北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 309-316. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.02.014
3D打印生物可降解WE43镁合金支架的生物相容性及对骨缺损的治疗
- 北京大学第三医院骨科,骨与关节精准医学教育部工程中心,北京 100191
Biocompatibility of 3D printed biodegradable WE43 magnesium alloy scaffolds and treatment of bone defects
- Department of Orthopedics, Peking University Third Hospital; Engineering Research Center of Bone and Joint Precision Medicine, Ministry of Education, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
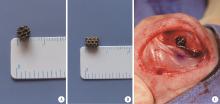
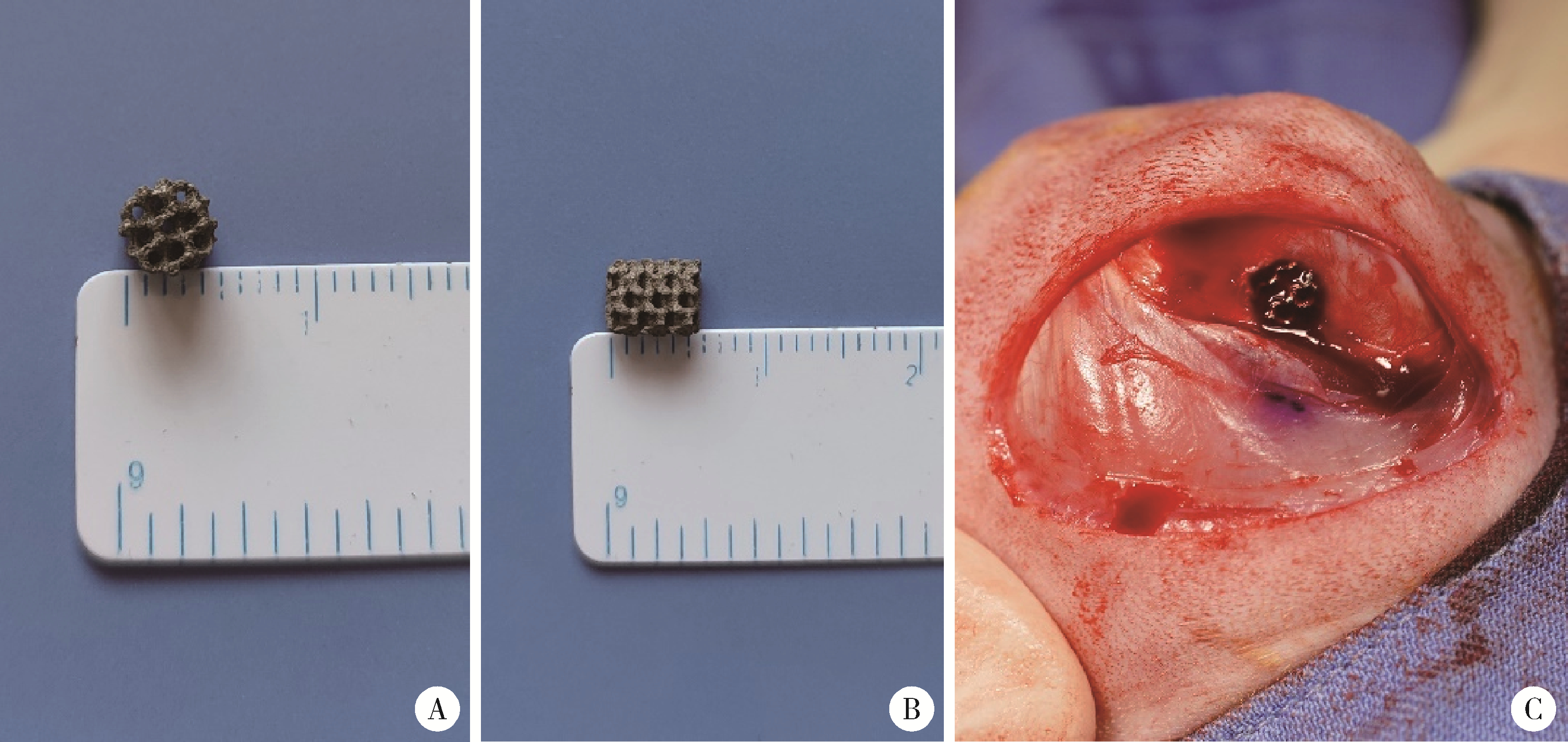
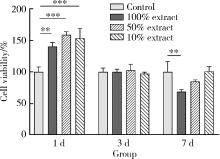
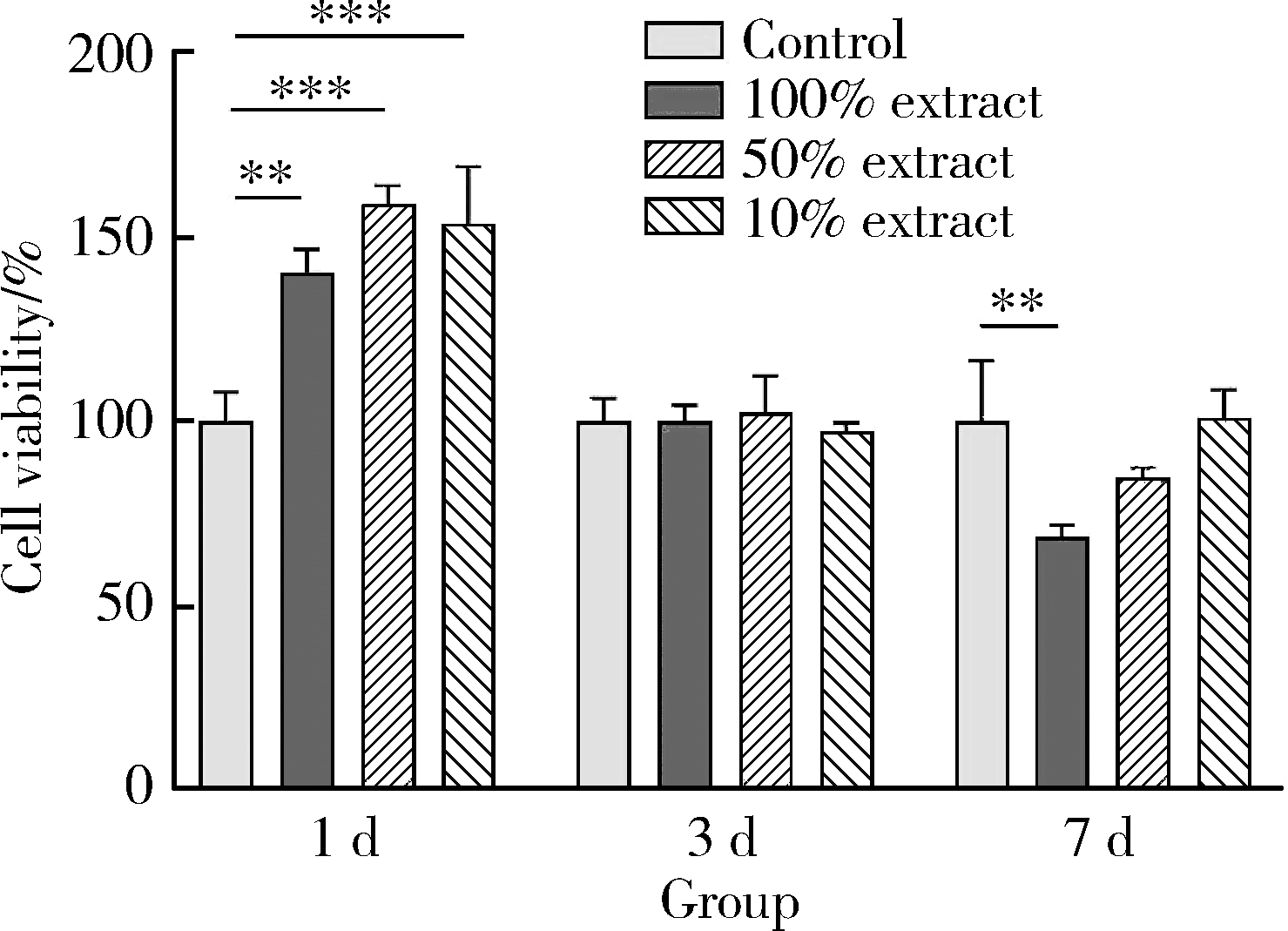
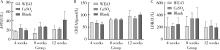
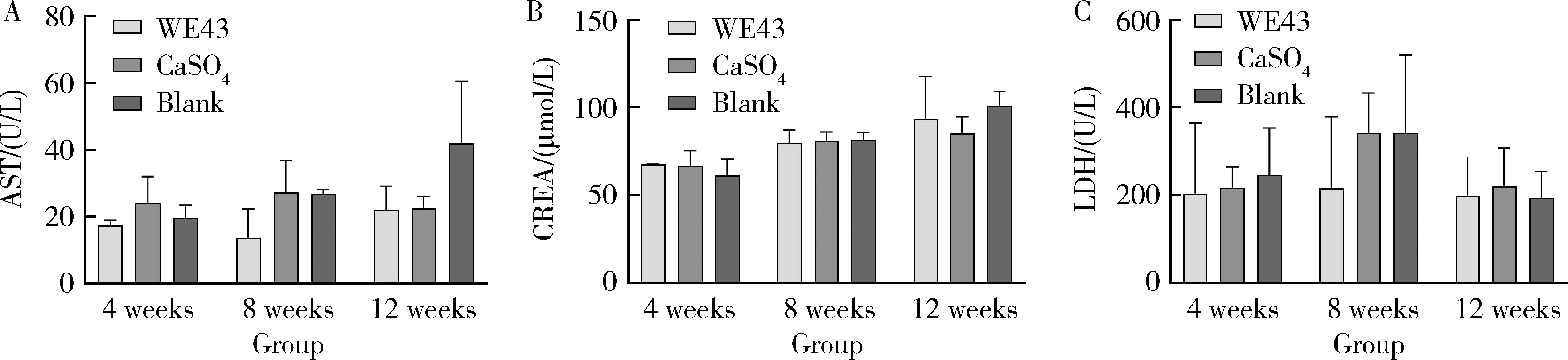
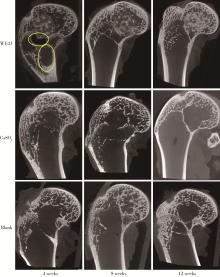
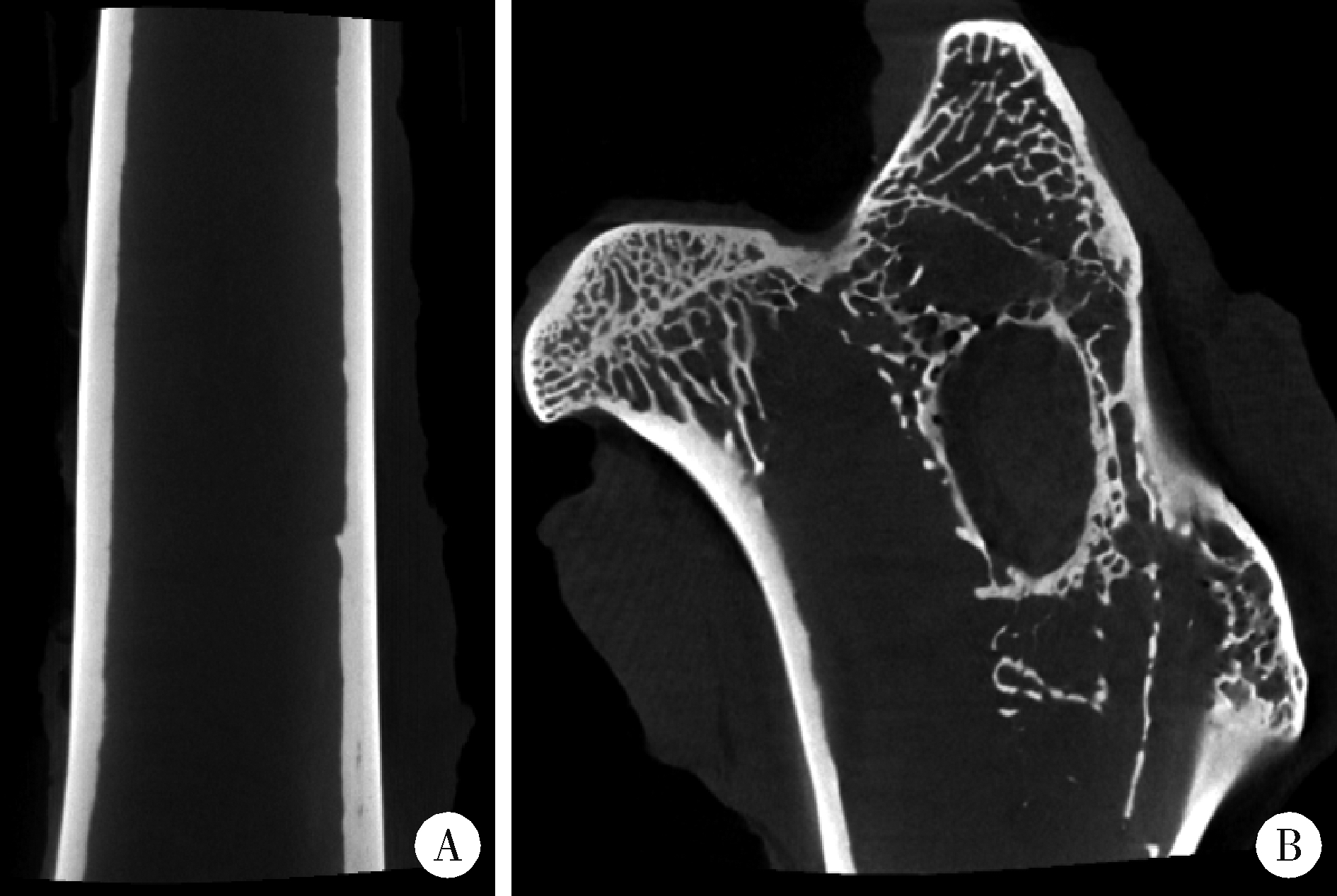
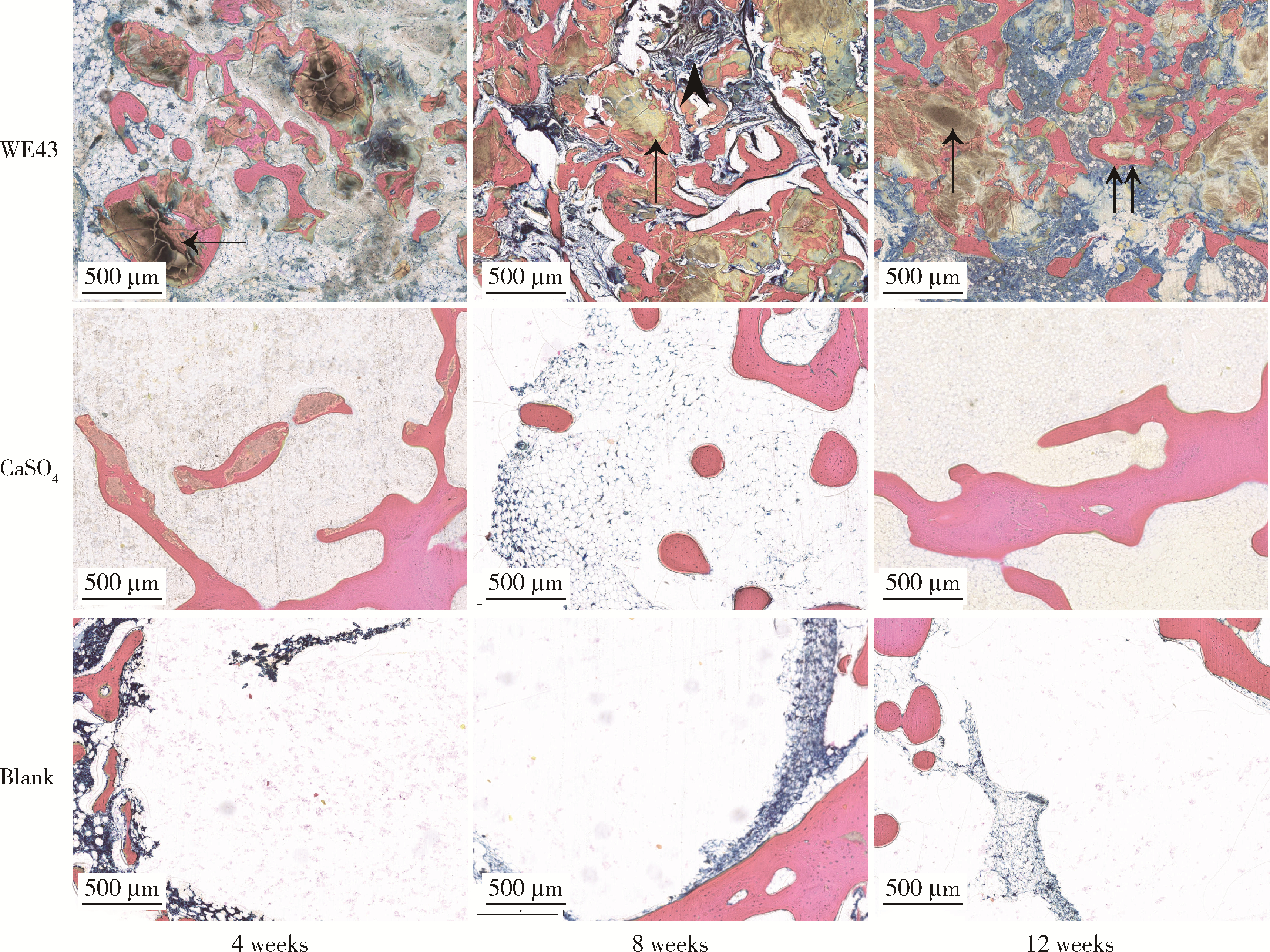
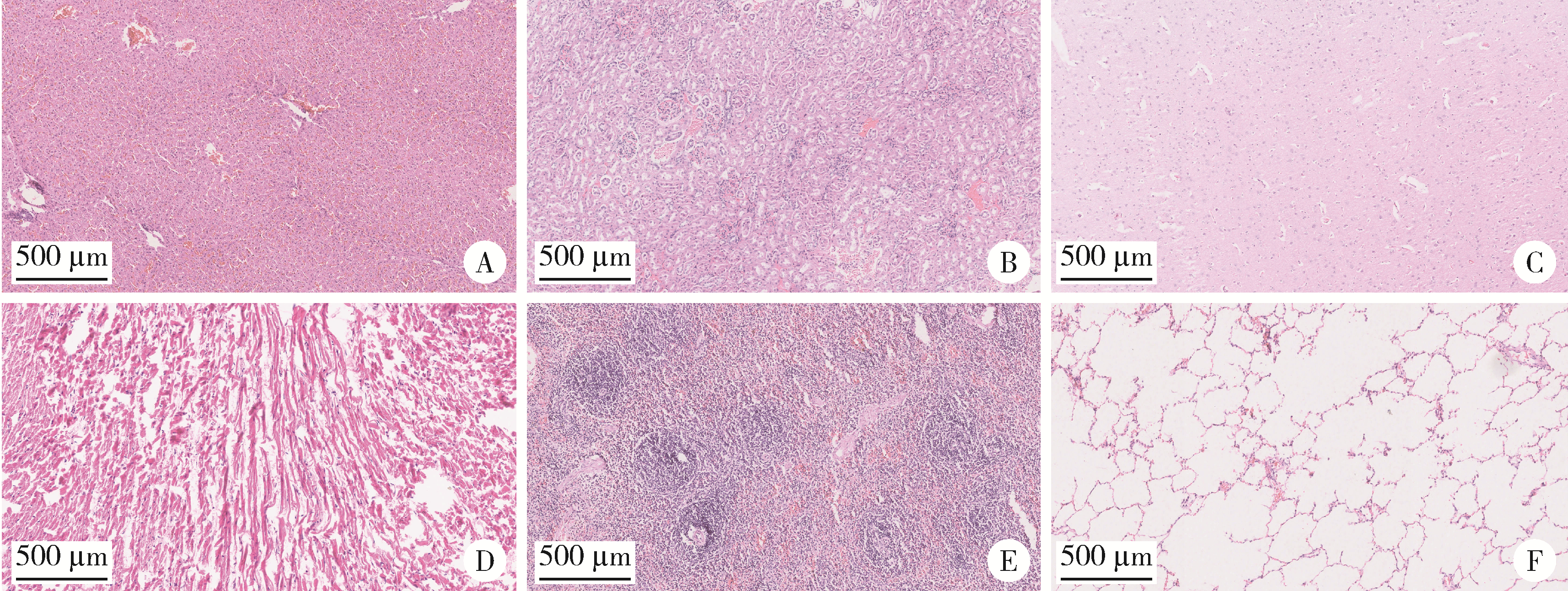
目的: 探讨3D打印工艺制造的多孔WE43镁合金支架的生物相容性, 并观察其治疗新西兰大白兔股骨缺损的效果。方法: 利用Sprague Dawley(S-D)大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞进行体外细胞毒性试验, 根据培养液不同将细胞分为100%浸提液组、50%浸提液组、10%浸提液组及对照组, 将各组细胞分别培养1、3及7 d后, 采用细胞计数试剂盒8(cell counting kit-8, CCK-8)法测定各组细胞活性。体内实验中, 随机将3.0~3.5 kg新西兰大白兔分成实验组、骨水泥组与空白组3组, 每组9只, 每只均对左侧股骨外侧髁进行手术, 利用骨钻制造直径5 mm、深6 mm的骨缺损, 其中实验组植入WE43镁合金支架, 骨水泥组植入硫酸钙骨水泥, 空白组不做植入。在术后4、8与12周分别对每组3只进行二氧化碳麻醉法安乐死, 对股骨及重要内脏器官进行取材, 对左股骨外侧髁进行微计算机断层扫描(micro-computed tomography, Micro-CT)。对重要内脏器官制备切片, 并使用苏木精-伊红(hematoxylin-eosin, HE)染色, 对股骨外侧髁制作硬组织切磨片, 使用亚甲基蓝酸性品红染色, 在显微镜下观察。结果: 细胞毒性试验中, 培养1 d时, 100%浸提液组细胞存活率高于对照组(140.56% vs. 100.00%, P<0.05); 培养3 d时, 各组细胞存活率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);培养7 d时, 100%浸提液组细胞存活率低于对照组(68.64% vs. 100.00%, P<0.05)。体内实验中Micro-CT扫描发现实验组在4周时大部分支架均已降解, 高密度的支架所剩很少, 12周时已无明显支架轮廓。在4周时, WE43镁合金支架周围有一定量气体生成, 在8~12周时, 气体明显减少。硬组织切磨片显示, 实验组4周时支架周围有一定量细胞外基质和类骨质生成, 骨水泥组中硫酸钙骨水泥已大部分降解, 8周时实验组支架及其降解产物周围的类骨质明显增多, 12周时实验组支架周围有新生骨与支架接触, 骨水泥组与空白组新生骨较少。结论: 3D打印工艺制造的多孔WE43镁合金支架生物相容性良好, 具有良好的成骨性能, 有潜力成为修补骨缺损的新型材料。
中图分类号:
- R681.8
| 1 | Archunan MW , Petronis S . Bone grafts in trauma and orthopaedics[J]. Cureus, 2021, 13 (9): e17705. |
| 2 |
Grambart ST , Anderson DS , Anderson TD . Bone grafting options[J]. Clin Podiatr Med Surg, 2020, 37 (3): 593- 600.
doi: 10.1016/j.cpm.2020.03.012 |
| 3 |
Lodoso-Torrecilla I , van den Beucken J , Jansen JA . Calcium phosphate cements: Optimization toward biodegradability[J]. Acta Biomater, 2021, 119, 1- 12.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.10.013 |
| 4 |
Kani KK , Porrino JA , Chew FS . External fixators: Looking beyond the hardware maze[J]. Skeletal Radiol, 2020, 49 (3): 359- 374.
doi: 10.1007/s00256-019-03306-w |
| 5 |
Deng F , Liu L , Li Z , et al. 3D printed Ti6Al4V bone scaffolds with different pore structure effects on bone ingrowth[J]. J Biol Eng, 2021, 15 (1): 4.
doi: 10.1186/s13036-021-00255-8 |
| 6 |
Sumner DR . Long-term implant fixation and stress-shielding in total hip replacement[J]. J Biomech, 2015, 48 (5): 797- 800.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2014.12.021 |
| 7 | Karunakaran R , Ortgies S , Tamayol A , et al. Additive manufacturing of magnesium alloys[J]. Bioact Mater, 2020, 5 (1): 44- 54. |
| 8 | Zhang J , Jiang Y , Shang Z , et al. Biodegradable metals for bone defect repair: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on animal studies[J]. Bioact Mater, 2021, 6 (11): 4027- 4052. |
| 9 | Witte F , Hort N , Vogt C , et al. Degradable biomaterials based on magnesium corrosion[J]. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci, 2008, 12 (5/6): 63- 72. |
| 10 | Saris NE , Mervaala E , Karppanen H , et al. Magnesium. An update on physiological, clinical and analytical aspects[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2000, 294 (1/2): 1- 26. |
| 11 |
Janning C , Willbold E , Vogt C , et al. Magnesium hydroxide temporarily enhancing osteoblast activity and decreasing the osteoclast number in peri-implant bone remodelling[J]. Acta Biomater, 2010, 6 (5): 1861- 1868.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2009.12.037 |
| 12 | Zhang X , Chen Q , Mao X . Magnesium enhances osteogenesis of BMSCs by tuning osteoimmunomodulation[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2019, 2019, 7908205. |
| 13 |
Leem YH , Lee KS , Kim JH , et al. Magnesium ions facilitate integrin alpha 2- and alpha 3-mediated proliferation and enhance alkaline phosphatase expression and activity in hBMSCs[J]. J Tissue Eng Regen Med, 2016, 10 (10): E527- E536.
doi: 10.1002/term.1861 |
| 14 | Chen K , Xie X , Tang H , et al. In vitro and in vivo degradation behavior of Mg-2Sr-Ca and Mg-2Sr-Zn alloys[J]. Bioact Mater, 2020, 5 (2): 275- 285. |
| 15 | Xia D , Liu Y , Wang S , et al. In vitro and in vivo investigation on biodegradable Mg-Li-Ca alloys for bone implant application[J]. Sci China Mater, 2018, 62 (2): 256- 272. |
| 16 | Li Z , Gu X , Lou S , et al. The development of binary Mg-Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone[J]. Biomaterials, 2008, 29 (10): 1329- 1344. |
| 17 | He LY , Zhang XM , Liu B , et al. Effect of magnesium ion on human osteoblast activity[J]. Braz J Med Biol Res, 2016, 49 (7): e5257. |
| 18 | International Organization for Standardization. Biological evaluation of medical devices. Part 12: Sample preparation and reference materials: ISO 10993-12: 2021[S]. Switzerland: Vernier, 2021: 01. |
| 19 | Morgan EF , Unnikrisnan GU , Hussein AI . Bone mechanical pro-perties in healthy and diseased states[J]. Annu Rev Biomed Eng, 2018, 20, 119- 143. |
| 20 | Cuppone M , Seedhom BB , Berry E , et al. The longitudinal Young's modulus of cortical bone in the midshaft of human femur and its correlation with CT scanning data[J]. Calcif Tissue Int, 2004, 74 (3): 302- 309. |
| 21 | Lu WC , Pringa E , Chou L . Effect of magnesium on the osteogenesis of normal human osteoblasts[J]. Magnes Res, 2017, 30 (2): 42- 52. |
| 22 | Zheng YF , Gu XN , Witte F . Biodegradable metals[J]. Mater Sci Eng R Rep, 2014, 77, 1- 34. |
| 23 | Gu XN , Xie XH , Li N , et al. In vitro and in vivo studies on a Mg-Sr binary alloy system developed as a new kind of biodegradable metal[J]. Acta Biomater, 2012, 8 (6): 2360- 2374. |
| 24 | von der Höh N , von Rechenberg B , Bormann D , et al. Influence of different surface machining treatments of resorbable magnesium alloy implants on degradation-EDX-analysis and histology results[J]. Materwiss Werksttech, 2009, 40 (1/2): 88- 93. |
| 25 | Witte F , Fischer J , Nellesen J , et al. In vitro and in vivo corrosion measurements of magnesium alloys[J]. Biomaterials, 2006, 27 (7): 1013- 1018. |
| 26 | Feyerabend F , Fischer J , Holtz J , et al. Evaluation of short-term effects of rare earth and other elements used in magnesium alloys on primary cells and cell lines[J]. Acta Biomater, 2010, 6 (5): 1834- 1842. |
| 27 | Li F , Gong A , Qiu L , et al. Simultaneous determination of trace rare-earth elements in simulated water samples using ICP-OES with TODGA extraction/back-extraction[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12 (9): e0185302. |
| 28 | Angrisani N , Reifenrath J , Zimmermann F , et al. Biocompatibility and degradation of LAE442-based magnesium alloys after implantation of up to 3.5 years in a rabbit model[J]. Acta Biomater, 2016, 44, 355- 365. |
| [1] | 展新新,曹露露,项东,汤皓,夏丹丹,林红. 成型方向对3D打印口腔义齿基托树脂材料物理性能及力学性能的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 345-351. |
| [2] | 胡攀攀,李彦,刘啸,唐彦超,李梓赫,刘忠军. 自稳式人工椎体在颈椎前路手术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 161-166. |
| [3] | 黄莹,吴志远,周行红,蔡志刚,张杰. 股前外侧皮瓣修复上颌骨缺损术后面部软组织对称性感观分级[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 708-715. |
| [4] | 周华,王仁吉,刘忠军,刘晓光,吴奉梁,党礌,韦峰. 3D打印人工椎体在颈椎脊索瘤全脊椎切除术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 144-148. |
| [5] | 开地尔娅·阿不都热合曼,张荣赓,钱浩楠,邹振洋,丹尼娅·叶斯涛,范田园. 个性化剂量熔融沉积成型3D打印茶碱片剂的制备和体外评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1202-1207. |
| [6] | 孙玉春,郭雨晴,陈虎,邓珂慧,李伟伟. 口腔精准仿生修复技术的自主创新研发与转化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 7-12. |
| [7] | 王京旗,王霄. 掺锶磷酸钙骨水泥材料生物学性能的动物实验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 378-383. |
| [8] | 康一帆,单小峰,张雷,蔡志刚. 游离腓骨瓣修复重建上颌骨术后腓骨瓣位置变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(5): 938-942. |
| [9] | 曹畅,王菲,王恩博,刘宇. β-磷酸三钙用于下颌第三磨牙拔除术后骨缺损修复的自身对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 97-102. |
| [10] | 李博文,吴唯伊,唐琳,张一,刘玉华. 改良猪小肠黏膜下层可吸收膜在兔下颌骨缺损早期愈合中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 887-892. |
| [11] | 张达,王林川,周彦恒,刘晓默,李晶. 3D打印间接粘接托槽精度[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 704-708. |
| [12] | 王圣林,杨钟玮,闫明,刘忠军. 术中CT引导下寰枢椎复位、固定[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(3): 512-517. |
| [13] | 郭福新,姜玉良,吉喆,彭冉,孙海涛,王俊杰. 3D打印非共面模板辅助CT引导125Ⅰ粒子植入治疗锁骨上复发转移癌的剂量学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(3): 506-511. |
| [14] | 章文博,于尧,王洋,刘筱菁,毛驰,郭传瑸,俞光岩,彭歆. 数字化外科技术在上颌骨缺损重建中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(1): 1-005. |
|
||