北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 171-176. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.01.029
上消化道固有肌层肿瘤经内镜黏膜下隧道肿瘤切除术和黏膜下肿瘤挖除术的治疗对比
- 北京大学第三医院消化科, 北京 100191
Comparative treatment analysis of upper gastroenterology submucosal tumors originating from muscularis propria layer: submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection versus endoscopic submucosal excavation
Xue-li TIAN,Yong-hui HUANG( ),Wei YAO,Yuan LI,Jing-jing LU
),Wei YAO,Yuan LI,Jing-jing LU
- Department of Gastroenterology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
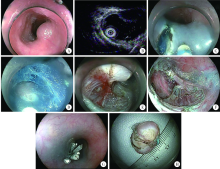
目的:评价内镜经黏膜下隧道肿瘤切除术(submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection,STER)和黏膜下肿瘤挖除术(endoscopic submucosal excavation,ESE)治疗上消化道固有肌层肿瘤的疗效和安全性。方法:选择2013 年4 月至2016 年12 月在北京大学第三医院诊断为上消化道固有肌层肿瘤并行STER治疗(n=28)和ESE治疗(n=14)的患者病例资料进行回顾分析,分析比较两组的临床病理和内镜结果、治疗和并发症发生情况。结果:42 例病变均顺利完成切除,成功率100%。两组间(STER组 vs. ESE组)从性别、年龄、病变大小[1.5(1.0~6.0) cm vs. 1.3(0.5~2.0) cm,P=0.056]差异均无统计学意义,STER组的病变切除时间长于ESE组[46.5(11.0~163.0) min vs. 19.5(6.0~56.0) min, P=0.007],创面钛夹缝合时间短于ESE组[3.5(1.0~11.0) min vs. 8.0(2.0~33.0) min, P=0.006],两组差异均有统计学意义,但总的手术时间的差异无统计学意义[52.0(14.0~167.0) min vs. 31.5(10.0~88.0) min,P=0.080]。术后一次性整块切除率(92.9% vs. 85.7%)、治疗后住院时间、术后并发症(10.7% vs. 0)两组间差异无统计学意义。STER组术后发生肺炎2 例,纵隔气肿1 例,保守对症支持治疗后痊愈;ESE组术后无并发症发生。术后经常规病理及免疫组化染色确诊平滑肌瘤28 例,间质瘤14 例。STER组6 例间质瘤均为极低危险度;ESE组4 例间质瘤为极低危险度,4例间质瘤为中等危险度[病变大小约1.0~2.0 cm,核分裂像(6~8)个/50 高倍视野]。所有患者中位随访时间46.5 个月(24~60个月),中等危险度间质瘤的患者最短随访时间为32个月,均未见肿瘤残留、复发及隧道内种植。结论:STER和ESE均可成为治疗来源于上消化道固有肌层的黏膜下肿瘤的有效、安全的方案选择之一,与STER相比,ESE切除病变时间短,但创面缝合时间长,总的手术时间相当。
中图分类号:
- R735
| [1] |
周平红, 姚礼庆, 徐美东 , 等. 消化道黏膜下肿瘤的内镜黏膜下挖除术治疗[J]. 中国医疗器械信息, 2008,14(10):3-5.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6586.2008.10.002 |
| [2] |
Xu MD, Cai MY, Zhou PH ,et a1. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection: a new technique for treating upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2012,75(1):195-199.
doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.08.018 pmid: 22056087 |
| [3] |
Lu J, Jiao T, Zheng M , et al. Endoscopic resection of submucosal tumors in muscularis propria: the choice between direct excavation and tunneling resection[J]. Surg Endosc, 2014,28(12):3401-3407.
doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-3610-y pmid: 24986008 |
| [4] |
李江虹, 刘枫施, 施新岗 , 等. 内镜黏膜下肿物挖除术及内镜经黏膜下隧道肿瘤切除术治疗胃食管连接处固有肌层肿瘤的对比分析[J]. 中华消化内镜杂志, 2017,34(3):173-176.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-5232.2017.03.006 |
| [5] |
Du C, Chai N, Linghu E , et al. Treatment of cardial submucosal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer: submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection versus endoscopic submucosal excavation[J]. Surg Endosc, 2018,32(11):4543-4551.
doi: 10.1007/s00464-018-6206-0 pmid: 29766300 |
| [6] |
Koo DH, Ryu MH, Kim KM . Asian consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastrointestinal stromal tumor[J]. Cancer Res Treat, 2016,48(4):1155-1166.
doi: 10.4143/crt.2016.187 pmid: 27384163 |
| [7] | Koga T, Hirayama Y, Yoshiya S , et al. Necessity for resection of gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors </= 20mm[J]. Anticancer Res, 2015,35(4):2341-2344. |
| [8] |
Abe N, Takeuchi H, Ohki A , et al. Comparison between endoscopic and laparoscopic removal of gastric submucosal tumor[J]. Dig Endosc, 2018,30(Suppl 1):7-16.
doi: 10.1111/den.2018.30.issue-S1 |
| [9] |
Goto O, Takeuchi H, Kitagawa Y , et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and related rechniques as precursors of “new notes” resection methods for gastric neoplasms[J]. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am, 2016,26(2):313-322.
doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2015.12.006 pmid: 27036900 |
| [10] |
Chen T, Lin ZW, Zhang YQ , et al. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection vs. thoracoscopic enucleation for large submucosal tumors in the esophagus and the esophagogastric junction[J]. J Am Coll Surg, 2017,225(6):806-816.
doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2017.09.002 pmid: 28923691 |
| [11] |
Zhang Y, Ye LP, Mao XL . Endoscopic treatments for small gastric subepithelial tumors originating from muscularis propria layer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015,21(32):9503-9511.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9503 pmid: 26327758 |
| [12] |
Wong VWY, Goto O, Gregersen H , et al. Endoscopic treatment of subepithelial lesions of the gastrointestinal tract[J]. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol, 2017,15(4):603-617.
doi: 10.1007/s11938-017-0152-0 pmid: 29030800 |
| [13] |
Al-Bawardy B, Rajan E, Wong Kee Song LM . Over-the-scope clip-assisted endoscopic full-thickness resection of epithelial and subepithelial GI lesions[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2017,85(5):1087-1092.
doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2016.08.019 pmid: 27569858 |
| [14] |
Fernández JÁ, Gómez-Ruiz ÁJ, Olivares V , et al. Clinical and pathological features of “small” GIST (≤2 cm). What is their prognostic value[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2018,44(5):580-586.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2018.01.087 pmid: 29478742 |
| [1] | 侯卫华,宋书杰,石中月,金木兰. 幽门螺杆菌阴性早期胃癌的临床病理特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 292-298. |
| [2] | 刘菊梅,梁丽,张继新,戎龙,张梓怡,吴悠,赵旭东,李挺. 411例早期胃癌及癌前病变内镜黏膜下剥离术标本的病理学评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 299-307. |
| [3] | 郑炜,黄永辉,常虹,姚炜,李柯,闫秀娥,张耀朋,王迎春,刘文正. 内镜下逆行胰胆管造影在胆肠吻合术后患者中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1178-1184. |
| [4] | 史成梅,王雪冬,刘又鲲,邓莹,郭向阳. 地塞米松联合盐酸奥布卡因凝胶用于预防鼻内镜术后咽喉痛[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 289-293. |
| [5] | 牛占岳,薛艳,张静,张贺军,丁士刚. 胃腺瘤性息肉的内镜和病理特点及癌变的危险因素分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1122-1127. |
| [6] | 越雷,王月田,白纯碧,陈浩,付豪永,于峥嵘,李淳德,孙浩林. 内镜治疗中青年双节段腰椎间盘突出症患者的手术策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 734-739. |
| [7] | 王迎春,黄永辉,常虹,姚炜,闫秀娥,李柯,张耀鹏,郑炜. 十二指肠乳头息肉良、恶性病变比较及活检准确性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 204-209. |
| [8] | 武颖超,蔡云龙,戎龙,张继新,刘金,汪欣. 早期胃癌淋巴结转移规律及内镜黏膜下剥离术治疗早期胃癌的疗效评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(6): 1093-1097. |
| [9] | 康宁,蒋一航,蒋宇光,吴栗洋,张际青,牛亦农,张军晖. 内镜联合超声与单纯超声引导建立皮肾通道在多镜联合术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 692-696. |
| [10] | 张军晖,蒋一航,蒋宇光,张际青,康宁. 双侧同步内镜手术治疗双侧上尿路结石的临床效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 672-677. |
| [11] | 李潇,苏家增,张严妍,张丽琪,张亚琼,柳登高,俞光岩. 131I相关唾液腺炎的炎症分级及内镜治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 586-590. |
| [12] | 刘鑫,张静,王晔,张贺军,丁士刚,周丽雅. 早期胃癌白光内镜下特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 302-306. |
| [13] | 修倩,陈曦, 刘潼,陈明星,姚平,辛伟红. 气管切开后再次出现呼吸困难2例及Mimics 10.01软件的临床应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 924-927. |
| [14] | 李士杰,王警,李子禹,步召德,苏向前,李忠武,吴齐. 内镜黏膜下剥离术在早期胃癌治疗中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(6): 945-951. |
| [15] | 尹焯, 杨金瑞, 王钊, 魏永宝, 严彬, 周克勤. 阴囊镜在睾丸附睾疾病诊断与治疗中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 648-652. |
|
||