北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 184-189. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2026.01.024
原发灶局限于胆囊壁内胆囊癌大体分型及其与预后和癌前病变的相关性
张铃福1,*, 陈明2,*, 赵小宇1, 王港1, 崔龙1, 凌晓锋1, 王立新1, 徐智1, 郭丽梅3,*( ), 侯纯升1,*(
), 侯纯升1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第三医院普通外科, 北京 100191
2. 北京大学第三医院放射科, 北京 100191
3. 北京大学第三医院病理科, 北京 100191
Gross classification of gallbladder cancer with primary lesion limited to the gallbladder wall and its correlation with prognosis and precancerous lesions
Lingfu ZHANG1, Ming CHEN2, Xiaoyu ZHAO1, Gang WANG1, Long CUI1, Xiaofeng LING1, Lixin WANG1, Zhi XU1, Limei GUO3,*( ), Chunsheng HOU1,*(
), Chunsheng HOU1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of General Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
3. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
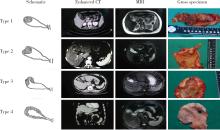
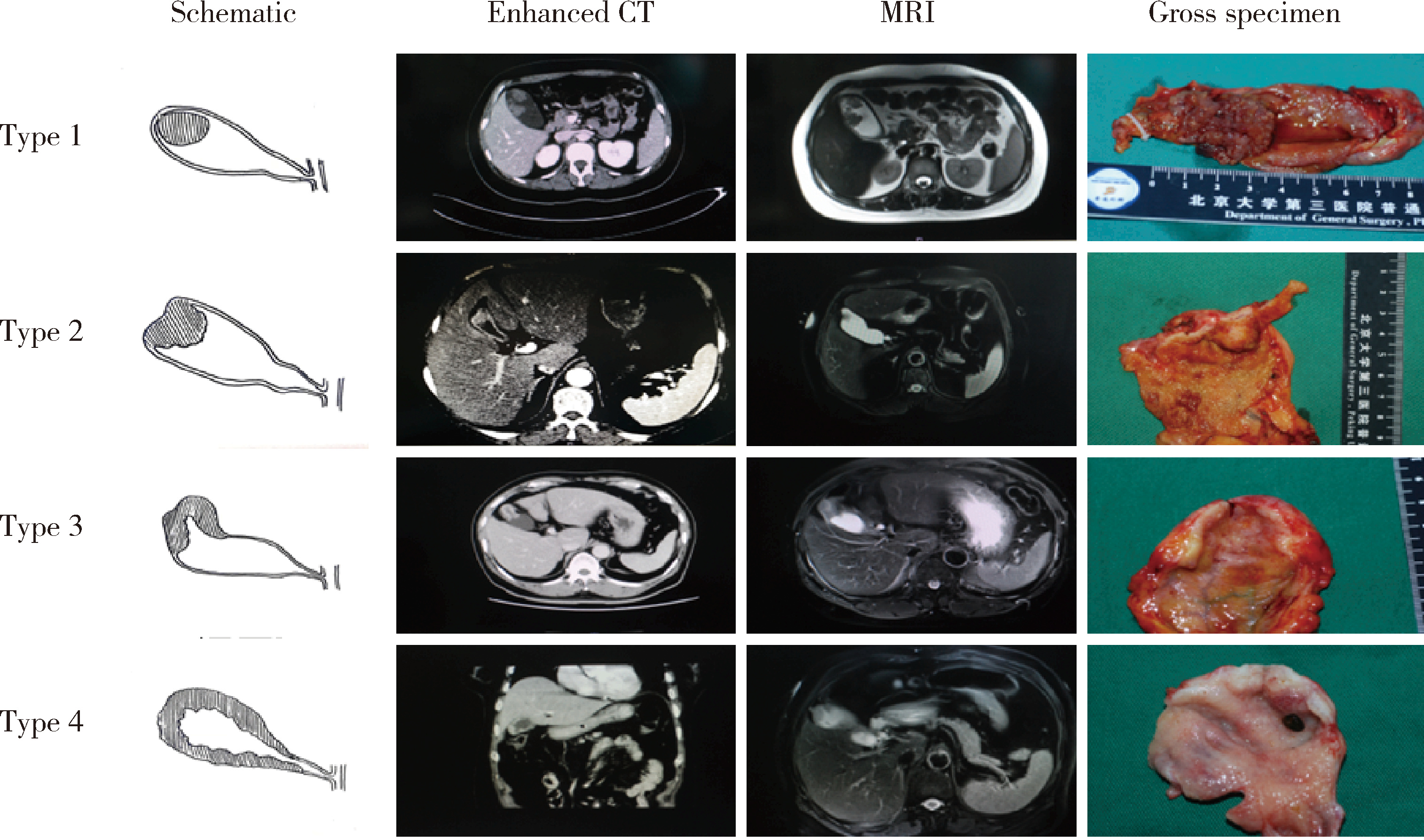
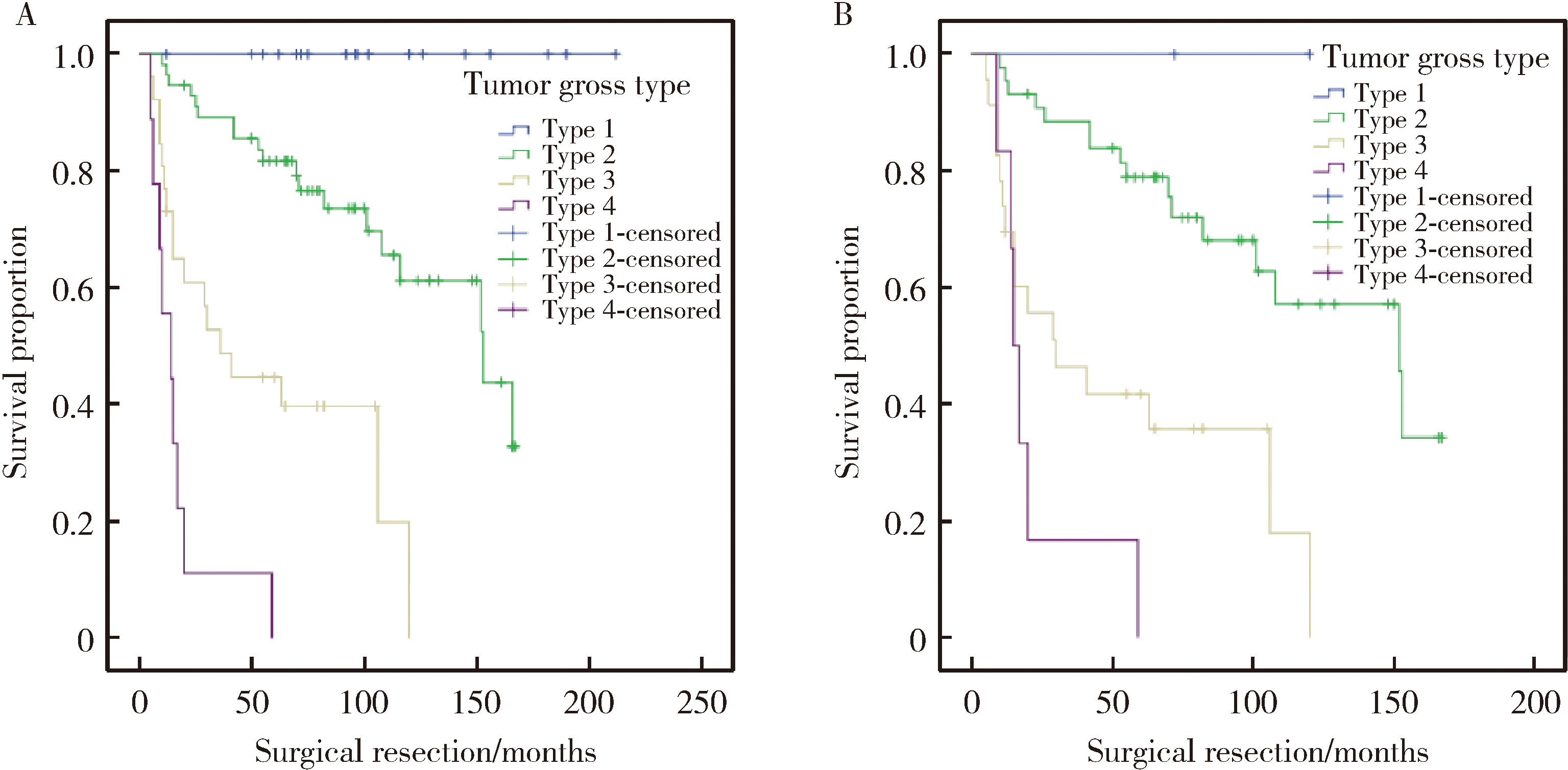
目的: 探讨原发灶局限于胆囊壁内胆囊癌的大体分型及其与预后和癌前病变相关性。方法: 回顾性纳入2006年1月至2020年12月北京大学第三医院收治的123例术前影像提示原发灶局限于胆囊壁内、且术后病理为腺癌患者。依据CT、MRI或大体标本分为如下4型:1型,局限性凸向腔内肿物,不伴肿物附着处胆囊壁增厚;2型,局限性凸向腔内肿物,伴肿物附着处胆囊壁增厚和/或增厚处浆膜皱褶;3型,局限于两个连续部分的胆囊壁环形增厚;4型,延续至两个以上连续部分的胆囊壁环形增厚。比较各分型之间的临床病理特征、癌前病变类型及生存情况。结果: 术前CT/MRI及术中大体标本均可以作为大体分型的依据,大体标本准确率最高。123例患者中13例无法分型,剩余110例完成大体分型。胆囊癌大体分型与T分期(P<0.001,rs=0.682)呈高强度相关,与淋巴结转移(P<0.001,rs=0.478)、组织分化程度(P<0.001,rs=0.484)、神经浸润(P<0.001,rs=0.490)以及脉管瘤栓(P<0.001,rs=0.334)等组织病理学参数呈中等强度相关,分型越高,不良组织病理学参数越多。另外,胆囊癌大体分型与患者手术治疗后残余病灶(P<0.001,rs=0.328)和术后复发(P<0.001,rs=0.619)呈中等强度和高等强度相关性。生存分析显示,分型越高,患者中位生存时间越短,1型96个月,2型73个月,3型30个月,4型14个月,P<0.001。多因素Cox回归表明胆囊癌大体分型是患者预后的独立影响因素(HR=3.609,95%CI:2.177~5.983,P<0.001)。在肿瘤生物学行为异质性最强的T2期患者中,胆囊癌大体分型同样与预后密切相关,中位生存时间分别为72个月、70个月、29个月和16个月, P<0.001。多因素Cox回归亦表明胆囊癌大体分型是患者预后的独立影响因素(HR=2.723,95%CI:1.566~4.736,P<0.001)。在肿瘤起源方面,胆囊癌大体分型与癌前病变类型显著相关:1型主要源自胆囊内乳头状肿瘤,3型与4型则多为高级别胆管上皮内瘤变或无癌前病变。肿瘤自然病程分析提示:1型进展缓慢,4型进展迅速,2型表现出较大异质性。结论: 原发灶局限于胆囊壁内胆囊癌大体分型与预后及癌前病变密切相关,可作为手术决策与分层管理的重要参考依据。
中图分类号:
- R735.8
| 1 |
doi: 10.1038/s41572-022-00398-y |
| 2 |
张铃福, 侯纯升, 徐智, 等. 腹腔镜胆囊切除术中或术后意外胆囊癌腹腔镜手术治疗: 单中心10年回顾性分析[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2019, 57 (4): 277- 281.
|
| 3 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2020.07.006 |
| 4 |
doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2021.05.001 |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2022.151911 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.2001.01749.x |
| 7 |
张铃福, 侯纯升, 郭丽梅, 等. 术中冰冻或术后石蜡病理报告T1b期胆囊癌的外科治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49 (6): 1034- 1037.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2017.06.017 |
| 8 |
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3567 |
| 9 |
doi: 10.3892/or.2012.1971 |
| 10 |
doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2021.101693 |
| [1] | 高雅静, 李正芳, 马梦思, 武丽君. SII和SIRI对白塞病葡萄膜炎的风险预测及疾病活动度和预后的评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(6): 1067-1073. |
| [2] | 郭博达, 陆敏, 王国良, 张洪宪, 刘磊, 侯小飞, 赵磊, 田晓军, 张树栋. 肾透明细胞癌与非透明细胞癌伴静脉癌栓患者的临床病理特征及预后比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 644-649. |
| [3] | 李伟浩, 李晶, 张学民, 李伟, 李清乐, 张小明. 术中回收式自体输血对颈动脉体瘤切除术后肿瘤预后的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(2): 272-276. |
| [4] | 毛雅晴, 陈震, 于尧, 章文博, 刘洋, 彭歆. 2型糖尿病对口腔鳞状细胞癌患者预后的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1089-1096. |
| [5] | 欧俊永,倪坤明,马潞林,王国良,颜野,杨斌,李庚午,宋昊东,陆敏,叶剑飞,张树栋. 肌层浸润性膀胱癌合并中高危前列腺癌患者的预后因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [6] | 刘帅,刘磊,刘茁,张帆,马潞林,田晓军,侯小飞,王国良,赵磊,张树栋. 伴静脉癌栓的肾上腺皮质癌的临床治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [7] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [8] | 周泽臻,邓绍晖,颜野,张帆,郝一昌,葛力源,张洪宪,王国良,张树栋. 非转移性T3a肾细胞癌患者3年肿瘤特异性生存期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [9] | 方杨毅,李强,黄志高,陆敏,洪锴,张树栋. 睾丸鞘膜高分化乳头状间皮肿瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [10] | 曾媛媛,谢云,陈道南,王瑞兰. 脓毒症患者发生正常甲状腺性病态综合征的相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [11] | 苏俊琪,王晓颖,孙志强. 舌鳞状细胞癌根治性切除术后患者预后预测列线图的构建与验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 120-130. |
| [12] | 李建斌,吕梦娜,池强,彭一琳,刘鹏程,吴锐. 干燥综合征患者发生重症新型冠状病毒肺炎的早期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [13] | 刘欢锐,彭祥,李森林,苟欣. 基于HER-2相关基因构建风险模型用于膀胱癌生存预后评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [14] | 薛子璇,唐世英,邱敏,刘承,田晓军,陆敏,董靖晗,马潞林,张树栋. 青年肾肿瘤伴瘤栓的临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [15] | 卢汉,张建运,杨榕,徐乐,李庆祥,郭玉兴,郭传瑸. 下颌牙龈鳞状细胞癌患者预后的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
|
||