Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 692-697. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
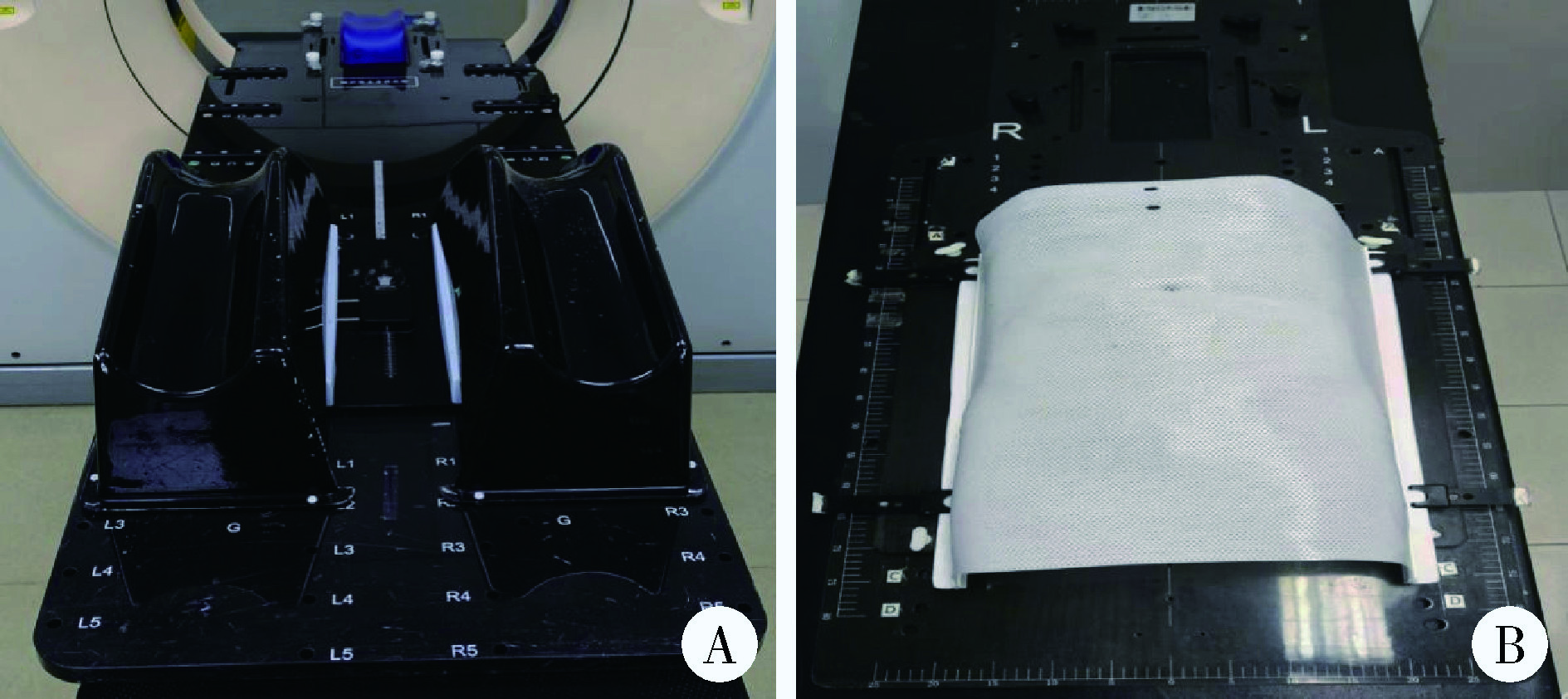
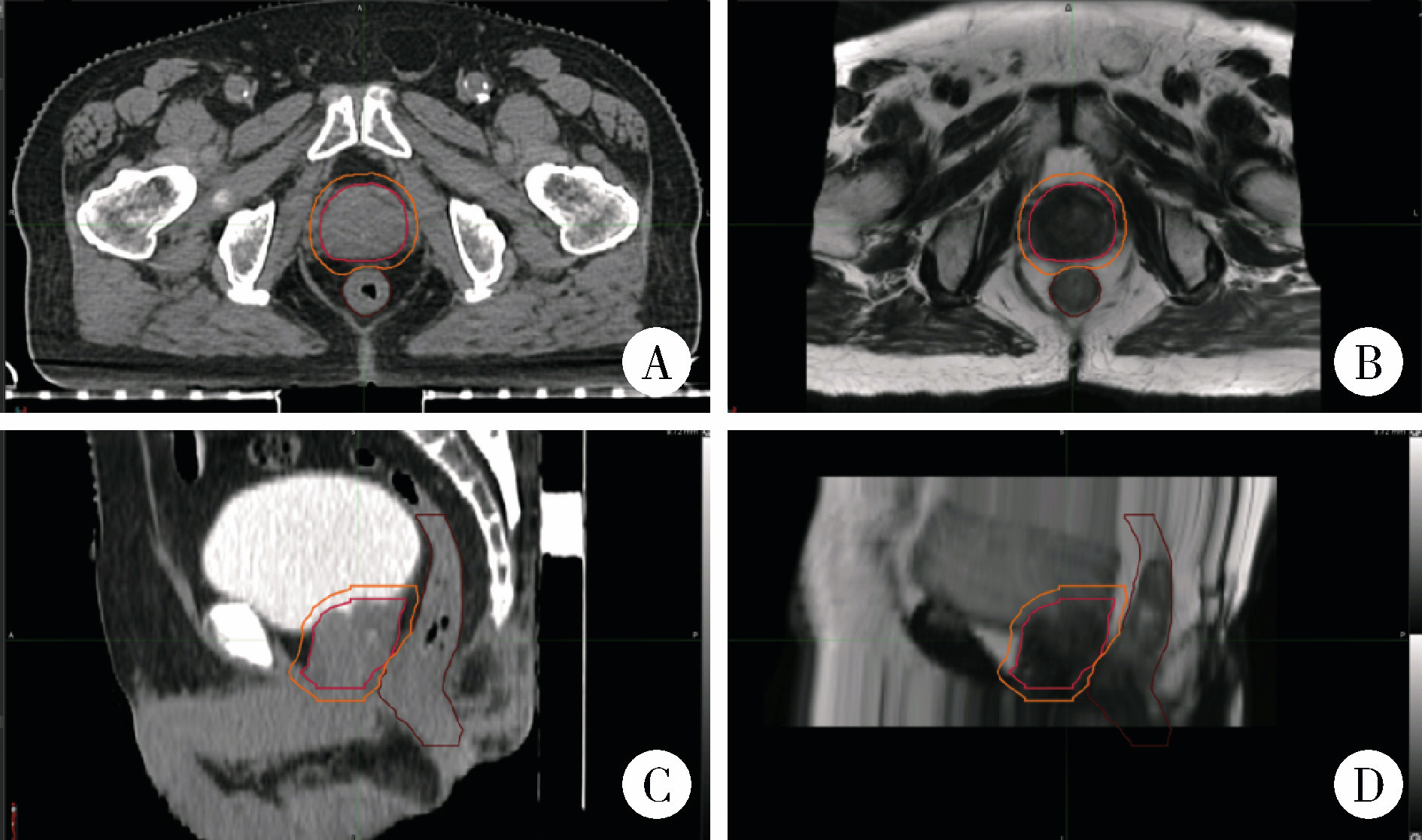
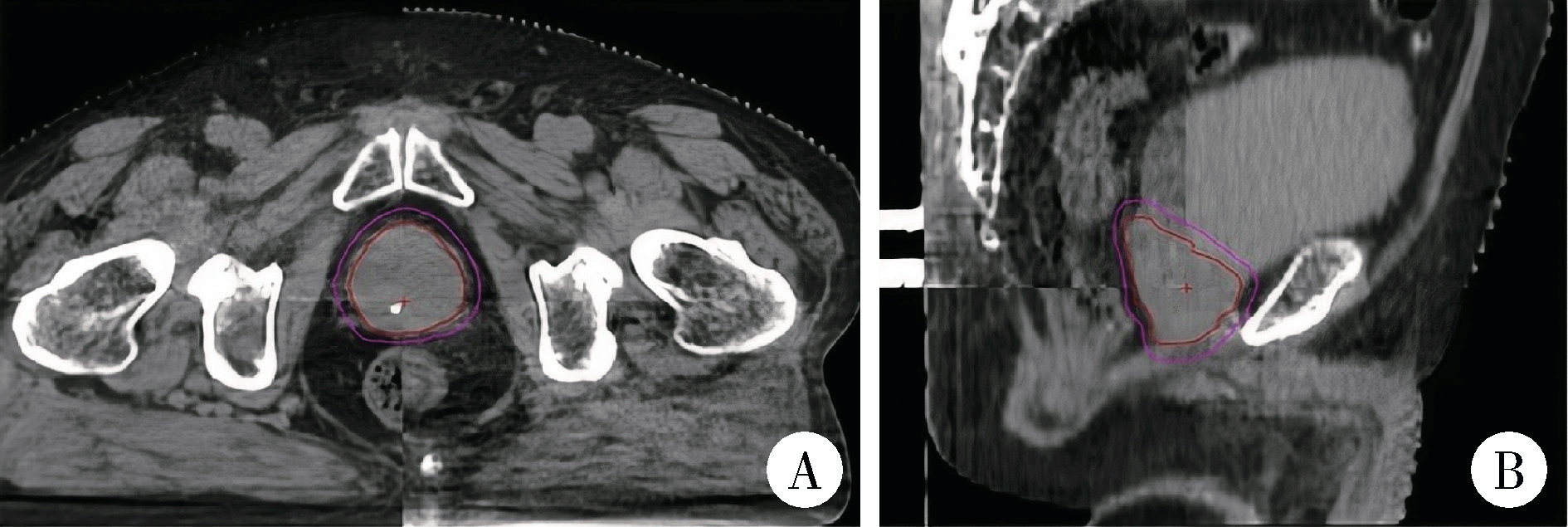
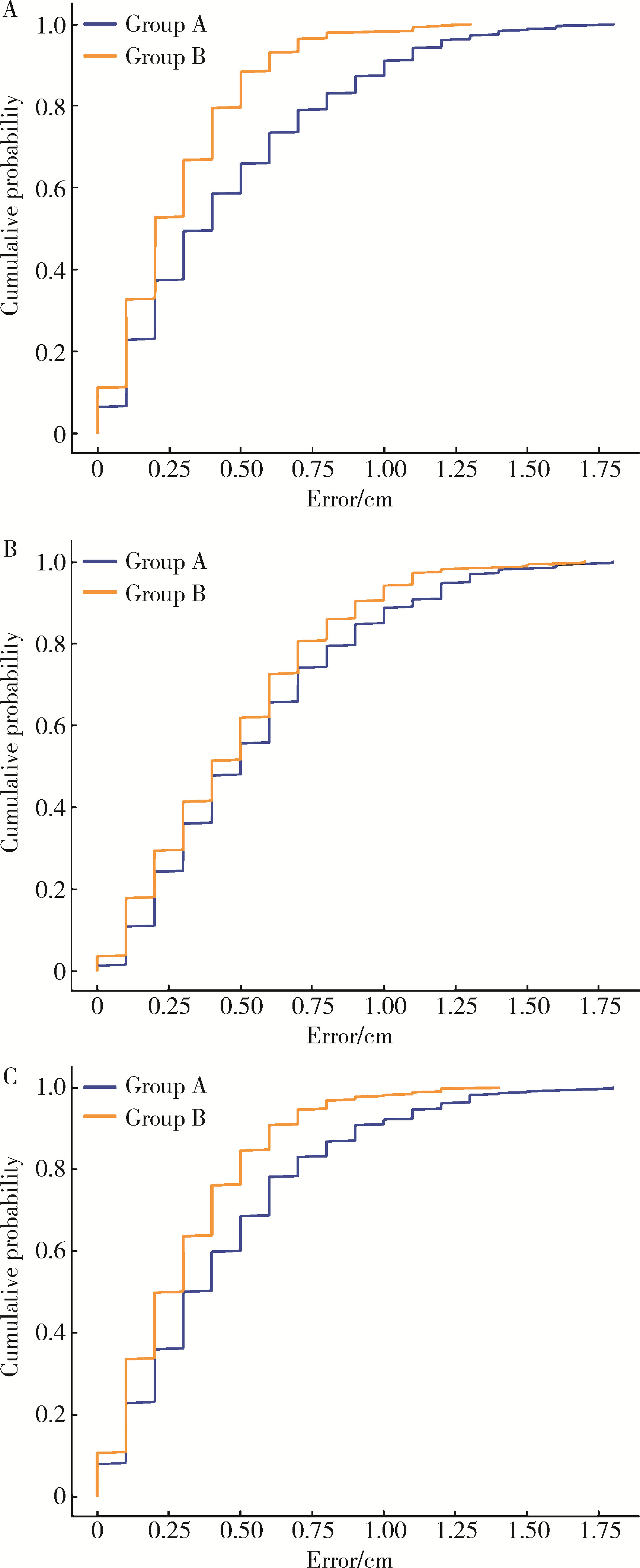
Comparison of setup errors between two immobilization methods in prostate cancer radiotherapy based on cone-beam computed tomography
Jie LIU, Mingwei MA*( ), Qing'an WANG, Ming SHI, Jinpeng YIN, Zhanping WANG, Jingtao SHEN, Xianshu GAO
), Qing'an WANG, Ming SHI, Jinpeng YIN, Zhanping WANG, Jingtao SHEN, Xianshu GAO
- Department of Radiation Oncology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R737.25
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
马广栋, 洪莉. 宫颈癌的图像引导放疗研究综述[J]. 中国医疗设备, 2018, 33(5): 117-120, 129.
|
| 11 |
于松茂, 孟繁里, 康加阜, 等. 真空垫制作方式对肺癌立体定向放疗摆位精度影响研究[J]. 医疗卫生装备, 2019, 40(12): 33-35, 40.
|
| 12 |
马茗微, 王淑莲, 覃仕瑞, 等. 面罩及乳腺托架固定下乳腺癌保乳术后放疗锁骨上下区摆位误差分析[J]. 中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2019, 28(3): 217- 221.
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
高研, 高献书, 马茗微, 等. 前列腺癌放疗时CBCT使用频率和匹配策略的剂量学分析[J]. 中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2024, 33(8): 733- 739.
|
| 15 |
|
|
||