北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 204-209. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.01.031
十二指肠乳头息肉良、恶性病变比较及活检准确性
- 北京大学第三医院消化科,北京 100191
Characteristics of benign and malignant lesions of ampullary polyps and the accuracy of forceps biopsy
WANG Ying-chun,HUANG Yong-hui( ),CHANG Hong,YAO Wei,YAN Xiu-e,LI Ke,ZHANG Yao-peng,ZHENG Wei
),CHANG Hong,YAO Wei,YAN Xiu-e,LI Ke,ZHANG Yao-peng,ZHENG Wei
- Department of Gastroenterology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
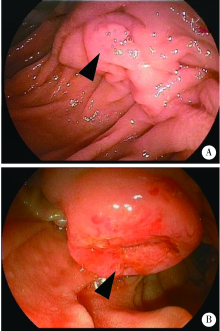
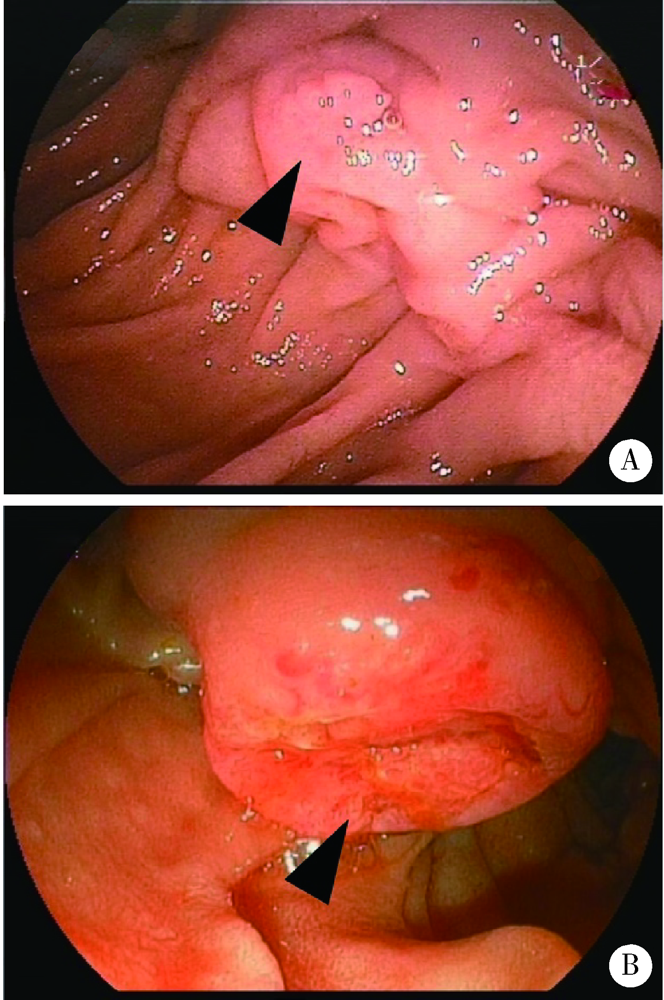
目的: 比较十二指肠乳头息肉良、恶性病变的内镜下及临床特点,探究内镜下预判十二指肠乳头腺瘤癌变的可行性,并评估内镜下乳头活检组织病理学诊断的准确性。方法: 选择2009年1月至2019年5月在北京大学第三医院内镜中心接受内镜下十二指肠乳头切除术(endoscopic papillectomy,EP)患者的临床资料及内镜图片,分为良性病变及癌两组,进行对比分析。结果: 研究共纳入42例患者,年龄35~83岁,50岁以上患者占83.3%(35/42)。42例患者中,炎性息肉2例(4.8%),神经内分泌瘤1例(2.4%),增生性息肉1例(2.4%),Ⅰ级腺瘤5例(11.9%),Ⅱ级腺瘤10例(23.8%),Ⅲ级腺瘤4例(9.5%),癌19例(45.2%),腺瘤和癌共占90.5%。良性病变(炎性息肉及腺瘤)组平均年龄(56.7±9.2) 岁,癌组(66.0±9.8) 岁,两组间差异有统计学意义(P=0.004)。癌[(2.3±0.8) cm]的直径显著大于良性病变[(1.6±0.6) cm, P=0.002]。良性病变均为山田(Yamada)Ⅰ型(57.1%)或Ⅱ型(42.9%)病变,而癌组山田Ⅰ型(36.8%)、Ⅱ型(31.6%)比例较低,31.5%为山田Ⅲ型病变。两组间山田分型差异有统计学意义,癌组带蒂倾向明显(P=0.046)。良性病变多与周围分界清楚(18/21,85.7%),而癌组分界多不明显,仅2例(10.5%)具有清晰的界限,两组间差异具有统计学意义(P<0.001)。息肉表面颜色(P=0.353)、表面形态(P=0.324)两组间差异无统计学意义。将差异有统计学意义的年龄、病变大小、山田分型、与周围界限是否清晰纳入Logistic回归分析,结果显示年龄(OR=1.186,95%CI: 1.025~1.373,P=0.022)、与周围是否有清晰界限(OR=66.218,95%CI: 3.421~1 281.840,P=0.006)为乳头癌变风险的独立预判因素。19例癌患者中,术前仅2例(10.5%)活检诊断提示癌。17例癌(17/19,89.5%)、4例Ⅱ级腺瘤(4/10,40%)术前病理均低于实际病理分级,占病例总数的55.3%(21/38)。结论: 十二指肠乳头息肉以腺瘤及癌为主,高龄、与周围黏膜界限不清为十二指肠乳头肿瘤癌变的独立预判危险因素,单纯活检组织病理诊断对乳头肿瘤良、恶性的鉴别意义有限。
中图分类号:
- R574.51
| [1] |
Ridtitid W, Tan D, Schmidt SE, et al. Endoscopic papillectomy: risk factors for incomplete resection and recurrence during long-term follow-up[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2014,79(2):289-296.
pmid: 24094466 |
| [2] |
Ridtitid W, Schmidt SE, Al-Haddad MA, et al. Performance characteristics of EUS for locoregional evaluation of ampullary lesions[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2015,81(2):380-388.
doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.08.005 pmid: 25293823 |
| [3] |
Kang SH, Kim KH, Kim TN, et al. Therapeutic outcomes of endoscopic papillectomy for ampullary neoplasms: retrospective analysis of a multicenter study[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2017,17(1):69.
doi: 10.1186/s12876-017-0626-5 pmid: 28558658 |
| [4] |
El H, Coté GA. Endoscopic diagnosis and management of ampullary lesions[J]. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am, 2013,23(1):95-109.
doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2012.10.004 pmid: 23168121 |
| [5] | 顾宗廷, 张永杰. 十二指肠乳头肿瘤的诊断与外科治疗[J]. 国际消化病杂志, 2015,35(6):428-435. |
| [6] |
Chathadi KV, Khashab MA, Acosta RD, et al. The role of endoscopy in ampullary and duodenal adenomas[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2015,82(5):773-781.
doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2015.06.027 pmid: 26260385 |
| [7] | 陆鉴, 陆文洁, 吴育连. 十二指肠乳头肿瘤的临床特点及诊治分析[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2016,54(3):187-190. |
| [8] |
Attila T, Parlak E, Alper E, et al. Endoscopic papillectomy of benign ampullary lesions: Outcomes from a multicenter study[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2018,29(3):325-334.
doi: 10.5152/tjg.2018.17378 pmid: 29755017 |
| [9] |
Wanders LK, East JE, Uitentuis SE, et al. Diagnostic performance of narrowed spectrum endoscopy, autofluorescence imaging, and confocal laser endomicroscopy for optical diagnosis of colonic polyps: a meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2013,14(13):1337-1347.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70509-6 pmid: 24239209 |
| [10] |
Kim HN, Kim KM, Shin JU, et al. Prediction of carcinoma after resection in subjects with ampullary adenomas on endoscopic biopsy[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2013,47(4):346-351.
doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e318272f2ef pmid: 23442830 |
| [11] | 郝璐, 王伟, 施新岗, 等. 十二指肠乳头肿瘤内镜切除术的临床应用进展[J]. 中华消化内镜杂志, 2017,34(6):451-454. |
| [12] |
Wee E, Lakhtakia S, Gupta R, et al. The diagnostic accuracy and strength of agreement between endoscopic ultrasound and histopathology in the staging of ampullary tumors[J]. Indian J Gastroenterol, 2012,31(6):324-332.
doi: 10.1007/s12664-012-0248-3 pmid: 22996048 |
| [13] | 张荣春, 陈杰, 于卫华, 等. 十二指肠乳头肿瘤内镜切除术[J]. 中华消化内镜杂志, 2014,31(4):231-235. |
| [14] |
Bourgeois N, Dunham F, Verhest A, et al. Endoscopic biopsies of the papilla of Vater at the time of endoscopic sphincterotomy: difficulties in interpretation[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 1984,30(3):163-166.
doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(84)72357-1 pmid: 6735092 |
| [1] | 李志存, 吴天俣, 梁磊, 范宇, 孟一森, 张骞. 穿刺活检单针阳性前列腺癌术后病理升级的危险因素分析及列线图模型构建[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | 黄教悌,胡菁,韩博. 治疗相关神经内分泌前列腺癌机制研究与靶向治疗新进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 557-561. |
| [3] | 邢念增,王明帅,杨飞亚,尹路,韩苏军. 前列腺免活检创新理念的临床实践及其应用前景[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 565-566. |
| [4] | 颜野,李小龙,夏海缀,朱学华,张羽婷,张帆,刘可,刘承,马潞林. 前列腺癌根治术后远期膀胱过度活动症的危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 589-593. |
| [5] | 于书慧,韩佳凝,钟丽君,陈聪语,肖云翔,黄燕波,杨洋,车新艳. 术前盆底肌电生理参数对前列腺癌根治性切除术后早期尿失禁的预测价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 594-599. |
| [6] | 刘帅,刘磊,刘茁,张帆,马潞林,田晓军,侯小飞,王国良,赵磊,张树栋. 伴静脉癌栓的肾上腺皮质癌的临床治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [7] | 陈延,李况蒙,洪锴,张树栋,程建星,郑仲杰,唐文豪,赵连明,张海涛,姜辉,林浩成. 阴茎海绵体注射试验对阴茎血管功能影响的回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [8] | 庞博,郭桐君,陈曦,郭华棋,石嘉章,陈娟,王欣梅,李耀妍,单安琪,余恒意,黄婧,汤乃军,王艳,郭新彪,李国星,吴少伟. 天津与上海35岁以上人群氮氧化物个体暴露水平及其影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 700-707. |
| [9] | 和静,房中则,杨颖,刘静,马文瑶,霍勇,高炜,武阳丰,谢高强. 血浆中脂质代谢分子与颈动脉粥样硬化斑块、传统心血管危险因素及膳食因素的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 722-728. |
| [10] | 蔡珊,张依航,陈子玥,刘云飞,党佳佳,师嫡,李佳欣,黄天彧,马军,宋逸. 北京市中小学生身体活动时间现状及影响因素的路径[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 403-410. |
| [11] | 张祖洪,陈天娇,马军. 中小学生青春发动时相与心血管代谢危险因素的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 418-423. |
| [12] | 林郁婷,王华丽,田宇,巩俐彤,常春. 北京市老年人认知功能的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 456-461. |
| [13] | 朱金荣,赵亚娜,黄巍,赵微微,王悦,王松,苏春燕. 感染新型冠状病毒的血液透析患者的临床特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 267-272. |
| [14] | 赖展鸿,李嘉辰,贠泽霖,张永刚,张昊,邢晓燕,邵苗,金月波,王乃迪,李依敏,李玉慧,栗占国. 特发性炎性肌病完全临床应答相关因素的单中心真实世界研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 284-292. |
| [15] | 司筱芊,赵秀娟,朱凤雪,王天兵. 创伤出血性休克后急性呼吸窘迫综合征的危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 307-312. |
|
||