北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 68-73. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2026.01.009
直接免疫荧光在口腔黏膜寻常型天疱疮诊断中的价值: 基于多指标联合分析的回顾性研究
池彦廷1,*, 蒋鸿杰1,2,*, 陈艳1, 徐志秀1,*( ), 李斌斌1,*(
), 李斌斌1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院病理科, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
2. 重庆医科大学附属口腔医院, 口腔疾病研究重庆市重点实验室, 口腔生物医学工程重庆市高校市级重点实验室, 重庆市卫生健康委员会口腔生物医学工程重点实验室, 重庆 401147
Value of direct immunofluorescence in the diagnosis of oral mucosal pemphigus vulgaris: A retrospective study based on multi-index combined analysis
Yanting CHI1, Hongjie JIANG1,2, Yan CHEN1, Zhixiu XU1,*( ), Binbin LI1,*(
), Binbin LI1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral Pathology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Chongqing Medical University & Chongqing Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & Municipal Key Laboratory of Oral Biomedical Engineering of Higher Education & Chongqing Municipal Health Commission Key Laboratory of Oral Biomedical Engineering, Chongqing 401147, China
摘要:
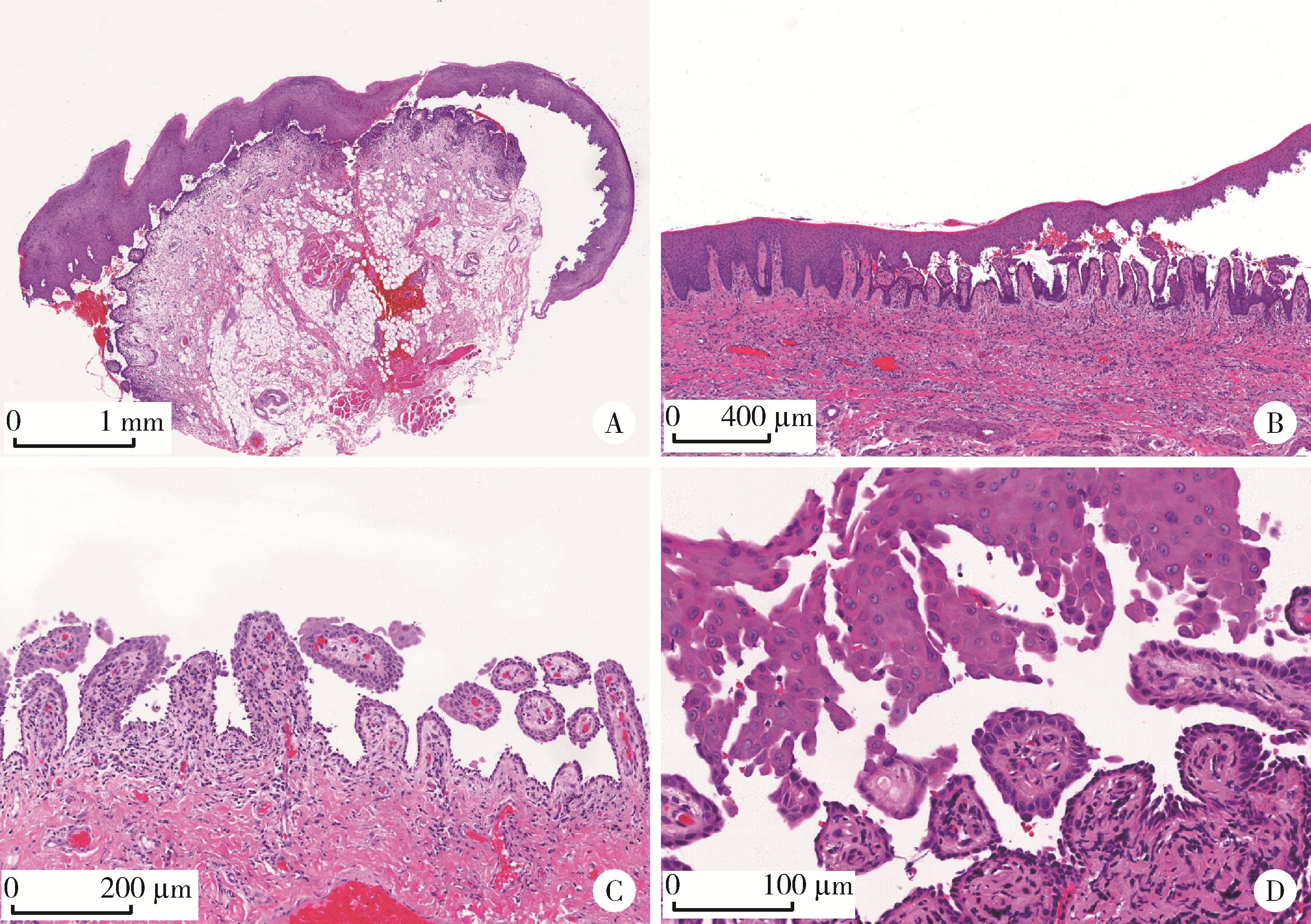
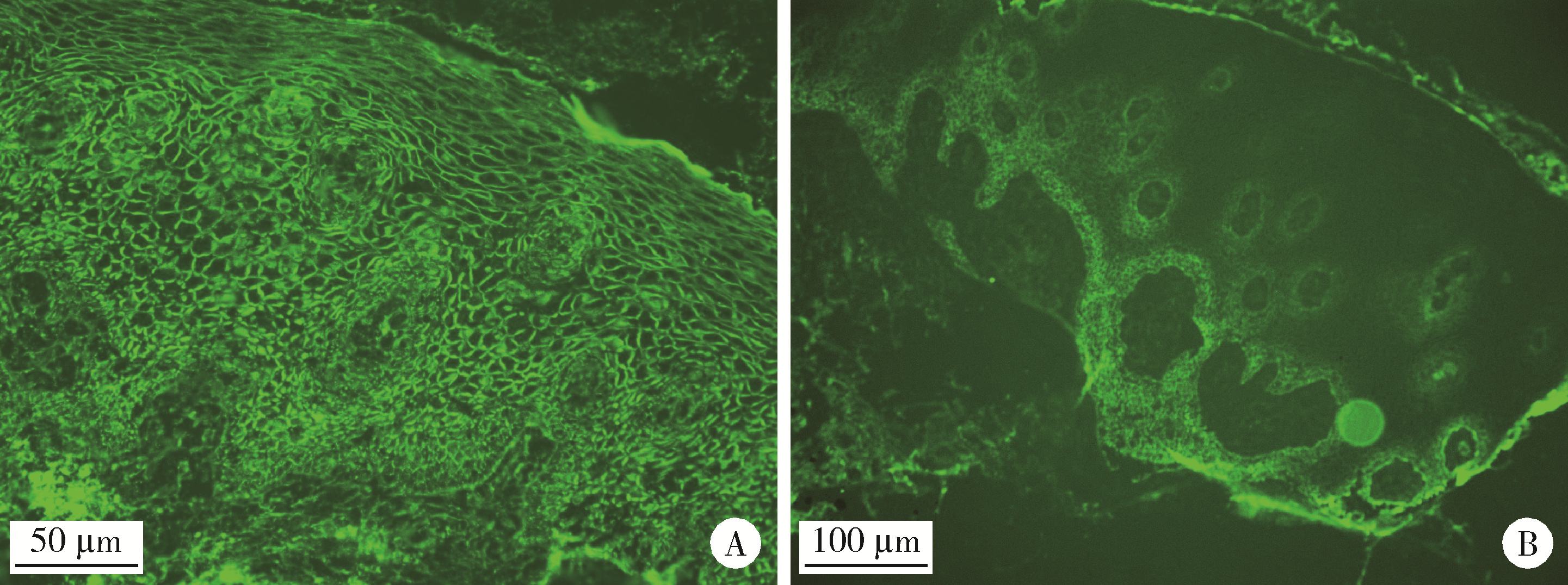
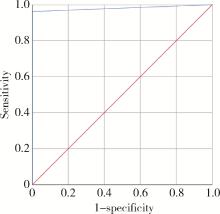
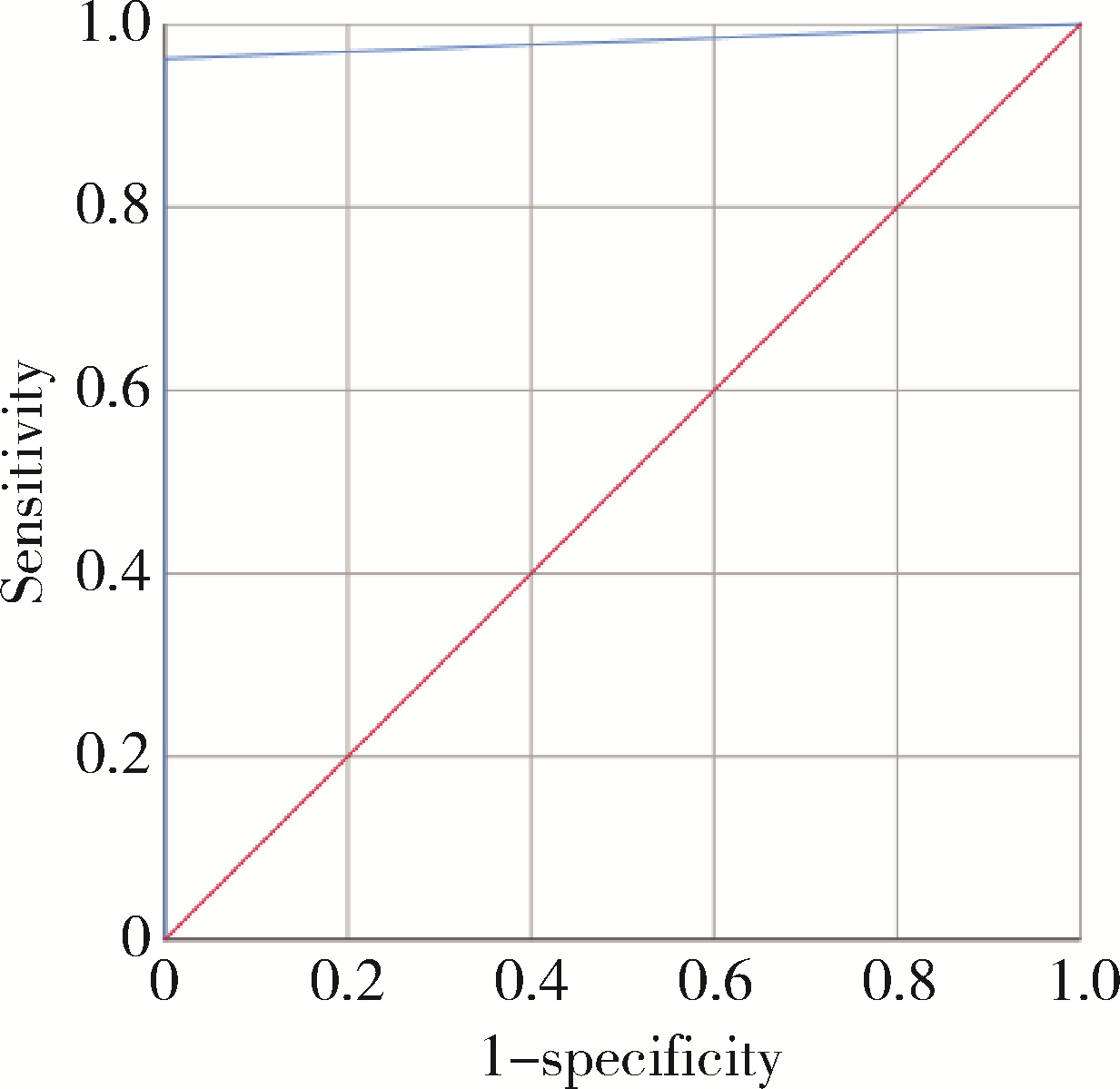
目的: 基于多指标联合分析,探讨直接免疫荧光(direct immunofluorescence,DIF)对口腔黏膜寻常型天疱疮(pemphigus vulgaris,PV)的诊断效能。方法: 回顾性分析53例确诊口腔黏膜PV的患者,收集患者临床资料及DIF、组织病理学、血清学酶联免疫吸附试验(enzyme-linked immunosorbnent assay,ELISA)检测结果,采用灵敏度、特异度、受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线的曲线下面积(area under curve,AUC)等指标评估各方法的诊断效能。结果: 患者以中老年女性为主,颊黏膜为最常见受累部位,大部分患者伴有起疱史。DIF检测的阳性率为96.23%,主要表现为上皮棘细胞间网状绿色荧光沉积,其诊断价值最高,灵敏度为96.23%,特异度为100.00%,AUC值为0.981;组织病理学次之,灵敏度为94.34%,特异度为100.00%,AUC值为0.972;ELISA检测的灵敏度为82.61%,特异度为82.35%,AUC值为0.825。DIF与组织病理学、ELISA及临床诊断具有互补性,联合检测可提高诊断准确性。结论: DIF是诊断口腔黏膜PV的核心指标,建议采用“临床表现-DIF-组织病理学-ELISA”综合诊断流程;该综合诊断体系不仅能显著提升口腔黏膜PV诊断的精准度,也契合了精准医疗的核心理念,可为个性化治疗提供依据。
中图分类号:
- R781.5
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
doi: 10.1007/s12026-018-8986-7 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1067/mjd.2003.438 |
| 4 |
doi: 10.1111/jdv.16752 |
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
中国医疗保健国际交流促进会皮肤科分会. 寻常型天疱疮诊断和治疗专家建议(2020)[J]. 中华皮肤科杂志, 2020, 53 (1): 1- 7.
|
| 9 |
doi: 10.3390/dermatopathology11010006 |
| 10 |
doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12486 |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1067/mjd.2001.117518 |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04853-y |
| 13 |
doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.60561 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2017.07.012 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2025.155989 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20143221 |
| 17 |
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.02.005 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.1186/s43556-025-00272-9 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.1111/ced.14854 |
| 20 |
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04132.x |
| 21 |
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.849790 |
| [1] | 赵业, 刁小莉, 熊焰. 细胞转移技术在微量细胞液病理诊断中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2026, 58(1): 208-213. |
| [2] | 王月, 梁宇红. 繁茂型牙骨质-骨结构不良1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2026, 58(1): 220-224. |
| [3] | 顾静妍, 李欣艺, 赵金霞, 穆荣. 误诊为类风湿关节炎、痛风的糖尿病致Charcot关节病1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(6): 1193-1197. |
| [4] | 肖晓笛, 夏有辰, 柳剑英, 付鹏. 左侧胸锁乳突肌间血管内乳头状内皮增生1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(5): 1002-1004. |
| [5] | 孙翔宇, 袁超, 周芯竹, 刁婧, 郑树国. 唾液微生态在口腔及全身疾病早期防治中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(5): 859-863. |
| [6] | 冷汶远, 高端, 李晓宇, 左炜, 胡伟民, 朱振鹏, 徐纯如, 林健, 李学松. 口腔黏膜补片与脱细胞真皮基质补片治疗长段尿道狭窄的疗效和安全性对比[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(5): 975-979. |
| [7] | 朱慧, 闵赛南, 苏家增, 陈艳, 彭歆, 于尧, 俞光岩. 口腔黏膜嗜酸性溃疡的临床病理分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(3): 620-625. |
| [8] | 陈钊, 邱永康, 康磊. 经典型Sweet综合征 18F-FDG PET/CT多脏器异常显像1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(2): 403-407. |
| [9] | 方媛媛, 徐帆, 雷杰, 张昊, 张文宇, 孙宇, 吴宏新, 傅开元, 毛伟玉. 基于颞下颌关节紊乱病诊断标准的临床自动诊断系统的建立及验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(1): 192-201. |
| [10] | 王鹃, 邱立新, 尉华杰. 下颌磨牙穿龈形态设计对种植体周围软组织影响的随机对照临床研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(1): 65-72. |
| [11] | 车佳璐, 刘子臣, 李琨, 张晨, 车南颖. 全自动EasyNAT核酸快速检测系统检测石蜡包埋组织诊断结核病的临床价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1047-1051. |
| [12] | 王杰, 王建伟, 夏海缀, 徐啸, 翟建坡, 何峰, 黄广林, 李贵忠. 阴茎远端尿道狭窄疾病的手术治疗方式[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1075-1082. |
| [13] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [14] | 钟华, 李原, 徐丽玲, 白明欣, 苏茵. 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [15] | 李正芳,罗采南,武丽君,吴雪,孟新艳,陈晓梅,石亚妹,钟岩. 抗氨基甲酰化蛋白抗体在诊断类风湿关节炎中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
|
||