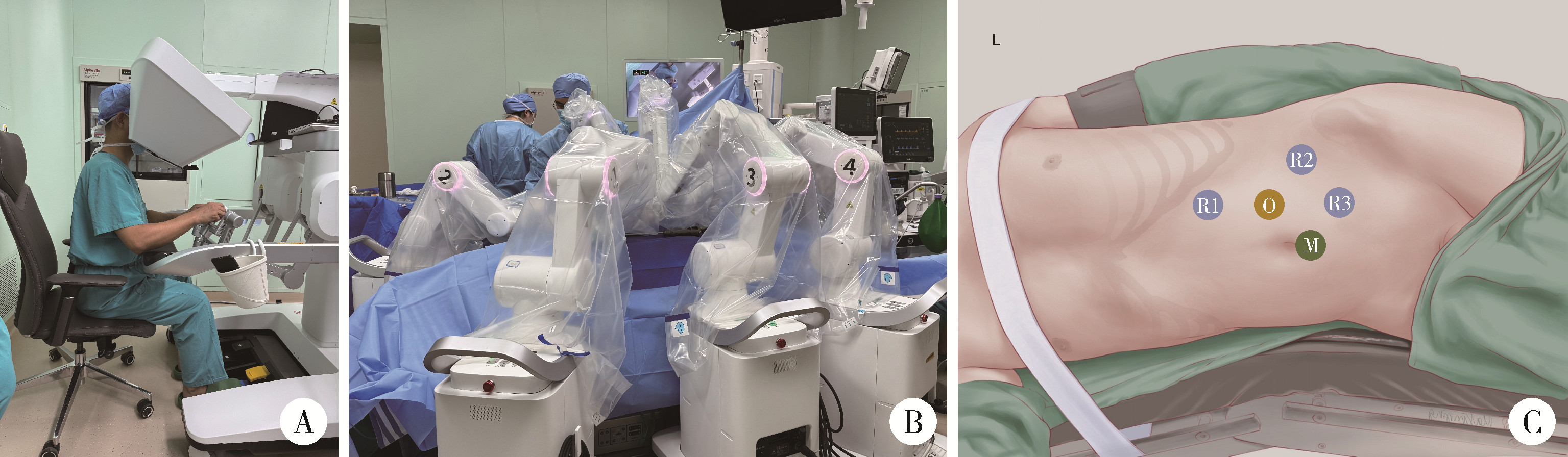
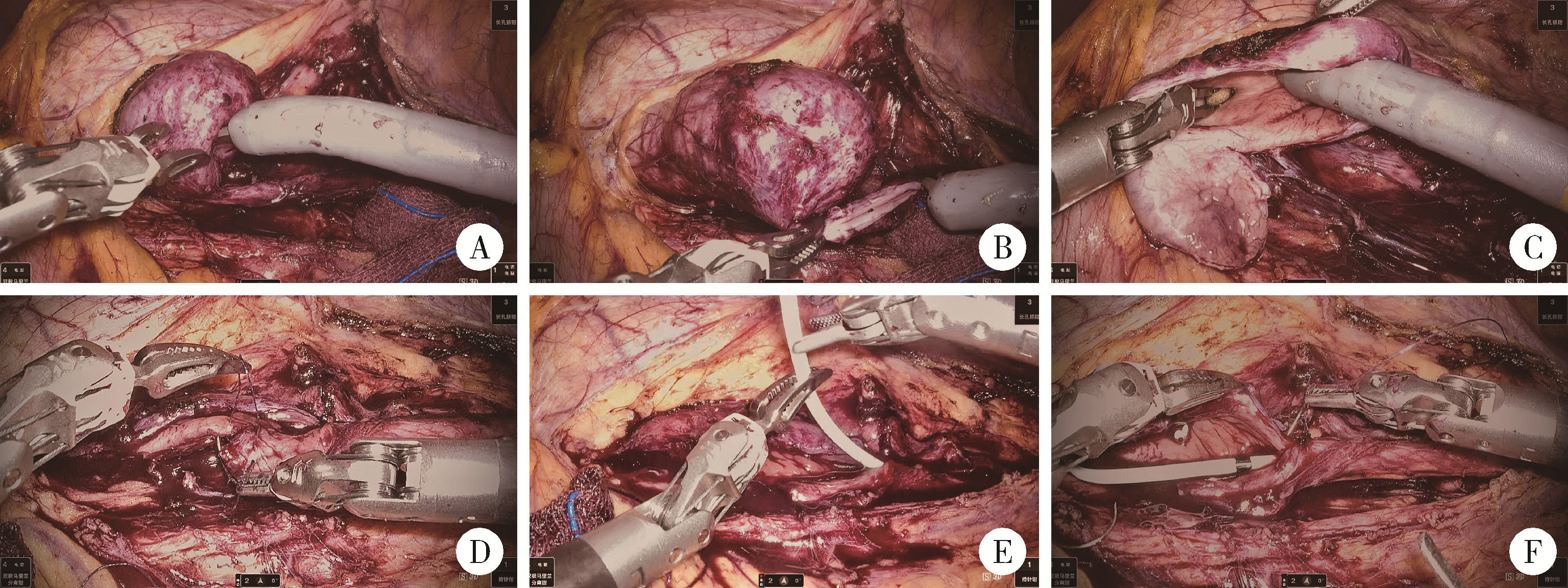
目的: 评估国产模块化海山一Ⓡ腔镜手术机器人辅助肾盂成形术在治疗肾盂输尿管连接处狭窄(ureteropelvic junction obstruction,UPJO)中的技术可行性与围术期安全性。方法: 前瞻性纳入2024年11—12月在北京大学第一医院接受海山一Ⓡ腔镜手术机器人辅助肾盂成形术的5例UPJO患者,收集其人口学特征、术中关键参数(包括设备对接时间、控制台时间和出血量等)、围术期相关指标、随访数据以及术者对系统性能的主观评价,采用描述性统计分析,连续变量以中位数(范围)表示,分类变量以频数和百分比表示。结果: 本研究包含4例女性和1例男性患者,均顺利完成机器人辅助肾盂成形术,无1例中转开放或腹腔镜手术。患者中位年龄32岁(24~37岁),中位体重指数为21.6 kg/m2(15.8~27.3 kg/m2)。设备对接中位时间8 min(3~12 min),中位控制台时间91 min(71~125 min),术中出血量均为20 mL。中位术后引流管留置时间3 d(0~4 d),中位术后住院时间4 d(4~9 d),围术期所有患者未出现Clavien-Dindo分级≥Ⅲ的并发症,中位随访时间6个月(5~6个月),所有患者在术后2个月拔出双J管,5例患者术前患侧肋腹部疼痛均得到缓解,手术主观成功率100%。术者反馈显示,设备运行稳定,手术过程中未出现机械臂干涉或视野漂移等影响操作流畅度的设备异常。结论: 模块化海山一Ⓡ腔镜手术机器人辅助肾盂成形术具有良好的可行性与安全性。
中图分类号:
- R693.2
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
郑浩轲, 于栓宝, 王泽远, 等. 国产模块化手术机器人系统辅助肾部分切除术的可行性和安全性分析[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2025, 40 (1): 39- 42.
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
应沂岑, 杜毅聪, 李志华, 等. 机器人辅助腹腔镜下颊黏膜补片输尿管成形术治疗复杂输尿管狭窄[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56 (4): 640- 645.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.04.016 |
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
李学松, 樊书菠, 熊盛炜, 等. 国产内窥镜手术机器人系统在肾部分切除术中的初步临床应用[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2021, 42 (5): 375- 380.
|
| 18 |
张忠, 代海涛, 刘远华, 等. 图迈国产机器人辅助腹腔镜在泌尿外科手术中的安全性研究[J]. 微创泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 12 (4): 229- 232.
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| [1] | 刘帅, 刘茁, 管允鹤, 王国良, 田晓军, 张洪宪, 刘磊, 马潞林, 张树栋. 机器人辅助腹腔镜下腔静脉节段性切除术治疗肾肿瘤瘤栓侵犯血管壁[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 796-802. |
| [2] | 王焕瑞, 赖世聪, 胡浩浦, 丁泽华, 徐涛, 胡浩. 腹腔镜与输尿管软镜联合定位治疗复杂输尿管狭窄的疗效分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 784-788. |
| [3] | 张启鸣, 陈泽波, 田雨, 潘大猛, 刘磊, 张洪宪, 赵磊, 张树栋, 马潞林, 侯小飞. 机器人辅助腹腔镜移植肾切除术经验总结[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 666-669. |
| [4] | 李宗瀚, 黄洋阅, 李宁, 李明磊, 宋宏程, 张潍平, 刘超. 国产单孔蛇形臂机器人手术系统在儿童肾盂成形术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 662-665. |
| [5] | 应沂岑,杜毅聪,李志华,张一鸣,李新飞,王冰,张鹏,朱宏建,周利群,杨昆霖,李学松. 机器人辅助腹腔镜下颊黏膜补片输尿管成形术治疗复杂输尿管狭窄[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 640-645. |
| [6] | 张树栋,谢睿扬. 机器人手术时代的肾癌合并腔静脉瘤栓治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 562-564. |
| [7] | 安立哲,熊六林,陈亮,王焕瑞,陈伟男,黄晓波. 腹腔镜肾盂成形术联合肾盂镜超声碎石取石术治疗肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻合并肾结石[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 746-750. |
| [8] | 左炜,高菲,袁昌巍,熊盛炜,李志华,张雷,杨昆霖,李新飞,刘靓,魏来,张鹏,王冰,谷亚明,朱宏建,赵峥,李学松. 基于多中心数据库的10年上尿路修复手术术式及术型变化趋势[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 692-698. |
| [9] | 周利群,徐纯如. 机器人时代中央型肾肿瘤的手术治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 587-591. |
| [10] | 郝瀚,刘越,陈宇珂,司龙妹,张萌,范宇,张中元,唐琦,张雷,吴士良,宋毅,林健,赵峥,谌诚,虞巍,韩文科. 机器人辅助前列腺癌根治术后患者的控尿恢复时间[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 697-703. |
| [11] | 熊盛炜,王杰,朱伟杰,程嗣达,张雷,李学松,周利群. 二次肾盂成形术在复发性肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻中的研究进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 794-798. |
| [12] | 程嗣达,李新飞,熊盛炜,樊书菠,王杰,朱伟杰,李子奡,丁光璞,俞婷,李万强,孙永明,杨昆霖,张雷,郝瀚,李学松,周利群. 机器人辅助腹腔镜上尿路修复手术:单一术者108例经验总结[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 771-779. |
| [13] | 郑蒙蒙,丁光璞,朱伟杰,杨昆霖,樊书菠,关豹,李新飞,蔡宇坤,张进生,李学松,周利群. 术前三维影像重建在治疗肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 705-710. |
| [14] | 陈伟男,叶雄俊,刘士军,熊六林,黄晓波,徐涛,王晓峰. 三种手术方式治疗肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻的疗效及并发症比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(5): 817-821. |
|
||