北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1067-1070. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.016
2017版美国放射学会甲状腺影像学报告与数据系统应用价值探索
- 北京大学第三医院超声诊断科,北京 100191
Applicational value of 2017 ACR TI-RADS stratification in diagnosing thyroid nodules
Peng FU,Wen CHEN( ),Li-gang CUI,Hui-yu GE,Shu-min WANG
),Li-gang CUI,Hui-yu GE,Shu-min WANG
- Department of Ultrasound, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
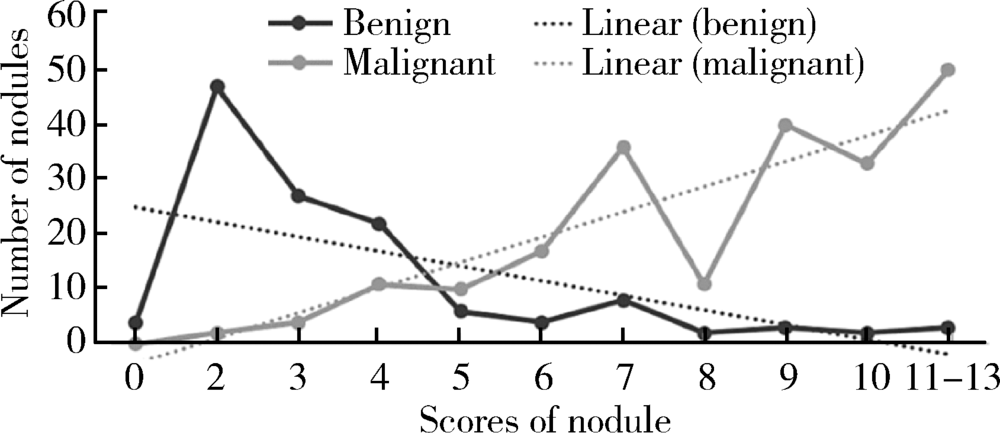
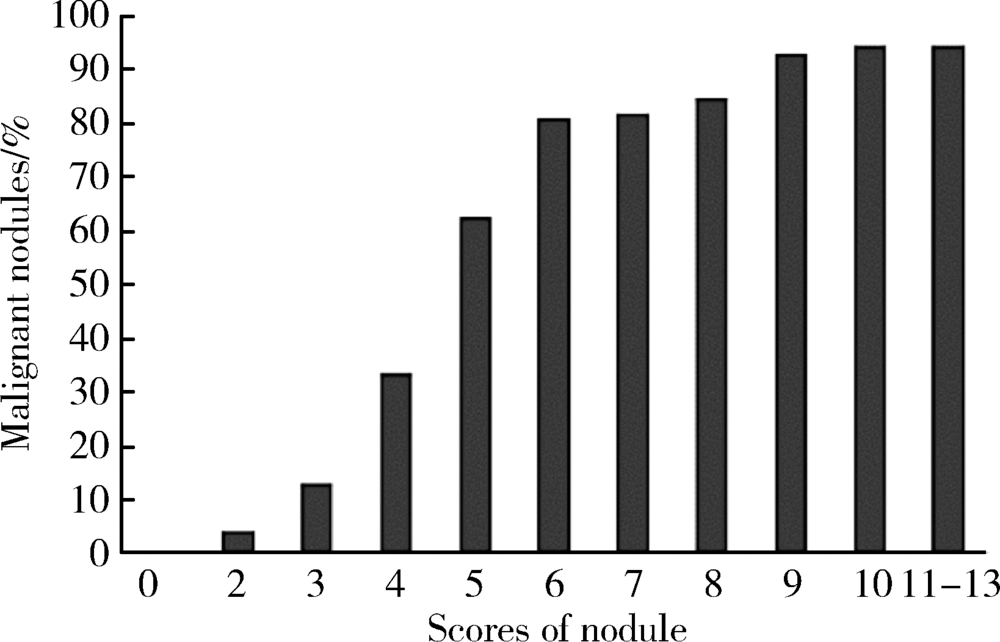
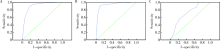
目的 评估应用2017年美国放射学会(American College of Radiology,ACR)发布的甲状腺影像学报告与数据系统(thyroid imaging reporting and data system,TI-RADS) 对甲状腺进行危险分层的价值,并依据结果提出优化分类的建议。方法 回顾性分析北京大学第三医院应用2017版ACR TI-RADS评估的342例影像资料完整的甲状腺结节,将评分结果与病理结果进行对比,获得不同分值区间恶性结节的比例,并分别对最大径>1 cm及最大径≤1 cm的结节使用ROC曲线评价诊断效能。结果 利用该评分系统对结节进行危险分层,全部结节、最大径>1 cm的结节、最大径≤1 cm的结节ROC曲线下面积分别为0.907、0.936、0.717。随着评分值的增加,良性结节比例逐渐下降,恶性结节所占比例逐渐增长,评分值4~6分区间恶性结节比例增长明显,以评分值为3的恶性结节比例为基准,4、5、6分结节恶性结节分别增长1.6倍、3.8倍、5.3倍,6~8分区间恶性结节稳定在81%~84%,而9分及以上恶性结节比例稳定在93%~94%,依据恶性结节的比例分布特点调整分类,TI-RADS 1类、TI-RADS 2类、TI-RADS 3类仍然分别对应0分、2分、3分,TI-RADS 4类细分为TI-RADS 4a类、TI-RADS 4b类、TI-RADS 4c类,分别对应4分、5分、6~8分,而≥9分的结节划分为TI-RADS 5类。结论 2017版ACR TI-RADS对最大径>1 cm的甲状腺结节具有较高的诊断价值,而对最大径≤1 cm的结节诊断价值欠佳。根据不同评分值区间恶性结节比例的分布特点,适当调整分类将能更详细、准确地预测结节的恶性风险。
中图分类号:
- R736.1
| [1] | Tessler FN, Middleton WD, Grant EG , et al. ACR thyroid imaging, reporting and data system (TI-RADS): White paper of the ACR TI-RADS Committee[J]. J Am Coll Radiol, 2017,14(5):587-595. |
| [2] | Grant EG, Tessler FN, Hoang JK , et al. Thyroid ultrasound reporting lexicon: white paper of the ACR Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System (TIRADS) Committee[J]. J Am Coll Ra-diol, 2015,12(12):1272-1279. |
| [3] | Gharib H, Papini E, Garber JR , et al. AACE/AME Guidelines American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and Associazione Medici Endocrinologi medical guidelines for clinical practice for the diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules: 2016 update[J]. Endocr Pract, 2016,22(5):622-639. |
| [4] | Middleton WD, Teefey SA, Reading CC , et al. Multiinstitutional analysis of thyroid nodule risk stratification using the American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2017,208(6):1331-1341. |
| [5] | Kumbhar SS, O’Malley RB, Robinson TJ, et al. Why thyroid surgeons are frustrated with radiologists: Lessons learned from pre-and postoperative US[J]. Radiographics, 2016,36(7):150-250. |
| [6] | Gunderman RB, Mcneive LR . Is structured reporting the answer?[J]. Radiology, 2014,273(1):7-9. |
| [7] | Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC , et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American Thyroid Association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Thyroid, 2016,26(1):1-133. |
| [8] | Haddad RI, Lydiatt WM, Ball DW , et al. Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma, Version 2.2015[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2015,13(9):1140-1150. |
| [9] | Wémeau JL, Sadoul JL, d’Herbomez M, et al. Guidelines of the French Society of Endocrinology for the management of thyroid nodules[J]. Ann Endocrinol (Paris), 2011,72(4):251-281. |
| [10] | Shin JH, Baek JH, Chung J , et al. Ultrasonography diagnosis and imaging-based management of thyroid nodules: Revised Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology consensus statement and recommendations[J]. Korean J Radiol, 2016,17(3):370-395. |
| [11] | 刘红, 胡正明, 罗海愉 , 等. ACR TI-RADS分类在诊断甲状腺结节中的应用价值探究[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2018,34(8):673-675. |
| [12] | 钟敏莹, 石小红, 杨丽丽 , 等. TI-RADS分类系统对不同直径甲状腺结节的诊断价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2016,32(4):289-291. |
| [1] | 原晋芳, 王新利, 崔蕴璞, 王雪梅. 尿促黄体生成素在女童中枢性性早熟预测中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 788-793. |
| [2] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [3] | 钟华, 李原, 徐丽玲, 白明欣, 苏茵. 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [4] | 李正芳,罗采南,武丽君,吴雪,孟新艳,陈晓梅,石亚妹,钟岩. 抗氨基甲酰化蛋白抗体在诊断类风湿关节炎中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [5] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [6] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [7] | 时云飞,王豪杰,刘卫平,米岚,龙孟平,刘雁飞,赖玉梅,周立新,刁新婷,李向红. 血管免疫母细胞性T细胞淋巴瘤临床与分子病理学特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
| [8] | 李挺. 建设当代临床病理学科[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 197-200. |
| [9] | 周桥. 肿瘤病理学研究的进展和展望[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 201-209. |
| [10] | 熊焰,李鑫,梁丽,李东,鄢丽敏,李雪迎,邸吉廷,李挺. 甲状腺粗针穿刺活检病理诊断的准确性评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 234-242. |
| [11] | 沈棋,刘亿骁,何群. 肾黏液样小管状和梭形细胞癌的临床病理特点及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 276-282. |
| [12] | 侯卫华,宋书杰,石中月,金木兰. 幽门螺杆菌阴性早期胃癌的临床病理特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 292-298. |
| [13] | 刘菊梅,梁丽,张继新,戎龙,张梓怡,吴悠,赵旭东,李挺. 411例早期胃癌及癌前病变内镜黏膜下剥离术标本的病理学评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 299-307. |
| [14] | 农琳,王微,梁丽,李东,李鑫,李挺. 母细胞性浆样树突细胞肿瘤13例临床病理学特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 308-314. |
| [15] | 熊焰,张波,聂立功,吴世凯,赵虎,李东,邸吉廷. 胸部SMARCA4缺失性未分化肿瘤的病理诊断与联合免疫检测点抑制剂治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 351-356. |
|
||