北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 74-83. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2026.01.010
异种骨与人工合成骨在磨牙拔牙同期微翻瓣牙槽嵴保存术中的临床效果比较
张斯巧1,*, 刘建1,*, 徐涛2,*( ), 胡文杰1,*(
), 胡文杰1,*( ), 张浩筠1, 危伊萍1
), 张浩筠1, 危伊萍1
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院牙周科, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
2. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院急诊科, 国家口腔医学中心, 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心, 口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心, 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室, 北京 100081
Clinical comparison of xenograft versus synthetic bone graft materials in micro crestal flap-alveolar ridge preservation following extraction of molars
Siqiao ZHANG1, Jian LIU1, Tao XU2,*( ), Wenjie HU1,*(
), Wenjie HU1,*( ), Haoyun ZHANG1, Yiping WEI1
), Haoyun ZHANG1, Yiping WEI1
- 1. Department of Periodontology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Oral Emergency, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
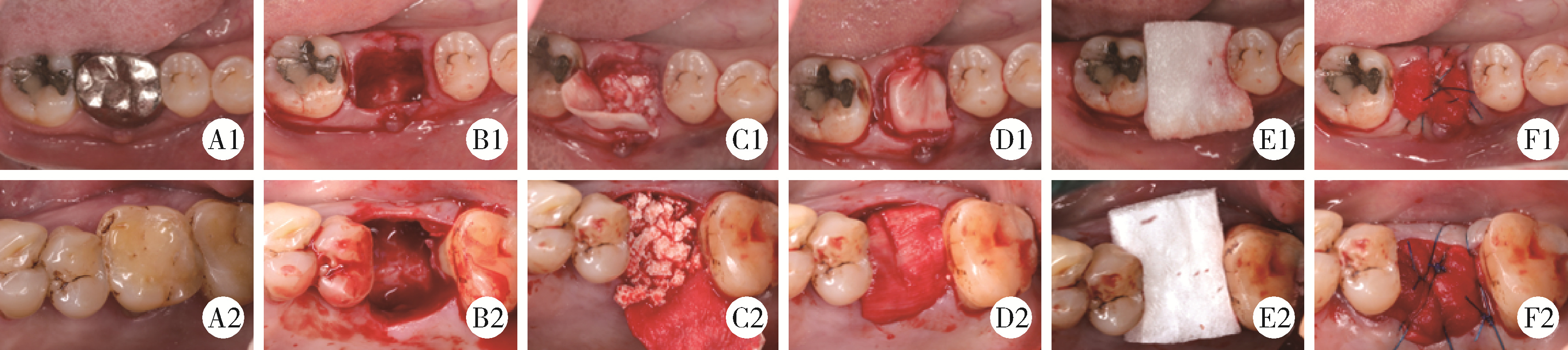
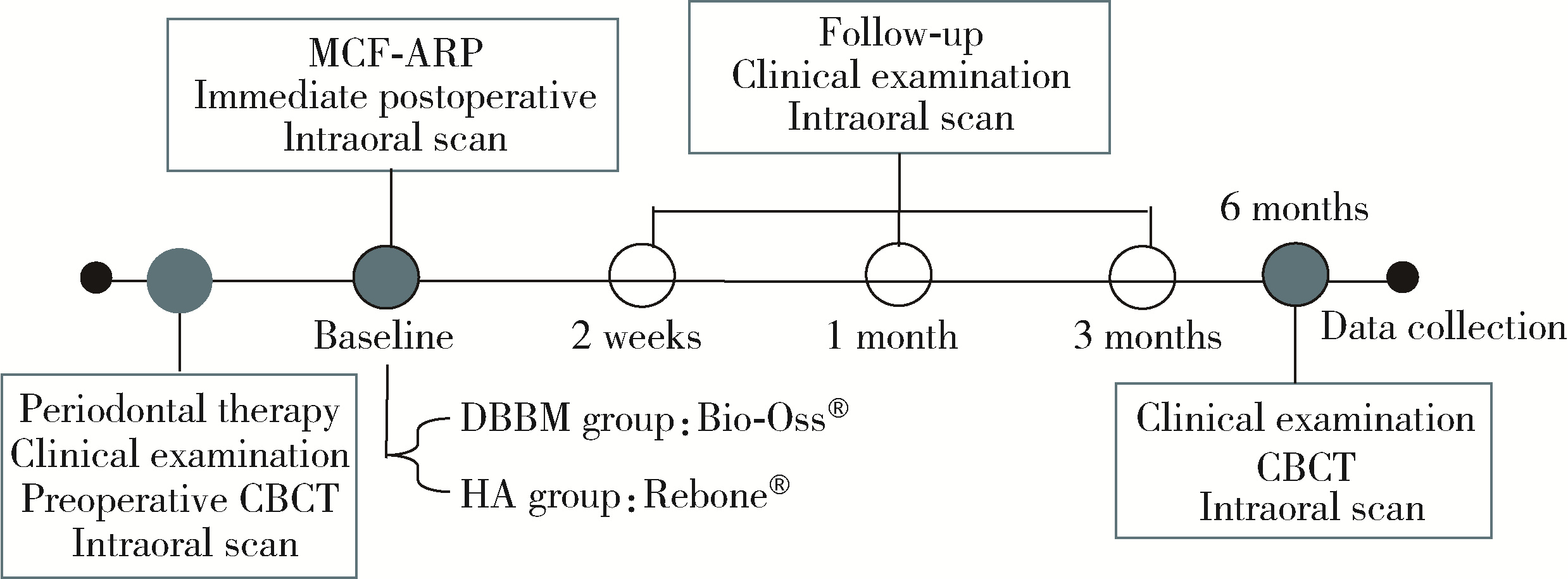
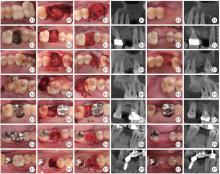
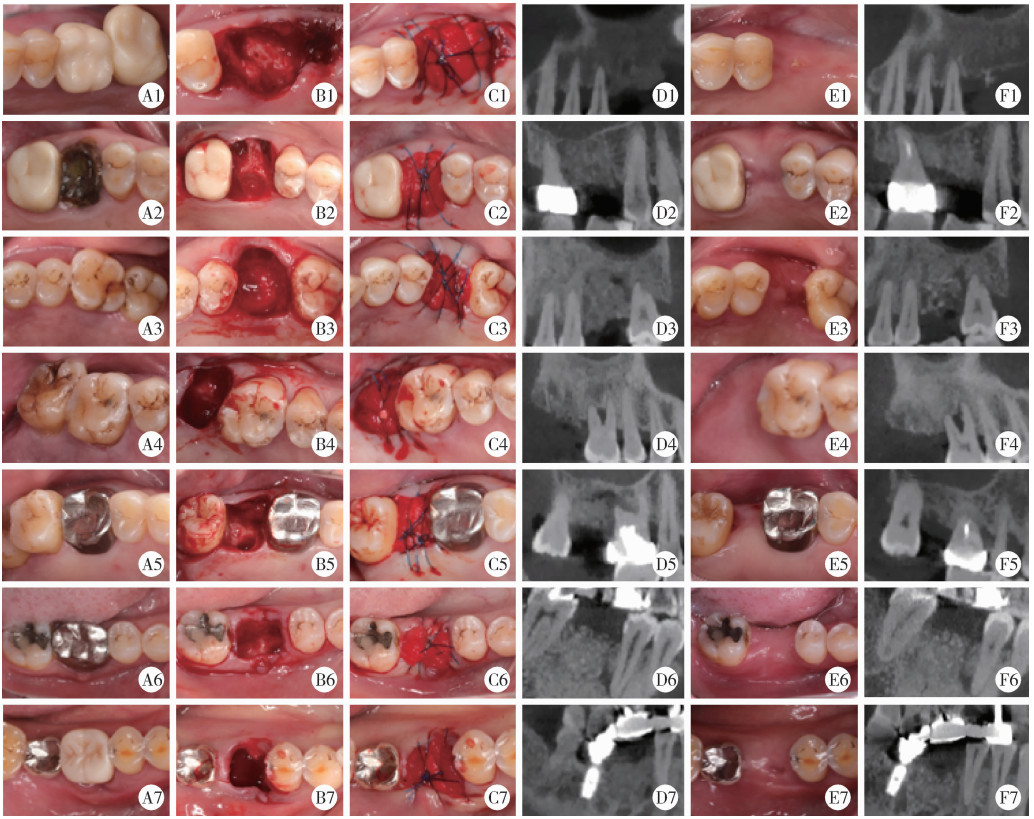
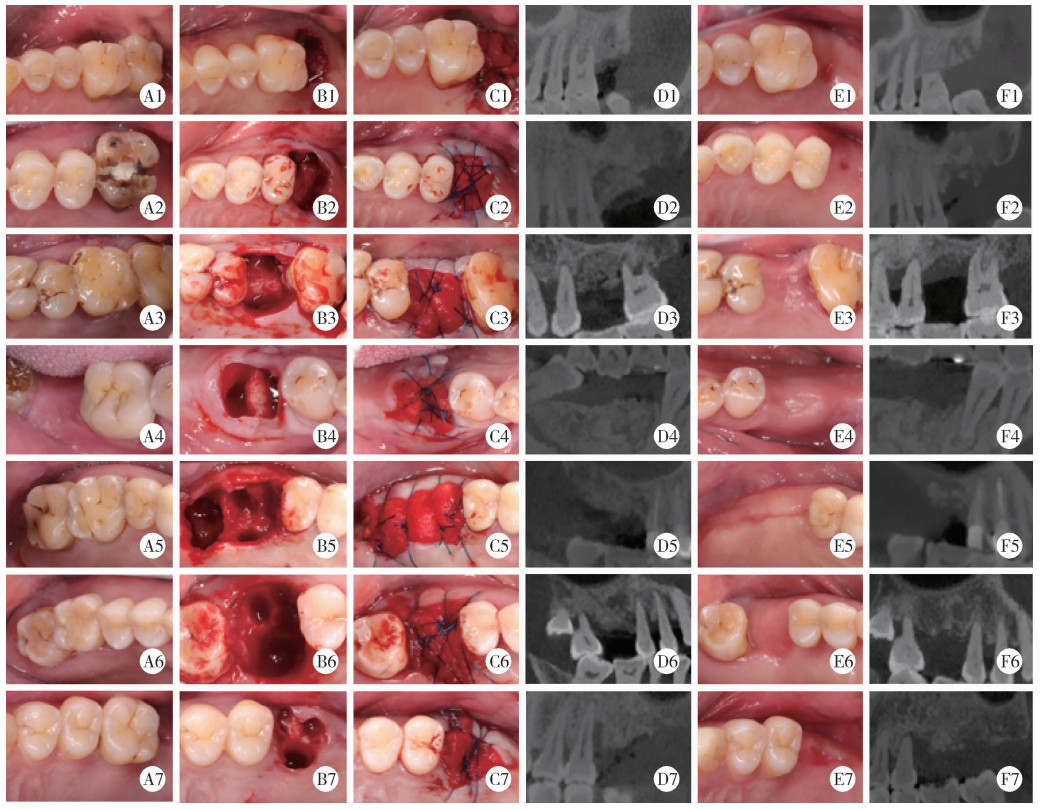
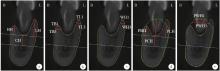
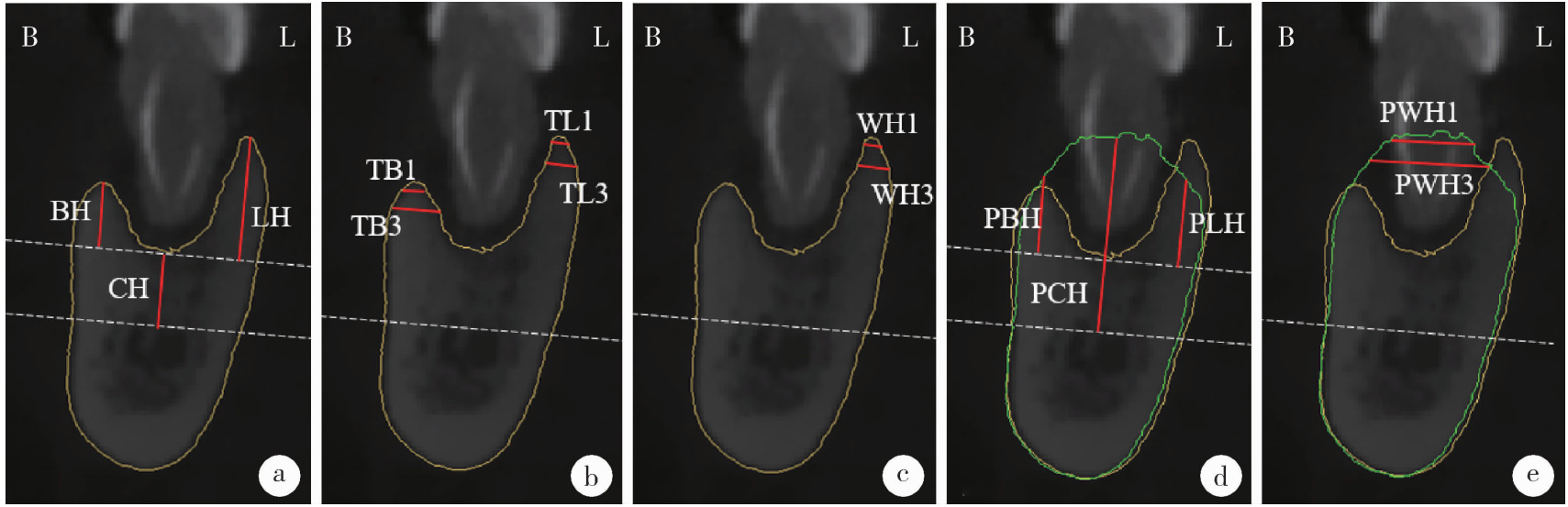
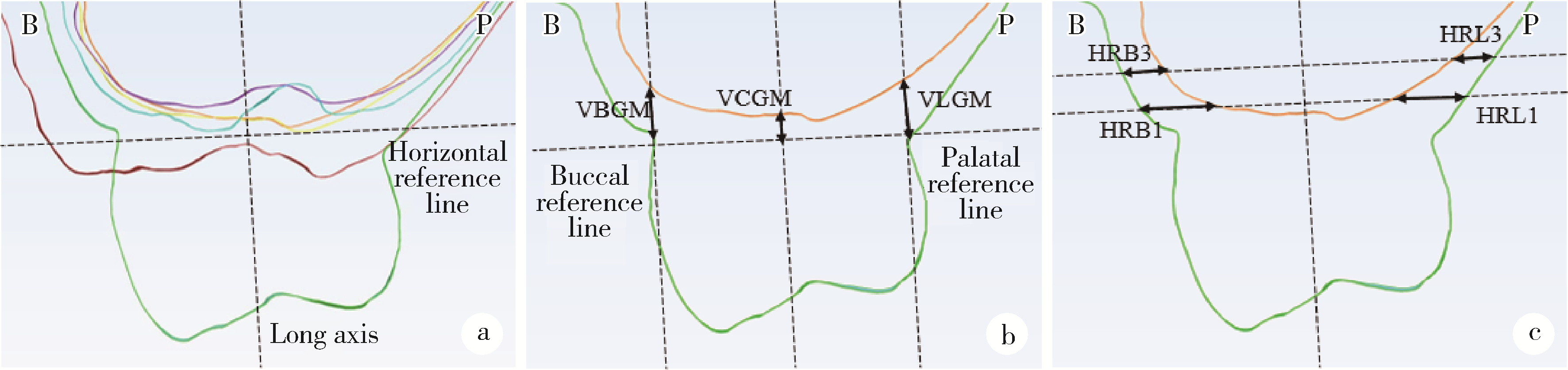
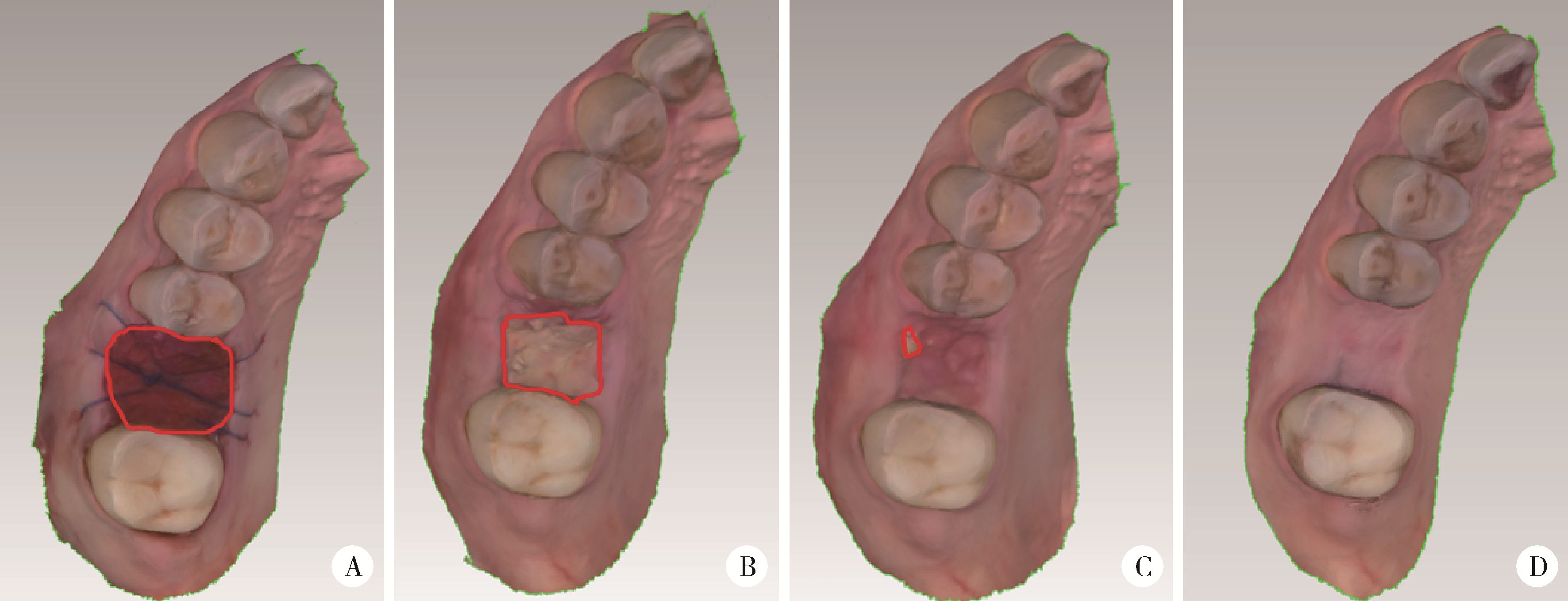
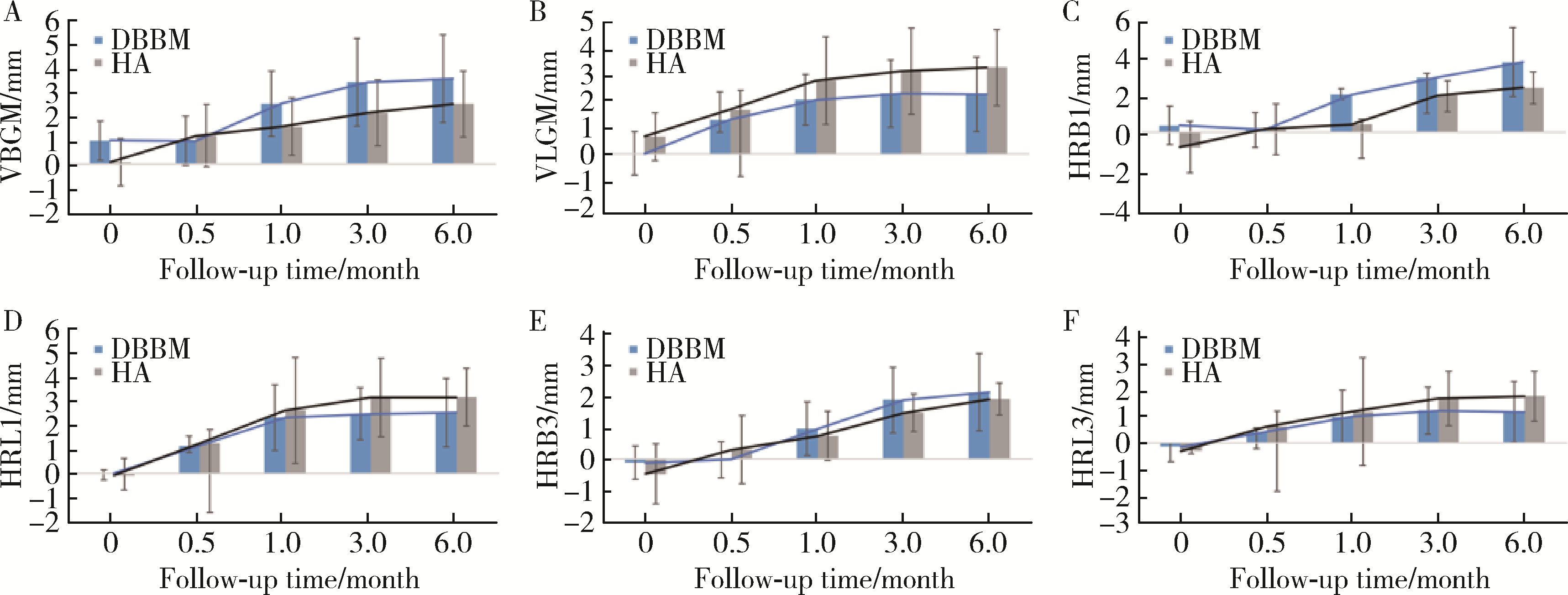
目的: 重度牙周病变的患者在磨牙拔牙同期实施微翻瓣牙槽嵴保存术(micro crestal flap-alveolar ridge preservation, MCF-ARP)时, 对采用以脱蛋白牛骨矿物基质(deproteinized bovine bone mineral, DBBM)为主要成分的异种骨移植材料和采用以羟基磷灰石(hydroxyapatite, HA)为主要成分的人工合成骨移植材料的临床效果进行比较, 为骨移植材料的临床应用推广提供参考。方法: 本研究为回顾性病例系列研究, 纳入2024年10月至2025年4月期间就诊的患者, 所有患者均在拔牙同期接受MCF-ARP手术, 分别植入DBBM或HA。使用锥形束计算机断层扫描(cone beam computed tomography, CBCT)结合口内扫描模型, 对比评估两组术前及术后6个月的硬组织变化及牙槽嵴轮廓塌陷量, 并分析术后软组织愈合过程。结果: 共纳入14例患者的14颗重度牙周病变磨牙, 术后6个月时, 两组患者在硬组织指标上的差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);术后2周和1个月时, HA组的拔牙窝中央轮廓垂直向塌陷量显著高于DBBM组[术后2周: (2.73±1.89) mm vs. (0.00±0.79) mm, P < 0.05;术后1个月: (2.74±1.13) mm vs. (0.35±2.34) mm, P < 0.05];后续愈合时间点的牙槽嵴轮廓塌陷量两组间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。创面愈合方面, HA组在术后2周和1个月时的创面未覆盖角化黏膜的面积比例显著高于DBBM组(术后2周: 47.88%±6.56% vs. 29.43%±14.25%, P < 0.05;术后1个月: 25.68%±13.06% vs. 7.19%±7.18%, P < 0.01)。结论: 本研究有限的样本分析显示, 重度牙周病变的患者在磨牙拔牙同期行MCF-ARP时, 使用DBBM和HA在术后6个月时的硬组织指标与牙槽嵴轮廓指标差异无统计学意义, 使用DBBM时早期软组织愈合更快, 未来需开展随机对照试验并结合组织学评估以进一步验证。
中图分类号:
- R782.1
| 1 |
doi: 10.1111/clr.13975 |
| 2 |
doi: 10.1111/cid.12585 |
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
doi: 10.11607/jomi.6399 |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01891.x |
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13231 |
| 8 |
doi: 10.1111/clr.13436 |
| 9 |
doi: 10.1007/s00784-021-04204-z |
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
doi: 10.1111/clr.12911 |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1002/JPER.19-0211 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.1111/prd.12469 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1111/jcpe.14045 |
| 15 |
赵丽萍, 詹雅琳, 胡文杰, 等. 不同测量方法评价磨牙拔牙位点保存术后牙槽骨的变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48 (1): 126- 132.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2016.01.023 |
| 16 |
赵丽萍, 胡文杰, 徐涛, 等. 罹患重度牙周病变磨牙拔牙后两种牙槽嵴保存方法的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51 (3): 579- 585.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.03.030 |
| 17 |
doi: 10.1111/clr.14204 |
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
doi: 10.1111/clr.12170 |
| 21 |
doi: 10.1111/clr.12712 |
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
doi: 10.1186/s40729-021-00305-2 |
| 24 |
doi: 10.11607/prd.4444 |
| 25 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2022.104323 |
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
朱磊, 刘庆成, 于洪波. 牙槽骨增量骨皮质切开术后2种植骨材料成骨的影像学分析[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2021, 19 (6): 525- 530.
|
| 28 |
doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04803-8 |
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2021.05.003 |
| 31 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2010.01918.x |
| 32 |
doi: 10.1007/s00784-025-06272-x |
| 33 |
doi: 10.11607/prd.0734 |
| 34 |
doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12027 |
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
doi: 10.1111/clr.13594 |
| 37 |
doi: 10.1186/s40902-021-00328-0 |
| [1] | 潘莲菲, 李文静, 王瑞洋, 焦剑, 曹战强, 高丽, 释栋. 口服抗生素辅助牙周机械治疗对重度牙周炎的短期疗效及影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2026, 58(1): 30-36. |
| [2] | 马保金, 李建华, 桑元华, 于洋, 仇吉川, 邵金龙, 李凯, 刘世岳, 杜密, 商玲玲, 葛少华. 基于微环境和干细胞调控的牙周组织再生关键技术的建立与应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(5): 841-846. |
| [3] | 曹沛, 栾庆先. 牙周炎与全身系统性疾病的思考与探索[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(5): 852-858. |
| [4] | 包振英, 王雅杰. 炎症指标和细胞因子联合检测在慢性牙周炎中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 772-778. |
| [5] | 石宇彤, 危伊萍, 胡文杰, 徐涛, 张浩筠. 罹患重度牙周炎下颌磨牙拔牙微翻瓣牙槽嵴保存效果评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(1): 33-41. |
| [6] | 李敬谦, 朱子璐, 焦剑, 施捷. 隐形矫治重度牙周炎患者前牙区病理性移位患牙的临床疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(1): 51-56. |
| [7] | 胡玉如,刘娟,李文静,赵亦兵,李启强,路瑞芳,孟焕新. Ⅲ期或Ⅳ期牙周炎患者龈沟液中有机酸浓度与牙周炎的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 332-337. |
| [8] | 张晗,秦亦瑄,韦帝远,韩劼. 牙周炎患者种植修复维护治疗依从性的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 39-44. |
| [9] | 殳畅,韩烨,孙雨哲,杨再目,侯建霞. Ⅲ期牙周炎患者牙周基础治疗前后炎症性贫血相关指标的变化[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 45-50. |
| [10] | 裴喜燕,阳雯,欧阳翔英,孙凤. 牙周内窥镜下根面清创与牙周翻瓣术疗效比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 716-720. |
| [11] | 温静,欧阳翔英,裴喜燕,邱善湧,刘健如,刘文逸,曹采方. 重度牙周炎患者4年自然进展失牙的多因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 70-77. |
| [12] | 朱小玲,李文静,王宪娥,宋文莉,徐莉,张立,冯向辉,路瑞芳,释栋,孟焕新. 细胞色素B-245α链及胆固醇酯转运蛋白基因多态性与广泛型侵袭性牙周炎易感性的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 18-22. |
| [13] | 徐欣然,霍芃呈,和璐,孟焕新,朱筠轩,靳东思奇. 伴与不伴糖尿病的牙周炎患者牙周基础治疗的疗效比较及其与白细胞水平的相关分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 48-53. |
| [14] | 郜洪宇,孟焕新,侯建霞,黄宝鑫,李玮. 钙结合蛋白在健康牙周组织和实验性牙周炎组织的表达分布[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 744-749. |
| [15] | 刘建,王宪娥,吕达,乔敏,张立,孟焕新,徐莉,毛铭馨. 广泛型侵袭性牙周炎患者牙根形态异常与相关致病基因的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 16-23. |
|
||